Macrotask / Microtask
브라우저 환경에서 실제 대기 시간은 0이 아닙니다.
브라우저는 HTML5 표준에서 정한 중첩 타이머 실행 간격 관련 제약을 준수한다. 해당 표준엔 "다섯 번째 중첩 타이머 이후엔 대기 시간을 최소 4밀리초 이상으로 강제해야 한다."라는 제약이 명시되어있다.
예시를 보며 이 제약 사항을 이해해보자. 예시 내 setTimeout은 지연 없이 함수 run을 다시 호출할 수 있게 스케줄링 되어 있다. 배열 times에는 실제 지연 간격에 대한 정보가 기록되도록 해놓았는데, 배열 times에 어떤 값이 저장되는지 알아보자.
let start = Date.now();
let times = [];
setTimeout(function run() {
times.push(Date.now() - start); // 이전 호출이 끝난 시점과 현재 호출이 시작된 시점의 시차를 기록
if (start + 100 < Date.now()) alert(times); // 지연 간격이 100ms를 넘어가면, array를 얼럿창에 띄워줌
else setTimeout(run); // 지연 간격이 100ms를 넘어가지 않으면 재스케줄링함
});
// 출력창 예시:
// 1,1,1,1,9,15,20,24,30,35,40,45,50,55,59,64,70,75,80,85,90,95,100앞쪽 타이머들은 스펙에 적힌 것처럼 지연 없이 바로 실행된다. 그런데 다섯 번째 중첩 타이머 이후엔 지연 간격이 4밀리초 이상이 되어 9, 15, 20, 24...와 같은 값이 저장되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
이런 제약은 setTimeout뿐만 아니라 setInterval에도 적용된다. setInterval(f)도 처음 몇 번은 함수 f를 지연 없이 실행하지만, 나중엔 지연 간격을 4밀리초 이상으로 늘려버린다.
이는 오래전부터 있던 제약인데, 구식 스크립트 중 일부는 아직 이 제약에 의존하는 경우가 있어서 명세서를 변경하지 못하고 있는 상황.
한편, 서버 측엔 이런 제약이 없다. Node.js의 process.nextTick과 setImmediate를 이용하면 비동기 작업을 지연 없이 실행할 수 있다. 위에서 언급된 제약은 브라우저에 한정된다.
아시다시피 브라우저는 시간이 오래 걸리든 아니든 상관없이 현재 작업 중인 태스크가 끝나야 DOM 변경분을 화면에 렌더링해준다.
https://meetup.toast.com/posts/89
https://dev.to/lydiahallie/javascript-visualized-event-loop-3dif
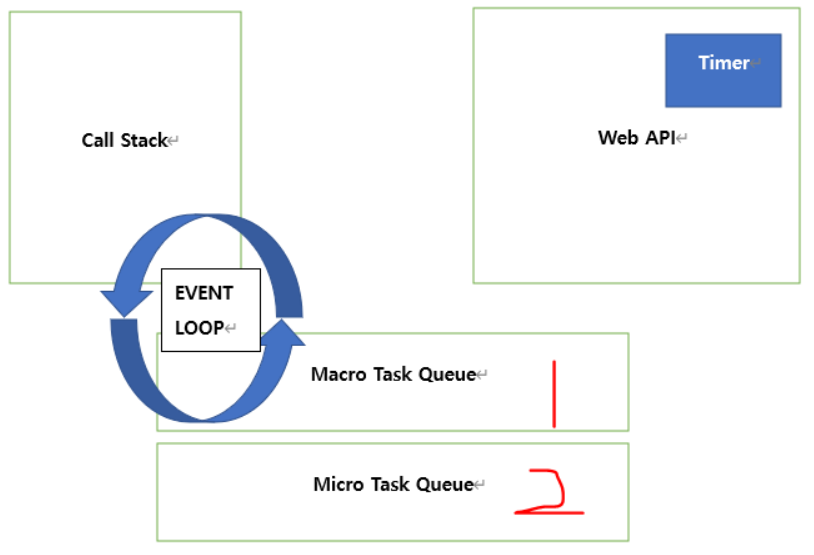
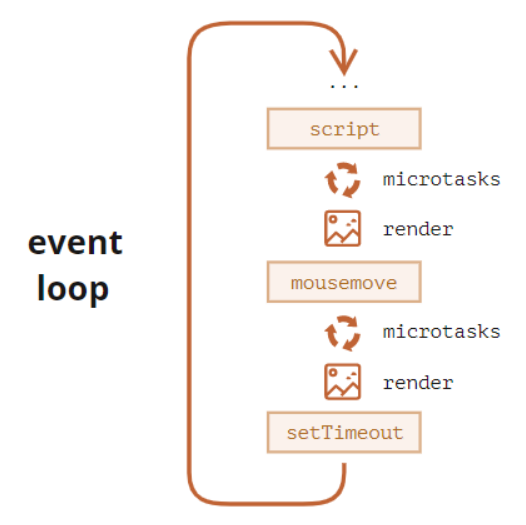
Event loop 상세 설명 사항
One go-around of the event loop will have exactly one task being processed from the macrotask queue (this queue is simply called the task queue in the WHATWG specification). After this macrotask has finished, all available microtasks will be processed, namely within the same go-around cycle. While these microtasks are processed, they can queue even more microtasks, which will all be run one by one, until the microtask queue is exhausted.
What are the practical consequences of this?
If a microtask recursively queues other microtasks, it might take a long time until the next macrotask is processed. This means, you could end up with a blocked UI, or some finished I/O idling in your application.
However, at least concerning Node.js's process.nextTick function (which queues microtasks), there is an inbuilt protection against such blocking by means of process.maxTickDepth. This value is set to a default of 1000, cutting down further processing of microtasks after this limit is reached which allows the next macrotask to be processed)
So when to use what?
Basically, use microtasks when you need to do stuff asynchronously in a synchronous way (i.e. when you would say perform this (micro-)task in the most immediate future). Otherwise, stick to macrotasks.
Examples
macrotasks: setTimeout, setInterval, setImmediate, requestAnimationFrame, I/O, UI rendering, event
microtasks: process.nextTick, Promises, queueMicrotask, MutationObserver
JS has three "stacks":
- standard stack for all synchronous calls (one function calls another, etc)
- microtask queue (or job queue or microtask stack) for all async operations with higher priority (process.nextTick, Promises, Object.observe, MutationObserver)
- macrotask queue (or event queue, task queue, macrotask queue) for all async operations with lower priority (setTimeout, setInterval, setImmediate, requestAnimationFrame, I/O, UI rendering)
And event loop works this way:
- execute everything from bottom to top from the stack, and ONLY when the stack is empty, check what is going on in queues above
- check micro stack and execute everything there (if required) with help of stack, one micro-task after another until the microtask queue is empty or don't require any execution and ONLY then check the macro stack
- check macro stack and execute everything there (if required) with help of the stack
Micro stack won't be touched if the stack isn't empty. The macro stack won't be touched if the micro stack isn't empty OR does not require any execution.
-
Callstack에 Task 가 들어옴
-
Task의 return 값이 반환 됨. macrotask 관련 작업 경우는 Wep API에서 Macrotask queue로 전달됨.
-
Event loop는 Callstack이 빈 순간 macrotask의 Task 1개를 Callstack에 올려서 execute.
-
그 후 Microtask queue가 빌 때까지 모든 Task 실행.(1 Loop에서 실행될 수 있는 Microtasks의 개수는 정해져 있음.)
-
그 다음 Callstack empty 확인 후 Macrotask queue의 다음 task 실행
