gcc
gcc:- GNU C/C++ Compiler의 약자.
- Linux계열 system에서 가장 많이 사용되는 compiler.
- 주로 C program을 compile할 때 사용된다.
gcc는 C program 뿐만 아니라 ADA, Java와 같은 다양한 language를 compile할 수 있도록
architecture가 설계되어 있다. - C++ Program을 compile하려면 g++라는 별도의 compiler를 사용.
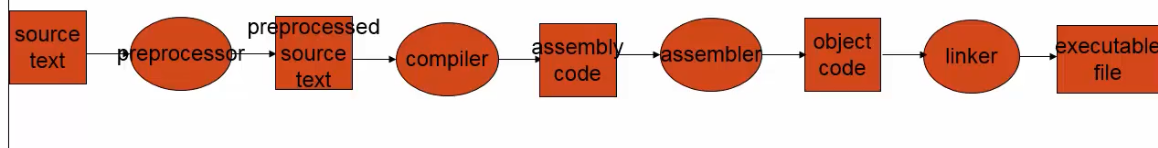
- gcc는 소스파일부터 실행파일까지 여러 일을 수행한다.
- preprocessing : 매크로 처리
- compilation, assembly
- linking
cross-compile:
예를 들어 x86에서 ARM용 object code를 생성하는 cross-compile도 gcc를 통해서 한다.
Building an executable file
-
xxx.c라는 source file이 있다고 가정.
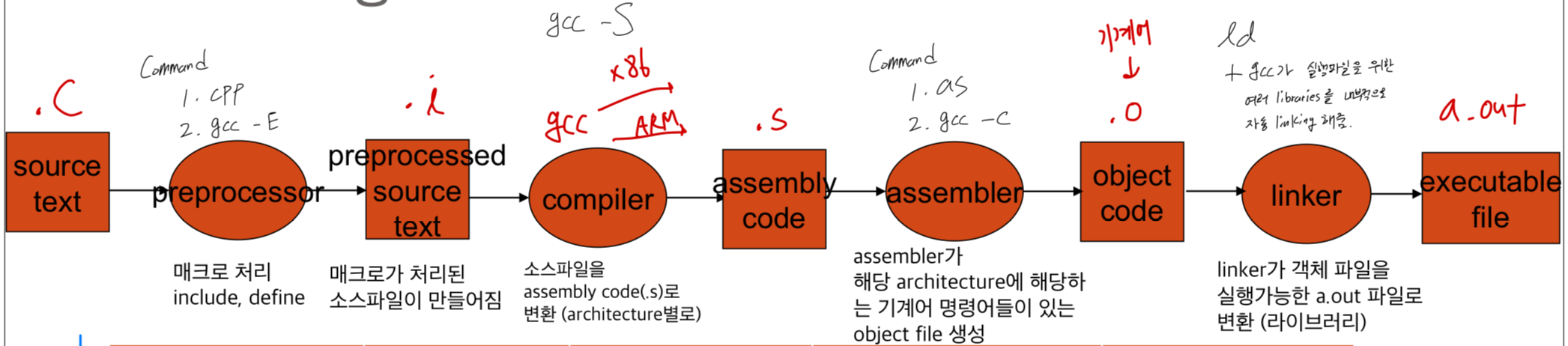
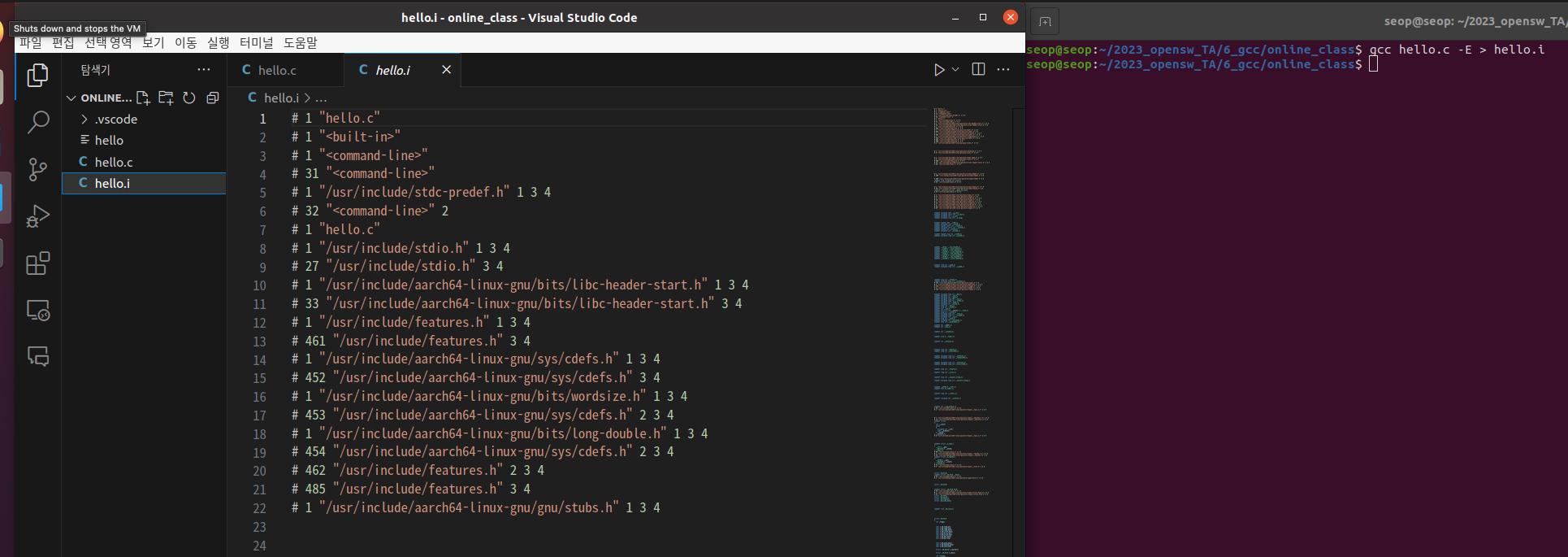
preprocessing:
gcc가cpp(C Preprocess)라는 명령어를 수행하여.c(source code)에 있는 macro들(#inclue, #define)을 처리하여
compile하기 직전에 또 다른.i(preprocessed code)로 만들어 준다.
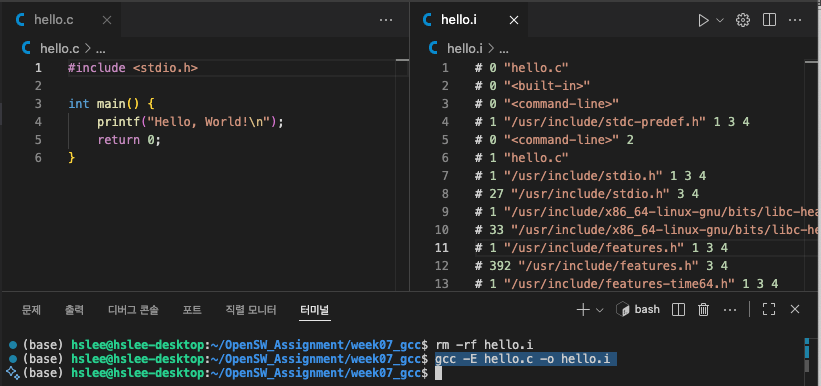
gcc 명령어서는 preprocessing까지만 하고 싶으면gcc -E옵션
- cpp 명령어 사용한 preprocessing
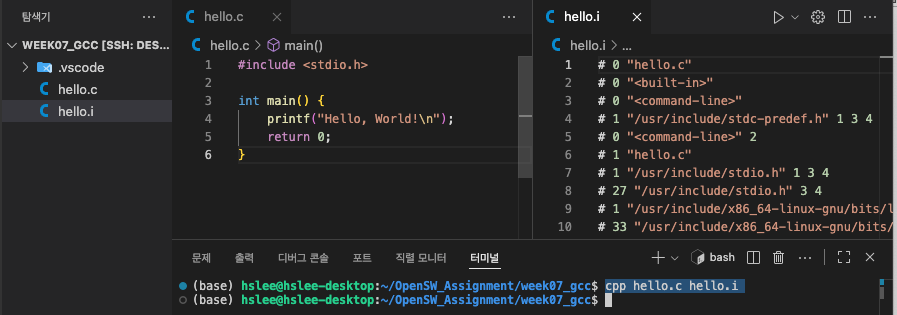
- gcc -E 명령어 사용한 preprocessing ("-o file.i"를 해야 생성됨. -o 없으면 stdout으로 출력만 되고 파일이 생성되지 않음)
compiling:
여기서, 실제적으로 gcc가 메인으로 하는 일.
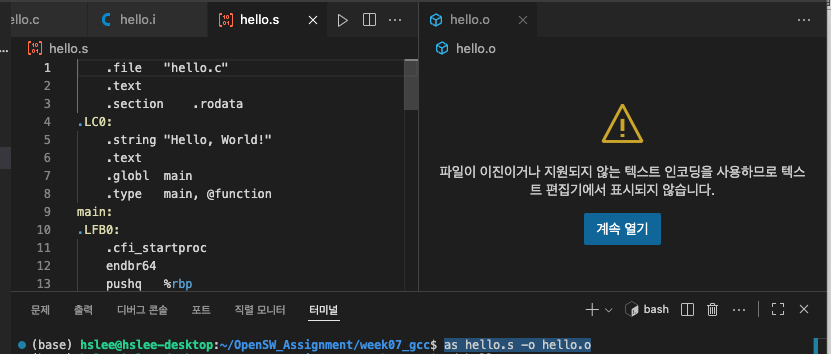
gcc -S는.c(source code) 또는 .i(preprocessed code)을.s(assembly code)로만들어준다.
예를 들어 x86을 사용한다면, x86용 assembly code를 생성.
ARM을 사용한다면, ARM용 assembly code를 생성.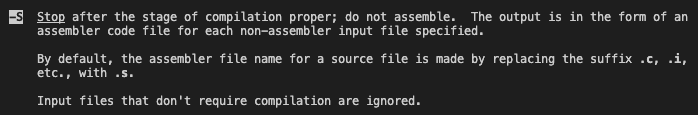
assembling:
as라고 하는 assembler가.s(assembly code)를.o(object file)로 만들어 준다.
object file은 우리가 사용하는 architecture(x86 or ARM)에 해당하는 기계어 명령어들이 들어가 있는 코드. (이제부터 인간이 읽을 수 없음)
gcc 명령어에서는gcc -c
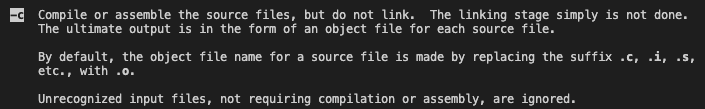
- gcc -c를 이용한 assembling (compiling or assemble the source files, but do not link)
- as를 이용한 assembling
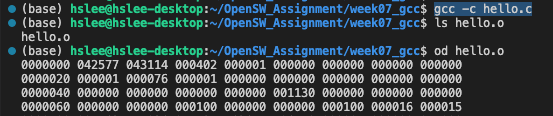
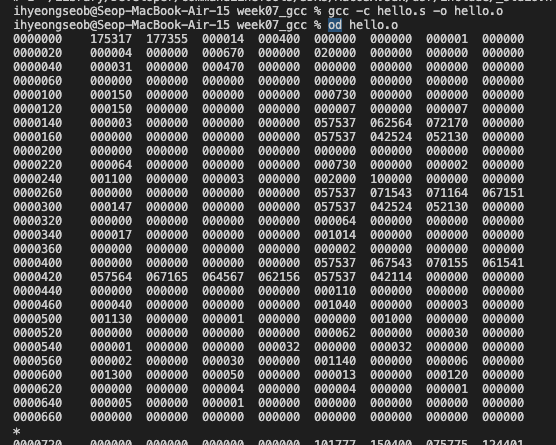
- od: 바이너리 파일의 내부 데이터를 확인할 때 사용함.
*.o = 기계어(바이너리 코드) 파일을 읽을 수 있도록 아래와 같이 od 명령어 사용.
linking:
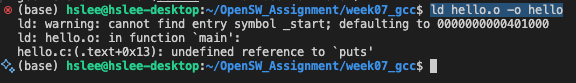
ld라고 하는 linker가 object file(*.o)와 library들을 linking하여 실행파일(a.out)로 만들어줌
아래에서 ld 명령어가 실패한 이유는 ld 명령어는 linker이지만, 실행 파일로 만들기 위한 library와 runtime code(crt1.o, libc 등)을 자동으로 추가하지 않기 때문임.
 반면, 아래와 같이 gcc 명령어는 내부적으로 ld를 호출하면서 필요한 모든 파일을 자동으로 linking해줌. (-v 옵션은 gcc가 내부적으로 어떻게 동작하는지 확인하기 위함)
반면, 아래와 같이 gcc 명령어는 내부적으로 ld를 호출하면서 필요한 모든 파일을 자동으로 linking해줌. (-v 옵션은 gcc가 내부적으로 어떻게 동작하는지 확인하기 위함)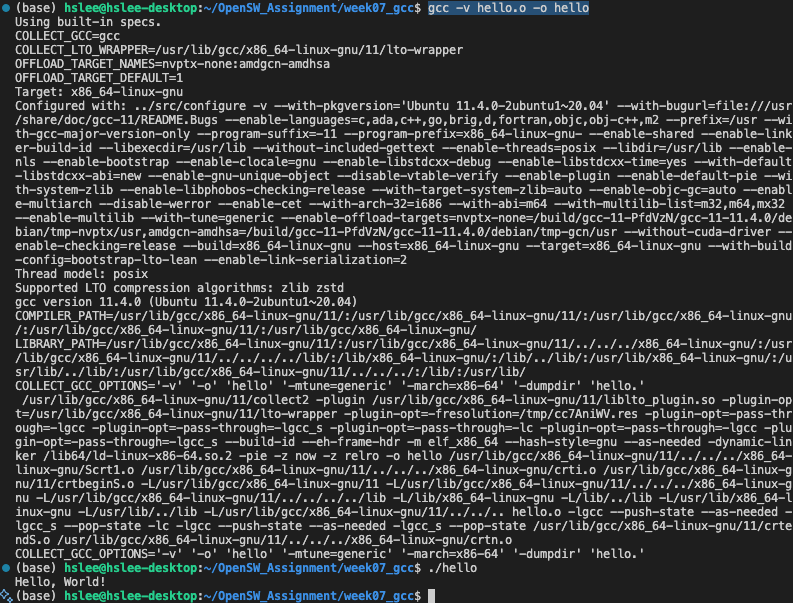
- gcc가 직접적으로 일을 할 때는 2.뿐이고,
Preprocessing(cpp), assembling(as), linking(ld)할 때는 gcc가 기타 명령어들(cpp, as, ld)을 내부적으로 호출하여 사용함.
gcc architecture (FrontEnd, MiddleEnd, BackEnd)
- gcc라는 SW는 크게 세 개의 components로 나누어져 있음
- Front End
- Middle End
- Back End
- gcc architecture는 왜 3단계로 나누어져 있는가?
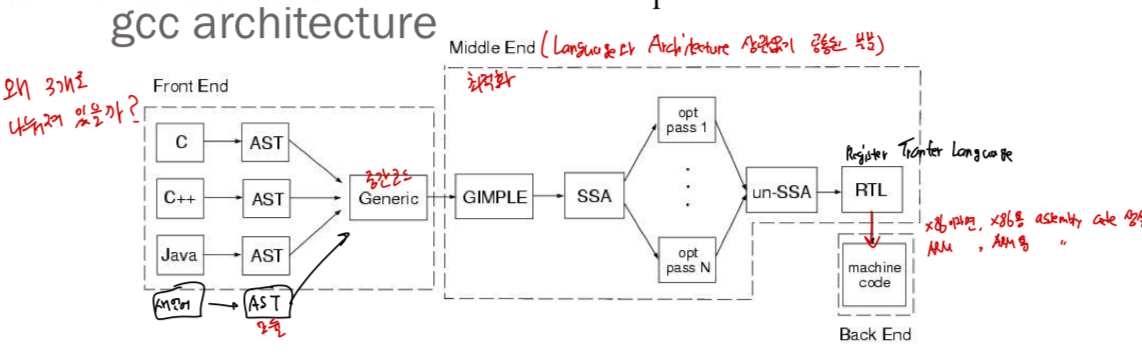
Front End:
어떠한 language(C, C++, Java, etc)가 오든 AST(Abstract Syntax Tree) 형태로 바꿈.
(AST는 high-level language라고 생각하면 됨..)
그리고나서 AST 형태를 Generic이라고 하는 중간 코드로 변환한다.
만약 우리가 새로운 언어(MYLANG)를 만들었다면,
MYLANG을 AST 형태로 바꿔주는 부분을 설계해야 한다.Middle End:
Front End에서 생성된 Generic(중간코드)을 최적화하는 과정을 거친다.
opt(optimization pass 1 ~ N)
최적화를 통해 RTL(Register Transfer Language)이라는 언어로 변환한다.
(RTL은 low-level language라고 생각하면 됨... 가상의 assembly language)Back End:
RTL 형태의 중간코드를 사용하는 platform에 맞게, 실제 machine code로 변환한다.
x86이라면 x86용 assembly code로 만들고,
ARM이라면 ARM용 assembly code로 만듦.
➡️ language와 target architecture에 관계없이 항상 공통되었다.
그래서 새로운 언어를 개발했으면,
middle end와 back end는 그대로 사용하고,
front end에서 새로운 언어에 대한 generic format으로 만들어 줄 module만 넣어주면 된다.
즉, 새로운 언어를 AST 형태로 바꿔주는 module
➡️ 만약 새로운 architecture(instruction set을 갖는 CPU)를 개발했다면,
새로운 architecture에 대해 assembly code로 변환시킬 back end를 만들면 된다.
즉, RTL을 새로운 architecture의 machine code에 맞게 바꿔주는 backend module을 개발하면 된다.
(정리) 그래서 왜 gcc SW는 세 가지 components로 나눠져 있나?
새로운 언어 또는 새로운 CPU(platform)가 개발되었다면?
FrontEnd 또는 BackEnd에서 각 상황에 맞는 부분만 개발하면 되기 때문
(새로운 코드 -> AST 형태), (RTL -> (machine code) -> 새로운 platform)
gcc 간단한 사용법
- gcc -o hello hello.c -g -Wall
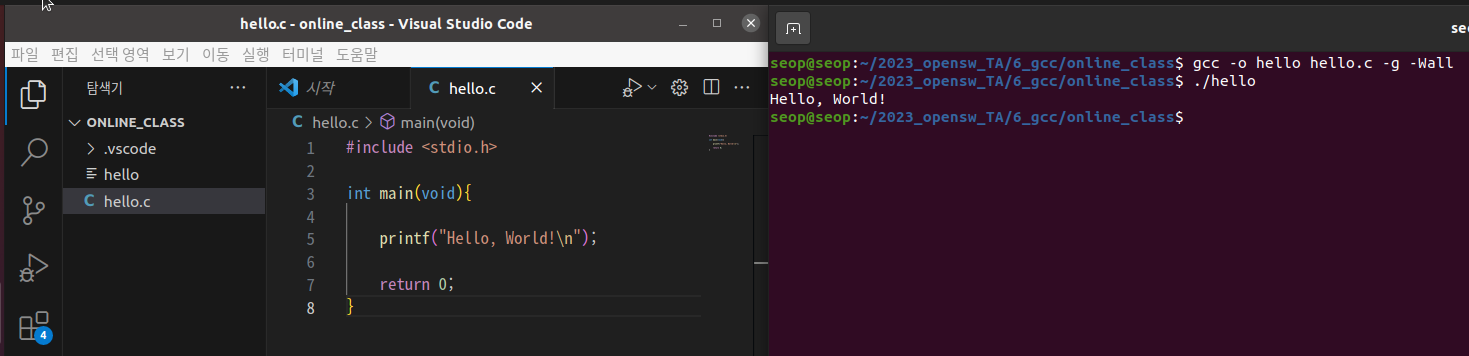
-o: tells the compiler to name the executable
(실행파일 이름 지정)-g: adds symbolic information to hello for debugging
(debugging symbol을 실행파일에 포함시켜라. debugging을 가능하게 하기 위함)-Wall: tells it to print out all warnings
gcc major options
-E: generate preprocessed code-S: generate assembly code-c: generate object code (compile without linking)-o<filename>: specify output filename-g: include debugging symbols-Wall: show all warnings-ansi,pedantic: be stubborn aboutn standards-O,-O0,-O1,-O2,-Os...: Optimizations
(중요) Compiler input/output options
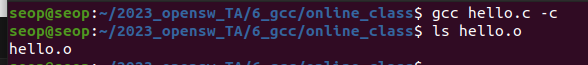
-
-c : Stop after creating object files, don't link
(linking단계 직전인 assembling까지만 하라.)
= (실행파일을 만들지 말고 object file까지만 만들어라)
-
-o file명 : 지정한 file명으로 실행파일을 생성하라.
Compiler control options
- -ansi : c90이라는 문법 standard에 맞게 compile하라
- -pedantic : c standard에 있는 문법들만 사용하고, extension을 사용하지 마라
- -std=c99 : c99에 맞게 compile하라.
- -static: supr
- -O[lev] : 최적화 level을 설정.
(0, 1-default, 2, 3가 있는데, 2 level을 주로 사용한다)
MiddleEnd에서 code optimization을 한다고 했는데, 그 단계를 정해줌 - -Os : 속도를 위한 최적화가 아닌, code size를 위한 최적화를 해라
Compiler path options
- -Idir : 해당 dir에서 header file을 cumulative하게(반복해서) 찾아라.
- -Ldir : 해당 dir에서 library를 cumulative(반복해서) 찾아라.
- -: Link to lib;
- foo : links to libfoo.so(shared library) if it exists, or to libfoo.a(static library) as a second choice
Compiler preprocessor options
- - : Preprocessing only
(gcc가 preprocessor까지만 불러서 사용하고 그 다음인 compiling, assembling, linking을 하지 말고 멈춰라.)
- -def : Define def
(외부 define을 사용할 수 있다.) - -def : Undefin def
(외부 define을 사용할 수 없다.)
Compiler warning options
- - : verbose mode.
(message를 많이 찍어줘라 + gcc version 정보) - - : Suppress warnings
(message를 적게 찍어줘라) - - : More verbose mode
(-보다 더 많이 찍어줘라) - -all : 모든 warning을 찍어줘라
Complier debugging options
- -g : gdb의 정보를 포함하라
- -pg : profiler의 정보를 포함하라
(profiler를 통해 어떤 함수의 어떤 부분에서 시간을 많이 소요하는지 정보를 얻을 수 있음)
Common set of options
-O2 -Wall -pedantic:- -O2 : Level 2까지 optimization 해라.
- -Wall : 모든 Warning message를 출력해라
- -pedantic : gcc extension 말고, 순수한 C언어 문법에만 맞도록 compile하라.
Linux kernel을 compile할 때는 gcc extension을 많이 사용하기 때문에 -pedantic 옵션을 사용하면 안된다.
Example of compilation
-
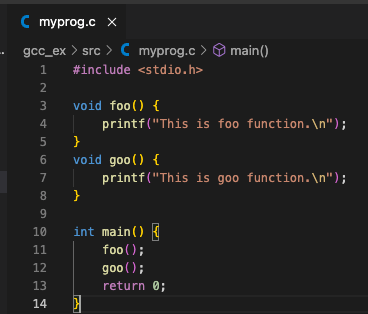
example 1:
main 함수에 foo()함수와 goo()함수 호출 후 종료
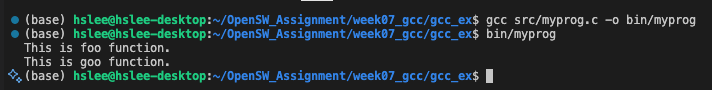
-
example 2: moduling programming & linking each object files- foo() 함수와 goo() 함수 선언을 foo.c와 goo.c에 각각 선언하고,
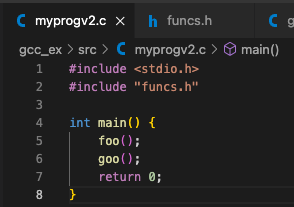
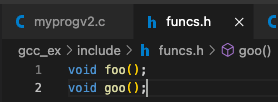
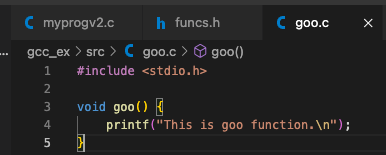
- foo() 함수와 goo() 함수 선언을 foo.c와 goo.c에 각각 선언하고,
-
각각의 source file들을 object files로 compile (linking 직전까지)
이때, ./include 디렉토리에 funcs.h라는 header file을 선언했기 때문에, gcc -Idir 옵션으로 header file 탐색 경로를 지정해줘야 함.
그렇지 않으면 아래와 같이 header file을 못 찾음.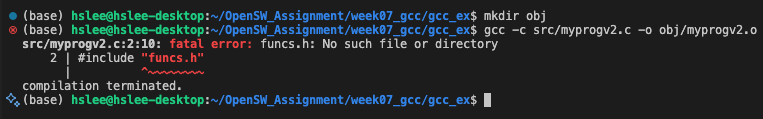
이제 제대로 gcc -Idir 을 사용해서 각 source file들을 object file로 compile (linking 직전까지)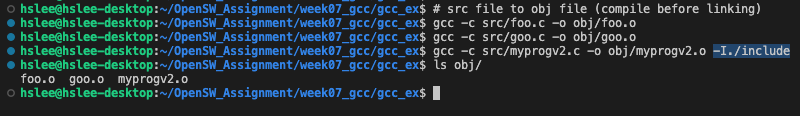
- 각 object files들을 linking하여 executable file을 최종 생성
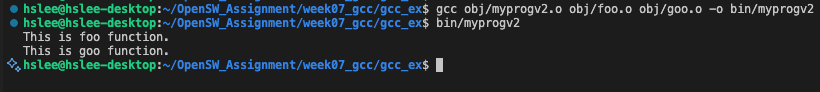
- 각 object files들을 linking하여 executable file을 최종 생성
-
example 3: example 2 + 'header guard' in funcs.h- 여러 파일(foo.c, goo.c)에서 <stdio.h>를 include하면 중복이 많아지기 때문에
아래와 같이 funcs.h header file에 header guard를 선언할 수 있다.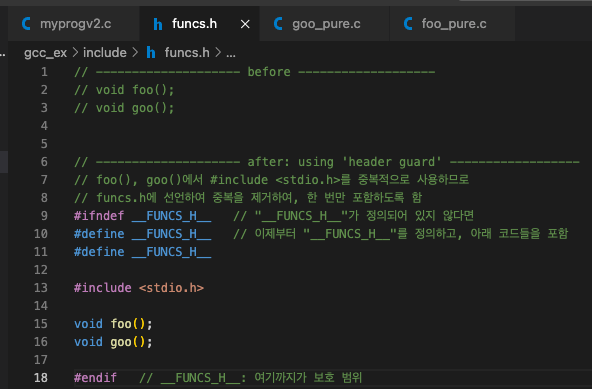
- 그러면 기존의 foo.c, goo.c에서 중복되는 #include <stdio.h>를 제거할 수 있음.
단, "funcs.h"를 include해야 함.
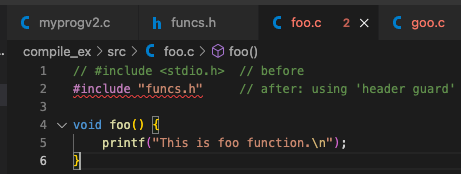
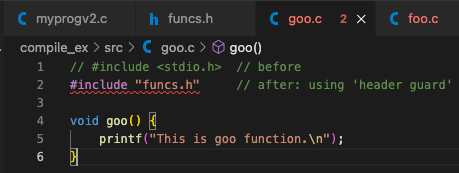

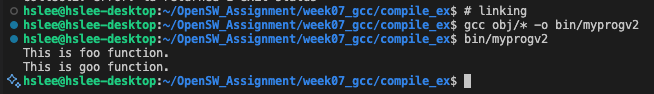
- 여러 파일(foo.c, goo.c)에서 <stdio.h>를 include하면 중복이 많아지기 때문에
Example of compilation in macOS
-
mac에서는 default compiler를 gcc 말고, clang을 사용.
그래서 gcc --version 하면, 내부적으로 clang을 실행.
gcc는 clang의 alias.
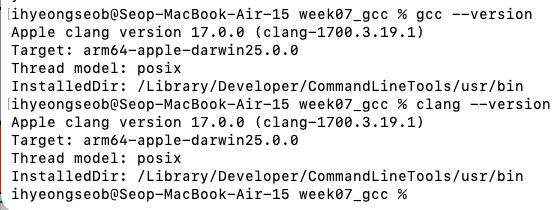
-
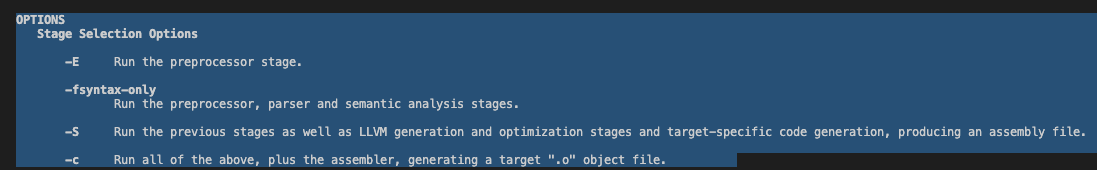
아래는 clang의 manual page 일부.
gcc의 옵션과 유사함.
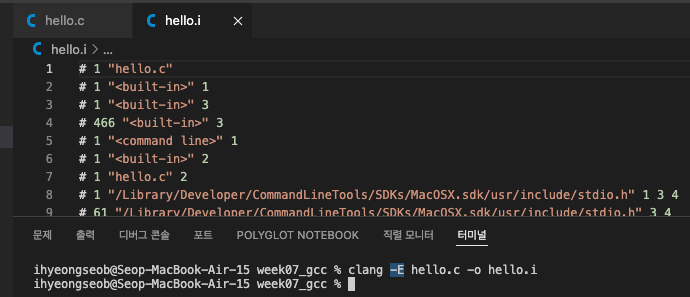
preprocessing (clang -E, *.i)
- gcc -E 옵션과 마찬가지로, clang -E
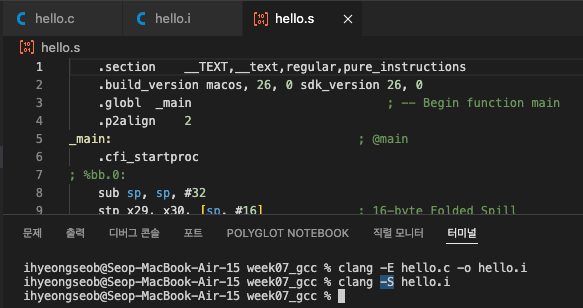
compiling (clang -S, *.s)
- gcc -S 옵션과 마찬가지로, clang -S
assembling (clang -c, *.o)
- gcc -c 옵션과 마찬가지로, clang -c
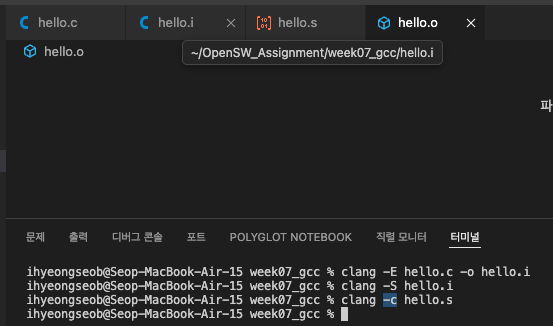
linking
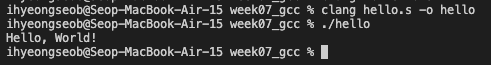
Library
-
Library:
compile된 다양한 object file(.o file)들을 모아놓은 file들.
(libc라는 library 안에 printf, scanf, strcmp, ...)
(libthread라는 library 안에 pthreadcreate, pthreadjoing, ...) -
Library는 두가지 type으로 나눌 수 있다.
- Static Library (정적 라이브러리)
- Shared Library = Dynamic Library (공유 라이브러리 = 동적 라이브러리)
1. Static Library
Static Library (*.a): Link at compile time
우리가 작성한 object file과 libc.a와 같이 기존에 있는 object code library(printf, scanf, ...)를 linking하여 executable file을 만듦.
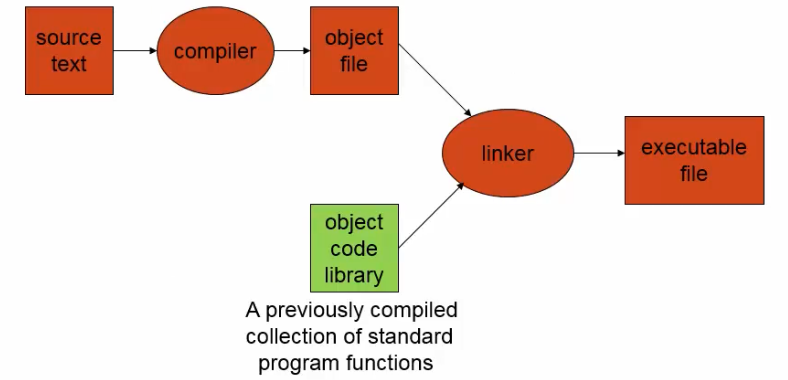
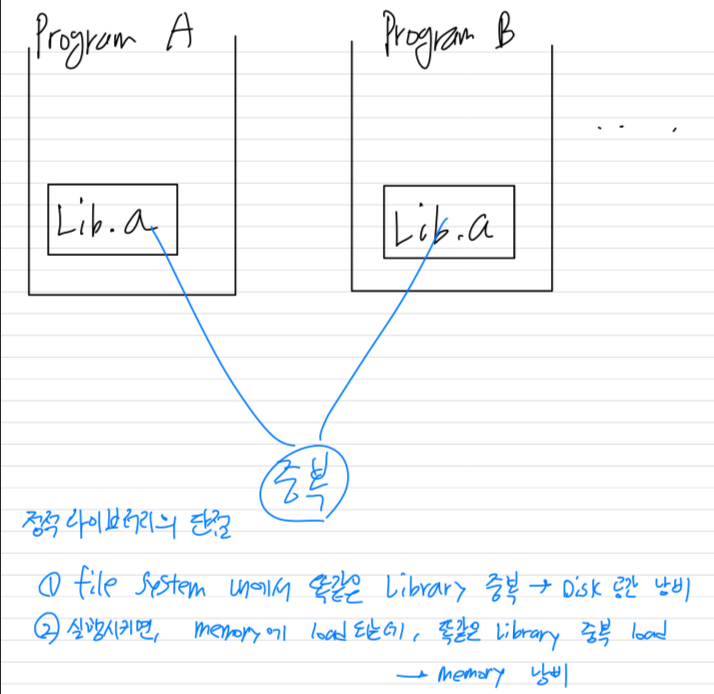
How to build/use an archive file(=static library)
-
ar: creates, updates, lists and extracts files from the library

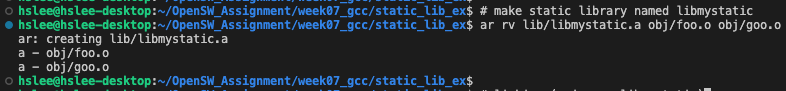
- r 옵션: 뒤에 나오는 *.o file들을 funcs라는 static library에 insert하라.
- funcs라는 static library 가 생성됨
- -L. : 현재 디렉토리에서 library를 찾아라.
- -lfuncs: link하고 싶은 library는 funcs 라는 library이다.
- -static: 여러 library가 있을 때, static library만 쓰겠다.
-
nm: 생성한 정적 라이브러리에 어떤 함수들이 있는지 확인할 수 있다.
Example
example 1: 'libmystatic' 이라는 static library 만들기 (이 library에는 foo.o, goo.o가 있음)- 먼저 main.c, foo.c, goo.c funcs.h 생성
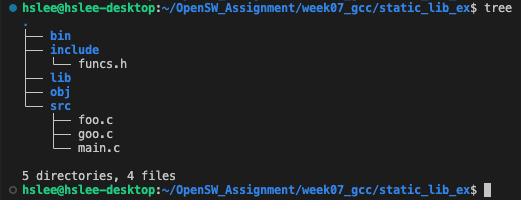
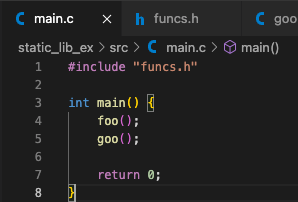
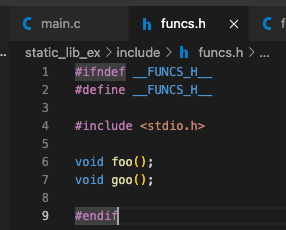
- foo.c와 goo.c를 object file로 만들기

- foo.o와 goo.o를 'libmystatic'이라는 static library로 만들기
- main.c와 'libmystatic' static library를 linking하여 executable file 만들기
( 옵션은 library를 찾을 directory를 명시)
( 옵션은 자동으로 앞에 lib 접두사와 .a 확장자를 자동으로 붙여주기 때문에 mystatic은 libmystatic.a를 찾으라는 것임)- 방법 1: -L과 -l 사용

- 방법2: 직접 경로 지정

- 방법 1: -L과 -l 사용
- 먼저 main.c, foo.c, goo.c funcs.h 생성
-
example 2: nm(생성한 정적 라이브러리에 만든 함수들이 있는지 확인할 수 있다.)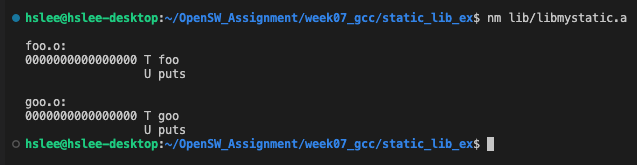
-
example 3: ldd (print shared object dependencies)- 아래와 같이 -static 옵션 없이 compile한 실행 파일은 ldd 확인 가능.
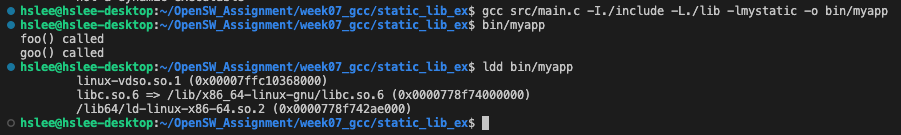
- 하지만, -static 옵션으로 compile한 실행파일은 ldd 확인 불가능.
실제 compile시에 linking 과정에서 libmystatic.a library 말고도 다른 libc.so, ld-linux.so 같은 기본 shared library들을 링크하는데,
-static 옵션을 주기 때문에 모든 library들을 정적으로 link함.
따라서 ldd는 shared object dependencies를 찾을 수 없다고 출력하는 것임.
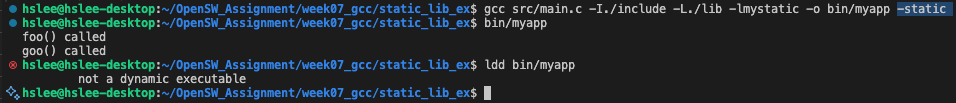
- 아래와 같이 -static 옵션 없이 compile한 실행 파일은 ldd 확인 가능.
-
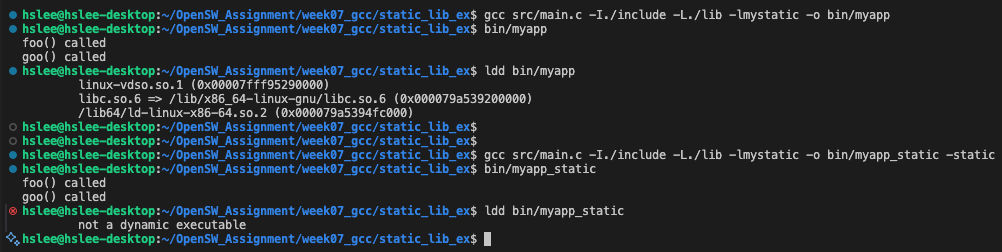
example 4: -static option. example 3와 똑같음.
Example in macOS
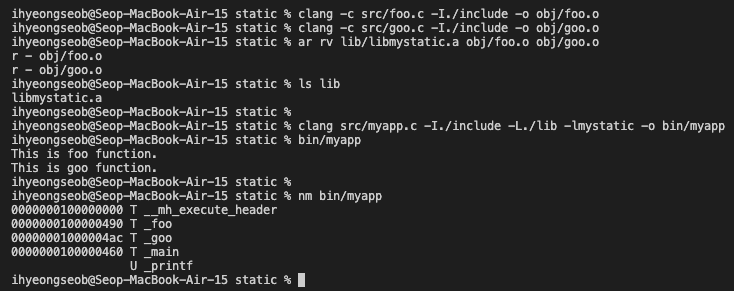
2. Shared Library
Shared Library: Linked to any program at run-time
library의 코드 전체를 linking하는게 아니라,
"어떤 library를 쓴다"라는 pointer(symbolic link)를 사용한다.
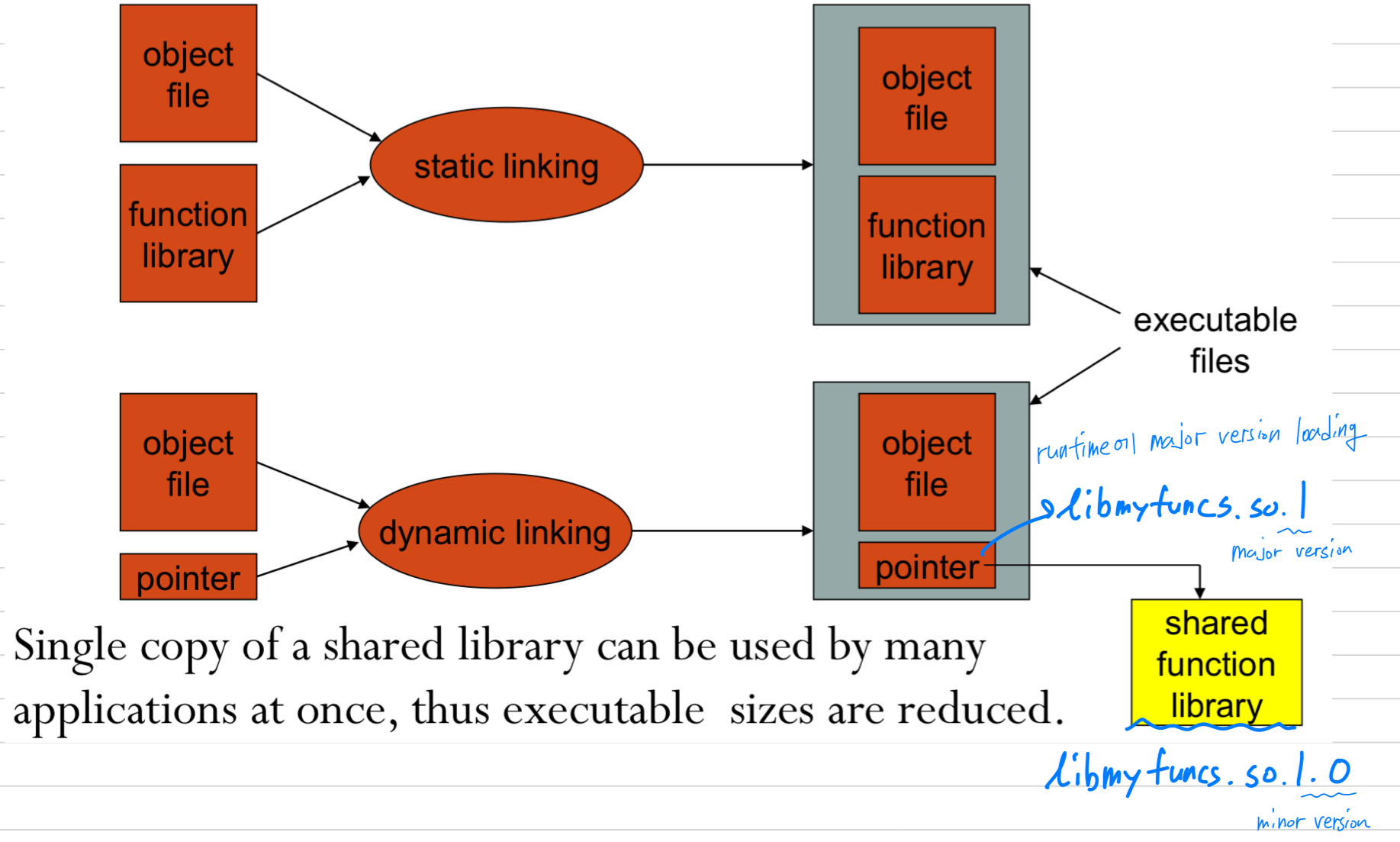
Advantages of Shared Library
shared library 장점 1:
static library를 사용할 때보다 executable file의 크기가 훨씬 작아짐shared library 장점 2:
shared library를 memory에 한 번만 loading하면, 서로 다른 program들이 그 library를 sharing하여 사용할 수 있다.
Building a Shared Library
- Functions must be
reentrant=No global variables:
여러 program들이 공유 라이브러리를 공유할 때, 간섭효과를 없애야 한다(전역변수가 있으면 안된다) - Code must be
position-independent:
공유 라이브러리가 memory 어디에 load될지 가정하고 program을 짜면 안된다.
항상 바뀌기 때문.
Shared library names
- .so in Linux
.dll in Windows
.dylib in macOS
- myfuncs라는 library를 위해서 세 개의 파일이 필요함
libmyfuncs.so:- .so는 실제 파일이 아니라, libmyfuncs.so.1의 symbolic link이다.
(libmyfuncs.so libmyfuncs.so.1) - .so file은 compile할 때, 즉 gcc를 이용해서 library를 linking할 때 사용함.
- .so는 실제 파일이 아니라, libmyfuncs.so.1의 symbolic link이다.
libmyfuncs.so.1:- 실제 파일이 아니라, libmyfuncs.so.1.0의 symbolic link이다.
(libmyfuncs.so.1 libmyfuncs.so.1.0). - .1은 major version (.so.1.0, .so.1.1, ...).
- major version은 큰 update가 있는 경우.
예를 들어, interface(argument, return값)가 바뀜. - .so.1 (major version)은 runtime에 사용될 때, 누구를 pointing하는지에 따라 어떤 version이 사용될지 결정된다
- 실제 파일이 아니라, libmyfuncs.so.1.0의 symbolic link이다.
libmyfuncs.so.1.0:- 실제로 생성한 library
- .0은 minior version. interface는 그대로지만 내부 구현이 수정됨.

- PIC: Position Independent Code로 compile하라.
- -lc: compile하면서 libc도 같이 linking하라. (상황에 안넣어도 됨)
Finding shared libraries at runtime
- library를 link할 때, 모든 directory를 다 찾아볼 수 없으니까 어느 directory를 찾아볼지 지정해줄 수 있다.
(위 그림에 있는 -L /mypath/lib 은 compile 할 때 compiler에게 알려주는 거지..
runtime에 알려주는게 아니니까)- 자체 library : LD_LIBRARY_PATH라는 환경변수에 해당 공유라이브러리가 있는 경로를 적어준다.
ex:LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$HOME/foo/lib - system library :
/etc/ld.so.conf 에 library 경로를 저장시켜놓고나서
ldconfig -p 명령어를 실행하면, system의 전체 사용자들이 해당하는 library를 빠르게 찾아볼 수 있음.
- 자체 library : LD_LIBRARY_PATH라는 환경변수에 해당 공유라이브러리가 있는 경로를 적어준다.
Example
example 1:- 먼저 myapp.c, foo.c, goo.c, funcs.h 생성
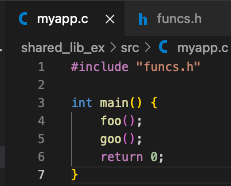
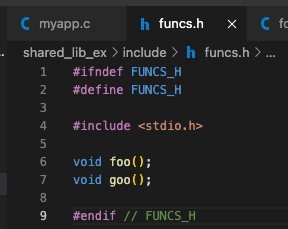
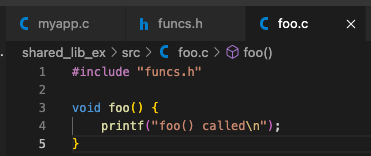
- foo.c, goo.c를 object file foo.o, goo.o로

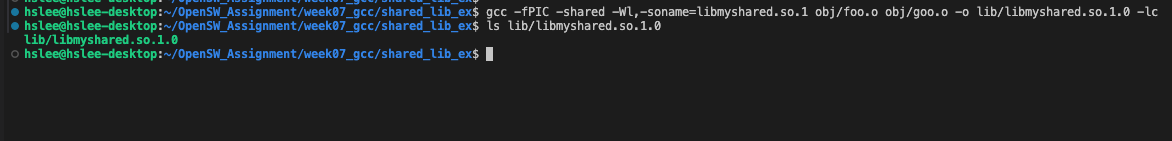
- foo.o와 goo.o를 묶어 'libmyshared.so.1.0'라는 "실제" shared library 생성
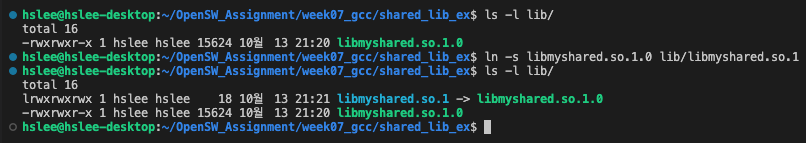
- runtime 시 사용하는 'libmyshared.so.1' 라는 symbolic link 생성 ('libmyshared.so.1' 'libmyshared.so.1.0')
(여기서, 주의사항은 lib/libmyshared.so.1이라는 symbolic link가 가리키는 "문자열"은 libmyshared.so.1.0이다.
symbolic link가 가리키는 것은 파일의 실제 경로가 아니라 단순한 문자열이기 때문에
"lib/libmyshared.so.1"이 아니라 "libmyshared.so.1"을 가리키도록 해야 한다.)
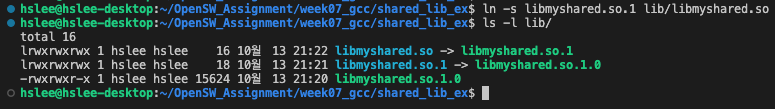
- compile 시 사용하는 'libmyshared.so' 라는 symbolic link 생성 ('libmyshared.so' 'libmyshared.so.1')
- 이제 src/myapp.c와 직접 만든 shared library인 'libmyshared.so'를 linking하여 executable file 생성

- runtime시, 어느 directory에 있는 shared library를 사용해야 하는지 경로를 알려줘야 함.
이는 LD_LIBRARY_PATH라는 환경 변수에 지정해주면 됨
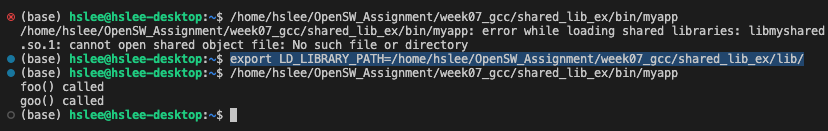
(아래는 새로운 터미널. 즉, 새로운 bash를 실행하여 bin/myapp을 실행한 결과임
처음에는 shared library 경로를 찾지 못해서 에러 발생.
LD_LIBRARY_PATH에 shared library 경로를 지정하면 해결 가능)
- 먼저 myapp.c, foo.c, goo.c, funcs.h 생성
Example in macOS (.dylib)
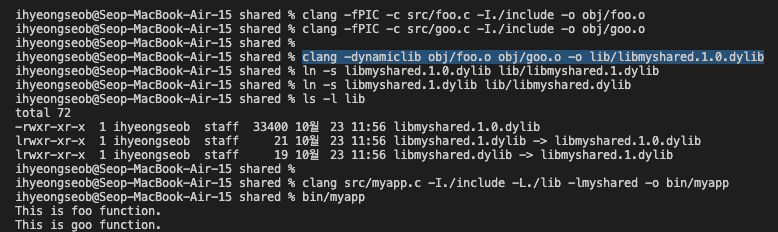
-
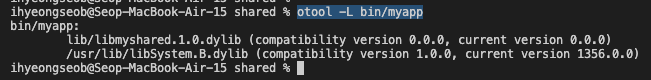
mac에서는 ldd 명령어가 없음.
대신,otool(object file displaying tool) 명령어 사용.
-
mac에서는 LD_LIBRARY_PATH라는 환경 변수가 아니라
DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH라는 환경 변수에 library path를 추가해야 함.- 새로운 터미널을 띄워서, 위에서 만든 실행 파일 실행하려고 하면 아래와 같이 library file path를 못 찾는다는 에러 발생.
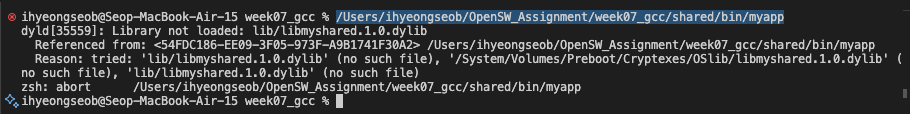
- DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH 환경변수에 library path 추가 후 실행.

- 새로운 터미널을 띄워서, 위에서 만든 실행 파일 실행하려고 하면 아래와 같이 library file path를 못 찾는다는 에러 발생.