TREE
-
이진탐색트리
탐색
삽입
삭제
-
B-트리
탐색
삽입
삭제
이진탐색트리
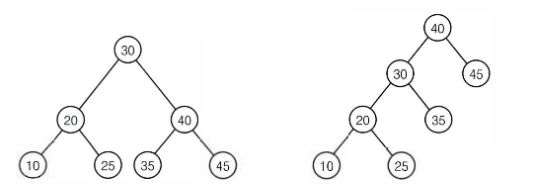
이진탐색트리는 다음과 같은 특성을 갖는다.
-
- 이진탐색트리의 각 노드는 키값을 하나씩 갖는다. 각 노드의 키값은 모두 달라야 한다.
-
- 최상위 레벨에 루트 노드가 있고, 각노드는 최대 두개의 자식 노드를 갖는다.
-
- 임의의 노드의 키값은 자신의 왼쪽 자식 노드의 키값보다 크고, 오른쪽 자식 노드의 키값보다 작다.
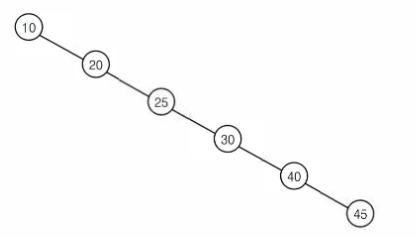
이진탐색트리의 시간복잡도는 O(h) 이다.
h는 트리의 높이인데 이를 n으로 치환하면 n = 2^h - 1 이므로 h = log(n-1)
즉 O(logn) 이 된다.
하지만 한쪽으로만 몰리게 되는 경우 최악의 시간복잡도는 O(n) 이 된다.
이진탐색트리 - 탐색 알고리즘
treeSearch(t,x) // t = 트리의 루트 노드 x = 검색하고자 하는 키
{
if(t=NIL or key[t] = x) then return t; // 검색하고자 했던키가 루트 노드인 경우
// t = NIL이면 NIL을 리턴해 검색이 실패했음을 알려야 하는데 그게 없다.
if(x < key[t]) // 루트 노드 t의 키값과 x를 비교한다
then return treeSearch(left[t],x); //key[t]>x = 왼쪽 서브트리에 x
else return treeSearch(right[t],x); //key[t]<x 오른쪽 서브트리에 x
}
이진탐색트리 - 탐색 알고리즘 파이썬
def search(self, data):
self.base = self.root
while self.base:
if self.base.data == data:
return True
elif self.base.data > data:
self.base = self.base.left
else:
self.base = self.base.right
return False
이진탐색트리 - 탐색 알고리즘 자바
public MyNode search(Integer data) {
MyNode cursor = this.head;
while(true) {
if(cursor == null) {
System.out.println(data+" not exists");
return null;
}
if(cursor.value == data) {
return cursor;
} else {
if(data > cursor.value) {
cursor = cursor.right;
} else {
cursor = cursor.left;
}
}
}}
이진탐색트리 - 삽입
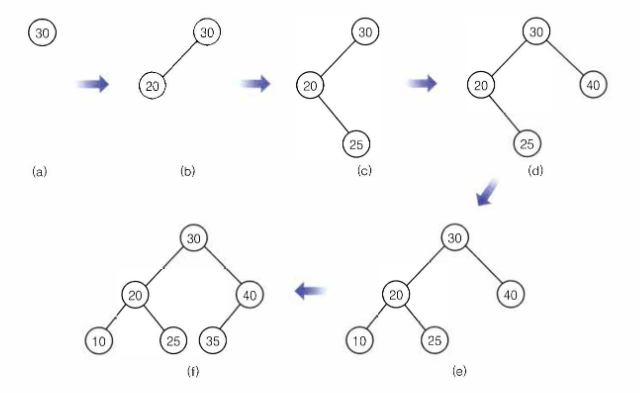
삽입은 탐색과 상당히 유사하다.
첫 삽입시에만 루트 노드로 취급하고 이후에는 루트 노드와 비교하여
작다면 왼쪽으로 크다면 오른쪽으로 자리를 찾아 삽입하게 된다.
이진탐색트리 - 삽입 알고리즘
treeInsert(t,x) // t = 트리의 루트 노드 x = 검색하고자 하는 키
{
if(t=NIL) then {
key[r] <- x; left[r] <- NIL; right[r] <-NIL; //r = 새노드
return r;
}
if(x < key[t]) // 루트 노드 t의 키값과 x를 비교한다
then {left[t] <- treeInsert(left[t],x); return t;}
else {right[t] <- treeInsert(right[t],x); return t;}
}
이진탐색트리 - 삽입 알고리즘 파이썬
def insert(self, data):
if self.root is None:
self.root = Node(data)
else:
self.base = self.root
while True:
if data == self.base.data:
print("중복된 KEY 값")
break
elif data > self.base.data:
if self.base.right is None:
self.base.right = Node(data)
break
else:
self.base = self.base.right
else:
if self.base.left is None:
self.base.left = Node(data)
break
else:
self.base = self.base.left이진탐색트리 - 삽입 알고리즘 자바
public boolean insert(Integer data) {
MyNode newNode = new MyNode(data);
MyNode cursor = this.root;
// case 1 : 트리가 비어있는 경우
if (root == null) {
this.root = newNode;
size++;
} else {
// case 2 : 최소 1개 이상의 노드가 트리에 존재하는 경우
while (true) {
// case 2-1 : 커서가 가리키고 있는 노드가 새로운 노드보다 큰 경우
// 커서를 트리의 왼쪽 방향으로 이동한다
if (cursor.value > data) {
if (cursor.left == null) {
cursor.left = newNode;
return true;
} else {
cursor = cursor.left;
}
// case 2-2 : 커서가 가리키고 있는 노드가 새로운 노드보다 작거나 같은 경우
// 커서를 트리의 오른쪽 방향으로 이동한다
} else {
if (cursor.right == null) {
cursor.right = newNode;
return true;
} else {
cursor = cursor.right;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}이진탐색트리 - 삭제
이진탐색트리에서 삭제는 앞서 소개한 탐색, 삽입보다 어려운 편이다.
이진탐색트리에서 원하는 노드 r을 삭제 하려면 다음 세 가지의 경우에 따라
각각 다르게 처리를 해주어야 한다.
-
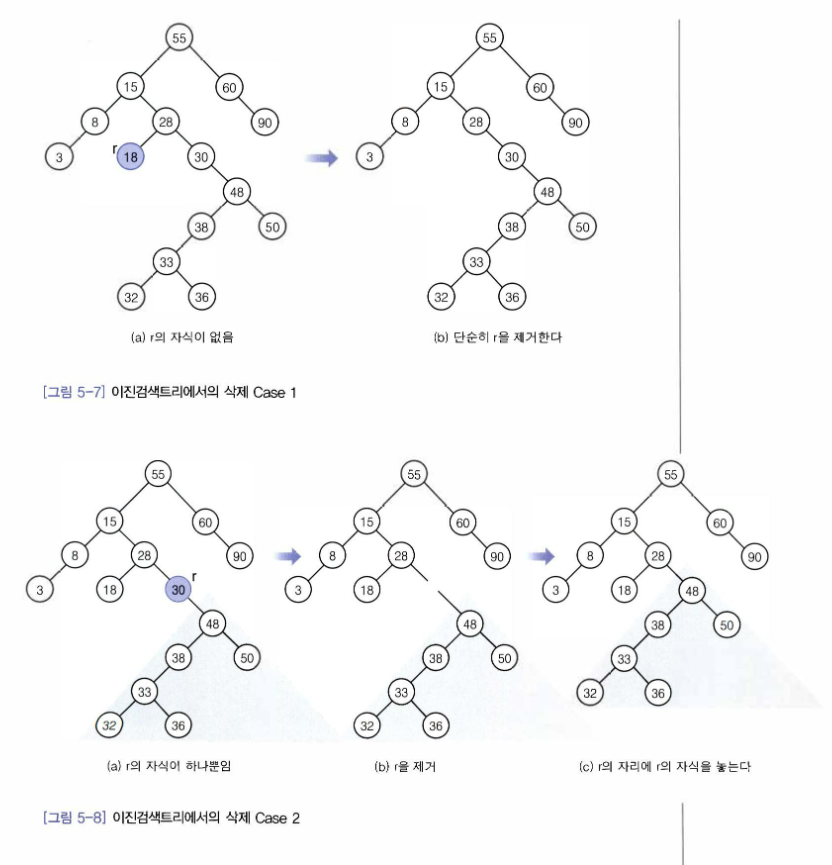
Case 1 : r이 리프 노드인 경우
-
Case 2 : r의 자식 노드가 하나인 경우
-
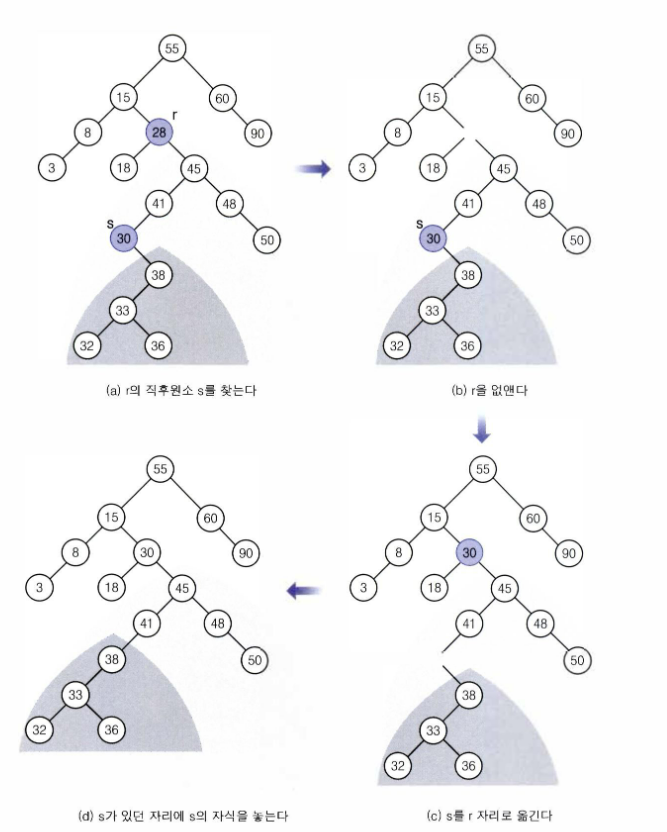
Case 3 : r의 자식 노드가 두 개인 경우
Case 1, 2 는 처리가 비교적 간단하지만, Case 3는 다소 복잡하다.
Case 1 인 경우 선택한 r을 그냥 제거 하면된다.
Case 2 인 경우 r의 부모가 r의 자식을 직접 가리키도록 해야한다.
Case 3 인 경우 r의 오른쪽 서브트리의 최소원소 노드 s를 삭제하고,
s를 r 자리에 놓아야한다.
이때 s 는 왼쪽 서브트리보다 크고 오른쪽 서브트리보다 작은 값을 가져야한다.
이진탐색트리 - 삭제 알고리즘
treeDelete(t,r,p) // t: 트리의 루트 노드 r: 삭제하고자 하는 노드 p: r의 부모 노드
{
if(r=t) then root <- deleteNode(t);
else if (r=left[p])
then left[p] <- deleteNode(r);
else right[p] <- deleteNode(r);
}
deleteNode(r)
{
if(left[r] = right[r] =NIL) then return NIL; //Case 1
else if(left[r] = NIL and right[r] != NIL) then return right[r]; // Case 2
else if(left[r] != NIL and right[r] = NIL) then return left[r];
// Case 2
else{ // Case 3
s <- right[r]; // r의 오른쪽 자식 노드를 s로 지정
while(left[s] != NIL) // s의 왼쪽 자식 노드가 없을때까지 실행 즉 s가 최소값이 될때까지 실행
{ parent <- s; s <- left[s];} //s였던 노드는 s의 부모가 되고 왼쪽 자식 노드값이 s값이 된다.
key[r] <- key[s];
if (s=right[r]) then right[r] <- right[s];
else left[parent] <- right[s];
return r;
}
}
이진탐색트리 - 삭제 알고리즘 파이썬
def remove(self, data):
self.searched = False
self.cur_node = self.root
self.parent = self.root
while self.cur_node:
if self.cur_node.data == data:
self.searched = True
break
elif self.cur_node.data > data:
self.parent = self.cur_node
self.cur_node = self.cur_node.left
else:
self.parent = self.cur_node
self.cur_node = self.cur_node.right
if self.searched:
# root를 지우는 경우
if self.cur_node.data == self.parent.data:
self.root = None
else:
# [CASE 1] 삭제하는 node가 leaf node인 경우
if self.cur_node.left is None and self.cur_node.right is None:
if self.parent.data > self.cur_node.data:
self.parent.left = None
else:
self.parent.right = None
# [CASE 2] 삭제하는 node의 자식이 하나인 경우
elif self.cur_node.left is not None and self.cur_node.right is None:
if self.parent.data > data:
self.parent.left = self.cur_node.left
else:
self.parent.right = self.cur_node.left
elif self.cur_node.left is None and self.cur_node.right is not None:
if self.parent.data > data:
self.parent.left = self.cur_node.right
else:
self.parent.right = self.cur_node.right
# [CASE 3] 삭제하는 node의 자식이 둘인 경우
elif self.cur_node.left is not None and self.cur_node.right is not None:
self.tmp_parent = self.cur_node.right
self.tmp_cur = self.cur_node.right
while self.tmp_cur.left:
self.tmp_parent = self.tmp_cur
self.tmp_cur = self.tmp_cur.left
if self.tmp_cur.right is not None:
self.tmp_parent.left = self.tmp_cur.right
else:
self.tmp_parent.left = None
if self.parent.data > data:
self.parent.left = self.tmp_cur
else:
self.parent.right = self.tmp_cur
self.tmp_cur.left = self.cur_node.left
self.tmp_cur.right = self.cur_node.right
else:
print("존재하지 않는 데이터")이진탐색트리 - 삭제 알고리즘 자바
if(cursor.left == null && cursor.right == null) {
if(cursor != root) {
if(parent.left == cursor) {
parent.left = null;
} else {
parent.right = null;
}
} else {
root = null;
}
}
else if (cursor.left != null && cursor.right != null) {
// 삭제될 노드와 그 부모노드 사이의 최소 값을 지닌 노드를 찾는다.
MyNode temp = findMinNode(cursor.right);
int tempValue = temp.value;
// 최소값 노드를 삭제 후, 삭제될 노드에 최소값을 삽입한다.
remove(root, temp.value);
cursor.value = tempValue;
}
else {
MyNode child = (cursor.left != null) ? cursor.left : cursor.right;
if(cursor != root) {
if(cursor == parent.left) {
parent.left = child;
} else {
parent.right = child;
}
} else {
root = child;
}
}B- 트리
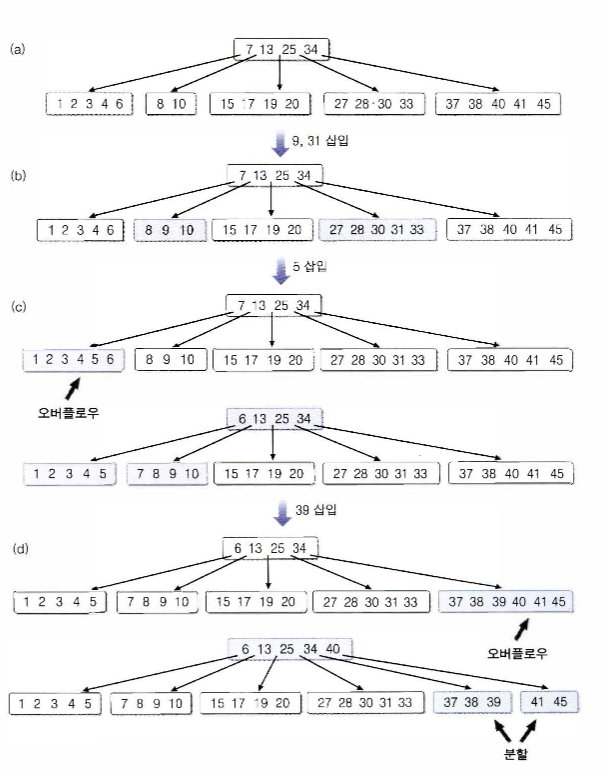
B-트리는 균형잡힌 다진검색트리로 다음의 성질을 만족한다.
- 루트를 제외한 모든 노드는 k/2 ~ k 개의 키를 갖는다.
- 모든 리프 노드는 같은 깊이를 가진다.
B-트리는 분기의 수를 가능하면 늘리되 균형을 맞추기 위해
각 노드가 채울 수 있는 최대 허용량의 반내림 이상의 키는 채워야 하는 검색트리다.
이진탐색트리와 공통점 은 좌,우 자식 노드 개수의 밸런스를 유지한다는것이고,
차이점 은 이진탐색트리에서는 하나의 노드에 하나의값 만 저장하지만
B-트리에서는 하나의 노드에 여러개의 값 을 저장한다는 점이다.
B- 트리의 시간복잡도는 이진탐색트리와 같은 O(logN) 이다.
B- 트리 - 탐색 알고리즘
treeSearch(t,x) // t = 트리의 루트 노드 x = 검색하고자 하는 키
{
if(t=NIL or key[t] = x) then return t; // 검색하고자 했던키가 루트 노드인 경우
// t = NIL이면 NIL을 리턴해 검색이 실패했음을 알려야 하는데 그게 없다.
if(x < key[t]) // 루트 노드 t의 키값과 x를 비교한다
then return treeSearch(left[t],x); //key[t]>x = 왼쪽 서브트리에 x
else return treeSearch(right[t],x); //key[t]<x 오른쪽 서브트리에 x
}
B- 트리의 탐색알고리즘 구조는 위의 이진탐색트리와 같다.
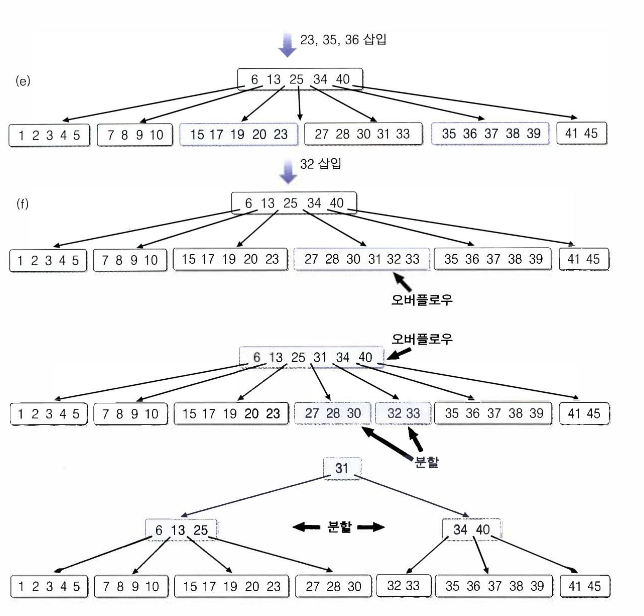
B- 트리 - 삽입 알고리즘
BTreeInsert(t,x) // t = 트리의 루트 노드 x = 검색하고자 하는 키
{
x를 삽입할 리프 노드 r을 찾는다;
x를 r에 삽입한다;
if(r에 오버플로우 발생) then clearOverflow(r);
}
clearOverflow(r)
{
if(r의 형제 노드 중 여유가 있는 노드가 있음)then{
r의 남는 키를 넘긴다
};
else{
r을 둘로 분할하고 가운데 키를 부모 노드로 넘긴다;
if(부모 노드 p에 오버플로우 발생)then clearOverflow(p);
}
}
B- 트리 - 삭제 알고리즘
BTreedelete(t,x,v) // t = 트리의 루트 노드 x = 검색하고자 하는 키
v= x를 갖고 있는 노드
{
if(v가 리프 노드 아님)then{
x의 직후 원소 y를 가진 리프노드를 찾는다;
x와y를 맞바꾼다;
}
리프 노드에서 x를 제거하고 이 리프 노드를 r이라고 한다;
if(r에서 언더플로우 발생)then clearUnderflow(r);
}
clearUnderflow(r)
{
if(r의 형제 노드 중 키를 하나 내놓을 수 있는 여분을 가진 노드가 있음)
then {r의 키를 넘겨 받는다;}
else{
r의 형제 노드와 r을 병합한다;
if(부모 노드 p에 언더플로우 발생) then clearUnderflow(p);
}
}
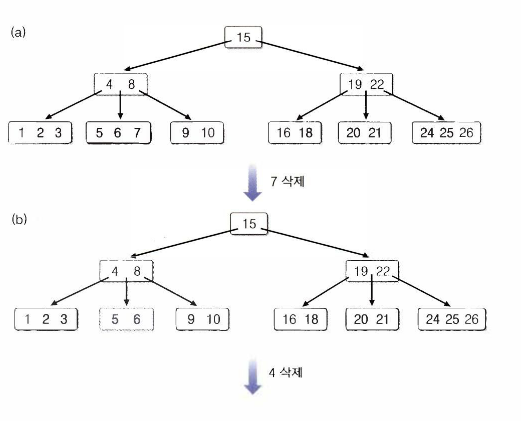
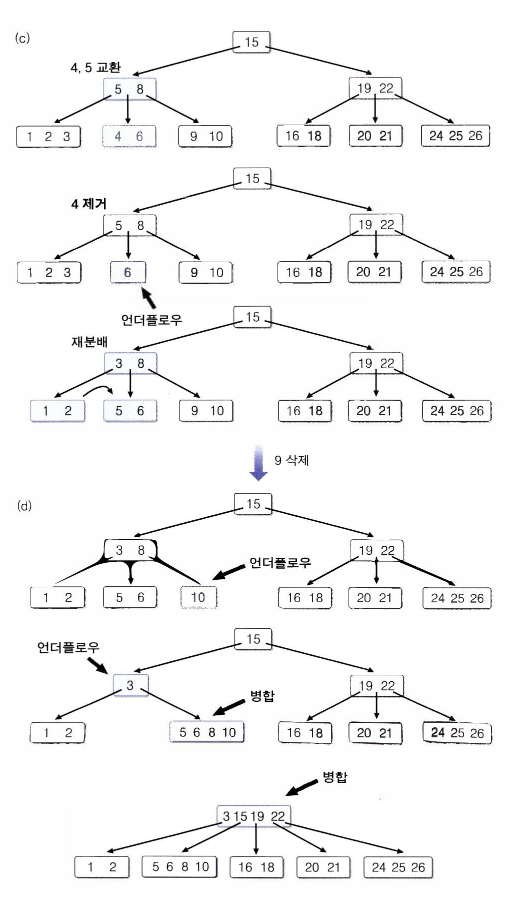
출처 - 쉽게 배우는 알고리즘
