출력 로그
출력 로그
VS Code에서는 Unreal Engine 4 Snippets를 설치하면 언리얼에 관련된 인텔리센스를 확인할 수 있다
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("Your message"));UE_LOG 인수는 차례대로
1. 로그 카테고리 유형이 무엇인지 나타냄
2. 로그의 수준을 나타냄
3. 로그에 어떤 메세지를 나타낼지를 나타냄
출력 로그에 변수 값을 기록해 보기
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, Category="Moving Platform")
float MoveDistance =100;헤더 파일의 float 타입의 MoveDistance를 로그에 출력하기 위해 cpp 파일 Beginplay() 부분에 코드 작성
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("Configured Moved Distance: %f"), MoveDistance);
레벨에 배치된 MovingPlatform 액터들의 수 만큼 플레이를 하면 설정된 MoveDistance의 값이 로그에 찍히는 것을 확인할 수 있다
//문자열 출력하기
//FString을 UE_LOG에서 사용하기 위해서는 변수 앞에 *을 붙여줘야 한다
FString MyString = "My String Value";
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("Here's My String: %s"), *MyString);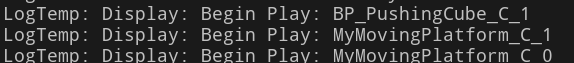
//액터의 이름을 문자열로 출력하기
//FString을 UE_LOG에서 사용하기 위해서는 변수 앞에 *을 붙여줘야 한다
FString Name = GetName();
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("Begin Play: %s"), *Name);
//또는 이렇게 작성 가능
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("%s Rotating.."), *GetName());멤버 함수
플래폼을 움직이는 멤버 함수
- 헤더 파일에 멤버 함수 선언
//멤버 함수 선언
void MovePlatform(float DeltaTime);- cpp 코드에 멤버 함수 정의
// Called every frame
void AMovingPlatform::Tick(float DeltaTime)
{
Super::Tick(DeltaTime);
MovePlatform(DeltaTime);
}
void AMovingPlatform::MovePlatform(float DeltaTime)
{
//플랫폼의 위치를 앞뒤로 움직인다
//Move platform forwards
//Get current location
FVector CurrentLocation = GetActorLocation();
//Add vector to that location
//속도에 따라 위치를 업데이트
CurrentLocation = CurrentLocation + PlatformVelocity * DeltaTime;
//Set the location
//업데이트 된 위치를 설정
SetActorLocation(CurrentLocation);
//Send platform back if gone to far
//Check how far we've moved
//더블 콜론 연산자를 통해 FVector 클래스 안의 내부 함수를 가져온다
//시작 위치와 현재 위치를 넘겨 두 벡터 사이의 거리를 구한다
float DistanceMoved = FVector::Distance(StartLocation, CurrentLocation);
//Reverse direction of motion if gone too far
if(DistanceMoved > MoveDistance){
//PlatformVelocity의 크기가 1인 벡터를 가져온다(현재 이동 방향을 얻는다)
FVector MoveDirection = PlatformVelocity.GetSafeNormal();
//시작 위치를 업데이트
//현재 위치에서 현재 방향으로 이동한 거리를 더하여 새로운 시작 위치를 계산
StartLocation = StartLocation + MoveDirection * MoveDistance;
SetActorLocation(StartLocation);
//PlatformVelocity를 음수로 설정하여 반대 방향으로 이동하게 한다
PlatformVelocity = -PlatformVelocity;
}
}반환문
- 헤더 파일에 bool 타입 멤버 함수 선언
bool ShouldPlatformReturn();2.bool 타입 멤버 함수 정의
void AMovingPlatform::MovePlatform(float DeltaTime)
{
//플랫폼의 위치를 앞뒤로 움직인다
//Send platform back if gone to far
//Check how far we've moved
//Reverse direction of motion if gone too far
if(ShouldPlatformReturn())
{
//PlatformVelocity의 크기가 1인 벡터를 가져온다(현재 이동 방향을 얻는다)
FVector MoveDirection = PlatformVelocity.GetSafeNormal();
//시작 위치를 업데이트
//현재 위치에서 현재 방향으로 이동한 거리를 더하여 새로운 시작 위치를 계산
StartLocation = StartLocation + MoveDirection * MoveDistance;
SetActorLocation(StartLocation);
//PlatformVelocity를 음수로 설정하여 반대 방향으로 이동하게 한다
PlatformVelocity = -PlatformVelocity;
}
else{
//Move platform forwards
//Get current location
FVector CurrentLocation = GetActorLocation();
//Add vector to that location
//속도에 따라 위치를 업데이트
CurrentLocation = CurrentLocation + PlatformVelocity * DeltaTime;
//Set the location
//업데이트 된 위치를 설정
SetActorLocation(CurrentLocation);
}
}
bool AMovingPlatform::ShouldPlatformReturn()
{
//Check how far we've moved
//더블 콜론 연산자를 통해 FVector 클래스 안의 내부 함수를 가져온다
//시작 위치와 현재 위치를 넘겨 두 벡터 사이의 거리를 구한다
float DistanceMoved = FVector::Distance(StartLocation, GetActorLocation());
return DistanceMoved > MoveDistance;
}
- float 타입 멤버 함수 선언
float GetDistanceMoved();- float 타입 멤버 함수 정의
bool AMovingPlatform::ShouldPlatformReturn()
{
return GetDistanceMoved() > MoveDistance;
}
float AMovingPlatform::GetDistanceMoved()
{
return FVector::Distance(StartLocation, GetActorLocation());
}const 멤버 함수
const 함수 해당 함수가 클래스의 상태를 수정할 수 없게 만드는 것
const 함수 내에서는 const로 표시되지 않은 함수는 호출할 수 없다
//헤더파일에서 해당 함수 뒤에 const 키워드를 붙여준다
bool ShouldPlatformReturn() const;
//소스 코드에서도 const 함수 뒤에 const 키워드를 작성해줘야 한다
bool AMovingPlatform::ShouldPlatformReturn() const
{
return GetDistanceMoved() > MoveDistance;
}
포인터와 참조
포인터와 참조 모두 메모리의 주소를 값으로 갖는다.
포인터와 참조의 차이는 재할당 여부에 있다.
- 최초 생성된 후에 다른 주소를 가리킬 수 있는가?
- 포인터 : YES
포인터를 변경하여 새로운 메모리 주소, 액터, 컴포넌트를 가리킬 수 있다. - 참조 : NO
처음 생성해서 또 다른 변수를 가리킬 때 한 번만 설정
- null이 될 수 있는가?
null 포인터: 아무 것도 가리키지 않는 포인터- 참조는 처음 생설할 때 값이 있어야 하기 때문에 null이 될 수 없다
- 주소에 접근
- 포인터 : ActorPtr (포인터를 통해 액터 주소에 직접 접근)
- 참조 : &ActorRef (&연산자를 사용해 주소에 접근)
- 주소 변경
- 포인터 : ActorPtr = &Actor (포인터에 다른 액터의 주소를 대입)
- 참조 : 참조는 선언 이후 다른 객체로 재지정할 수 없다
- 값 변경
- 포인터 : *ActorPtr = Actor (포인터가 가리키는 주소의 객체 내용 변경)
- 참조 : ActorRef = Actor (참조를 통해 참조하는 대상의 내용 변경 가능)
포인터는 가리키는 주소의 객체 내용 변경 및 주소 재지정이 가능하지만, 참조는 참조하는 객체를 재지정할 수 없다. 참조하는 객체의 내용을 변경할 수만 있다.
이러한 차이점 때문에 참조가 포인터에 비해 안전하다. 값으 변경으로 인한 오류 발생의 걱정이 없기 때문이다.
float Damage = 0;
//Damage의 참조 DamageRef 선언
float& DamageRef = Damage;
//참조의 값을 변경한다
DamageRef = 5;
//DamageRef가 참조하는 Damage도 값이 변경됨을 확인할 수 있다
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("DamageRef : %f, Damage : %f"), DamageRef, Damage);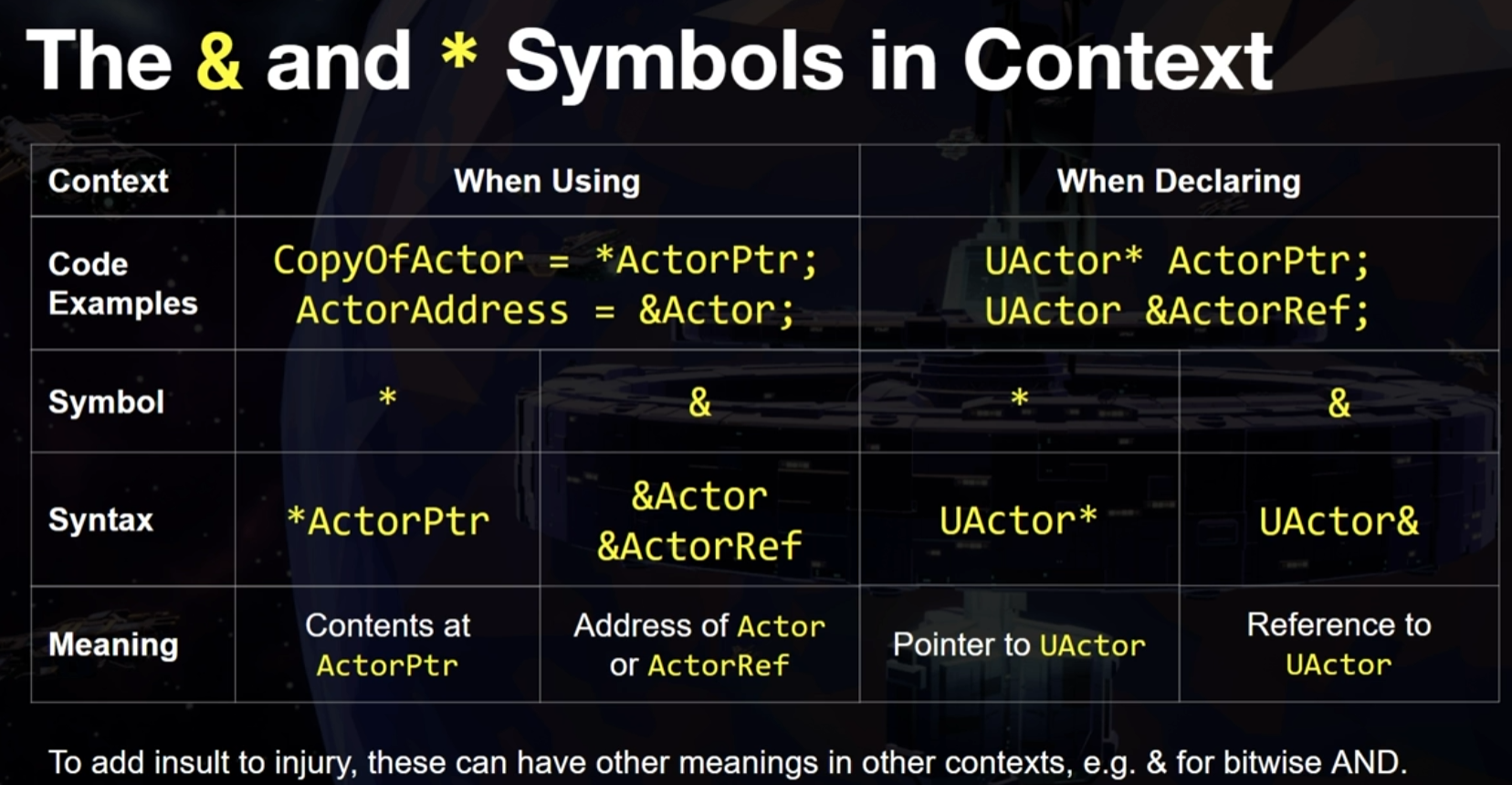
Const 참조 & Out 매개변수
함수에 인자로 참조를 전달하여, 함수 내에서 참조를 통해 변수의 값을 변경해 호출자에서 전달한 변수의 값도 변경되게 할 수 있다.
//참조로 매개변수를 선언
//함수 내에서의 Damage의 값 변경이 호출자의 변수에 영향을 미칠 수 있다
void PrintDamage(float& Damage);
void UGrabber::TickComponent(float DeltaTime, ELevelTick TickType, FActorComponentTickFunction* ThisTickFunction)
{
Super::TickComponent(DeltaTime, TickType, ThisTickFunction);
float Damage = 0;
PrintDamage(Damage);
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("Original Damage : %f"), Damage);
}
void UGrabber::PrintDamage(float& Damage)
{
Damage = 2;
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("Damage : %f"), Damage);
}
인자에 const 키워드를 사용하여 해당 참조를 통해 변수의 값을 변경하지 못하도록 제한할 수 있다.
호출자의 변수는 읽기 전용이 되며 함수 내에서 값을 변경할 수 없게 된다.
//const 키워드를 사용하여 참조 변경이 불가능하다 선언
void PrintDamage(const float& Damage);
void UGrabber::PrintDamage(const float& Damage)
{
//Damage는 상수 참조이기 때문에 값을 변경할 수 없다
//따라서 빌드를 하면 아래 코드 때문에 컴파일 에러가 발생한다
Damage = 2;
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("Damage : %f"), Damage);
}
Out 매개변수(출력 매개변수)를 사용하여 함수가 호출될 때 함수 내부에서 값을 변경하고, 그 값을 함수 외부로 반환할 수 있다.
void UGrabber::TickComponent(float DeltaTime, ELevelTick TickType, FActorComponentTickFunction* ThisTickFunction)
{
Super::TickComponent(DeltaTime, TickType, ThisTickFunction);
float Damage;
//함수로 전달하기 직전에 아무런 값도 초기화 되지 않았다는 것은
//함수가 대신 값을 넣어준다는 것이다
if(HasDamage(Damage))
{
PrintDamage(Damage);
}
}
void UGrabber::PrintDamage(const float& Damage)
{
//Damage = 2;
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Display, TEXT("Damage : %f"), Damage);
}
bool UGrabber::HasDamage(float& OutDamage)
{
//OutDamage에 값을 할당하여 함수 밖으로 값을 전달
Damage = 5;
return true;
}결국 출력 매개변수는 참조를 매개변수로 전달하는 것과 같은 것!!
#include <iostream>
void UpdateValue(int& value) {
value = 42;
}
int main() {
int myValue = 10;
std::cout << "Before Update: " << myValue << std::endl;
// UpdateValue 함수 호출 시 myValue에 대한 참조를 전달
UpdateValue(myValue);
// myValue 값이 변경됨
// myValue는 이제 42
std::cout << "After Update: " << myValue << std::endl;
return 0;
}