⚠️ 해당 포스팅은 인프런 공룡책 강의를 듣고 개인적으로 정리하는 글입니다. 정확하지 않은 정보가 있을 수 있으니 주의를 요합니다.
Section 03
Chapter 3 Process (2)
Interprocess Communcation
- 동시에 실행하는, 즉 동시성을 지닌 프로세스는 독립적인 프로세스(independent processes)이거나, 상호 협력적인 프로세스(cooperating processes)일 수 있다.
- 독립적인 프로세스는, 다른 프로세스와 공유할 데이터가 없다.
- 협력 프로세스는 다른 프로세스와 데이터를 공유하며 서로에게 영향을 주거나 받을 수 있다.
IPC (Inter-Process Communcation)
- 협력 프로세스는 IPC 메커니즘을 필요로 한다.
- 이는 데이터를 교환할 수 있게 해주며, 서로에게 데이터를 보내거나 받을 수 있게 해준다.
- IPC 모델은 2가지가 존재하는데, 이는 공유 메모리 방식(shared memory)과 메세지 패싱 방식(message passing)이다.
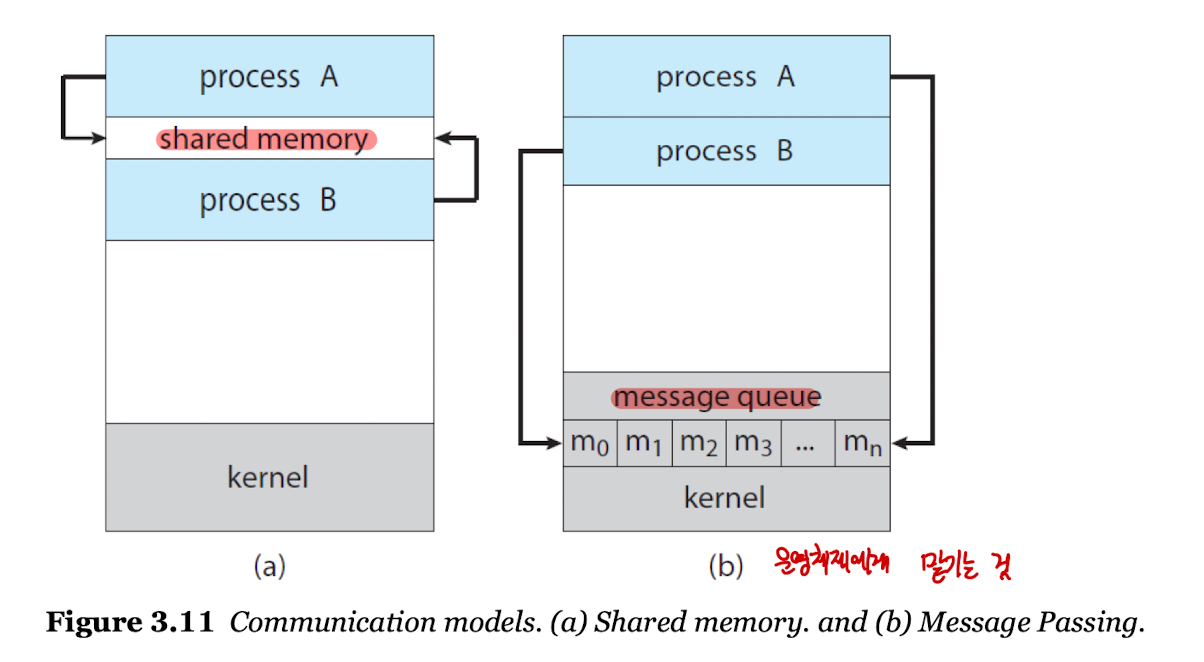
IPC in Shared-Memory Systems
- 공유 메모리 방식은 생성자-소비자 문제(Producer-Consumer Problem)를 고려해야 한다. 협력 프로세스를 설명하기 위한 기본적인 패러다임으로, 이를 숙지해야 기본적인 통신이 가능하다.
- 생성자-소비자 문제 : 생성자는 정보를 생산하고, 소비자는 정보를 소비하는 개념으로 두 가지 예를 들면,
- 컴파일러가 어셈블리 코드를 생성하면, 어셈블러가 이를 소비하는 방식이 있다.
- 웹 서버가 HTML 파일을 생성하면 브라우저가 이를 소비하는 방식이 있다.
- 공유 메모리는 생성자와 소비자 프로세스가 공유하는 메모리 영역이다.
- 공유 메모리를 사용할 때 기본적으로 생성자와 소비자는 동시성을 지니며 돌아간다.
- 버퍼를 사용해 정보를 공유하며 생성자는 버퍼를 채우고 소비자는 버퍼를 비우는 방식으로 진행된다.
- 버퍼가 가득 차면 생성자는
wait()시스템 콜을 진행하며 소비자는 이를 소비한다. - 버퍼가 비어있으면 소비자는
wait()시스템 콜을 진행하며 생성자는 버퍼를 채운다.
- 버퍼가 가득 차면 생성자는
// IPC in Shared-Memory Systems
#define BUFFER_SIZE 10
typedef struct {
. . .
} item;
item buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
int in = 0;
int out = 0;
item next_produced;
while(true) {
/* produce an item in next_produced */
while(((in + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE) == out);
buffer[in] = next_produced;
in = (in + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE;
}
item next_consumed;
while(true) {
while(in == out); /* do nothing */
next_consumed = buffer[out];
out = (out + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE;
/* consume the item in next_consumed */
}
- 공유 메모리 방식은 프로세스들이 메모리 영역을 공유해야 하며, 버퍼 관리, 메모리 접근 및 조작 등을 프로그래머가 직접 명시해주어야 한다는 단점이 있다.
- 공유 메모리 방식을 많이 사용하진 않지만, Prosumer 와 같이 생산과 동시에 소비까지 하는 프로세스의 경우 수백명이 동시에 사용하면 메세지 파싱 방식으론 힘들 수 있기 때문에 프로그래머가 직접 관리하기도 한다.
IPC in Message-Passing Systems
- O/S는 협력 프로세스를 위해 메세지 패싱을 통한 커뮤니케이션 방식을 지원한다.
- 메세지 패싱을 위해 두 가지 명령어가 존재한다.
send(message),receive(message)
message next_produced;
while(true) {
/* produce an item in next_produced */
send(next_produced);
}
message next_consumed;
while(true) {
receive(next_consumed);
/* consume the item in next_consumed */
/* in = out 이런 것을 O/S가 처리해주어 편리하다. */
}
Communcation Links
- 만약 P, Q 프로세스가 소통하길 바란다면 서로에게 메세지를 보내고 받을 때 링크가 필요한데, 이 링크를 연결할 수 있는 방법이 여러 개 있다.
- direct or indirect
- synchronous or asynchronous
- automatic or explicit buffering
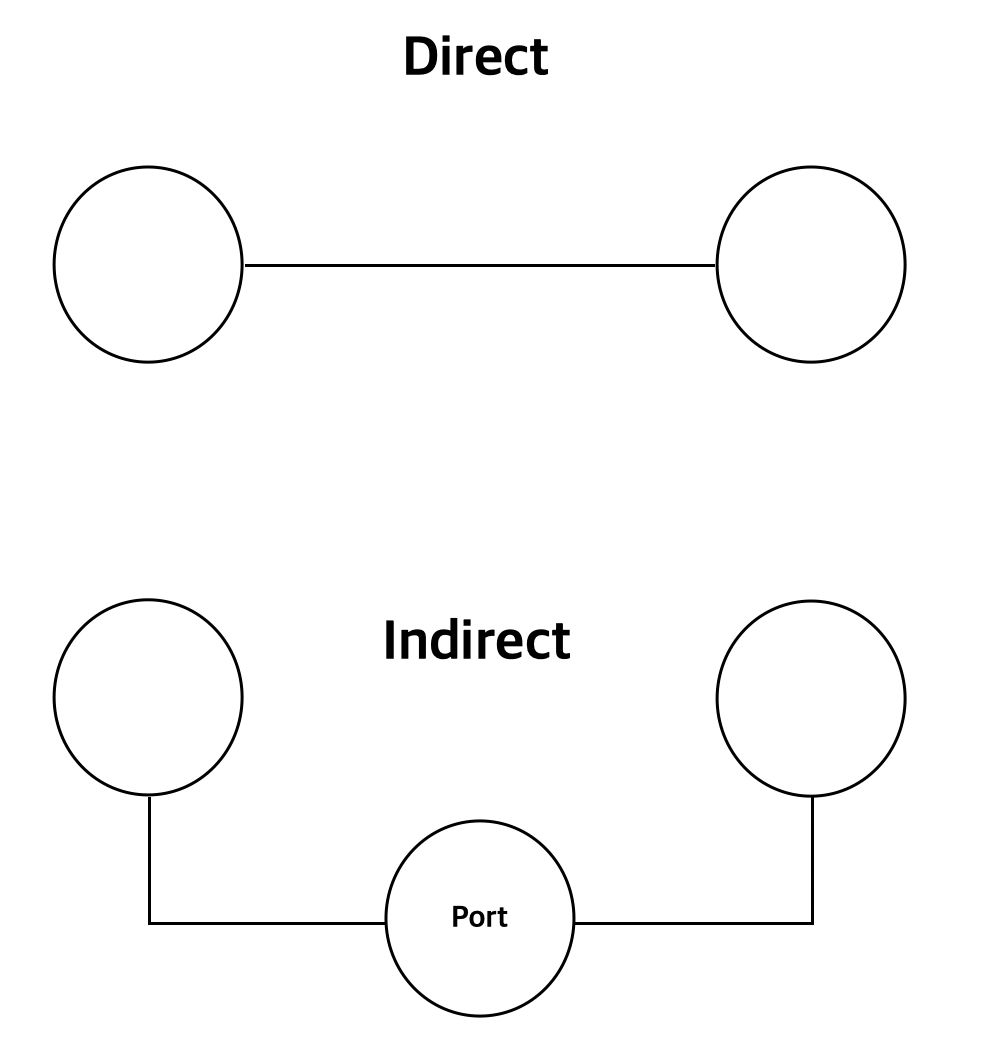
- direct communication
- direct 방식은 통신하고자 하는 상대방이 누구인지 명확하게 알 수 있을 때, 즉 받는 사람과 보내는 사람의 이름을 알고 있을 때 사용한다.
send(P, message),receive(Q, message)- 상대방이 누구인지 명시했으므로 링크는 자동으로 생성된다.
- 두 프로세스 간 링크는 하나만 존재한다.
- indirect communication
- indirect 방식은 매개체가 필요하며, 이는 port 라는 이름으로 잘 알려져 있다.
- 포트는 프로세스가 메모리를 보관하거나 삭제하는 공간이다.
send(P, port),receive(Q, port)- 두 프로세스가 같은 공유 포트를 가질 때 링크가 설정된다.
- 두 개 이상의 프로세스 할당이 가능하다.
- 여러 개의 다른 링크가 존재할 수 있다.
- O/S 에서는 프로세스가 포트를 생성하고, 포트에 메시지를 전송하고 받을 수 있게 설정하고, 포트를 삭제할 수 있게 메커니즘을 제공해야 한다.
- 또한 메세지 패싱 방식을 사용할 때 여러가지 옵션을 줄 수 있다.
- Blocking send : 보내는 프로세스는 메세지를 받을 때 까지 블락된다.
- Non-blocking send : 보내는 프로세스는 메세지를 보내고 다음 할 일을 진행한다.
- Blocking receive : 받는 프로세스는 메세지를 사용할 수 있을 때까지 블락된다.
- Non-blocking receive : 받는 프로세스는 유효 메세지 혹은 null 메세지를 계속해서 검색한다.
Examples of IPC Systems
- Shared Memory : POSIX Shared Memory
유닉스에서 사용하며 O/S 표준화를 시도하였다. - Message Passing : Pipes
유닉스의 초기 IPC 메커니즘 중 하나이다.
POSIX shared memory
- 공유 메모리 영역이 파일과 연결하는 메모리 매핑 파일을 이용해 구성되어 있다.
- 하드웨어에 파일을 생성하는 것이 아니라 메모리에 파일을 생성하여 속도를 올린다.
// Producer
int main() {
const int SIZE = 4096;
const char *name = "OS";
const char *message_0 = "Hello, ";
const char *message_1 = "Shared Memory!\n";
int shm_fd; // the file descriptor of shared memory
char *ptr; // pointer to shared memory
/* create the shared memory object */
shm_fd = shm_open(name, O_CREAT | O_RDWR, 0666);
/* configure the size of the shared memory */
ftruncate(shm_fd, SIZE); // 4096 byte 씩 읽고 쓰기
/* map the shared memory object */
ptr = (char *)mmap(0, SIZE, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, shm_fd, 0);
/* write to the shared memory */
sprintf(ptr, "%s", message_0);
ptr += strlen(message_0);
sprintf(ptr, "%s", message_1);
ptr += strlen(message_1);
return 0;
}// Consumer
int main() {
const int SIZE = 4096;
const char *name = "OS";
int shm_fd; // the file descriptor of shared memory
char *ptr; // pointer to shared memory
/* create the shared memory object */
shm_fd = shm_open(name, O_RDONLY, 0666);
/* map the shared memory object */
ptr = (char *)mmap(0, SIZE, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, shm_fd, 0);
/* read from the shared memory object */
printf("%s", (char *)ptr);
/* remove the shared memory */
shm_unlink(name);
return 0;
/* 첫 번째 실행 -> Hello, Shared Memory
두 번째 실행 -> Segmintation Fault (포인트가 뒤로 밀려 쓰레기값 출력) */
}
Pipes
- 두 프로세스 통신을 위한 통로 역할을 수행한다.
- Shared Memory 에서는 일일이 open, write, read, close 등을 수행하며 부담이 갔던 단점을 보완한 방법이다.
- Pipe 를 구성할 때는 4가지 이슈가 존재한다.
- 단방향(unidirectional) 인지, 양방향(bidirectional) 인지?
(양방향 통신을 사용할 때는 서로 통신을 진행하다가 충돌이 일어날 수 있는 가능성 있음) - 양방향 통신을 구성한다면, half-duplex 인지 full-duplex 인지?
(half-duplex(무전기), full-duplex(전화기) 로 대입하여 생각하면 편리) - 부모-자식과 같이 프로세스 사이에 명확한 관계가 있어야 하는지?
- 파이프에서 네트워크를 통해 통신할 수 있는지?
- 단방향(unidirectional) 인지, 양방향(bidirectional) 인지?
- Ordinary pipes(평범한 파이프)
- 일반적으로 부모 프로세스가 파이프를 생성하면 자식 프로세스가 통신을 위해 이를 사용한다.
- 단방향 통신만 가능하며, 양방향 통신을 원한다면 두 개의 파이프를 생성하면 된다.
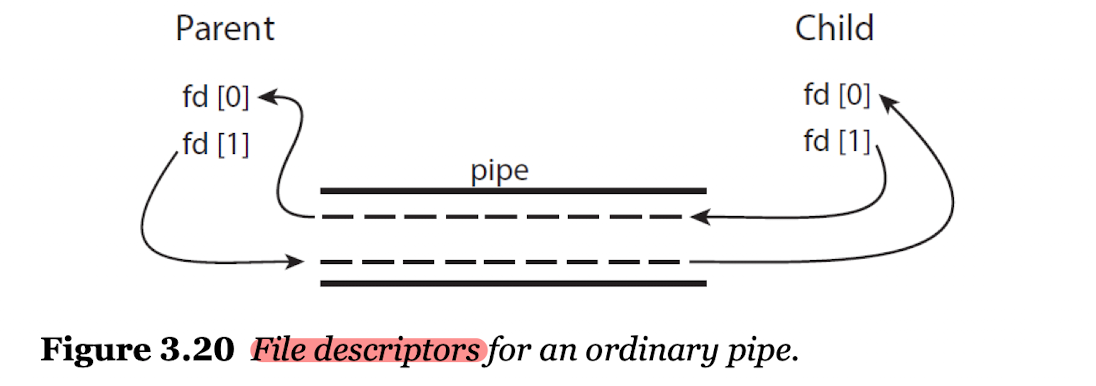
- 일반적으로 유닉스 시스템에서 파이프를 구성할 때
fd[0]의 경우 읽기 전용,fd[1]의 경우 쓰기 전용으로 구성한다.
- Named pipes
- 부모-자식 관계를 넘어 여러 관계 형성이 가능하다.
Communication in Client-Server Systems
- 일반적으로 클라이언트-서버 시스템을 구축할 때 Socket을 사용하는 전략과 RPCs를 사용하는 전략이 존재한다.
Socket
- 통신을 위해 endpoint 를 정의한다.
- port 번호와 연결된 IP 주소로 식별된다.
public class DateServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(6013);
/* Now listen for connections */
while (true) {
Socket client = server.accept();
PrintWriter pout = new PrintWriter(client.getOutputStream(), true);
/* write the Date to the socket */
pout.println(new java.util.Date().toString());
/* close the socket and resume listening for connections */
client.close();
}
}
}
public class DateClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/* make connection to server socket */
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 6013);
InputStream in = socket.getInputStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
/* read date from the socket */
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null)
System.out.println(line);
/* close the socket connections */
socket.close();
}
}
RPC (Remote Procedure Call)
- 원격지 함수를 호출하는 방법이다.
- 클라이언트는 로컬에서 프로시저를 호출하는 것처럼 원격 호스트에서 프로시저를 호출한다.
- 클라이언트 측에서 stub 을 제공하여 통신이 발생할 때 세부 정보를 숨긴다.
- 클라이언트 측 stub은 서버를 찾고 마샬링(데이터 직렬화)된 매개변수를 전송한다.
- 서버 측 stub은 메세지를 받고, 마샬링된 매개변수를 압축 해제하고 서버에서 요청한 프로시저를 수행한다.
- 복잡하고 어려운 방법이다.
만약 프로시저를 호출하는데, 한 컴퓨터는 64bit에 little-endian 방식을 사용하고, 다른 컴퓨터는 32bit에 big-endian 방식을 사용한다면, 어떻게 데이터를 주고받을 것인지 생각해야 한다. - IPC는 내부에서 프로세스끼리 통신하던 반면, RPC는 네트워크에서 컴퓨터끼리 통신한다. 즉 확장된 개념이다.
