1. Postgres에 데이터 Insert
- 예전에 프로젝트를 할 때,
import psycopg2 # postgres
import pymysql # mysql
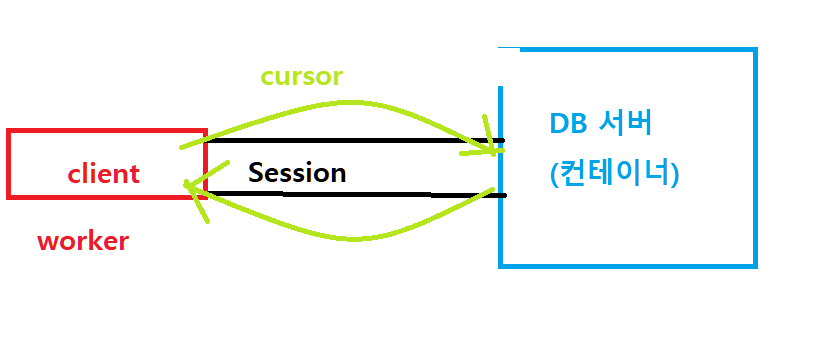
# DB서버와의 연결(Session)객체 생성
conn = psycopg2.connect(...)
~~~~
conn.close()
# 마찬가지로
conn = pymysql.connect(...)
~~~~
conn.close()이런식으로 입력해줬는데, with 문과 함께 from contextlib import closing을 사용하면 conn객체 생성하고, 쿼리를 날리는 cursor 객체 생성한 뒤, cursor.execute() cursor.commit() 한 후에 conn객체가 자동으로 닫아진다.
- Table 생성하자.
create table py_opr_drct_insert (
dag_id varchar(100),
task_id varchar(100),
run_id varchar(100),
msg text
)
table명은 py_opr_drct_insert로 이렇게 작명한 이유는 postgresql에 direct로 insert할시의 문제점을 소개해주기 위해서 위와 같이 작명해주었다. 칼럼은 dag_id, task_id, run_id가 들어간다. 해당 부분은 airflow의 ti객체(task instance)에 들어있는 값이다.
- 실행시킬 DAG 코드를 작성해주자.
from airflow import DAG
import pendulum
from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator
with DAG(
dag_id="dags_python_with_postgres",
start_date=pendulum.datetime(2023, 8, 1, tz="Asia/Seoul"),
catchup=False,
schedule=None
) as dag:
def insert_postgres(ip, port, dbname, user, passwd, **kwargs):
import psycopg2
from contextlib import closing
with closing(psycopg2.connect(host=ip, dbname=dbname, uesr=user, password=passwd, port=int(port))) as conn:
with closing(conn.cursor()) as cursor:
dag_id = kwargs.get("ti").dag_id
task_id = kwargs.get("ti").task_id
run_id = kwargs.get("ti").run_id
msg = "insert 추출"
sql = "insert into py_opr_drct_insert values (%s, %s, %s, %s);"
cursor.execute(sql, (dag_id, task_id, run_id, msg))
conn.commit()
insert_postgres = PythonOperator(
task_id = "insert_postgres",
python_callable=insert_postgres,
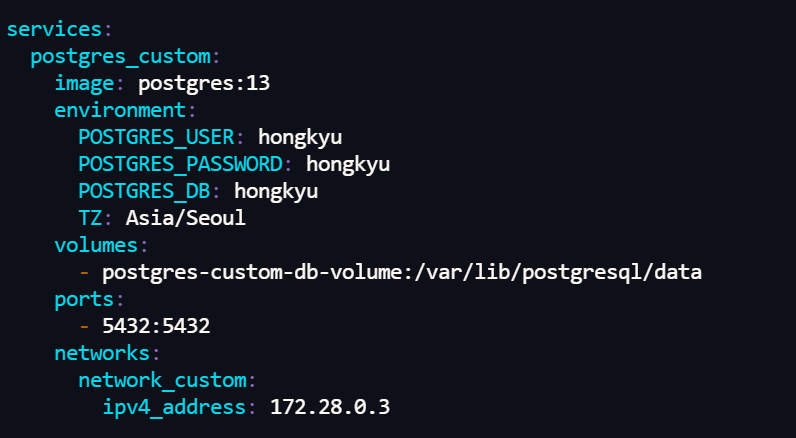
op_args=['172.28.0.3', '5432', 'hongkyu', 'hongkyu', 'hongkyu']
)
insert_postgres
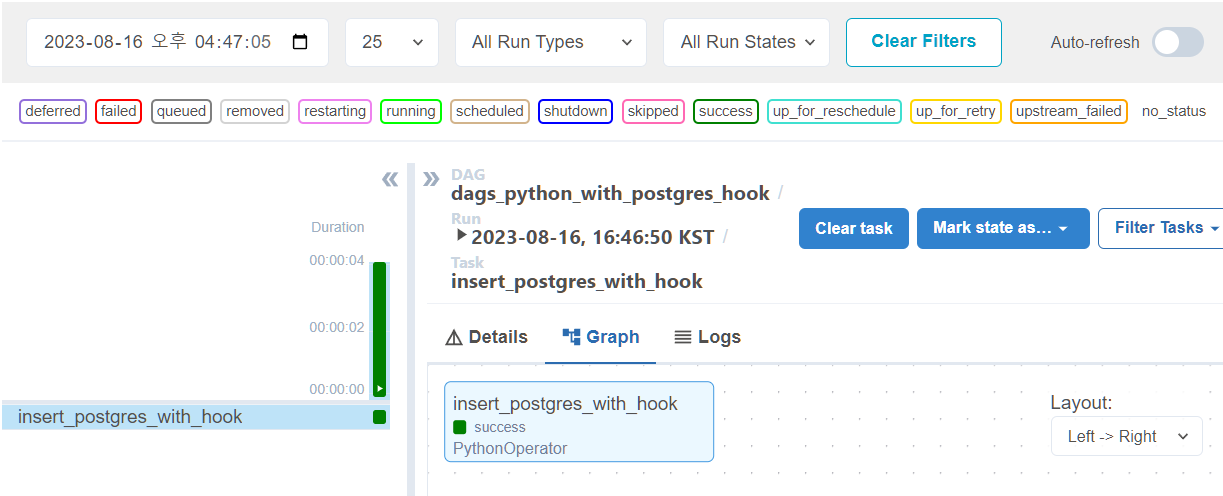
-
airflow success 확인
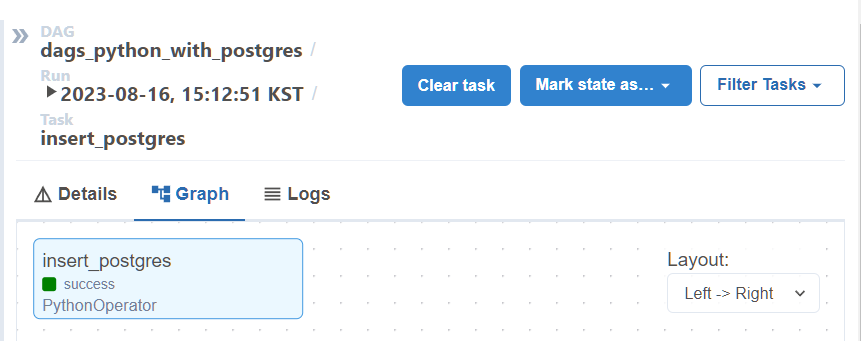
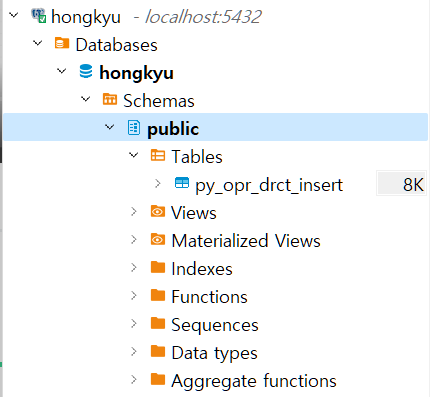
-
table에 해당 값이 잘 들어왔는지 확인
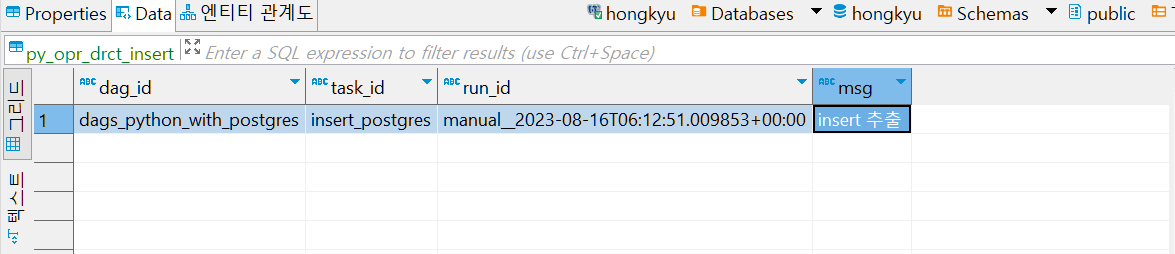
2. 문제점 및 해결방법
작성한 DAG 코드에서 문제점을 생각해보자.
- 문제점
-
(1) 접속정보 노출: postgres DB에 대한 User, Password 등
-
(2) 접속정보 변경시 대응이 어렵다.
- 만약, 직접 접속하는 DAG가 수백 개라면?
-
- 해결 방법
- (1) Variable 이용: 전역변수 사용 (User, Password 등을 Variable에 등록하고 꺼내오기)
- (2) Hook 이용 (Variable 등록 필요없음)
3. Connection과 Hook의 개념
-
Connection
: airflow UI 화면에서 등록한 커넥션 정보 -
Hook의 개념
: airflow에서 외부 솔루션의 기능을 사용할 수 있도록 미리 구현된 메서드를 가진 클래스 -
Hook의 특징
(1) Connection 정보를 통해 생성되는 객체
-> 접속정보를 Connection을 통해 받아오므로 접속정보가 코드상 노출되지 않는다는 장점이 있다.
(2) 특정 솔루션을 다룰 수 있는 메서드가 구현되어 있다.
(3) 오퍼레이터나 센서와 달리 Hook은 task를 만들어내지 못하므로, Custom Operator 안에서나 Python Operator 내 함수에서 사용된다.
4. Connection 등록
| Connection_id | conn-db-postgres-custom |
|---|---|
| Connection_type | Postgres |
| Host | 172.28.0.3 |
| Schema | hongkyu |
| Login | hongkyu |
| Password | hongkyu |
| Port | 5432 |
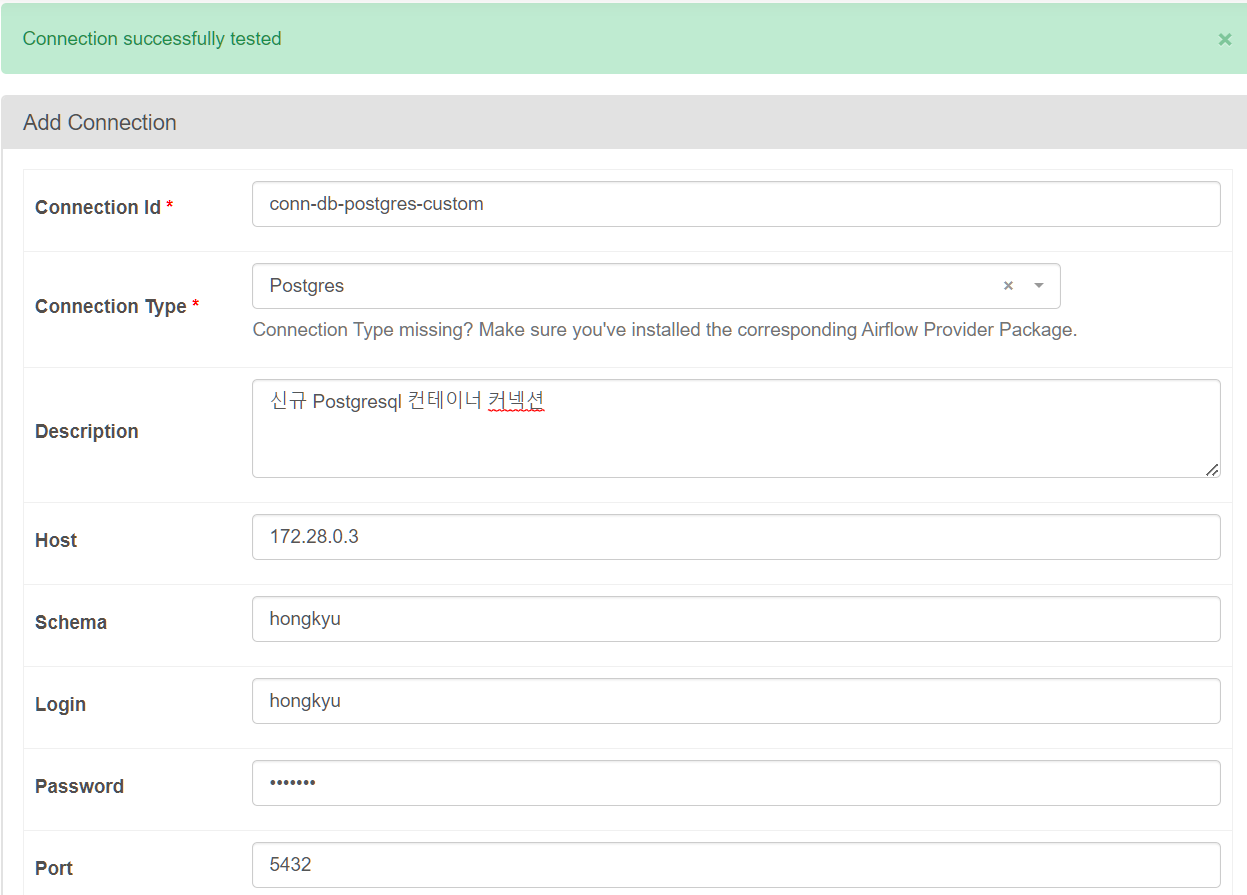
Admin -> Connections 클릭 후 새로운 Connection을 만들어준다.
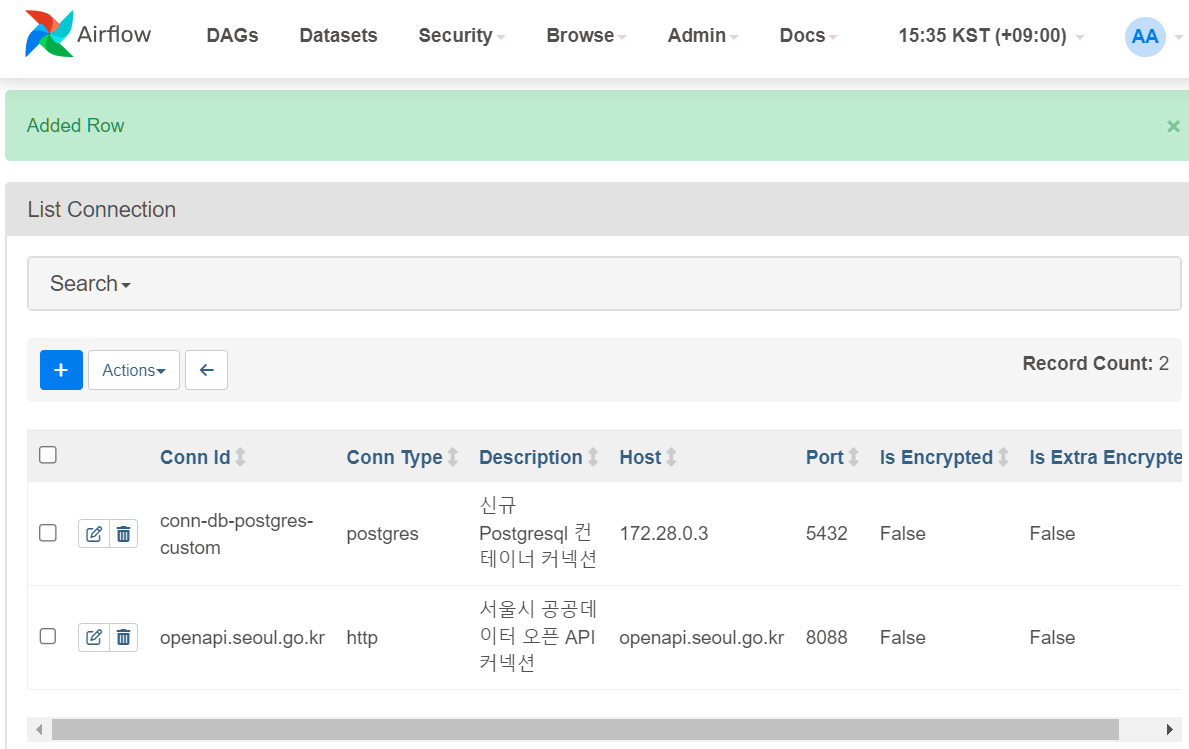
지난번 http 커넥션에 이어, Postgres커넥션이 잘 생성되었다.
5. Postgres Hook 명세 보기
apache-airflow-providers-postgres-hooks 명세 확인하기
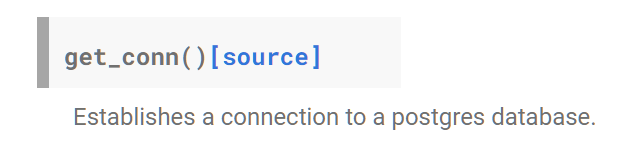
-> 해당 source를 들어가서 예제 함수를 살펴보자.
def get_conn(self) -> connection:
"""Establishes a connection to a postgres database."""
conn_id = getattr(self, self.conn_name_attr)
conn = deepcopy(self.connection or self.get_connection(conn_id))
# check for authentication via AWS IAM
if conn.extra_dejson.get("iam", False):
conn.login, conn.password, conn.port = self.get_iam_token(conn)
conn_args = dict(
host=conn.host,
user=conn.login,
password=conn.password,
dbname=self.database or conn.schema,
port=conn.port,
)
......
self.conn = psycopg2.connect(**conn_args)
return self.connget_conn()함수는 postgresql 데이터베이스 연결을 도와주는 함수이다. 코드 몇몇 부분이 아까 db에 direct로 연결해줬던 코드와 비슷하다. conn객체에 host, user, password, dbname, port가 들어가는 걸 볼 수 있다.
그렇다면 conn 객체는 어떻게 생성해주었을까?
conn = self.get_connection(conn_id)를 통해 생성해주었음을 알 수 있다.
해당 부분은 어디서 왔을까?
airflow.hooks.base에서 왔음을 알 수 있다.
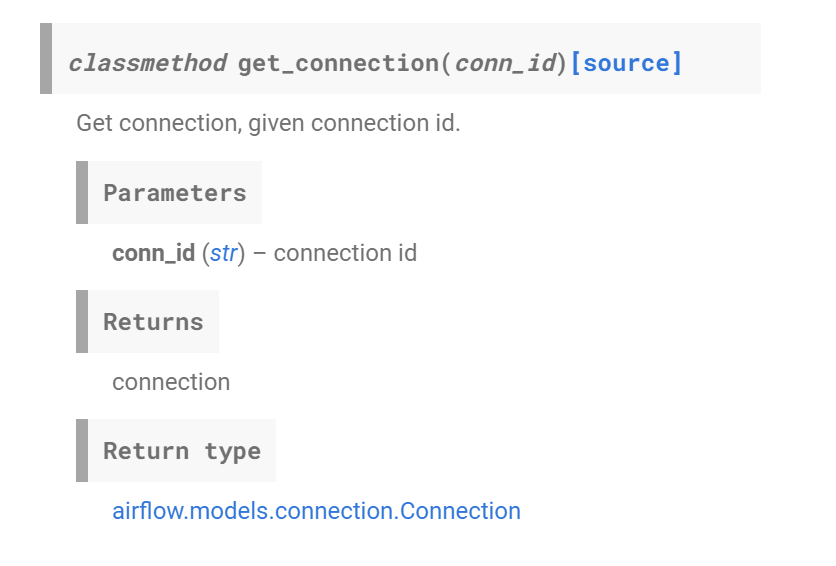
@classmethod
[docs] def get_connection(cls, conn_id: str) -> Connection:
"""
Get connection, given connection id.
:param conn_id: connection id
:return: connection
"""
from airflow.models.connection import Connection
conn = Connection.get_connection_from_secrets(conn_id)
log.info("Using connection ID '%s' for task execution.", conn.conn_id)
return conn
conn_id를 바탕으로 Connection 객체를 리턴함을 알 수 있다. 그런데 def문에서 from airflow.models.connection 모듈에서 Connection클래스를 불러오고 Connection 클래스의 get_connection_from_secrets 함수를 실행함으로서 conn 객체를 리턴하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
다시 타고 가보자.
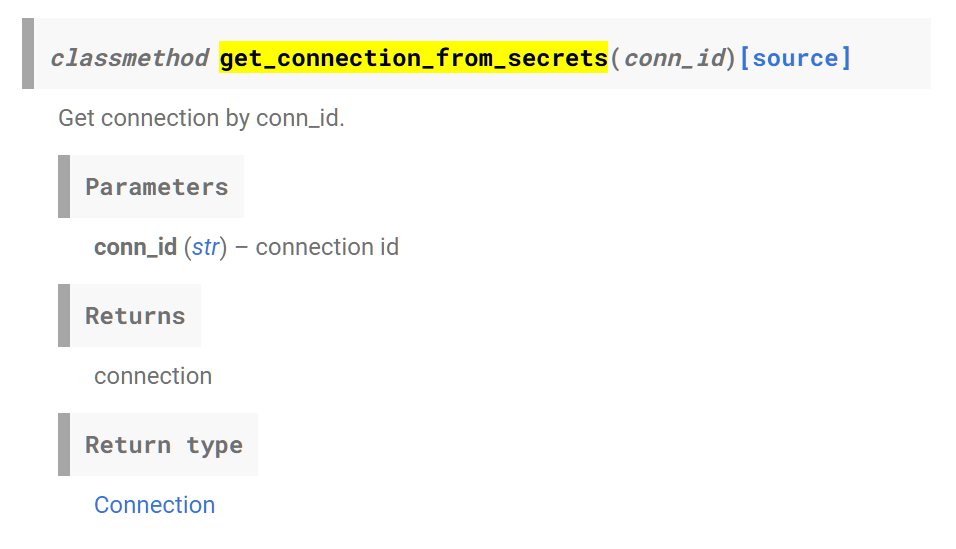
오마이갓. 산넘어산이다.
@classmethod
[docs] def get_connection_from_secrets(cls, conn_id: str) -> Connection:
"""
Get connection by conn_id.
:param conn_id: connection id
:return: connection
"""
for secrets_backend in ensure_secrets_loaded():
try:
conn = secrets_backend.get_connection(conn_id=conn_id)
if conn:
return conn
except Exception:
log.exception(
"Unable to retrieve connection from secrets backend (%s). "
"Checking subsequent secrets backend.",
type(secrets_backend).__name__,
)
raise AirflowNotFoundException(f"The conn_id `{conn_id}` isn't defined")
ensure_secrets_loaded() 는 리스트를 생성하는 것 같다. 해당 부분을 따라가보자.


def get_custom_secret_backend():
# type: (...) -> Optional[BaseSecretsBackend]
"""Get Secret Backend if defined in airflow.cfg"""
alternative_secrets_backend = conf.get(section=CONFIG_SECTION, key='backend', fallback='')
if alternative_secrets_backend:
try:
alternative_secrets_config_dict = json.loads(
conf.get(section=CONFIG_SECTION, key='backend_kwargs', fallback='{}')
)
except ValueError:
alternative_secrets_config_dict = {}
secrets_backend_cls = import_string(alternative_secrets_backend)
return secrets_backend_cls(**alternative_secrets_config_dict)
return None
def initialize_secrets_backends():
# type: (...) -> List[BaseSecretsBackend]
"""
* import secrets backend classes
* instantiate them and return them in a list
"""
backend_list = []
custom_secret_backend = get_custom_secret_backend()
if custom_secret_backend is not None:
backend_list.append(custom_secret_backend)
for class_name in DEFAULT_SECRETS_SEARCH_PATH:
secrets_backend_cls = import_string(class_name)
backend_list.append(secrets_backend_cls())
return backend_list
def ensure_secrets_loaded():
# type: (...) -> List[BaseSecretsBackend]
"""
Ensure that all secrets backends are loaded.
If the secrets_backend_list contains only 2 default backends, reload it.
"""
# Check if the secrets_backend_list contains only 2 default backends
if len(secrets_backend_list) == 2:
return initialize_secrets_backends()
return secrets_backend_list
secrets_backend_list = initialize_secrets_backends()
6. Hook을 이용한 Insert
사용법은 더 간단하다.
from airflow.providers.postgres.hooks.postgres import PostgresHook 으로 해당 클래스를 import 해온 뒤, PostgresHook(postgres_conn_id)를 넣어주면 된다.
여기서, 만약에 AWS와 연결하고 싶다면 conn_id인자에
"iam":true를 추가해주면 된다.
AWS의 redshift를 사용한다면, conn_id에"iam":true,"redshift":true를 전달해준다.
PostgresSQL Connection conn_id 설정법
host, schema, login, password를 전달해주면 되겠다.
from airflow import DAG
import pendulum
from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator
with DAG(
dag_id="dags_python_with_postgres_hook",
start_date=pendulum.datetime(2023, 8, 1, tz="Asia/Seoul"),
schedule=None,
catchup=False
) as dag:
def insert_postgres(postgres_conn_id, **kwargs):
from airflow.providers.postgres.hooks.postgres import PostgresHook
from contextlib import closing
postgres_hook = PostgresHook(postgres_conn_id)
# conn 객체 생성 (데이터베이스 연결)
with closing(postgres_hook.get_conn()) as conn:
# cursor 객체 생성(쿼리 작성하기 위함)
with closing(conn.cursor()) as cursor:
# task instance 객체에 속하는 value들을 가져온다.
dag_id = kwargs.get("ti").dag_id
task_id = kwargs.get("ti").task_id
run_id = kwargs.get("ti").run_id
msg = "hook insert 수행"
sql = 'insert into py_opr_drct_insert values (%s, %s, %s, %s);'
cursor.execute(sql, (dag_id, task_id, run_id, msg))
# 파이썬 오퍼레이터 작성
insert_postgres_with_hook = PythonOperator(
task_id = 'insert_postgres_with_hook',
python_callable=insert_postgres,
op_kwargs={'postgres_conn_id': 'conn-db-postgres-custom'}
)
insert_postgres_with_hook