AVL tree
AVL 트리란 서브트리의 높이를 적절하게 제어해 전체 트리가 어느 한쪽으로 늘어지지 않도록 한 이진탐색트리(BST) 의 일종이다. 트리의 높이가 h일때 이진탐색트리의 시간복잡도는 O(h)이기 때문에 균형된 트리를 만들어 h를 줄이고자 하는 발상에서 비롯됐다.
AVL 트리의 핵심 개념 가운데 하나가 Balance Factor(BF) 이다. 왼쪽 서브트리의 높이에서 오른쪽 서브트리의 높이를 뺀 것이다. 두 서브트리의 높이가 같거나 리프노트라면 BF는 0이다. (empty tree의 BF는 -1로 정의)
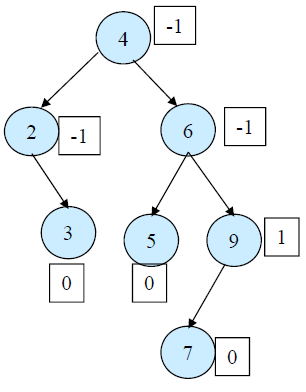
위 이진탐색트리의 루트노드의 BF는 -1이다. 왼쪽 서브트리의 높이는 1, 오른쪽은 2이기 때문이다. 9의 BF는 1이다. 9의 왼쪽 서브트리의 높이는 1, 오른쪽 서브트리는 존재하지 않아 0이기 때문이다. 리프노드인 3,5,7은 서브트리가 전혀 없기 떄문이 BF는 0이 된다. BF가 클 수록 불균형 트리라고 할 수 있다.
AVL 트리에서는 BF가 -1,0,1일 때만 균형있는 트리라고 본다. 값이 그보다 커지거나 작아지면 균형이 무너진 것이다.. 균형이 무너지는 경우에는 4가지 경우가 있다.
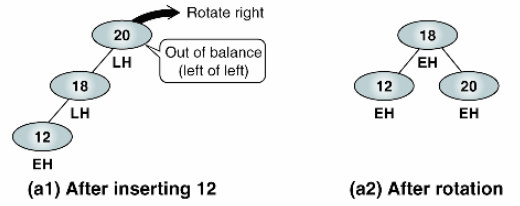
LL
왼쪽은 2인데 오른쪽은 0이여서 20의 BF가 2가 된다. 2 차이가 나서 균형이 무너졌다. 이럴때는 우회전을 한번 해준다.
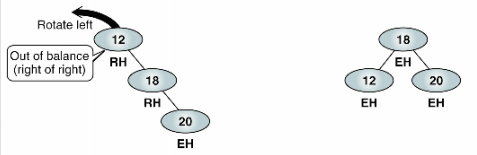
RR
오른쪽은 2인데 왼쪽이 0이어서 12의 BF가 -2가 된다. 균형이 무너진 상태이다. 이럴때는 좌회전을 한번 해준다.
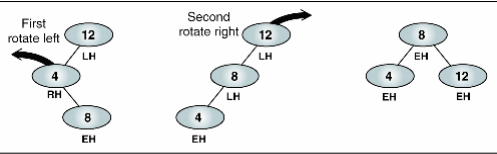
RL
왼쪽은 2, 오른쪽은 0인데 LL과의 차이는 왼쪽 서브트리의 모양이 다르다. 이때는 두번째 노드를 좌회전 한 후, 전체 노드를 우회전 해준다.
LR
두번째 노드를 우회전 한 후, 전체 노드를 좌회전 한다.
코드
정의부
var AVL = (function() {
function AVL() {
this.count = 0;
this.root;
this.taller;
this.shorter;
this.success;
}
function Node(data) {
this.data = data;
this.left;
this.right;
this.bal = 0; // 왼쪽과 오른쪽의 차이를 저장
}
// 삽입부 코드를 여기에
// 삭제부 코드를 여기에
AVL.prototype.insert = function(data) {
this.taller = false;
var node = new Node(data);
this.root = this._insert(this.root, node);
this.count++;
};
AVL.prototype.delete = function(key) {
this.shorter = false;
this.succuess = false;
var newRoot = this._delete(this.root, key);
if (this.success) {
this.root = newRoot;
this.count--;
return true;
}
return false;
};
AVL.prototype.search = function(key) {
if (this.root) {
return this._search(key, this.root);
}
return false;
};
AVL.prototype._search = function(key, root) {
if (root) {
if (key < root.data) {
return this._search(key, root.left);
} else if (key > root.data) {
return this._search(key, root.right);
} else {
return root;
}
}
return;
};
AVL.prototype._rotateLeft = function(root) {
var temp = root.right; // temp를 중간 노드로 생각하면 이해하기 쉽다.
root.right = temp.left;
temp.left = root;
return temp;
};
AVL.prototype._rotateRight = function(root) {
var temp = root.left; // temp를 중간 노드로 생각하면 이해하기 쉽다.
root.left = temp.right;
temp.right = root;
return temp;
};
return AVL;
})();삽입부
AVL.prototype._insert = function(root, node) { // 내부적 insert 메소드
if (!root) { // 트리의 말단 부분에 도달하면 바로 넣는다.
root = node;
this.taller = true;
console.log('no root', root);
return root;
}
if (node.data < root.data) { // 새 값이 루트 값보다 작으면
root.left = this._insert(root.left, node);
console.log('go left', this.taller, root.bal);
if (this.taller) { // 삽입으로 인해서 한 쪽이 더 길어졌으면
switch (root.bal) {
case 1: // 왼쪽이 더 긴 상태에서 또 왼쪽에 넣어줬으므로 LL 또는 RL
root = this._insLeftBal(root);
break;
case 0: // 균형이었던 상태에서 왼쪽에 넣어줬으므로 왼쪽이 길어짐
root.bal = 1;
break;
case -1: // 오른쪽이 길었던 상태에서 왼쪽에 넣어줬기 때문에 균형
root.bal = 0;
this.taller = false;
break;
}
}
return root;
} else { // 새 값이 루트 값보다 크면
root.right = this._insert(root.right, node);
console.log('go right', this.taller, root.bal);
if (this.taller) { // 삽입으로 인해서 한 쪽이 더 길어졌으면
switch (root.bal) {
case 1: // 왼쪽이 긴 상태에서 오른쪽에 넣어줬기 때문에 균형
root.bal = 0;
this.taller = false;
break;
case 0: // 균형이었던 상태에서 오른쪽에 넣어줬기 때문에 오른쪽이 길어짐
root.bal = -1;
break;
case -1: // 오른쪽이 긴 상태에서 또 오른쪽에 넣어줬으므로 RR 또는 LR
root = this._insRightBal(root);
break;
}
}
return root;
}
};
AVL.prototype._insLeftBal = function(root) {
var left = root.left;
console.log('insLeftBal', left.bal);
switch (left.bal) {
case 1: // LL의 경우입니다.
root.bal = 0;
left.bal = 0;
root = this._rotateRight(root); // 우회전 한 번
this.taller = false;
break;
case 0: // 균형인 경우는 없습니다.
throw new Error('불가능한 경우');
case -1: // RL의 경우입니다.
var right = left.right;
switch (right.bal) {
case 1:
root.bal = -1;
left.bal = 0;
break;
case 0:
root.bal = 0;
left.bal = 1;
break;
case -1:
root.bal = 0;
left.bal = 1;
break;
}
right.bal = 0;
root.left = this._rotateLeft(left); // 좌회전 후
root = this._rotateRight(root); // 우회전
this.taller = false;
}
};
AVL.prototype._insRightBal = function(root) {
var right = root.right;
console.log('insRightBal', right.bal);
switch (right.bal) {
case -1: // RR의 경우입니다.
root.bal = 0;
right.bal = 0;
root = this._rotateLeft(root); // 좌회전 한 번
this.taller = false;
break;
case 0: // 균형일 수는 없습니다.
throw new Error('불가능한 경우');
case 1:
var left = right.left;
switch (left.bal) { // LR의 경우입니다.
case 1:
root.bal = -1;
right.bal = 0;
break;
case 0:
root.bal = 0;
right.bal = 1;
break;
case -1:
root.bal = 0;
right.bal = 1;
break;
}
left.bal = 0;
root.right = this._rotateRight(right); // 우회전 후
root = this._rotateLeft(root); // 좌회전
this.taller = false;
}
return root;
};switich문에서 root.bal이 1이면 왼쪽이 긴 상태, 0이면 균형, -1이면 오른쪽이 더 긴상태.
insLefrBal, insRightBal은 어떤 유형의 불균형인지 판단 후 회전을 시켜주는 부분
삭제부
AVL.prototype._delete = function(root, key) {
if (!root) { // 지울 게 없습니다.
console.log('no root to delete');
this.shorter = false;
this.success = false;
return;
}
if (key < root.data) { // 지울 값이 루트 값보다 작으면
root.left = this._delete(root.left, key);
console.log('go left', root.left, this.shorter);
if (this.shorter) { // 삭제로 인해 짧아졌으면
root = this._delRightBal(root);
}
} else if (key > root.data) { // 지울 값이 루트 값보다 크면
root.right = this._delete(root.right, key);
console.log('go right', root.right, this.shorter);
if (this.shorter) { // 삭제로 인해 짧아졌으면
root = this._delLeftBal(root);
}
} else { // key와 일치하는 데이터를 찾았을 때
console.log('found', key, root);
if (!root.right) { // 오른쪽 자식이 없으면 노드가 제거됐을 때 왼쪽 자식이 루트
var newRoot = root.left;
this.success = true;
this.shorter = true;
return newRoot;
} else if (!root.left) { // 왼쪽 자식이 없으면 노드가 제거됐을 때 오른쪽 자식이 루트
var newRoot = root.right;
this.success = true;
this.shorter = true;
return newRoot;
} else { // 삭제할 노드를 계속 왼쪽으로 보내서 제거(트리 강좌 참고)
var temp = root.left;
while (temp.right) temp = temp.right;
root.data = temp.data;
root.left = this._delete(root.left, temp.data);
if (this.shorter) { // 삭제로 짧아졌으면
root = this._delRightBal(root);
}
}
}
return root;
};
AVL.prototype._delLeftBal = function(root) {
console.log('delLeftBal', root, root.bal, root.left);
switch (root.bal) {
case 1:
root.bal = 0;
break;
case 0:
root.bal = -1;
this.shorter = false;
break;
case -1:
var left = root.left;
if (left.bal === 1) { // RL의 경우
var right = left.right;
switch (right.bal) {
case 1:
left.bal = -1;
root.bal = 0;
break;
case 0:
root.bal = 0;
left.bal = 0;
break;
case -1:
root.bal = 1;
left.bal = 0;
break;
}
right.bal = 0;
root.left = this._rotateLeft(left);
root = this._rotateRight(root);
} else { // LL의 경우
switch (left.bal) {
case -1:
root.bal = 0;
left.bal = 0;
break;
case 0:
root.bal = -1;
left.bal = 1;
this.shorter = false;
break;
}
root = this._rotateRight(root);
}
}
return root;
};
AVL.prototype._delRightBal = function(root) {
console.log('delRightBal', root, root.bal);
switch (root.bal) {
case 1:
root.bal = 0;
break;
case 0:
root.bal = -1;
this.shorter = false;
break;
case -1:
right = root.right;
if (right.bal === 1) { // LR의 경우입니다.
left = right.left;
console.log('delRightBal LR', left.bal);
switch (left.bal) {
case 1:
right.bal = -1;
root.bal = 0;
break;
case 0:
root.bal = 0;
right.bal = 0;
break;
case -1:
root.bal = 1;
right.bal = 0;
break;
}
left.bal = 0;
root.right = this._rotateRight(right);
root = this._rotateLeft(root);
} else { // RR의 경우입니다.
console.log('delRightBal RR', right.bal);
switch (right.bal) {
case 0:
root.bal = -1;
right.bal = -1;
this.shorter = false;
break;
case -1:
root.bal = 0;
right.bal = 0;
break;
}
root = this._rotateLeft(root);
}
}
return root;
};