아래의 글은 제가 재학중인 UCLA의 CS 32: Data Structures의 렉쳐를 들으며 작성하는 글입니다.
📝 Stack
Why do we learn it?
Every CPU has a built-in stack used to hold
- local variables
- function parameters
LIFO (Last-In-First-Out)
You can only access the top item of the stack, since the other items are covered!
code (if I implement it on my own)
class Stack
{
public:
Stack();
void push(int i);
int pop();
bool is_empty(void);
private:
int m_stack[SIZE];
int m_pop;
}Using STL
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
stack<int> istack; // stack of ints
istack.push(10);
istack.push(20);
cout << istack.top();
istack.pop();
}Things to note:
- The STL
pop()command simply throws away the top item from the stack, but it does not return it.
Class challenge
Show the resulting stack after the following program runs:
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
stack<int> istack; // stack of ints
istack.push(6);
for (int i=0; i<2; i++)
{
int n = istack.top();
istack.pop();
istack.push(i);
istack.push(n*2);
}
}📝 Postfix Expression
- what people use : infix expression
e.g.:A+B - what computers prefer: postfix expression
e.g:A B+
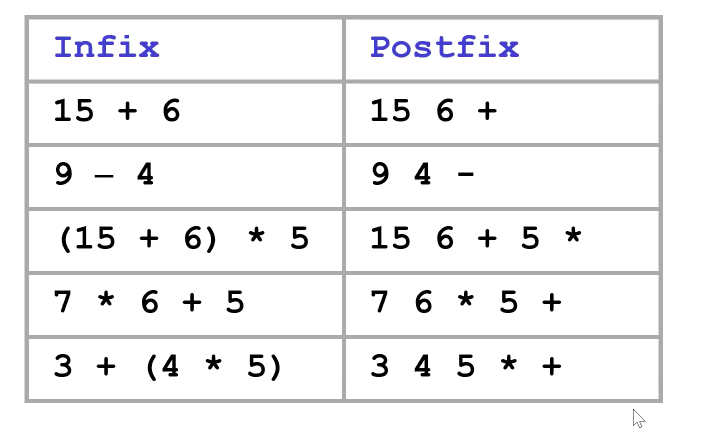
Postfix expressions are easier for a computer to compute than infix expressions since they're unambiguous.
Postfix Evaluation Algorithm
- Start with the left-most token.
- If the token is a number:
a. push it onto the stack
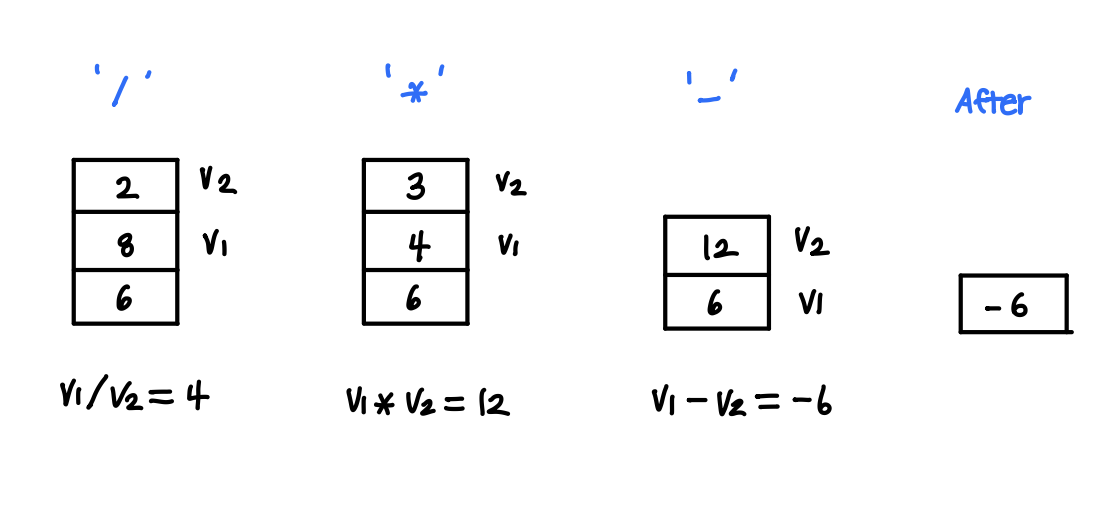
- Else if the token is an operator:
a. Pop the top value into a variable called v2 and the second-to-top value into v1.
b. Apply operator to v1 and v2 (e.g., v1/v2)
c. Push the result of the operation on the stack
- If there are more tokens, advance to the next token and go back to step #2.
- After all tokens have been processed, the top number on the stack is the answer!
Class Challenge
Given the following postfix expression: `6 8 2 / 3 * -``
Show the contents of the stack after the 3 has been processed by our postfix evaluation algorithm.
Infix to Postfix conversion
- Begin at left-most Infix token.
- If it's a number, append it to end of postfix string followed by a space.
- If it's a "(", push it onto the stack.
- If it's an operator and the stack is empty,
a. Push the operator on the stack
- If it's an operator and the stack is not empty:
a. Pop all operators with greater or equal precedence off the stack and append them on the postfix string.
b. Stop when you reach an operator with lower precednece or a (.
c. Push the new operator on the stack.
- If you encounter a ")", pop operators off the stack and append them onto the postfix string until you pop a matching "(".
- Advance to next token and go to #2.
- When all infix tokens are gone, pop each operator and append it } to the postfix string.
📝 Queue
FIFO (First-In-First-Out)
Code
- simple operations
enqueue(int a)
- inserts an item on the rear of the queue
int dequeue():
- removes and returns the top item from the front of the queue
- However, unlike a stack, we can use an array or a linked list, but there is a cost!
Circular Queue
The circular queue is a clever type of array-based queue.
private data:
an array: arr
an integer: head
an integer: tail
an integer: count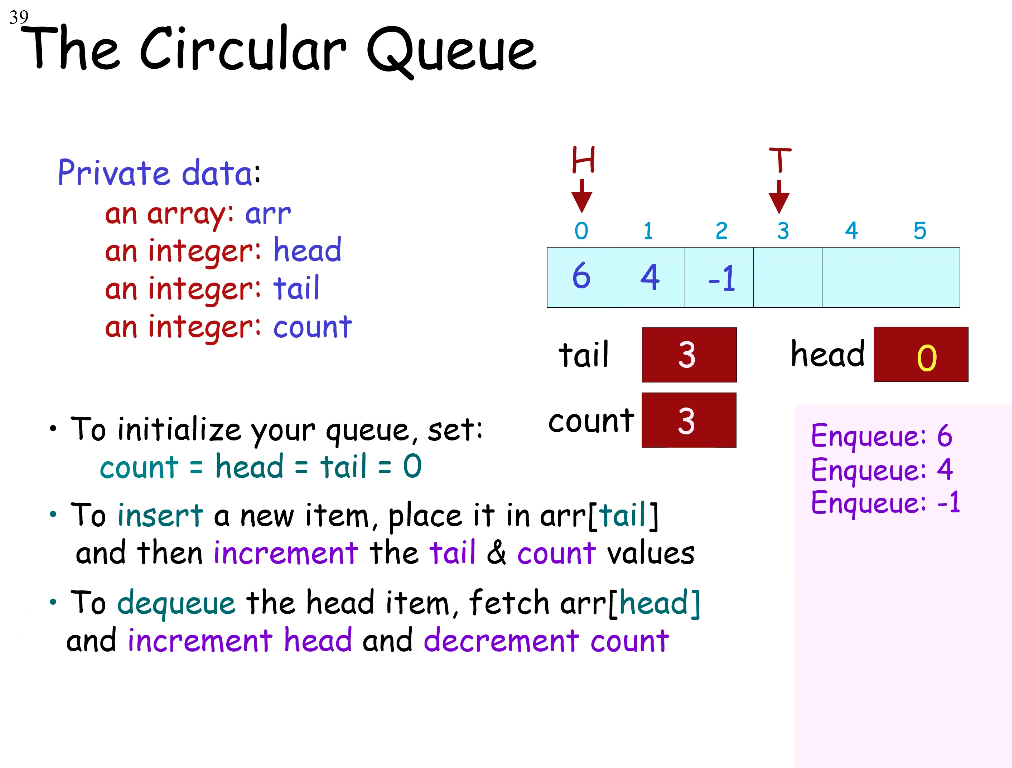
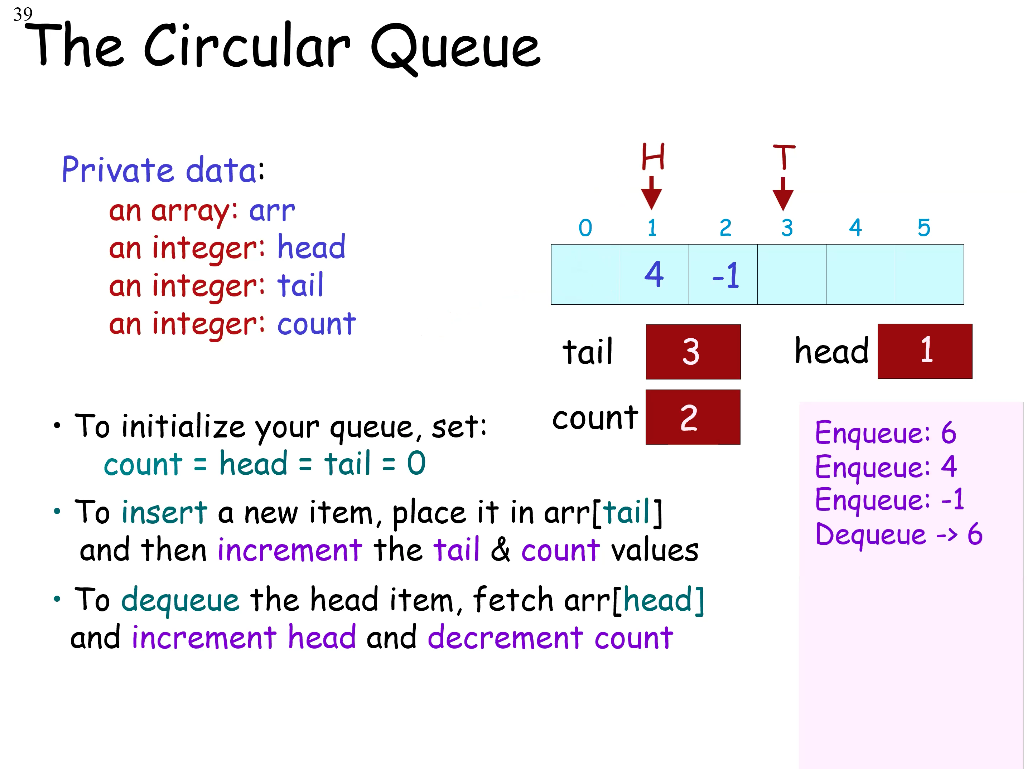
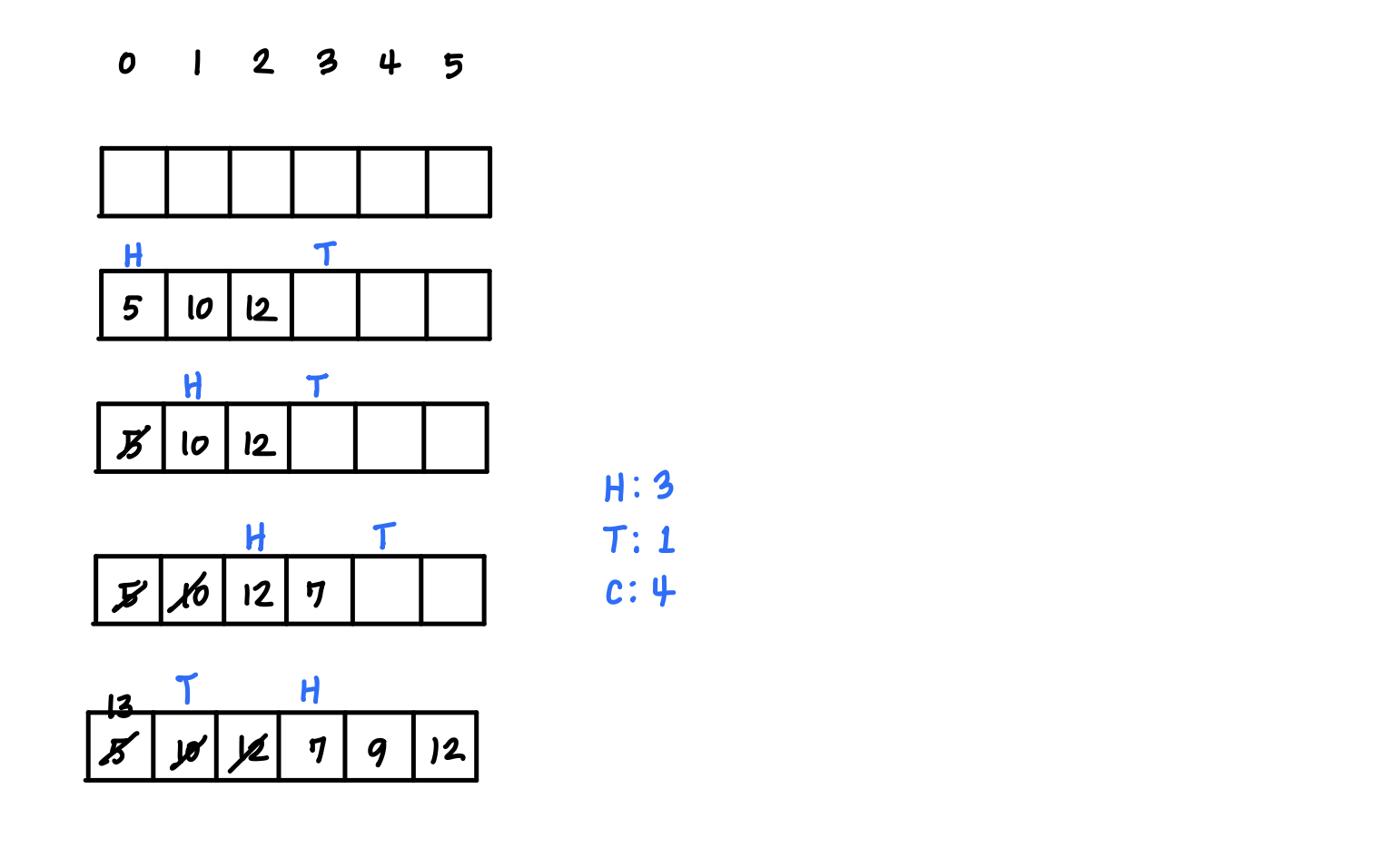
Class Challenge
Given a circular queue of 6 elements, show the queue's contents and the Head and Tail pointers after the following operations are complete.
enqueue(5)
enqueue(10)
enqueue(12)
dequeue()
enqueue(7)
dequeue()
enqueue(9)
enqueue(12)
enqueue(13)
dequeue()