Shell Script Programming
Shell
-
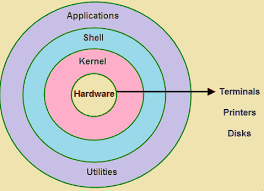
Shell은 command-line interpreter이다.
(출처: https://saurabhshivde.hashnode.dev/day-4-90daysofdevops)
-
위 그림처럼, shell은 keyboards 또는 shell script file을 입력으로 받아서
linux kernel를 통해 system의 HW와 interact
Shell script는 왜 쓰는가?
- 업무 자동화
- Combine long and repetitive sequences of commands into one simple command
- Share procedures among several users
- Provide a controlled interface to users
- Create new commands using combination of utilities
- Quick prototyping, no need to compile
Shell script interpreter
- shell interpreter마다 약간의 문법이나 확장이 다르지만, linux에서는 대부분 bash
- bash (born again shell) : Default in most Linux distros
- sh: original shell인데 요즘은 잘 안씀
- csh: C-like syntax
- zsh: Advanced scripting features: default in MacOS
Shell script
-
shell script: 'x' 실행권한을 갖고 실행하는 text file
일일이 terminal에 입력했던 command들을 shell script에 넣어서 한꺼번에 자동으로 처리하도록 할 수 있음. -
그래서 shell scripts는 다음의 것들을 포함할 수 있음
- linux commands (e.g, ls, pwd, find, etc.)
- Control flows (e.g, if-else and loops)
- Variables
- Functions
a simple example
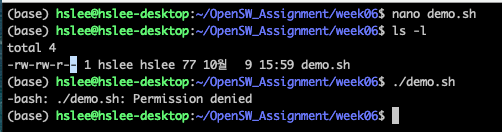
아래와 같은 shell script를 생성. demo.sh
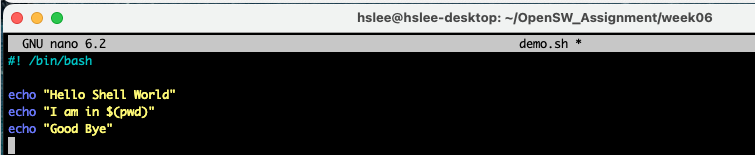 처음 생성하고 나서,
처음 생성하고 나서,
user에 대한 실행 권한이 없어서 demo.sh를 실행할 수 없음.
user에 대해서만 실행 권한 부여 후, 아래와 같이 실행할 수 있음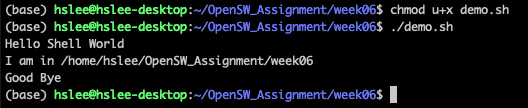
Shell script Syntax
Special Characters
-
#: 주석 -
#!: 어떠한 interpreter를 쓸 것인지 지정.
ex) #! /bin/bash -
\: end of a line -
;: Used to interpret what follows as a new command (명령어를 연속으로 실행) -
&&: The action will be performed only if the conditions evaluate to true
(앞 명령어가 에러 없이 정상종료하게 되면 그 다음 명령어로 이어가라)
(앞 명령어가 에러가 발생하면, 거기서 실행을 멈추고 뒤 명령어들은 실행 X)
(실패할 때까지 실행하라) -
||: The action will be performed if any of the conditions evaluate to true
(성공할 때까지 실행하라)
(cat file1 || cat file2 || cat file3 -> file1에서 성공했으면 거기서 멈춤) -
$: $변수, ${변수}, $(command) 이거는 command substitution

-
!: NOT -
'': strong quotes. (안에 있는 변수를 변수로 안보고, string으로 봄)
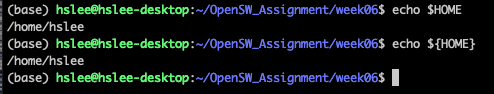
echo '$HOME'
-> $HOME을 변수로 보지 않고, $HOME 이라는 string으로 봄 -
"": weak quotes (안에 있는 변수를 변수로 봄)
-> $HOME을 환경변수 HOME으로 보고, 값을 읽어옴
Examples
-
'',""example:

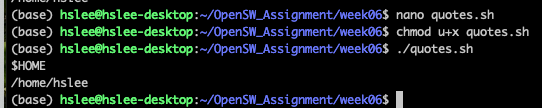
-
||,&&example:
Variables
-
shell script에서 variable의 type이 없이, 모두 다 string type
-
local variable 선언:
변수명=string (중간에 공백이 없다는 가정) 또는
변수명="string" (중간에 공백이 있다면)
= 앞,뒤로 공백이 있으면 안됨

-
local variable 사용:
$변수 또는 ${변수}
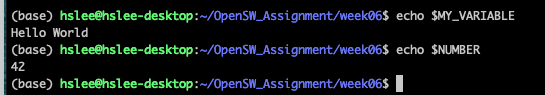

-
위와 같은 local variable 말고,
environment variables도 사용 가능
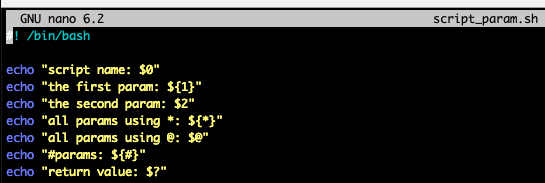
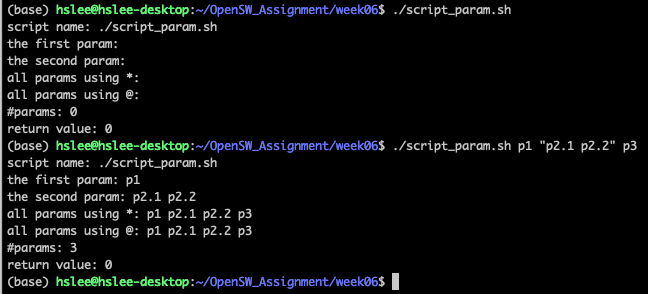
Script parameters
- shell script에 argument를 넘겨줄 수 있음
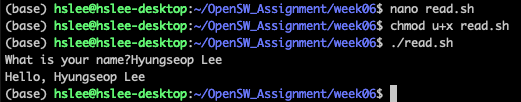
ex>./myscript.sh hello world
(위 예제는 myscript.sh를 실행하는데, "hello"와 "world"를 argument로 넘겨줌)$0: Script name (myscript.sh)$1: First parameter (hello)$2, $3: Second, third parameter, ... (world, ...)$*or$@: All parameters (hello world)$#: Number of parameters (2)$?: Return value
examples
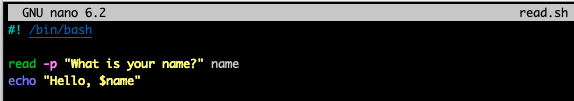
Built-in Shell Commands (read, ...)
https://linuxhint.com/bash_builtin_examples/
echo: printf와 유사read: scanf와 유사
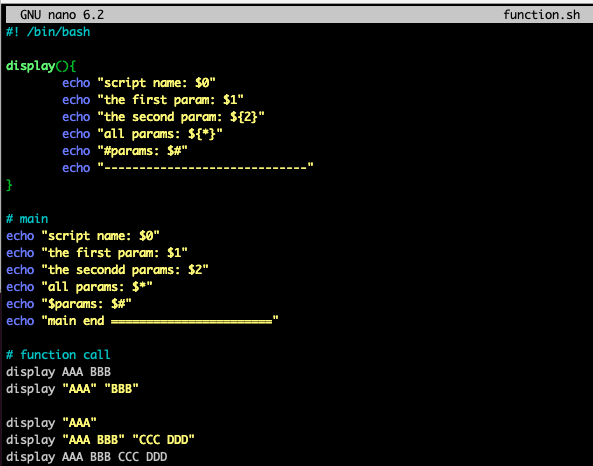
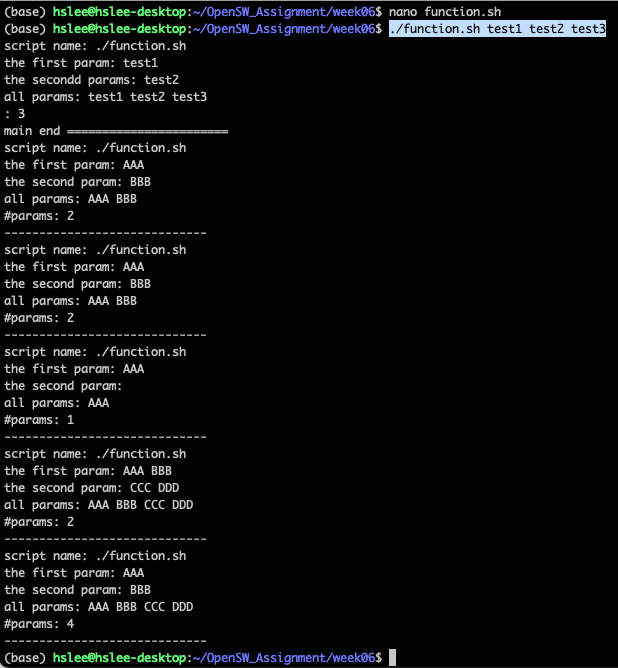
Functions
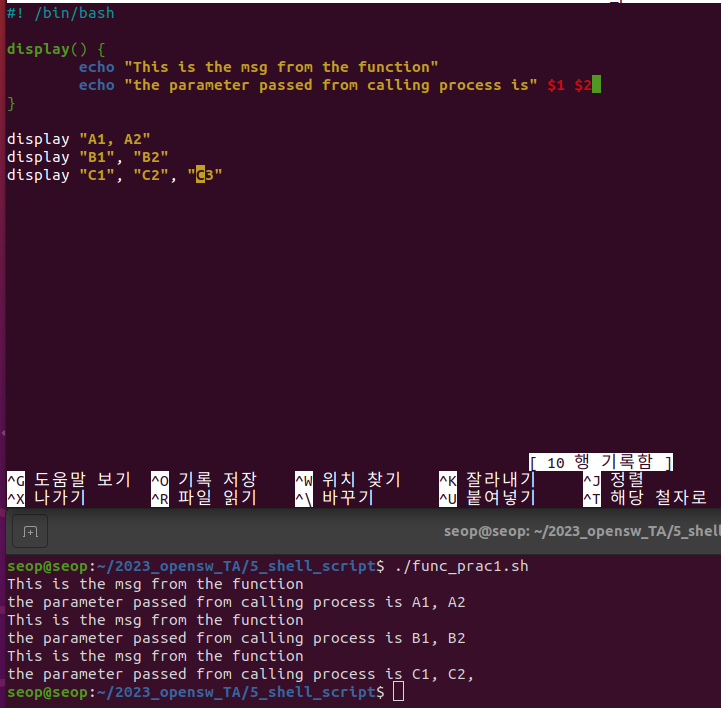
- Function parameter도 Script parameter와 동일하게 아래와 같은 parameter를 가짐.
- parameter들은 공백을 기준으로 구분
하지만, function 내에서 아래의 parameter를 사용하면, local variable(function 호출시 넘겨준 argument)를 사용함$0: script name$1: First parameter$2, $3: Second, third parameter$*or$@: All parameters$#: Number of parameters$?: Return value
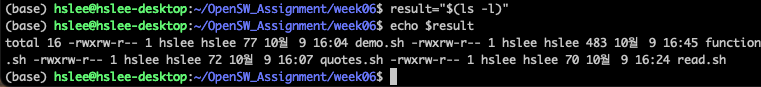
Command Substitution
- 명령어의 결과를 다른 명령의 일부로 사용가능
$(command) 또는
`command` (`은 backtick
example
- $(command)
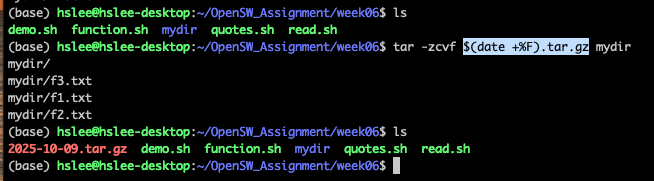
- `command`
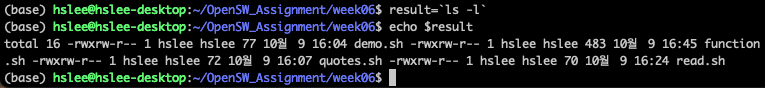
Exporting Variables
- script 내에서 선언된 변수는 script 안에서만 유효함.
child process가 변수를 접근하도록 하기 위해서는 export를 명시적으로 해줘야 함.
export VAR=value
VAR=value; export VARif
-
if-then-fi

-
if-then-elif-then-else-fi

-
여기서, []는 test 명령어임.
Conditional expression (Numeric, String, File)
-
[ conditional expression ]
대괄호 안에 여러가지 condition을 test할 수 있다.
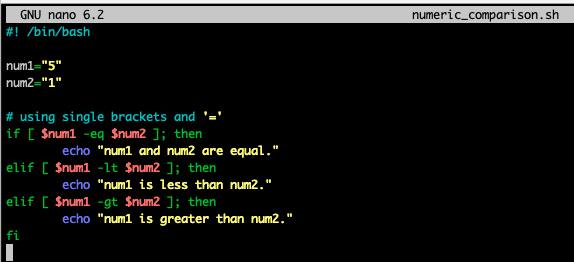
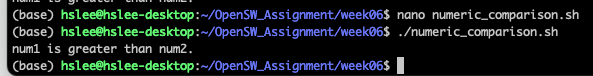
returns 0 if conditional expression is true; otherwise returns 1 (false)Numeric comparison
ex> [ $a -eq $b ]- -eq (eqaul)
- -ne (not equal)
- -gt (greater than)
- -lt (less tan)
- -ge (greater or equal)
- -le (less or equal)
(아래 예제처럼 if문의 test 명령어 [ ]는 어떤 비교 연산자를 사용했느냐에 따라 변수의 값을 string으로 취급할지, 숫자로 취급할지가 결정됨)
String comparison
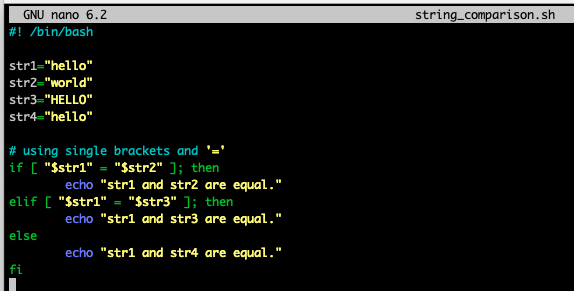
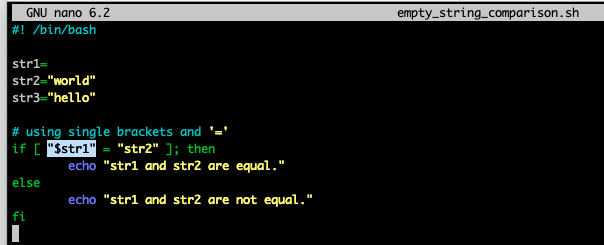
ex> [ "$a" = "$b" ]- = (equal)
- != (not equal)
- -z (empty)
- -n (not empty)
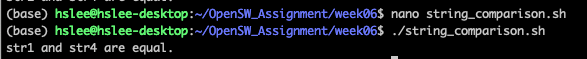
"" 를 해주는 이유:
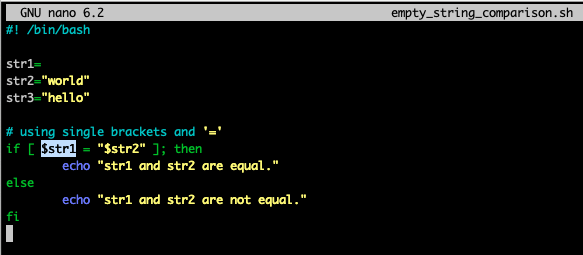
아래와 같이 아무 값도 없는 str1과 비교하려고 했을 때,
""이 없으면 아무런 값과도 비교하지 않는 것이므로 syntax error가 남.
즉, [ = "str2"] 같음.
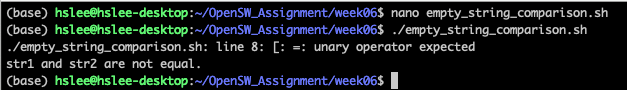 (위에서 syntax error message가 출력됨에도 불구하고, 끝까지 실행된 이유:
(위에서 syntax error message가 출력됨에도 불구하고, 끝까지 실행된 이유:
test 명령어는 문법에 맞지 않다고 판단하여 error message를 출력하고,
실패했음을 알리는 0이 아닌 error code를 반환하기 때문에 해당 조건을 false로 판단함.
그래서 else까지 수행이 되기는 함.
아래는 이에 대한 실험)
test 명령어 내부가 True일 때는 정상 종료 코드 0 return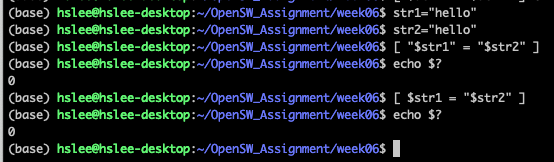
test 명령어 내부가 False일 때는 코드 1 return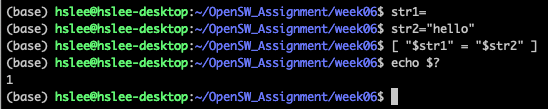
test 명령어 내부 syntax error일 때는 코드 2 return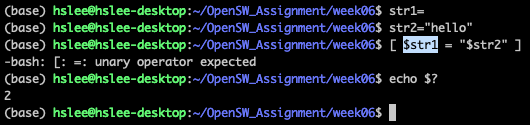
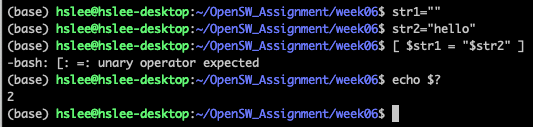
""를 해주면 아무 값도 없는 str1은 empty string("")으로 취급되기 때문에 syntax error가 발생하지 않음.
즉, [ "" = "str2"] 같음.

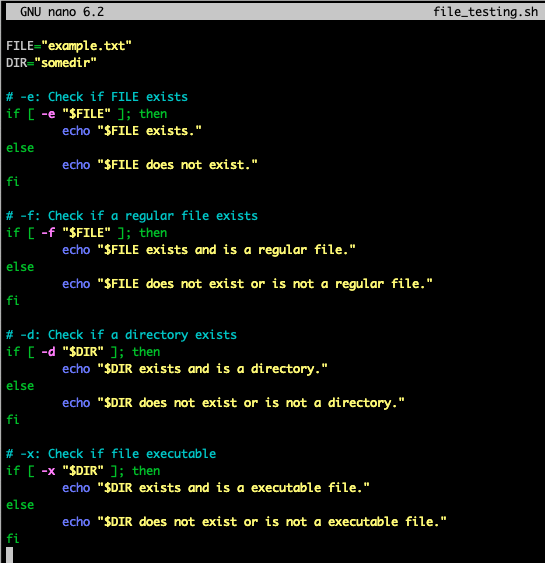
- File testing
- -e (file exists)
- -f (regular file exits)
- -d (directory exists)
- -x (file executable)
- -w (file writable)
- -r (file readable)
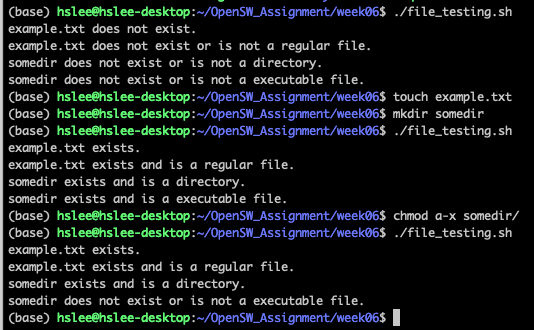
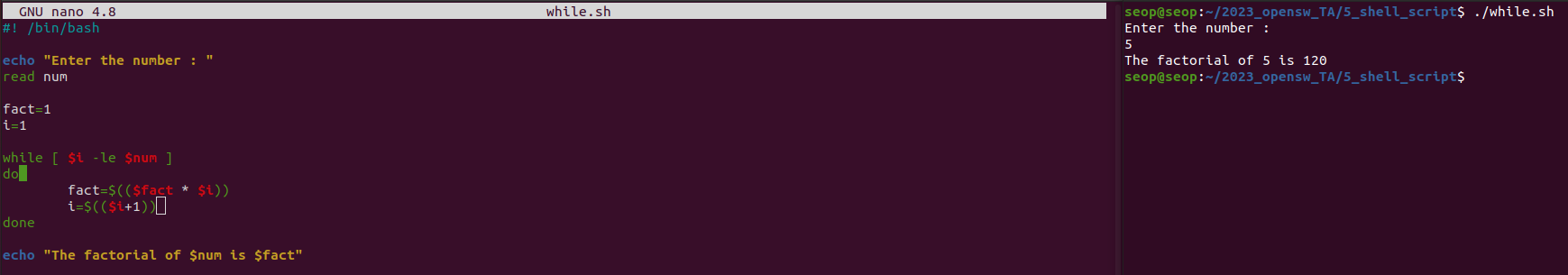
Arithmetic Expression
- shell script에서 선언된 변수들은 모두 string이라고 했었는데,
이 string들을 실제 숫자(정수)로 생각해서 연산하고 싶으면?
(단, 기본적으로 bash에서는 floating-point 연산을 하지 않음.
shell script는 command 자동화가 주목적이기 때문에)
- 산술 연산
- 현재 표준적으로 사용하는 것:
$((a+b)) - 과거에 사용했던 것:
$ (expr $a + $b)let sum=a+b
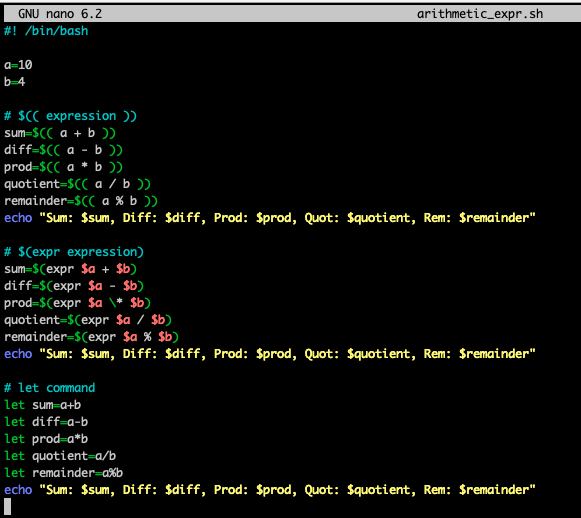
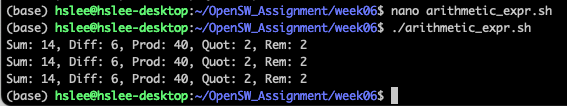
- 현재 표준적으로 사용하는 것:
Logical Operators
&&: AND||: OR!: Negation
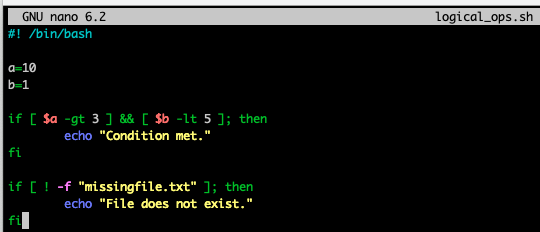
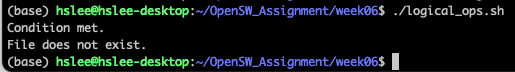
for loop
- list에 있는 원소들이 하나씩 variable에 assign되어 반복
(seq는 숫자들의 list를 만들어주는 명령어)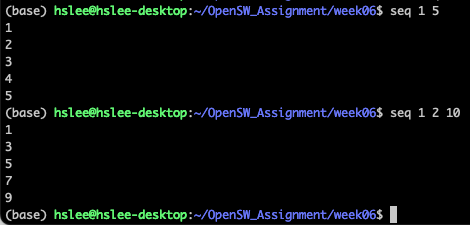
(아래 ex2처럼 command substitution $(command) or `command`를 이용하여
seq 1 2 10의 실행 결과를 입력으로 사용이 가능)
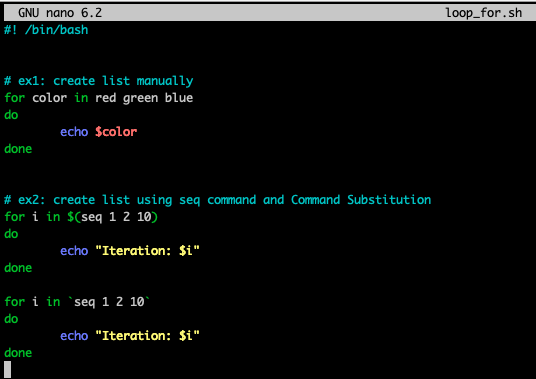
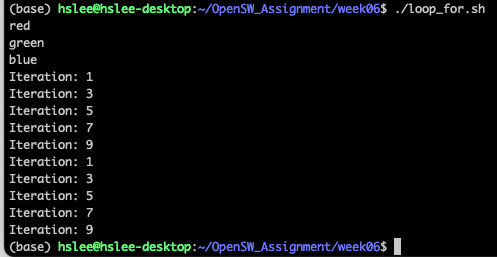
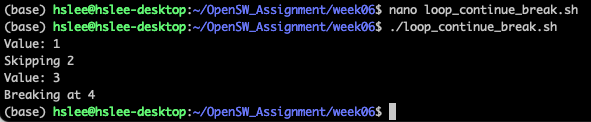
continue, break
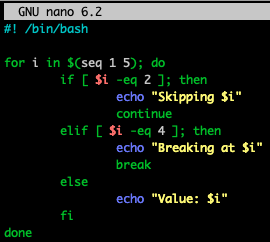
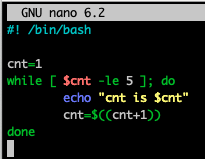
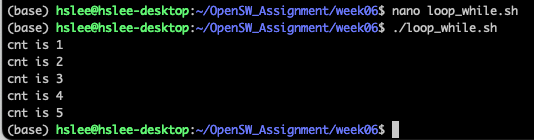
while loop

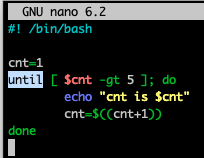
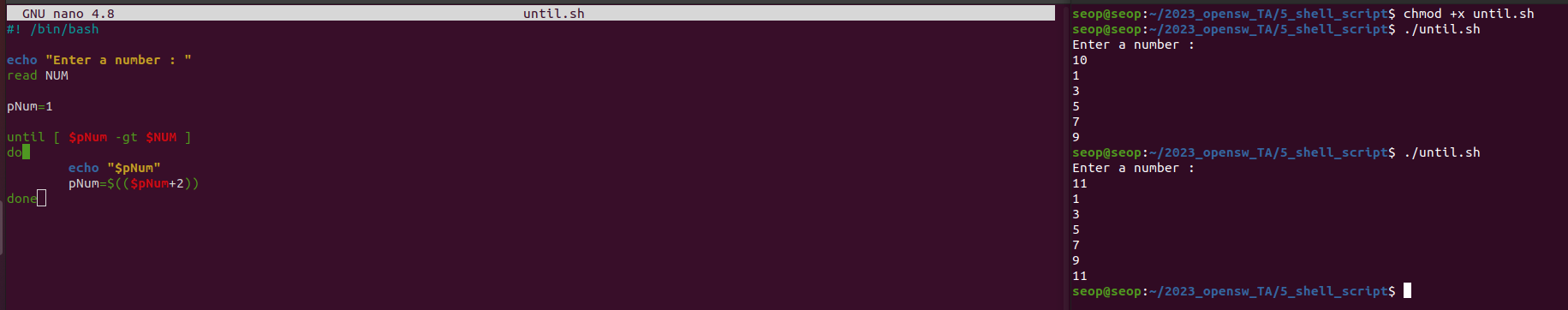
until loop


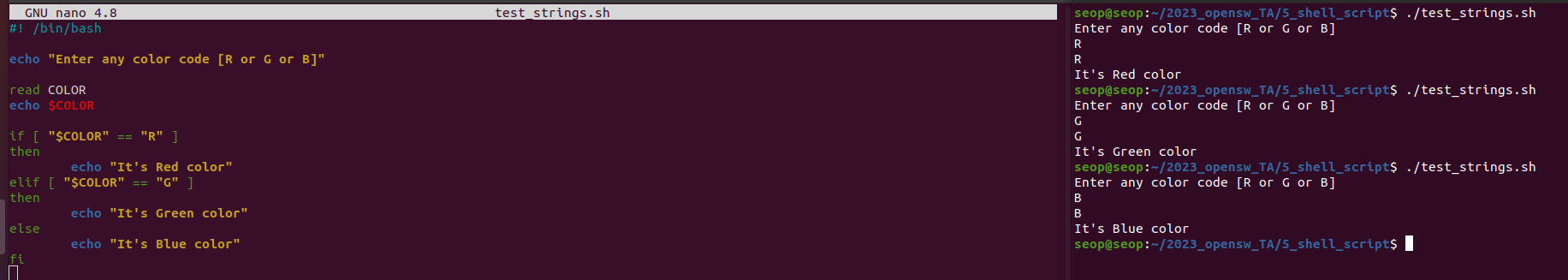
Example
-
R, G, B
-
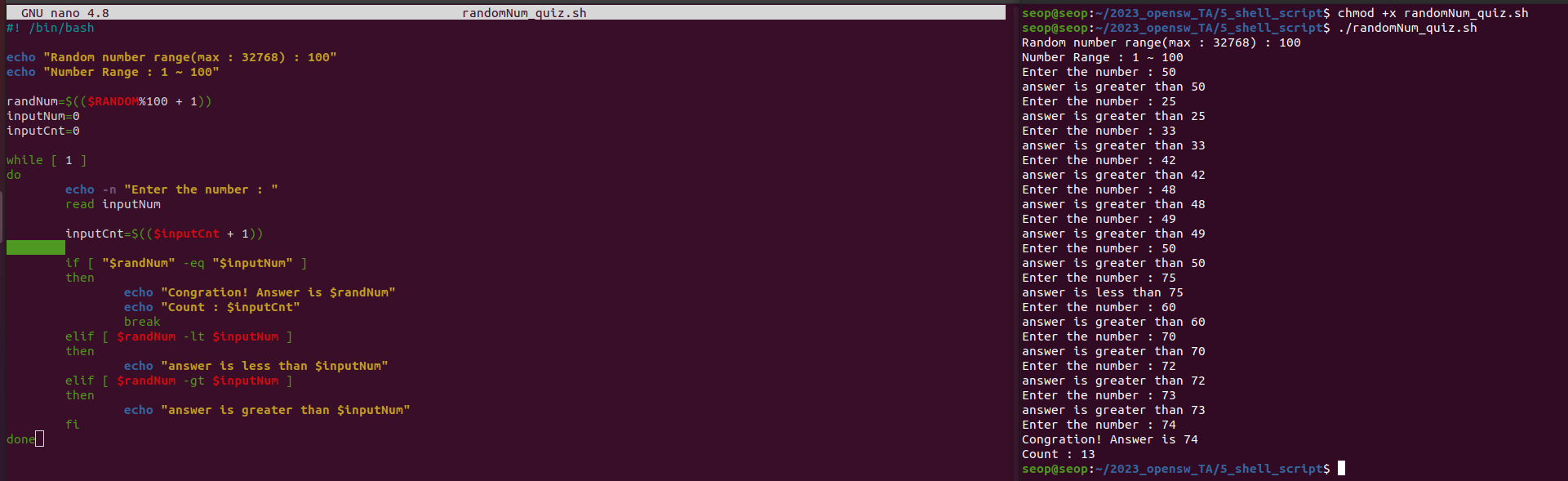
Up down 게임: 1~100 Random 숫자를 생성하여 사용자가 그 random 숫자를 맞추는 게임
-
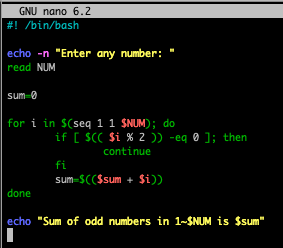
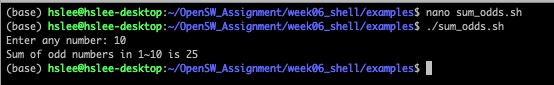
홀수만 sum:
헷갈리는 것 정리
-
변수 사용:
$변수, ${변수} -
command substitution:
$(command) -
arithmetic expression
$((expression)) -
$$: 실패할 때까지 실행 (exit code가 0이 아닐 때까지 실행)
-
||: 성공할 때까지 실행 (exit code가 0이 나올 때까지 실행)
응용
$?
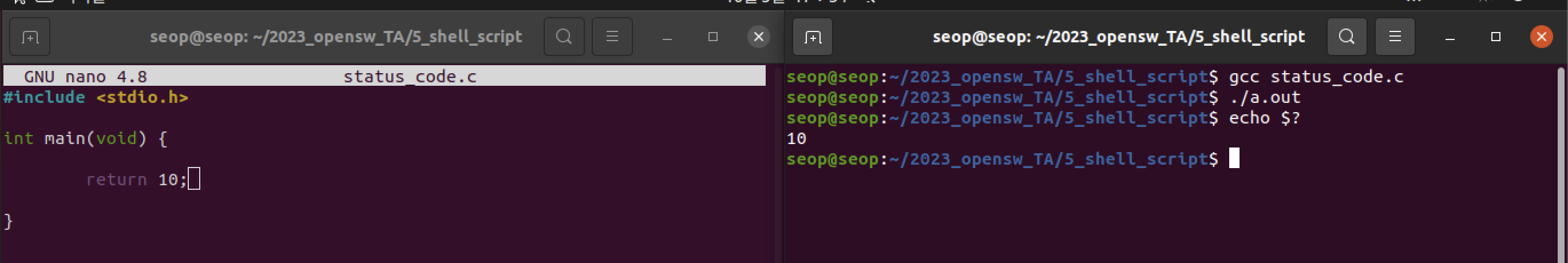
- $? :
status code를 반환하는 변수이다.
- main 함수에서 return 10을 했으니 10을 반환한다.
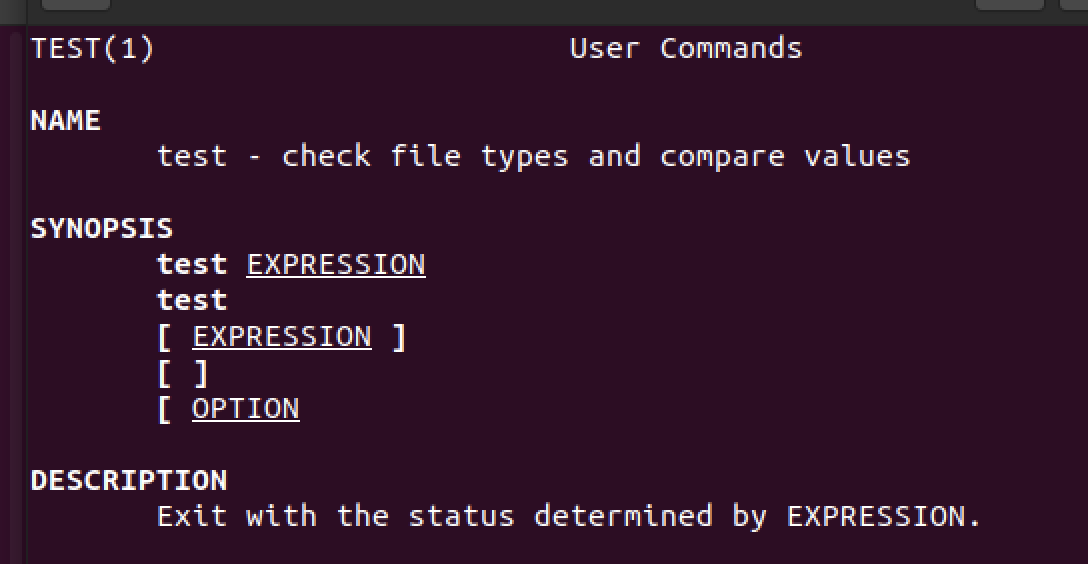
- 아래 예시는
test라는 명령어인데, []로 대체하여 사용할 수 있다.
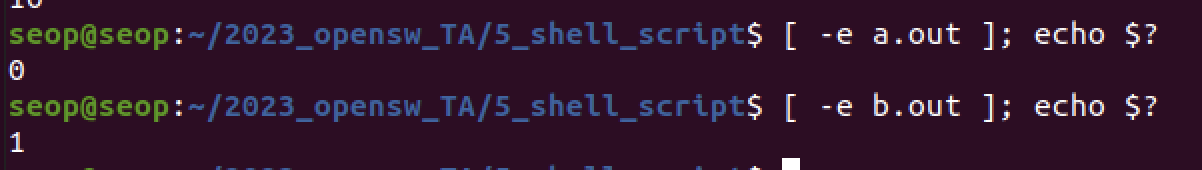
a.out이라는 실행파일이 있는지 를 확인하기 위해 -e 옵션을 붙임.
 a.out이라는 실행파일이 있으니 status code 0 반환.
a.out이라는 실행파일이 있으니 status code 0 반환.
b.out이라는 실행파일은 없으니 status code 1 반환.
; && ||
- ;
은 명령어를 순차적으로 실행하기 위해 사용된다.

- && :
앞의 명령어가 정상실행되면, 다음꺼 실행.
 (b.out은 없는 file이니까 exit code 0이 아닌 다른 숫자를 반환하므로,
(b.out은 없는 file이니까 exit code 0이 아닌 다른 숫자를 반환하므로,
그 다음 echo $?이 수행되지 않음.)
-
|| :
앞의 명령어가 정상종료가 될 때까지 실행.
 (b.out은 없는 file이니까 exit code 0이 아닌 1을 반환하므로,
(b.out은 없는 file이니까 exit code 0이 아닌 1을 반환하므로,
그 다음 echo $? 실행. echo $?은 정상적으로 실행되었으니 전체 명령어가 멈춤) -
예제1:
 b.out이 없기 때문에 [ -x b.out ]은 exit code 0이 아니고(실패) + || (성공할 때까지 실행)로 이어져 있기 때문에 그 다음 명령어 실행.
b.out이 없기 때문에 [ -x b.out ]은 exit code 0이 아니고(실패) + || (성공할 때까지 실행)로 이어져 있기 때문에 그 다음 명령어 실행.
echo $?에서 이전 [ -x b.out]의 exit code 1 출력 성공 + || (성공할 때까지 실행)로 이어져 있기 때문에 여기서 전체 명령어 종료. -
예제2:

b.out이 없기 때문에 [-x b.out]은 exit code 0이 아니고(실패) + ||(성공할 때까지 실행)로 이어져 있기 때문에 그 다음 명령어 실행.
echo $?에서 이전 [-x b.out]의 exit code 1 출력 성공 + &&(실패할 때까지 실행)로 이어져 있기 때문에 그 다음 명령어 실행.
echo $?에서 이전 echo $?의 exit code 0 출력.
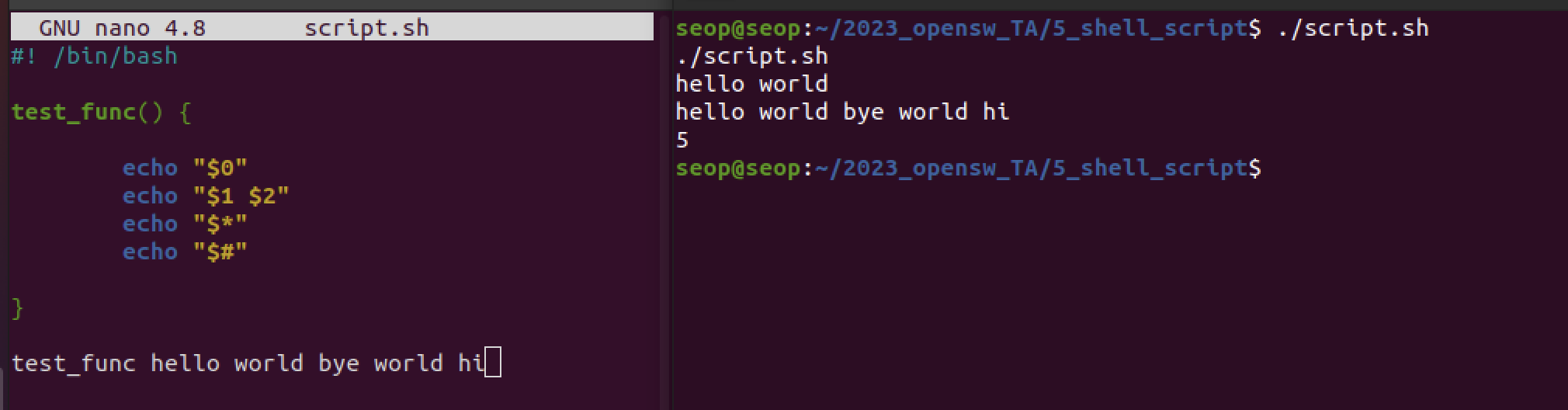
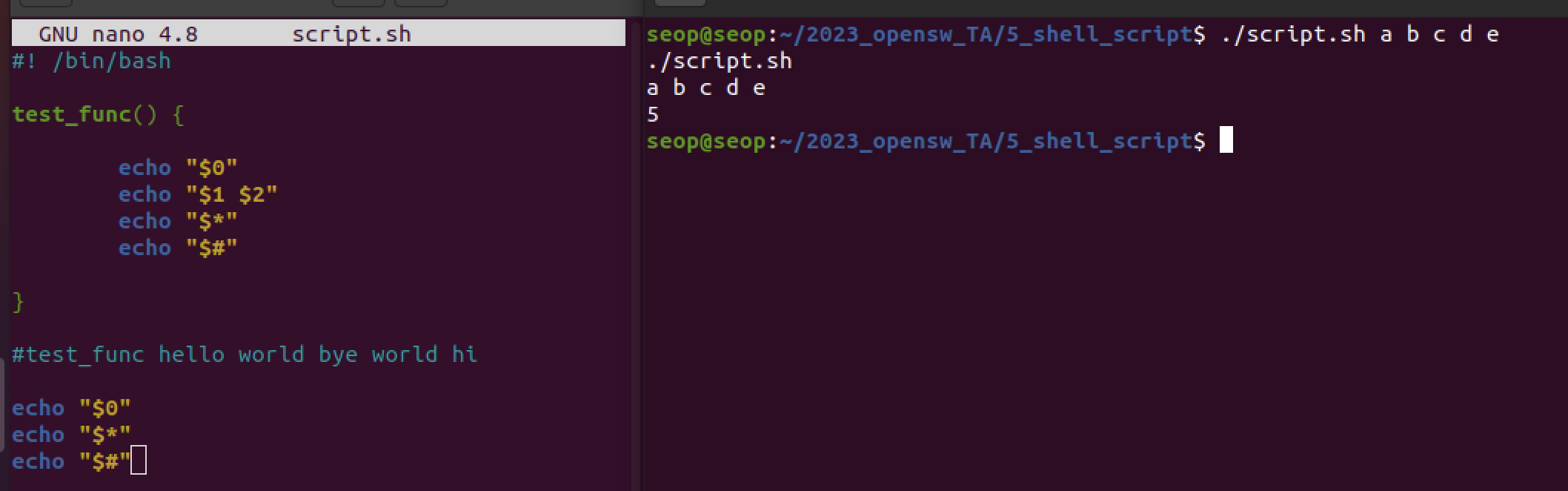
$*, $#
- $0 : 실행파일 이름
- $* : 모든 인자들
- $# : 인자의 개수
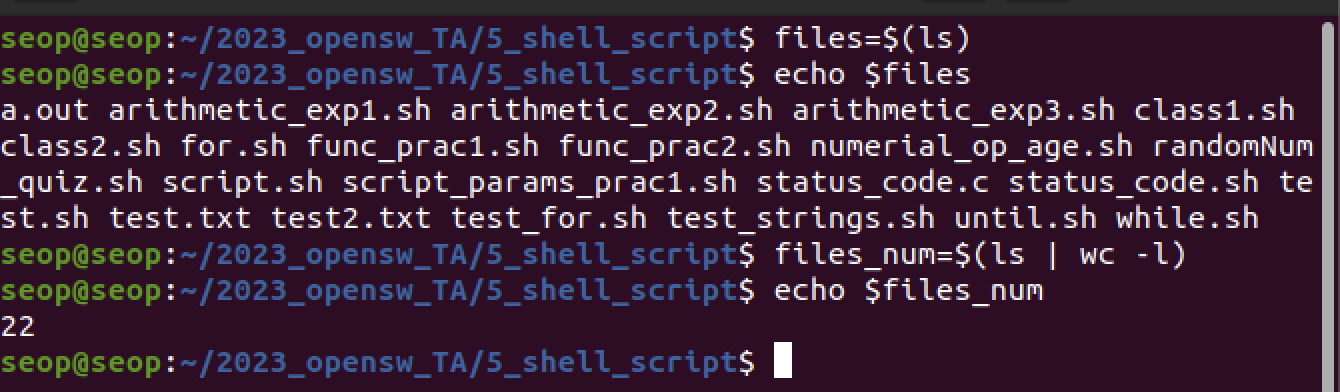
$()
ex1
ex2
- 현재 디렉터리에 있는 .txt 파일들과 해당 파일의 word count 출력
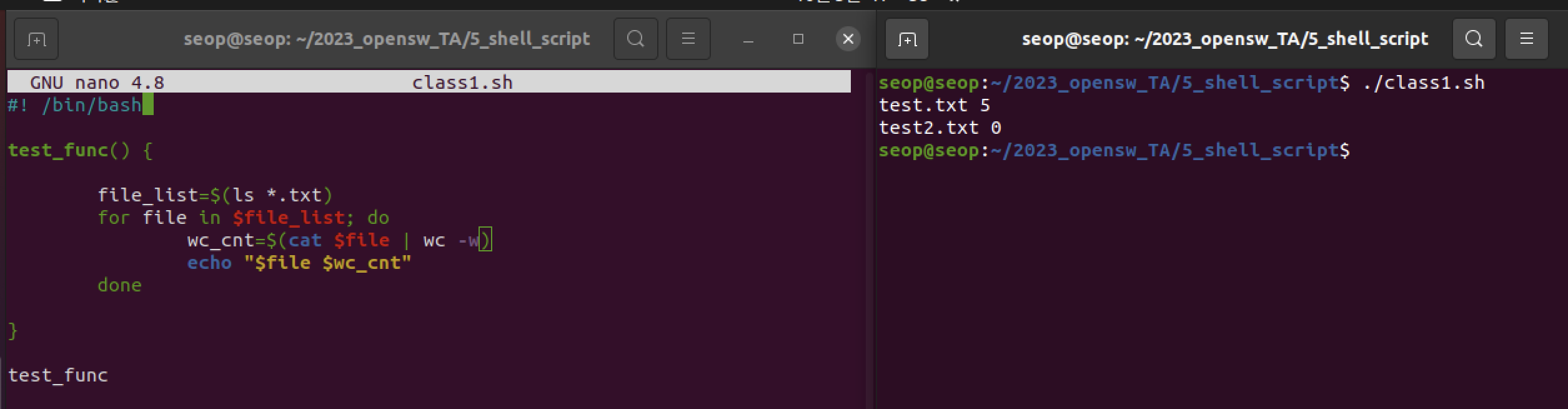
ex3
- 현재 디렉터리에 있는 모든 파일 출력. 단, 실행파일 제외.
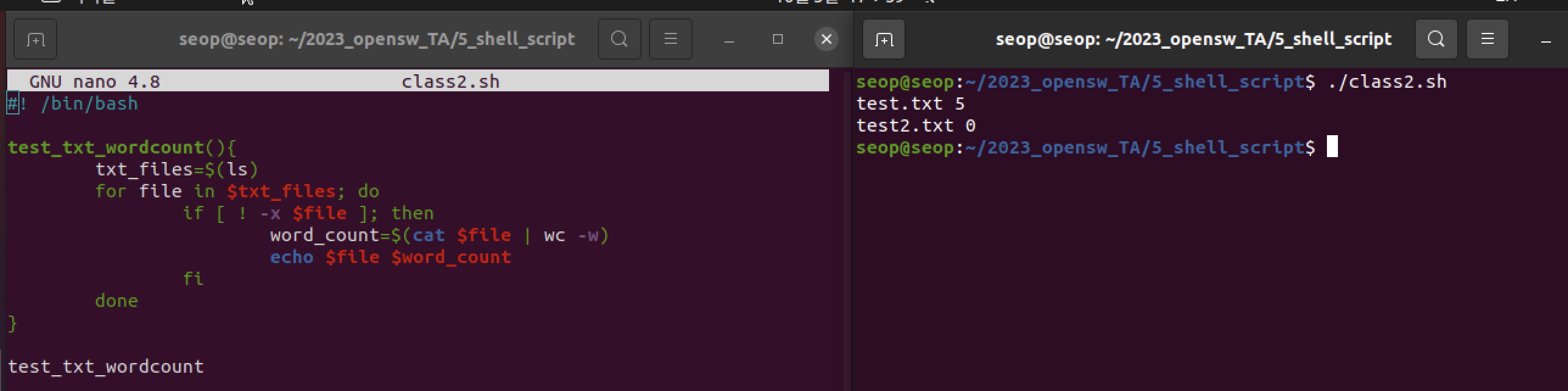
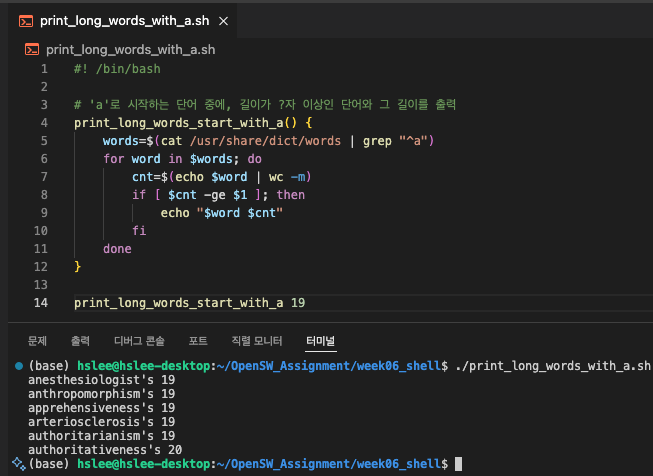
ex4
- /usr/share/dict/words 파일에서 'c'로 시작하는 단어 중에 입력 숫자보다 길이가 긴 단어만 출력