아래의 글은 제가 재학중인 UCLA의 CS 32: Data Structures의 렉쳐를 들으며 작성하는 글입니다.
📝 Recursion
Rules
- Every recursive function must have a stopping condition (base case).
- Recursive functions should never use global, static, or member variables. They should only use local variables and parameters.
Steps
1. Write the function header.
Figure out what arguments your function will take and what it needs to return.
2. Define your magic function.
Magic function here shows logic behind the recursive function. Before making a recursive function right away, write magic function.
3. Add your base case code.
There might be multiple base cases for a function depending on what it does.
4. Solve the problem by using the magic function.
Divide the problem into sub parts and arrange what the magic function returns
5. Remove the magic function.
6. Validate function with the simplest possible input, then more complex inputs.
Class Challenge
printArr
void printArr(int arr[], int size)
{
if (size == 0)
cout << *arr << "\n";
printArr(arr+1, size-1);
}reversePrint
void reversePrint(string arr[], int size)
{
if (size == 0)
cout << arr[0] << "\n";
reversePrint(arr+1, size-1);
}Recursion with Linked List
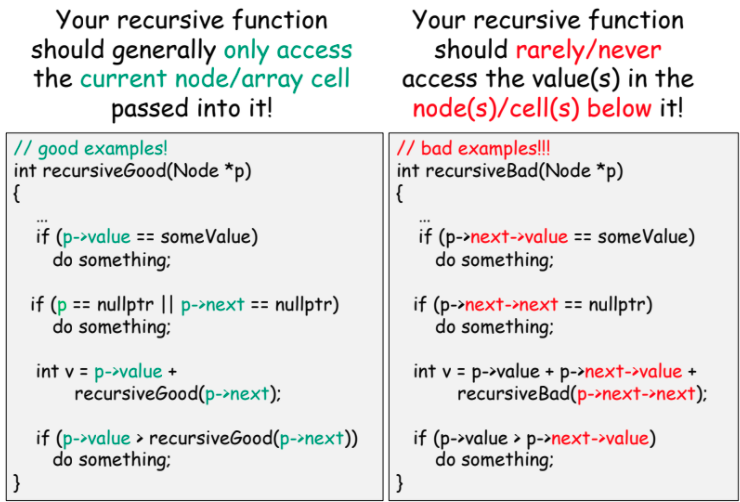
Tips
Your recursive function should generally only access the current node/array cell passed into it.
Your recursive function should rarely/never access the values in the node/cell below it.