📖 학습 주제
- Airflow 환경 설정
- Summary 테이블 구현
- Slack 연동하기
✏️ 주요 메모 사항 소개
airflow 환경설정
이제 다시 한번 docker 기반으로 Airflow를 실행해보자. curl -LfO 'https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/2.9.1/docker-compose.yaml' 명령어를 사용해서 docker-compose.yaml 파일을 내려받은 뒤 up 명령어를 사용하여 실행해 주면 되는데, 그 전에 yaml 파일을 살짝 수정해보자. 다음 코드를 변경 혹은 수정하면 된다.
...
environment:
AIRFLOW_VAR_DATA_DIR: /opt/airflow/data
_PIP_ADDITIONAL_REQUIREMENTS: ${_PIP_ADDITIONAL_REQUIREMENTS:- yfinance pandas numpy oauth2client gspread}
volumes:
...
-${AIRFLOW_PROJ_DIR:-.}/data:/opt/airflow/data
airflow-init:
...
mkdir -p /sources/logs /sources/dags /sources/plugins /sources/data
chown -R "${AIRFLOW_UID}:0" /sources/{logs,dags,plugins,data}
...- Requirements를 수정해서 필요한 라이브러리를 미리 설치
- data 폴더를 호스트 폴더에서 만들고 volume으로 공유 (임시 데이터를 저장할 폴더)
- 이를 docker volume으로 지정해서 나중에 디버깅에 사용
수정 후 docker compose up 명령어를 실행해 컨테이너를 실행시키고 Web UI에서 잘 작동하는지 확인해 보자.
yml 파일에서 환경변수로 설정한 DATA_DIR와 같은 변수는 Web UI에서는 안 보이지만 프로그램에서는 사용가능 하다. 실제로 Admin => Variables 탭에서 우리가 만든 DATA_DIR 변수는 안보이지만 터미널에서 docker exec -it airflow-docker-airflow-scheduler-1 airflow variables get DATA_DIR 명령어를 실행하면 DATA_DIR로 설정한 path가 출력되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.

우리는 Variables/Connections와 같은 설정을 어떻게 관리하는 것이 좋을지 고민해봐야 한다. docker-compose.yaml 파일에 environment 항복에 변수를 추가할지, Web UI에서 추가할 지 선택해야 한다. 보통 전자를 더 추천한다.
그리고 또한 어디까지 Airflow 이미지로 관리하고 무엇은 docker-compose.yaml에서 관리할 지도 생각해보아야 한다. yml 파일에 직접 환경 변수를 설정하는 것 말고도 환경 변수를 Airflow 자체 이미지에 넣고 이를 docker-compose.yaml 파일에서 사용하는 방법도 있다.
x-airflow-common:
&airflow-common
image: ${AIRFLOW_IMAGE_NAME:-apache/airflow:2.9.1}- AIRFLOW_IMAGE_NAME 환경변수가 정의되어 있다면 그걸 사용하고 아니면 기본값으로 apache/airflow:2.9.1 사용
DAG 코드도 마찬가지로 Airflow image로 DAG 코드를 복사하여 만드는 것이 좀더 깔끔한 방법이다. 아니면 docker-compose에서 host volume 형태로 설정하는 것도 있는데, 이는 개발/테스트용에 좀더 적합한 방법이다.
Summary 테이블 구현
예전에 SQL 실습할 때 만들었던 Summary 테이블들(mau_summary, nps_summary, channel_summary)을 DAG 형식으로 만들어서 구현해보자.
dags/Build_Summary.py: mau_summary 테이블 생성 DAG 코드
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator
from airflow.models import Variable
from airflow.hooks.postgres_hook import PostgresHook
from datetime import datetime
from datetime import timedelta
from airflow import AirflowException
import requests
import logging
import psycopg2
from airflow.exceptions import AirflowException
def get_Redshift_connection():
hook = PostgresHook(postgres_conn_id = 'redshift_dev_db')
return hook.get_conn().cursor()
def execSQL(**context):
schema = context['params']['schema']
table = context['params']['table']
select_sql = context['params']['sql']
logging.info(schema)
logging.info(table)
logging.info(select_sql)
cur = get_Redshift_connection()
sql = f"""DROP TABLE IF EXISTS {schema}.temp_{table};CREATE TABLE {schema}.temp_{table} AS """
sql += select_sql
cur.execute(sql)
cur.execute(f"""SELECT COUNT(1) FROM {schema}.temp_{table}""")
count = cur.fetchone()[0]
if count == 0:
raise ValueError(f"{schema}.{table} didn't have any record")
try:
sql = f"""DROP TABLE IF EXISTS {schema}.{table};ALTER TABLE {schema}.temp_{table} RENAME to {table};"""
sql += "COMMIT;"
logging.info(sql)
cur.execute(sql)
except Exception as e:
cur.execute("ROLLBACK")
logging.error('Failed to sql. Completed ROLLBACK!')
raise AirflowException("")
dag = DAG(
dag_id = "Build_Summary",
start_date = datetime(2021,12,10),
schedule = '@once',
catchup = False
)
execsql = PythonOperator(
task_id = 'mau_summary',
python_callable = execSQL,
params = {
'schema' : 'jwa4610',
'table': 'mau_summary',
'sql' : """SELECT
TO_CHAR(A.ts, 'YYYY-MM') AS month,
COUNT(DISTINCT B.userid) AS mau
FROM raw_data.session_timestamp A
JOIN raw_data.user_session_channel B ON A.sessionid = B.sessionid
GROUP BY 1
;"""
},
dag = dag
)위와 같이 PythonOperator를 만든 뒤 parmas 파라미터를 이용해서 구현하는 방법이 있는가 하면, CTAS 부분을 아예 별도의 환경설정 파일로 떼어내서 구현하는 방법도 있다. config 폴더를 생성한 뒤 안에 summary 테이블 별로 하나의 환경설정 파일을 생성해서 구현하면, 비개발자들이 사용할 때 어려움을 덜 느낄 수 있고, 더 다양한 테스트를 추가할 수 있다.
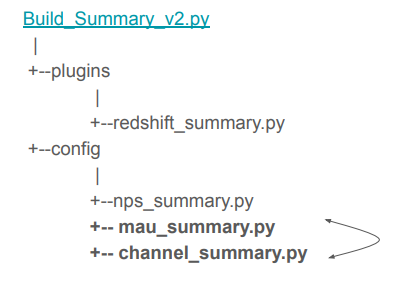
dags/Build_Summary_v2.py
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.macros import *
import os
from glob import glob
import logging
import subprocess
from plugins import redshift_summary
from plugins import slack
DAG_ID = "Build_Summary_v2"
dag = DAG(
DAG_ID,
schedule_interval="25 13 * * *",
max_active_runs=1,
concurrency=1,
catchup=False,
start_date=datetime(2021, 9, 17),
default_args= {
'on_failure_callback': slack.on_failure_callback,
'retries': 1,
'retry_delay': timedelta(minutes=1),
}
)
# this should be listed in dependency order (all in analytics)
tables_load = [
'nps_summary'
]
dag_root_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
redshift_summary.build_summary_table(dag_root_path, dag, tables_load, "redshift_dev_db")
dags/config/nps_summary.py
{
'table': 'nps_summary',
'schema': 'jwa4610',
'main_sql': """
SELECT LEFT(created_at, 10) AS date,
ROUND(SUM(CASE
WHEN score >= 9 THEN 1
WHEN score <= 6 THEN -1 END)::float*100/COUNT(1), 2)
FROM raw_data.nps
GROUP BY 1
ORDER BY 1;""",
'input_check':
[
{
'sql': 'SELECT COUNT(1) FROM keeyong.nps',
'count': 150000
},
],
'output_check':
[
{
'sql': 'SELECT COUNT(1) FROM {schema}.temp_{table}',
'count': 12
}
],
}
dags/plugins/redshift_summary.py
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.macros import *
from airflow.utils.decorators import apply_defaults
from airflow.exceptions import AirflowException
from airflow.hooks.postgres_hook import PostgresHook
from airflow.operators.python_operator import PythonOperator
import logging
from glob import glob
"""
Build a summary table under analytics schema in Redshift
- Check the input tables readiness first
- Run the SQL using a temp table
- Before swapping, check the size of the temp table
- Finally swap
"""
def load_all_jsons_into_list(path_to_json):
configs = []
for f_name in glob(path_to_json+ '/*.py'):
# logging.info(f_name)
with open(f_name) as f:
dict_text = f.read()
try:
dict = eval(dict_text)
except Exception as e:
logging.info(str(e))
raise
else:
configs.append(dict)
return configs
def find(table_name, table_confs):
"""
scan through table_confs and see if there is a table matching table_name
"""
for table in table_confs:
if table.get("table") == table_name:
return table
return None
def build_summary_table(dag_root_path, dag, tables_load, redshift_conn_id, start_task=None):
logging.info(dag_root_path)
table_confs = load_all_jsons_into_list(dag_root_path + "/config/")
if start_task is not None:
prev_task = start_task
else:
prev_task = None
for table_name in tables_load:
table = find(table_name, table_confs)
summarizer = RedshiftSummaryOperator(
table=table["table"],
schema=table["schema"],
redshift_conn_id=redshift_conn_id,
input_check=table["input_check"],
main_sql=table["main_sql"],
output_check=table["output_check"],
overwrite=table.get("overwrite", True),
after_sql=table.get("after_sql"),
pre_sql=table.get("pre_sql"),
attributes=table.get("attributes", ""),
dag=dag,
task_id="anayltics"+"__"+table["table"]
)
if prev_task is not None:
prev_task >> summarizer
prev_task = summarizer
return prev_task
def redshift_sql_function(**context):
"""this is a main Python callable function which runs a given SQL
"""
sql=context["params"]["sql"]
print(sql)
hook = PostgresHook(postgres_conn_id=context["params"]["redshift_conn_id"])
hook.run(sql, True)
class RedshiftSummaryOperator(PythonOperator):
"""
Create a summary table in Redshift
:param input_check: a list of input tables to check to make sure
they are fully populated. the list is composed
of sql (select) and minimum count
:type input_check: a list of sql and count
:param main_sql: a main sql to create a summary table. this should
use a temp table. this sql can have more than one
statement
:type main_sql: string
:input output_check: output validation. It is a list of sql (select)
and minimum count
:type output_check: a list of sql and count
:input overwrite: Currently this only supports overwritting (True)
Once False is supported, it will append to the table
:type overwrite: boolean
"""
@apply_defaults
def __init__(self,
schema,
table,
redshift_conn_id,
input_check,
main_sql,
output_check,
overwrite,
params={},
pre_sql="",
after_sql="",
attributes="",
*args,
**kwargs
):
self.schema = schema
self.table = table
self.redshift_conn_id = redshift_conn_id
self.input_check = input_check
self.main_sql = main_sql
self.output_check = output_check
# compose temp table creation, insert into the temp table as params
if pre_sql:
main_sql = pre_sql
if not main_sql.endswith(";"):
main_sql += ";"
else:
main_sql = ""
main_sql += "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS {schema}.temp_{table};".format(
schema=self.schema,
table=self.table
)
# now we are using "CREATE TABLE ... AS SELECT" syntax
# we used to create a temp table with the same schema as the main table and then insert into the temp table
main_sql += "CREATE TABLE {schema}.temp_{table} {attributes} AS ".format(
schema=self.schema,
table=self.table,
attributes=attributes
) + self.main_sql
if after_sql:
self.after_sql = after_sql.format(
schema=self.schema,
table=self.table
)
else:
self.after_sql = ""
super(RedshiftSummaryOperator, self).__init__(
python_callable=redshift_sql_function,
params={
"sql": main_sql,
"overwrite": overwrite,
"redshift_conn_id": self.redshift_conn_id
},
provide_context=True,
*args,
**kwargs
)
def swap(self):
sql = """BEGIN;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS {schema}.{table} CASCADE;
ALTER TABLE {schema}.temp_{table} RENAME TO {table};
GRANT SELECT ON TABLE {schema}.{table} TO GROUP analytics_users;
END
""".format(schema=self.schema,table=self.table)
self.hook.run(sql, True)
def execute(self, context):
"""Do input_check first
- input_check should be a list of dictionaries
- each item in the dictionary contains "sql" and "count"
"""
self.hook = PostgresHook(postgres_conn_id=self.redshift_conn_id)
for item in self.input_check:
(cnt,) = self.hook.get_first(item["sql"])
if cnt < item["count"]:
raise AirflowException(
"Input Validation Failed for " + str(item["sql"]))
"""
- create a temp table using create table like
- run insert into the temp table
"""
return_value = super(RedshiftSummaryOperator, self).execute(context)
"""Do output_check using self.output_check
"""
for item in self.output_check:
(cnt,) = self.hook.get_first(item["sql"].format(schema=self.schema, table=self.table))
if item.get("op") == 'eq':
if int(cnt) != int(item["count"]):
raise AirflowException(
"Output Validation of 'eq' Failed for " + str(item["sql"]) + ": " + str(cnt) + " vs. " + str(item["count"])
)
else:
if cnt < item["count"]:
raise AirflowException(
"Output Validation Failed for " + str(item["sql"]) + ": " + str(cnt) + " vs. " + str(item["count"])
)
"""Now swap the temp table name
"""
self.swap()
if self.after_sql:
self.hook.run(self.after_sql, True)
return return_valueSlack 연동하기
DAG가 실패했을 때 개발자가 바로 알 수 있도록 Slack을 연동해서 Slack 채널에 에러 메세지를 보내는 방법을 알아보자.
Slack Channel 설정
자신이 알림을 받을 Workspace를 정하고 에러 메시지를 받을 channel을 만들어 주자.
DataAlert App 만들기
https://api.slack.com/messaging/webhooks 링크를 따라가서 우리의 Workspace에 App을 추가해 주자.
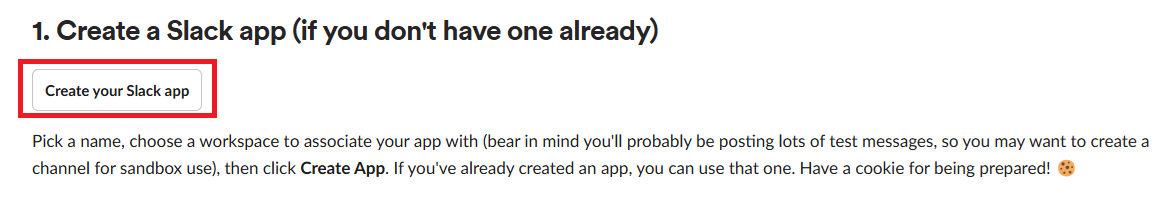
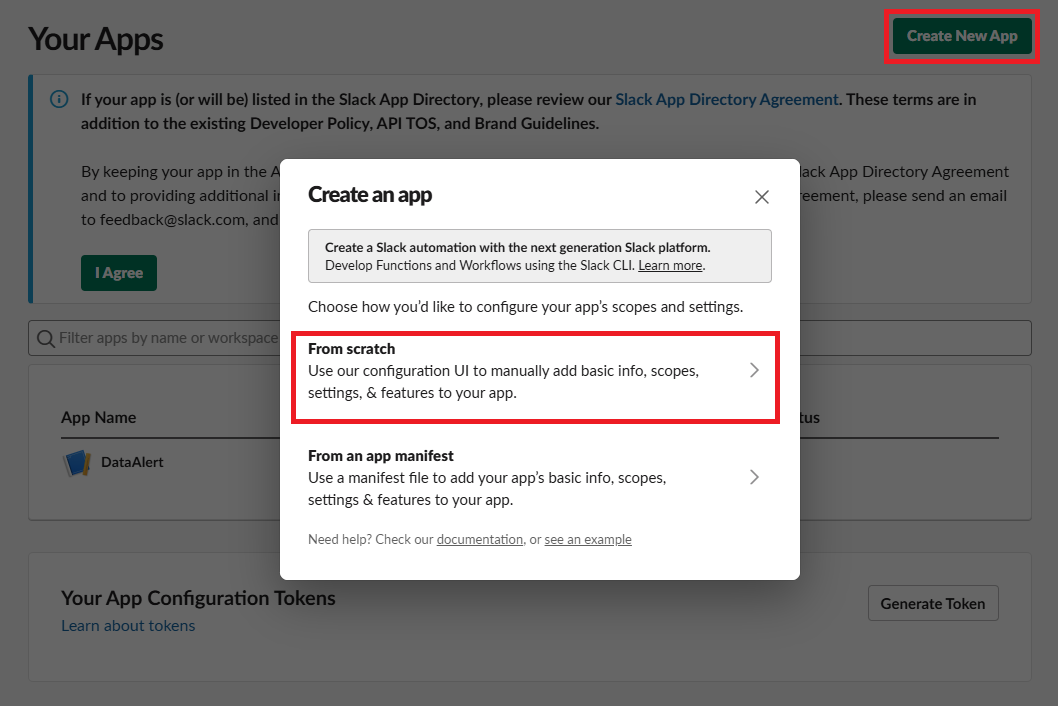
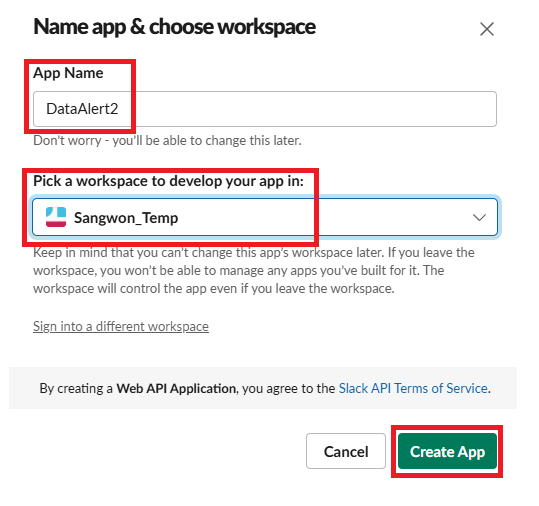
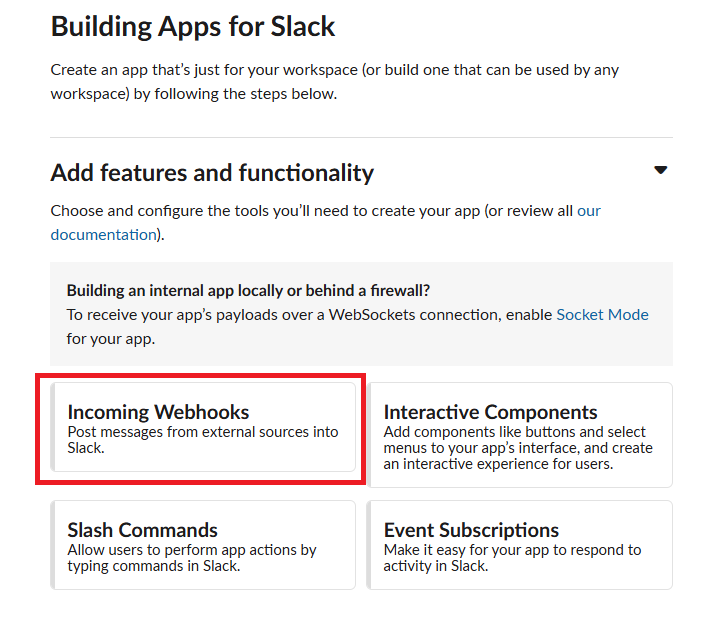
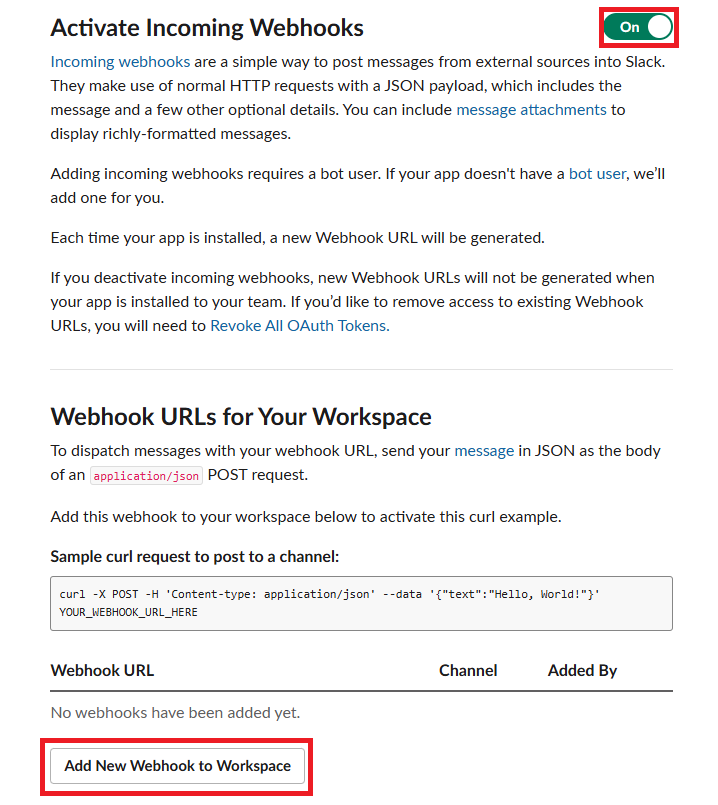
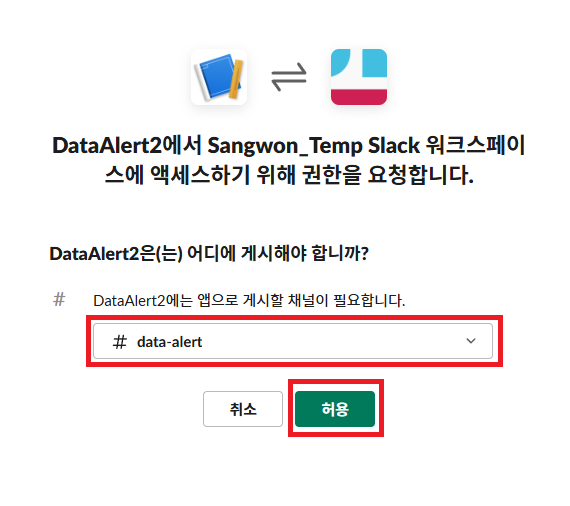
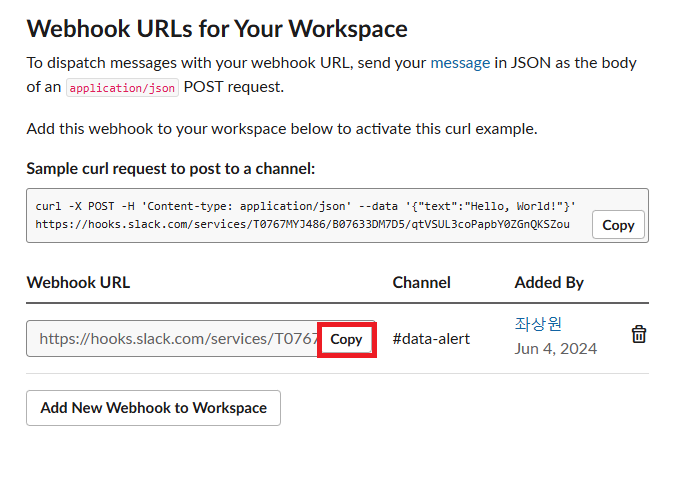
여기 까지 했다면 Workspace에 성공적으로 App이 만들어졌을 것이다. 우의 Sample curl requeest를 터미널해서 실행해보면 data-alert 채널에 Hello, World 메세지가 전송되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
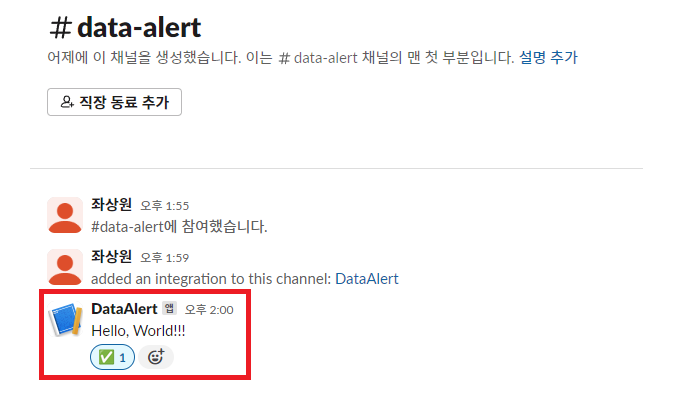
모듈 생성
이제 이 app을 통해서 DAG에서 에러가 발생했을 때 메세지를 보내는 모듈을 만들어 보자. 그리고 이를 DAG 인스턴스를 만들 때 에러 콜백으로 지정하면 된다.
일단, 위에 COPY한 Webhook URL의 services 뒷 부분의 값을 slack_url 이라는 Variable로 저장하자.
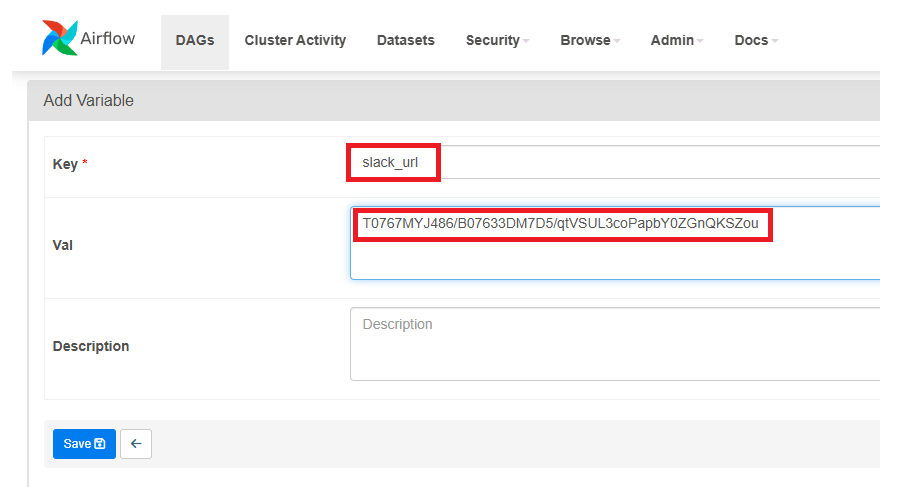
그 후, slack.py라는 에러 메세지를 발송하는 모듈을 dags/plugins에 만들어주고, 테스트해볼 DAG의 default_args에서 on_failure_callback을 설정해 주자. 에러가 나야하기 때문에 SQL문에서 문법 오류가 나게 살짝 건드려 주자.
dags/plugins/slack.py
from airflow.models import Variable
import logging
import requests
def on_failure_callback(context):
"""
https://airflow.apache.org/_modules/airflow/operators/slack_operator.html
Define the callback to post on Slack if a failure is detected in the Workflow
:return: operator.execute
"""
text = str(context['task_instance'])
text += "```" + str(context.get('exception')) +"```"
send_message_to_a_slack_channel(text, ":scream:")
# def send_message_to_a_slack_channel(message, emoji, channel, access_token):
def send_message_to_a_slack_channel(message, emoji):
# url = "https://slack.com/api/chat.postMessage"
url = "https://hooks.slack.com/services/"+Variable.get("slack_url")
headers = {
'content-type': 'application/json',
}
data = { "username": "Data GOD", "text": message, "icon_emoji": emoji }
r = requests.post(url, json=data, headers=headers)
return r
dags/NameGenderCSVtoRedshift_v4.py
...
# slack 모듈 import
from plugins import slack
...
dag = DAG(
dag_id = 'name_gender_v4',
start_date = datetime(2023,4,6), # 날짜가 미래인 경우 실행이 안됨
schedule = '0 2 * * *', # 적당히 조절
max_active_runs = 1,
catchup = False,
default_args = {
'retries': 1,
'retry_delay': timedelta(minutes=3),
# 에러 발생 시 실행할 코드 설정
'on_failure_callback': slack.on_failure_callback,
}
)
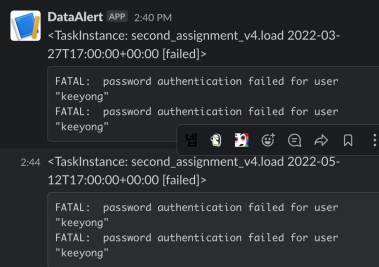
...이 NameGenderCSVtoRedshift_v4 파일의 DAG를 이제 실행해보면 에러가 발생하고 에러 메시지가 우리가 만든 slack 채널에 전송되는 것을 볼 수 있다.