특징
- 논리적 위치와 물리적 위치가 같음
- 저장할 수 있는 원소의 수가 정해져 있음
- 배열의 공백을 허락하지 않음
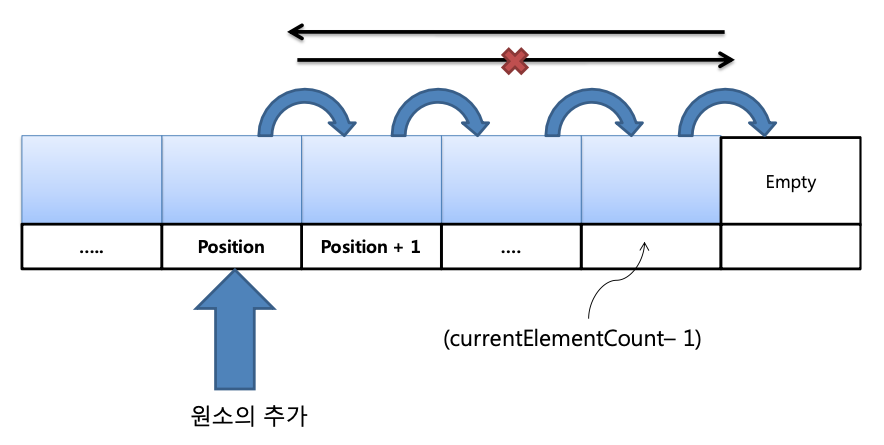
- 원소 추가 시 추가하려는 위치 뒤에 있는 원소들을 한칸씩 뒤로 이동시킨 후 새로운 원소를 추가해야 함
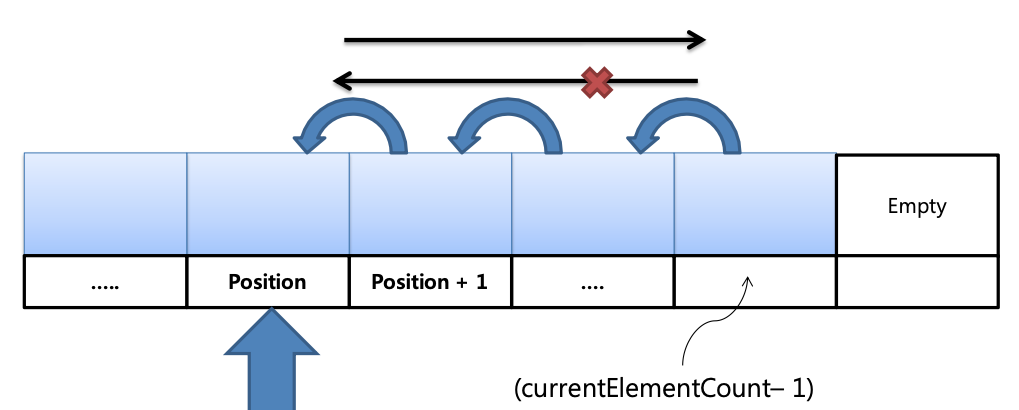
- 원소 삭제 시 삭제하려는 원소 삭제 후 삭제 위치에 있는 원소들을 한칸씩 앞으로 이동시켜야 함
- 자주 추가되거나 삭제되는 데이터를 담기에는 적절하지 않음
- 동일한 값을 중복 저장할 수 있음
장점
- 위치 인덱스를 활용하여 접근이 가능
- 자료들이 물리적으로 연결되어 있기 때문에 원하는 위치에 있는 원소를 빠르게 찾을 수 있음: O(1)
단점
- 원소가 많을 경우 원소의 추가/삭제에 많은 시간이 듦: O(n)
활용
- 가급적 순서대로 들어오는 정보를 처리할 때(값보다는 순서가 중요한 데이터)
- 데이터의 size가 잘 변하지 않는 자료를 처리할 때(resizing을 하지 않을 수 있도록)
- 다차원 데이터
- 특정 요소를 빠르게 읽어야 할 때(index) 접근
구현
1. arraylist.c
#include "arraylist.h"
ArrayList *createArrayList(int maxElementCount)
{
ArrayList *newAL;
newAL = malloc(sizeof(ArrayList));
if (!newArray)
return (NULL);
newAL->pElement = malloc(sizeof(ArrayListNode) * maxElementCount); // 원소 저장을 위한 배열 할당
if (!(newAL->pElement))
{
free(newAL); // 배열 할당 실패 시 이전에 할당한 List 구조체 free
return (NULL);
}
newAL->maxElementCount = maxElementCount;
newAL->currentElementCount = 0;
return (newArray);
}
int addALElement(ArrayList *pList, int position, ArrayListNode element)
{
ArrayListNode *newArray;
int idx;
if (!pList || position < 0 || position > pList-> currentElementCount) // 배열 혹은 원소가 존재하지 않거나, position 정보가 잘못되었을 경우 FALSE 리턴. 같은 경우는 배열의 마지막에 원소가 추가 됨
return (FALSE);
if (pList->currentElementCount == pList->maxElementCount) // 배열이 다 찼을 경우 새 배열 할당
{
newArray = malloc(sizeof(ArrayListNode) * pList->maxElementCount * 2); // 2배 크기로 할당
if (!newArray)
return (FALSE);
for (idx = 0; idx < pList->currentElementCount; idx++) // 현재 배열에 있는 원소의 개수만큼 기존 배열 복사
newArray[idx] = pList->pElement[idx];
free(pList->pElement); // 기존 배열 free
pList->pElement = newArray; // 새 배열 붙이기
pList->maxElementCount *= 2;
printf("Array is Full. New Array is allocated. Size of Array: %d\n", pList->maxElementCount); // 사용자가 크기를 확정지었기 때문에 배열 확장 시 안내
}
// 원소 추가 시 가장 마지막 원소부터 자신의 다음 position에 정보 저장 (앞에서부터 변경 시 정보 훼손)
// idx를 현재 원소 개수로 초기화 하면 배열은 0번째 인덱스부터 시작하기 때문에 현재 배열 가장 마지막 위치 + 1로 초기화 가능
// ++ 후위 연산을 통해서 idx 초기화 후 현재 원소 개수 정보 갱신
// idx가 position 전까지 idx를 줄여가며 복사
for (idx = pList->currentElementCount++; idx > position; idx--)
pList->pElement[idx] = pList->pElement[idx - 1];
pList->pElement[idx] = element; // idx = position에 추가하려는 element 삽입
return (TRUE);
}
int removeALElement(ArrayList *pList, int position)
{
int idx;
if (!pList || pList->currentElementCount == 0 || position < 0 || position >= pList->currentElementCount) // 배열 혹은 원소가 존재하지 않거나, position 정보가 잘못되었을 경우 FALSE 리턴
return (FALSE);
pList->currentElementCount--; // 현재 원소 개수 갱신
// 삭제하고자 하는 원소의 다음 position에 있는 정보를 자신의 position에 저장
for (idx = position; idx < pList->currentElementcount; idx++)
pList->pElement[idx] = pList->pElement[idx++];
return (TRUE);
}
ArrayListNode *getALElement(ArrayList *pList, int position)
{
if (!pList || pList->currentElementCount == 0 || position < 0 || position >= pList->currentElementCount)
return (FALSE);
return (&pList->pElement[position]); // 주소를 반환
}
int getArrayListLength(ArrayList *pList)
{
return (pList->currentElementCount);
}
void displayArrayList(ArrayList *pList)
{
int idx;
int count;
if (!pList)
{
printf("Error: No array.\n\n");
return ;
}
count = pList->currentElementCount;
printf("1. Size of array: %d\n", pList->maxElementCount);
printf("2. Current element count: %d\n", count);
printf("3. Elements: ");
if (count == 0)
printf("No element\n\n");
else
{
for (idx = 0; idx < count; idx++)
{
printf("[%d] %d", idx, pList->pElement[idx].data);
if (idx != count - 1) // 마지막 원소 제외 쉼표 출력
printf(", ");
}
printf("\n\n");
}
}
void clearArrayList(ArrayList *pList)
{
if (!pList)
return ;
pList->currentElementCount = 0; // 구조체 data 자료형이 int이기 때문에 자료 초기화 무의미 향후 자료형 변경 시 초기화가 필요하다면 초기화 처리
}
void deleteArrayList(ArrayList *pList)
{
clearArrayList(pList);
free(pList->pElement); // 배열 할당 해제
pList->pElement = NULL; // 할당 해제 된 메모리에 접근하지 못하도록 NULL 처리
free(pList); // 배열 구조체 할당 해제
}
2. arraylist_main.c
#include "arraylist.h"
int main(void)
{
ArrayList *pList = NULL;
ArrayListNode *element = NULL;
ArrayListNode node;
int loop = 1;
int opt = 0;
int position = 0;
while (loop)
{
printf("[1] Create [2] Add [3] Remove [4] Get Element [5] Length [6] Display [7] Clear [8] Delete [9] Exit ");
scanf("%d", &opt);
switch (opt)
{
case 1:
printf("Size of Array: ");
scanf("%d", &opt);
pList = createArrayList(opt);
if (pList) // 배열 생성 확인
printf("Create Array: Success\n");
else
printf("Create Array: Failed\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("Position: ");
scanf("%d", &position);
printf("Data: ");
scanf("%d", &node.data);
if (addALElement(pList, position, node))
{
printf("ADD: Success\n");
displayArrayList(pList);
}
else
printf("ADD: Failed\n\n");
break;
case 3:
printf("Position: ");
scanf("%d", &position);
if (removeALElement(pList, position))
{
printf("Remove: Success\n");
displayArrayList(pList);
}
else
printf("Remove: Failed\n\n");
break;
case 4:
printf("Position: ");
scanf("%d", &position);
element = getALElement(pList, position);
if (element)
printf("[%d]: %d\n", position, element->data);
else
printf("Failed\n");
break;
case 5:
printf("Length: %d\n", getArrayListLength(pList));
break;
case 6:
displayArrayList(pList);
break;
case 7:
if (!pList)
printf("Error: No arraylist\n");
clearArrayList(pList);
printf("Clear: Success\n");
break;
case 8:
if (!pList)
printf("Error: No arraylist\n");
else
{
deleteArrayList(pList);
pList = NULL; // 해제 된 메모리에 접근하지 못하도록 NULL 처리
printf("Delete: Success\n");
}
break;
case 9:
loop = 0;
break;
default:
printf("Please Enter a Valid Option\n");
break;
}
}
}
3. arraylist.h
#ifndef _ARRAYLIST_
#define _ARRAYLIST_
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct ArrayListNodeType
{
int data;
} ArrayListNode;
typedef struct ArrayList
{
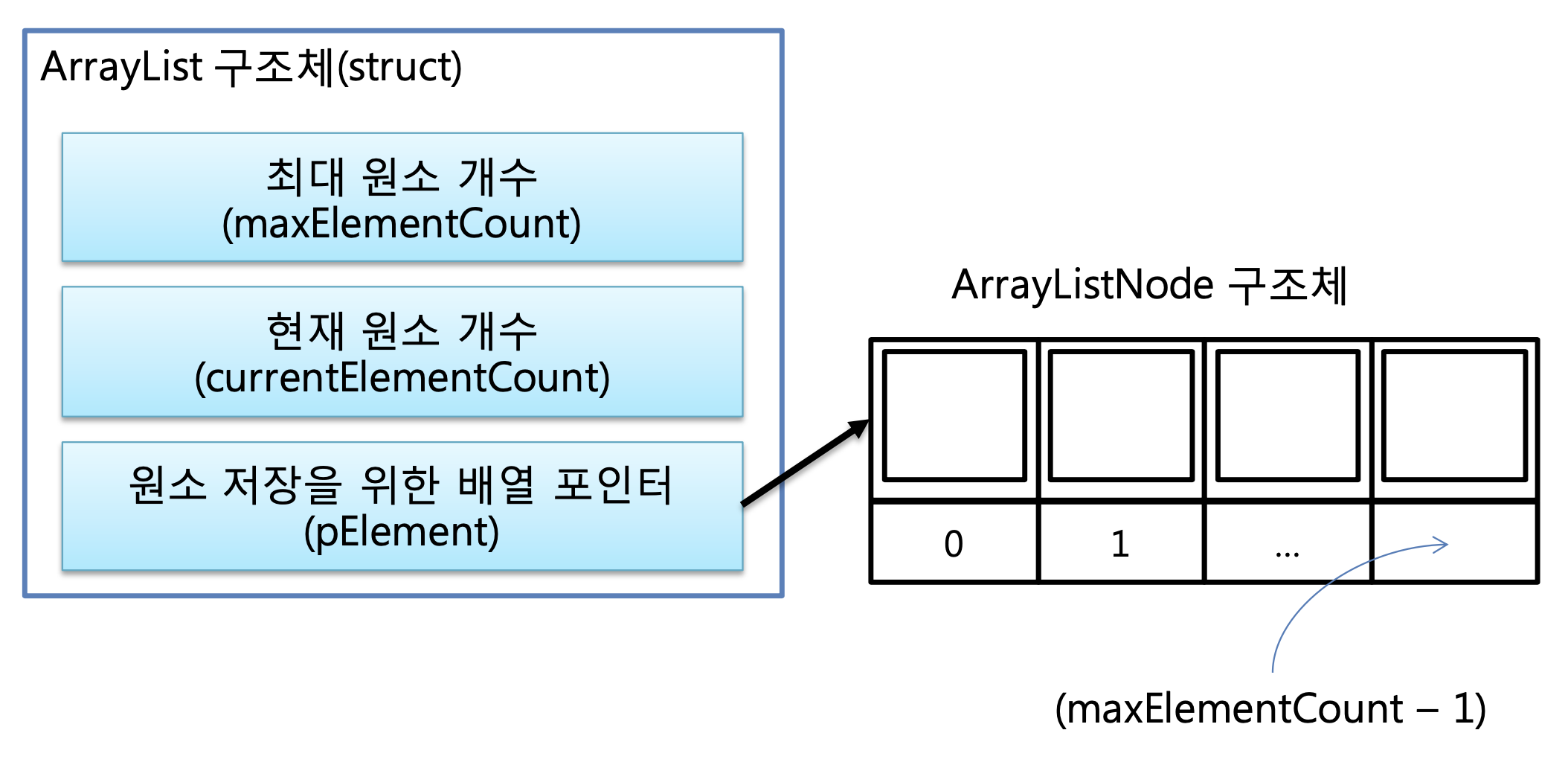
int maxElementCount; // 최대 원소 개수
int currentElementCount; // 현재 원소 개수
ArrayListNode *pElement; // 원소 저장을 위한 1차원 배열
} ArrayList;
ArrayList *createArrayList(int maxElementCount);
int addALElement(ArrayList *pList, int position, ArrayListNode element);
int removeALElement(ArrayList *pList, int position);
ArrayListNode getALElement(ArrayList *pList, int position);
int getArrayListLength(ArrayList *pList);
void displayArrayList(ArrayList *pList);
void clearArrayList(ArrayList *pList);
void deleteArrayList(ArrayList *pList);
#endif
#ifndef _COMMON_LIST_DEF_
#define _COMMON_LIST_DEF_
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#endif



