Data Understanding (GitHub)
Dataset
Instance== object, record, sample, entity, observationAttribute== characteristic, field, feature, dimension
Data Categorization
Numerical: Made of numbers- Continuous : Infinite options (Age, weight, blood pressure)
- Discrete : Finite options (Shoe size, number of children)
Categorical: Made of words- Ordinal : Data has a hierachy (Satisfaction rating, mood)
- Nominal : Data has no hierachy (Eye color, blood type)
Data Types
-
Record Data- The most widely used data type
- Consist of a collection of records
- Each record is compsed of a fixed number of attributes
-
Transaction data- Consist of a buyer and a list of purchased items dataset
-
Graph-based data
Data Preprocessing
- An important step in the data mining process
- Contain the cleaning, transforming, and integrating of data in order to analysis
- (goal) Improve the quality of data and make the data suitable for the specific task
- Garbage in, garbage out... (Importance of data preprocessing)
-
Data Cleaning: Remove noise and correct inconsistencies in data -
Data integration: Merge data from multiple sources into a coherent data store such as a data warehouse -
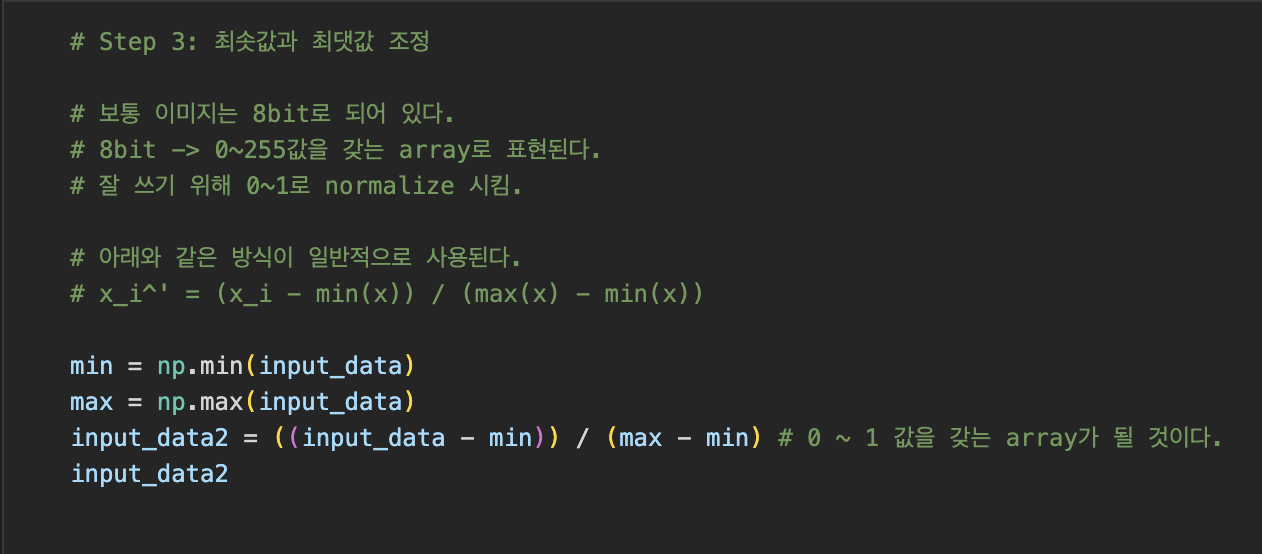
Data transformation / Discretization: Data are scaled to fall within a smaller range like 0 ~ 1 (Normalization)
Data reduction: Reduce data size by aggregating, eliminating redundant features, or clustering
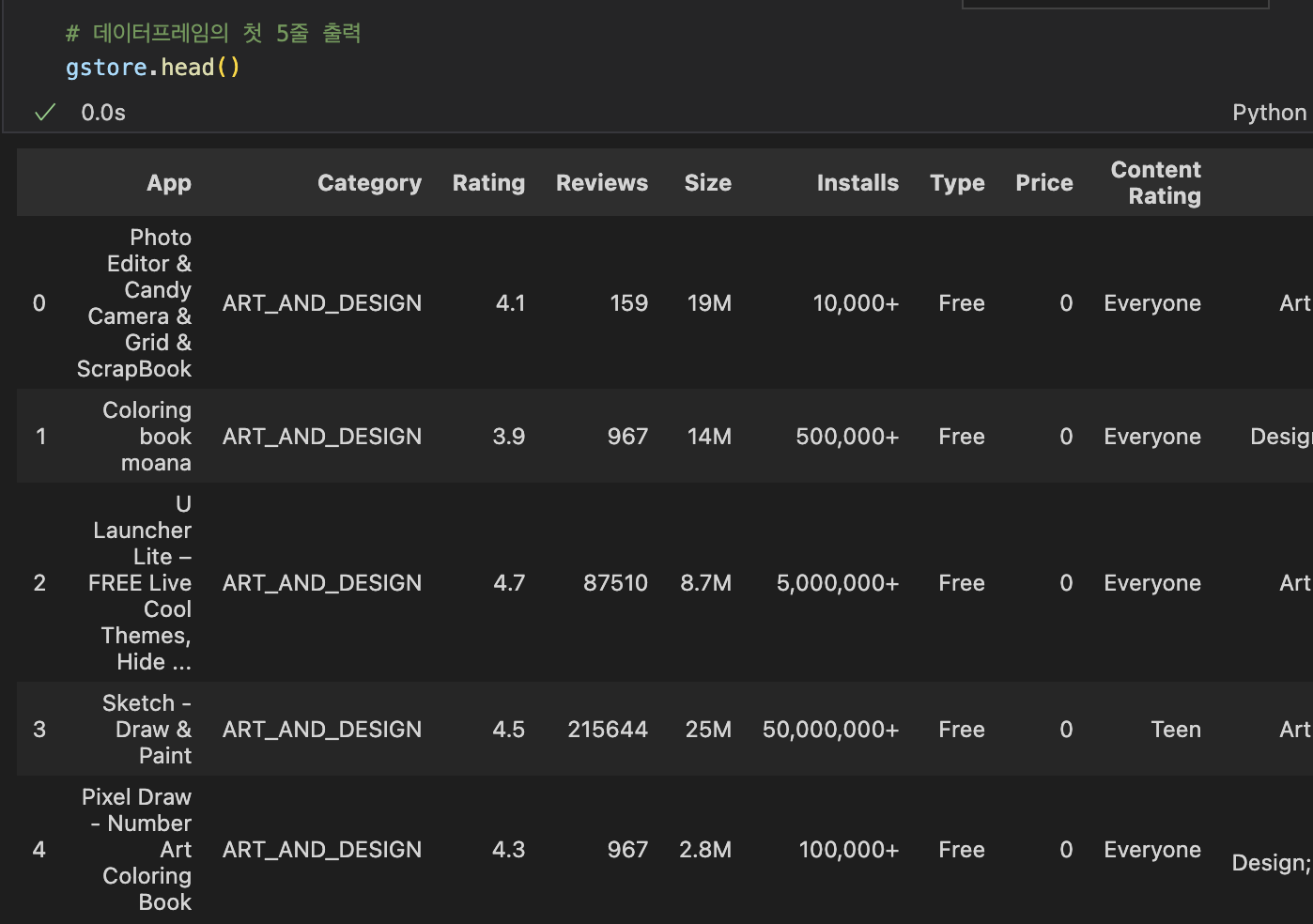
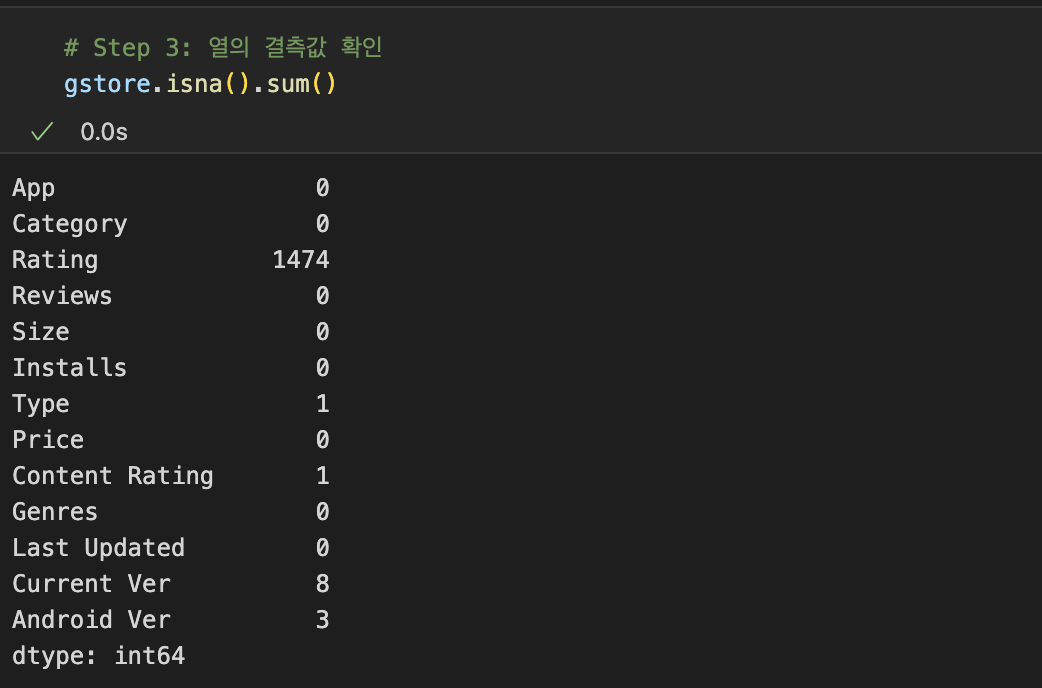
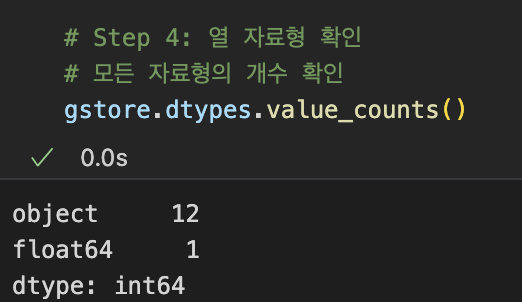
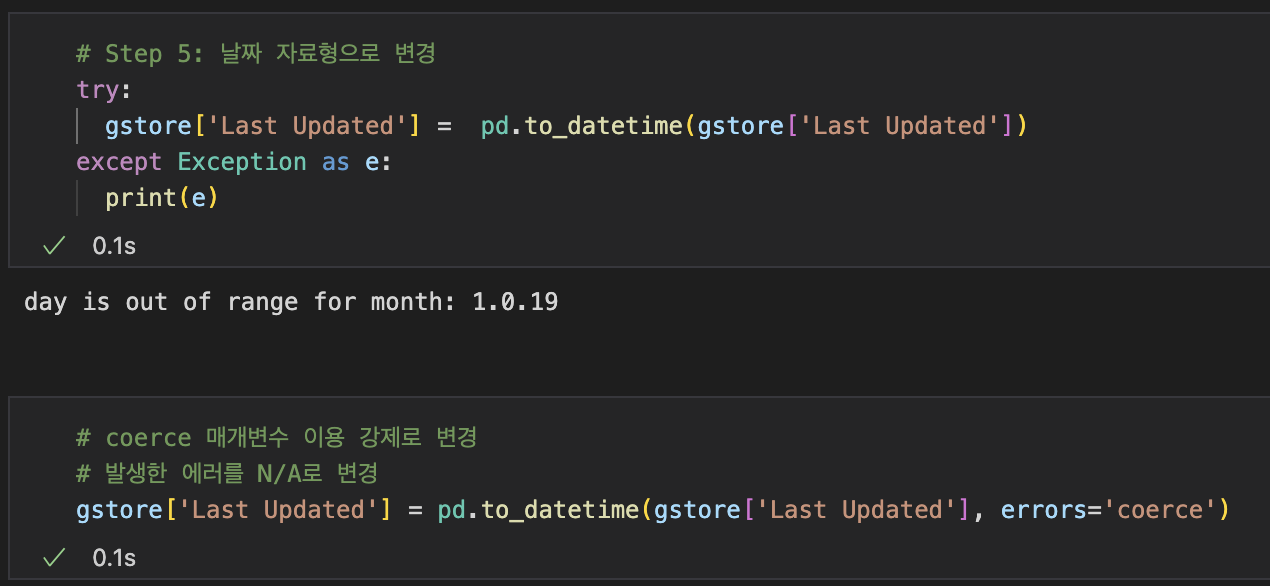
(Jupyter Notebook) 헷갈린 부분