리눅스 기본 명령어 - User environments, Manipulating text
User environments
- Linux는 multi user system이므로 user environments에 대해서 살펴본다
Identifying Current User
-
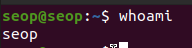
whoami: To identify the current user.
-
who: To list the currently logged-on users.

Users and Groups
-
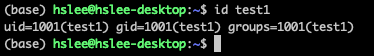
uid: user들은 각각 고유한 ID를 가짐.
(/etc/passwd 에서 user들의 정보를 확인 가능)
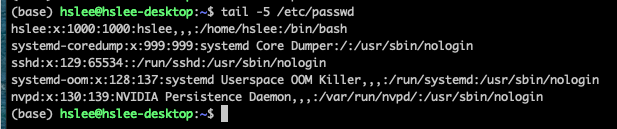
- line 하나하나가 모두 user이다.
- seop을 제외한 나머지 user들은 직접 만들지 않은 user들이다.
system이 접근 권한을 설정하기 위해서 내부적으로 만들어진 가상의 user. - x : passwd인데, 보안상 x로 표시
- 첫번째 1000 : UID
- 두번째 1000 : GID
- hslee : 사용자가 계정을 만들 때, 입력한 full name
- /home/seop : home directory
- /bin/bash : default로 사용하는 shell
-
gid: user들을 group으로 묶을 수 있고, group도 고유한 group ID를 가짐.
(/etc/group 에서 group들의 정보를 확인 가능)
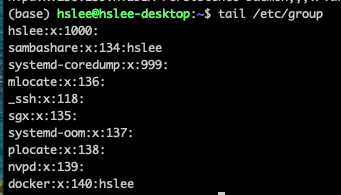
- sambashare라는 group에 hslee user가 포함됨.
Adding and Removing Users
useradd (모든 Linux) (불편)
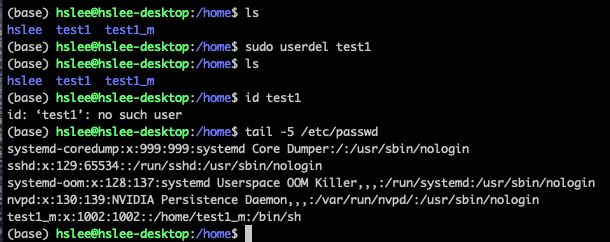
useradd로 test1이라는 user 생성
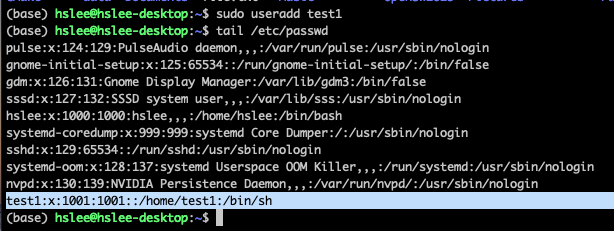
id명령어로 user에 대한 정보 확인 가능
- 그런데 /home/에 test1/이 없음.. 왜 그럴까?
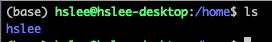 useradd는 기본적으로 홈 디렉토리를 생성하지 않음.
useradd는 기본적으로 홈 디렉토리를 생성하지 않음.
그래서 /home/test1 디렉토리가 자동으로 생성되지 않았던 것임.- 방법 1: sudo useradd
-mtest1
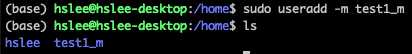
- 방법 1: sudo useradd
userdel (모든 Linux) (불편)
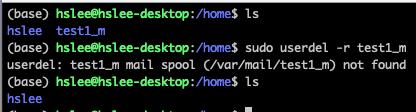
userdel로 test1 user 삭제
userdel은 useradd와 마찬가지로 기본적으로 /home/test1 디렉토리를 같이 제거해주지는 않지만, 시스템에서 user는 제거되었음.
- 방법 1: sudo userdel
-rtest1_m
-r 은 home directory까지 모두 지우라는 옵션
- 방법 1: sudo userdel
adduser (Debian 계열 배포판) (더 편함)
useradd, userdel은 user의 home directory를 자동으로 만들어주거나 제거해주지 않아서
-m, -r 옵션을 사용했어야 함.
반면에, adduser, deluser는 이러한 것들을 자동으로 해줘서 더 편함
sudo adduser로 test user 생성.
아래와 같이, 홈 디렉토리가 자동으로 생성됨.
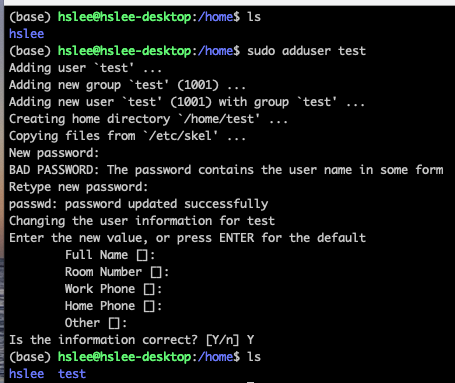
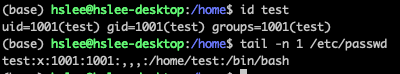
su (switch user)
su명령어는 switch user의 준말로, 다른 계정으로 전환하는 명령어.
test user 계정으로 전환해보자. (-옵션은 아예 해당 user의 환경으로 완전히 변환, 환경 변수, Path, 홈 디렉토리 등)
su - test
(test계정의 passwd 입력)
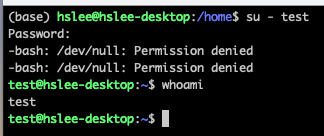 위와 같이, test user로 전환이 되었다.
위와 같이, test user로 전환이 되었다.
sudo 권한 부여 = sudo group에 추가
- test user는 adduser로 새로운 user를 생성할 수 있을까?
아래와 같이, test user는 아직 super user 권한이 없기 때문에 생성 권한도 없을 것이다.
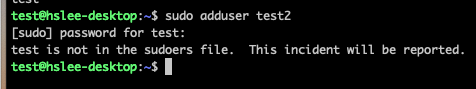
- 그럼 test user에게 super user 권한을 부여해보자.
그러기 위해 다시 sudo 권한이 있는 계정으로 복귀.방법 1:직접 /etc/group file을 수정
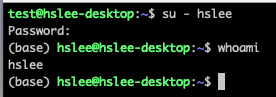 /etc/group에 sudo group을 설정할 수 있기 때문에 해당 라인을 수정해보자.
/etc/group에 sudo group을 설정할 수 있기 때문에 해당 라인을 수정해보자.

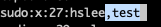
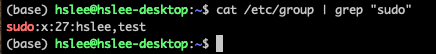 위와 같이 성공적으로 추가된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
위와 같이 성공적으로 추가된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
이제 다시, test user로 switching한 후에 sudo adduser를 재실행해보자.
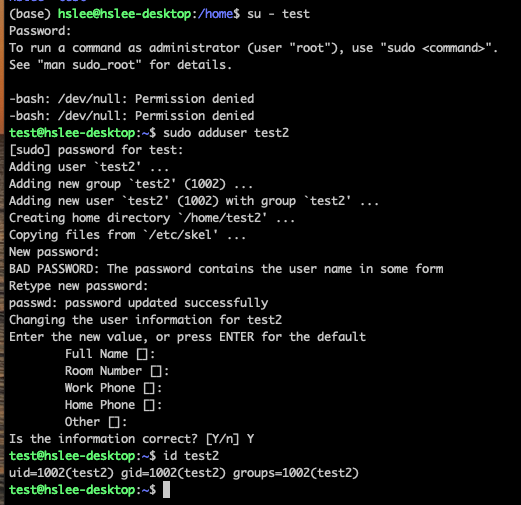 test user를 sudo group에 추가해줬기 때문에 sudo 권한을 통해 adduser test2를 성공했다.
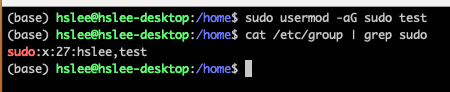
test user를 sudo group에 추가해줬기 때문에 sudo 권한을 통해 adduser test2를 성공했다.방법 2:sudo usermod -aG sudo [user명]
usermod 명령어는 user modify
-aG sudo: append to sudo Group
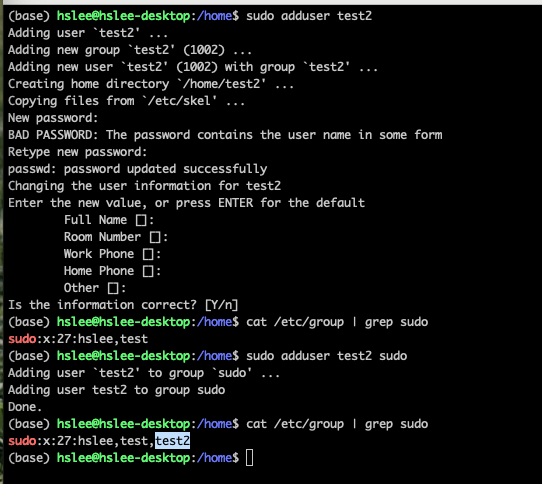
방법 3:sudo adduser [이미 존재하는 user명] sudo
(이미 존재하는 user명이어야 함. 존재하지 않으면 error)
deluser
- 이제
deluser명령어를 이용하여 test2 user를 제거해보자.
아래와 같이, 정상적으로 삭제되긴했지만 userdel과 마찬가지로 home directory까지 제거되진 않았다.
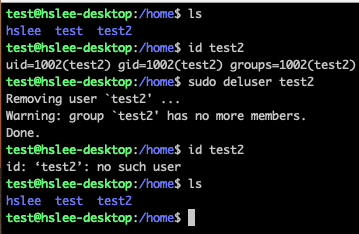
- 방법 1:
sudo deluser --remove-home test2
(userdel에서는 -r 옵션이었는데 deluser는 -r 옵션이 아님)
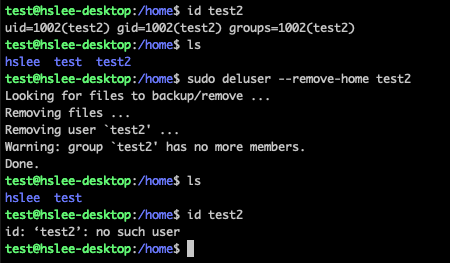
- 방법 1:
Adding and Removing Groups
-
groupaddoraddgroup:
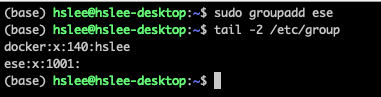
-
groupdelordelgroup:
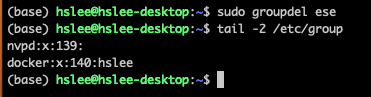
user add, del in MacOS
-
mac에서는 useradd, adduser 명령어가 없음
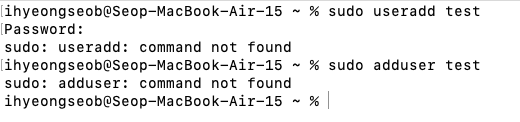
-
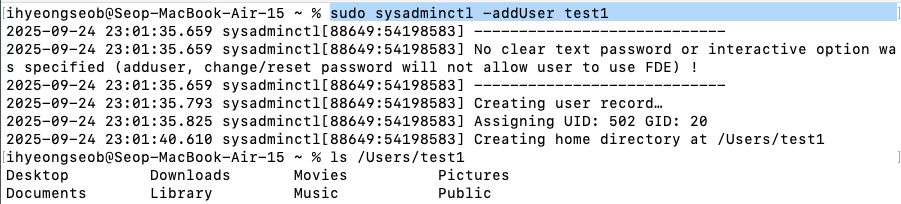
생성:
sudo sysadminctl -addUser [user명]

-
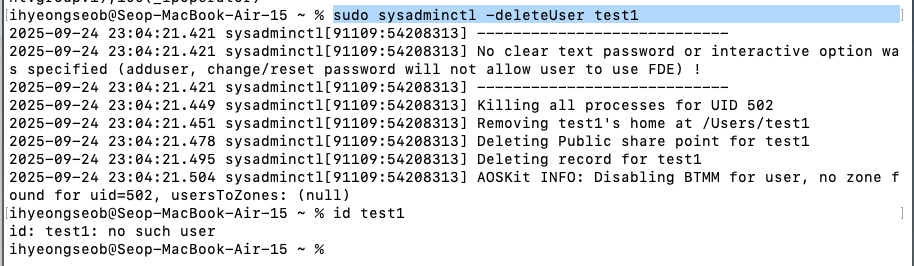
삭제:
sudo sysadminctl -deleteUser [user명]
root account and sudo command
-
root:
root user는 admin이기 때문에 모든 권한을 다 가짐.
root account를 다룬다는 것은 너무 위험하기 때문에
root 계정이 존재는 하지만 기본적으로 로그인할 수 없도록 잠겨있음.
그래서 sudo 명령어를 통해 root 권한을 일시적으로 부여받는 것임. -
sudo:
sudo gives temporary superuser privileges
ubuntu를 처음 설치했던 user가 처음 sudo 권한을 얻고, 그 이후의 user들은 sudo 권한이 없음.
File Ownership
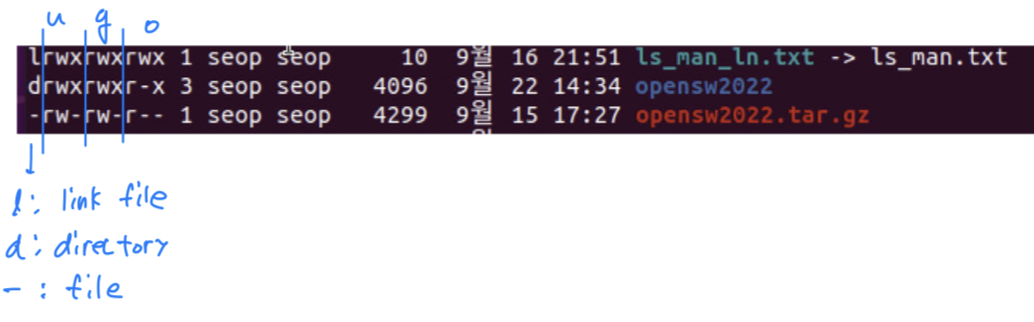
- In Linux, every file is associated with a user = u, a group = g and others = o
- Files have permissions(read = r, write = w, and execute = x)
chown: file 소유 user 변경chgrp: file 소유 group 변경chmod: Permission can be set separately for owner, group, and other- rwx:rwx:rwx ➡️ u:g:o
7 = ob111 ➡️ rwx
6 = ob110 ➡️ rw-
5 = ob101 ➡️ r-x
- rwx:rwx:rwx ➡️ u:g:o
- ls -l (file이름) : file에 대한 접근권한 확인하기
Example:
- 기존 myscript.sh file의 접근 권한 :
 user : rw-
user : rw-
group : rw-
others : r--
- chmod uo+x,g-w myscript.h :
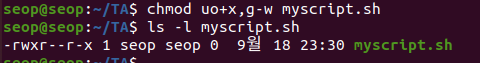 user : rwx
user : rwx
group : r--
others : r-x
- chmod 765 myscript.h
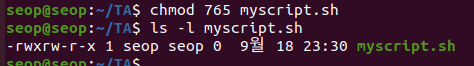 user : rwx
user : rwx
group : rw-
others : r-x
Example: user1이 file을 실행하는 것을 막기. = execute- "Hello World!\n"를 출력하는 실행파일인 helloworld를 생성.
defualt로 others는 execute의 권한이 있다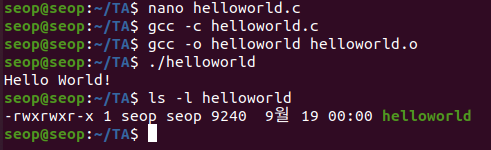
- others인 user1도 helloworld를 실행할 수 있다
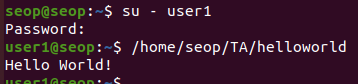
- seop계정에서 others의 execute 권한을 없애기
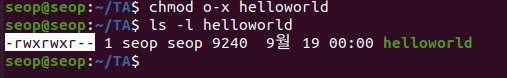
- 이제 others인 user1은 helloworld를 실행할 수 없다.
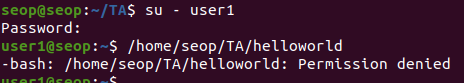
참고로 directory에 대한 execute 권한을 막는 것은 해당 directory에 접근을 못하도록 하는 것이다.
- "Hello World!\n"를 출력하는 실행파일인 helloworld를 생성.
Quiz >
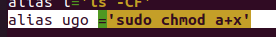
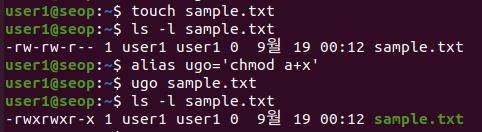
User, Group, Others 모두에게 실행권한을 주는 명령어를 별칭으로 생성한 후 아무 파일이나 만든 별칭을 사용해 실행권한을 추가하시오.
Environment Variables
Environment Variables:
각 사용자 별로 환경 변수를 다르게 설정하여 다른 값을 사용하도록 설정하는 변수(character string).
환경변수는 key-value pairs로 되어 있고, key는 보통 대문자로 표기한다.
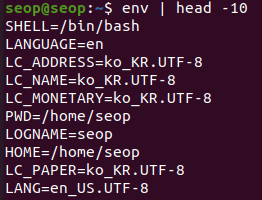
Setting Environment Variables
-
특정 환경변수를 보고 싶을 때, (환경변수이름) 앞에
$를 붙여서 echo로 확인한다.
echo는 단순히 text를 display해주는 명령어일 뿐.
중요한 것은$환경변수이름- Some Example Environment Variables :
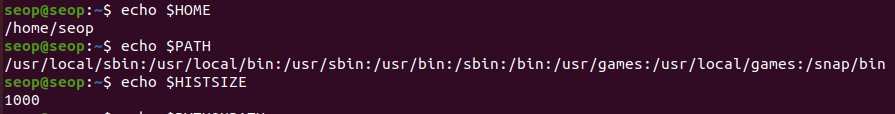
- echo $PATH에서 ':'이 자주 보이는데,
':'(column)은 각각이 실행파일들이 있는 directory라는 의미이다. (ls, pwd, ...) - HISTSIZE는 hist
- echo $PATH에서 ':'이 자주 보이는데,
- Some Example Environment Variables :
-
export: 새로운 환경변수를 만들고 싶을 때-
방법 1 : export (만들 환경변수이름)=value
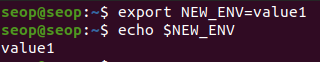
-
방법 2 : (만들 환경변수이름) = value; export (만들 환경변수이름)
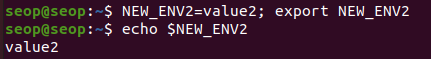
- 예제:
- 예제:
-
- 방법 3 : ':'(column)을 이용하여 기존 환경변수를 수정하는 방법


- 예제:
~/.bashrc:~/.zshrcin MacOS
로그인할 때마다 export하지 않고 자동으로 환경변수가 설정되도록.
즉, Add a variable permanently- (
Edit ~/.bashrc) and(source ~/.bashrcor./bashrc)

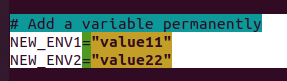
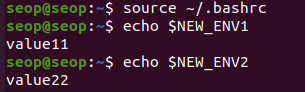
- (
User startup file : .bashrc
~/.bashrc: definesaliases(별명) and environment variables.alias: 매우 긴 명령어를 ~/.basrc file에 미리 축약해놓은 작은 명령어로 대신하여 사용
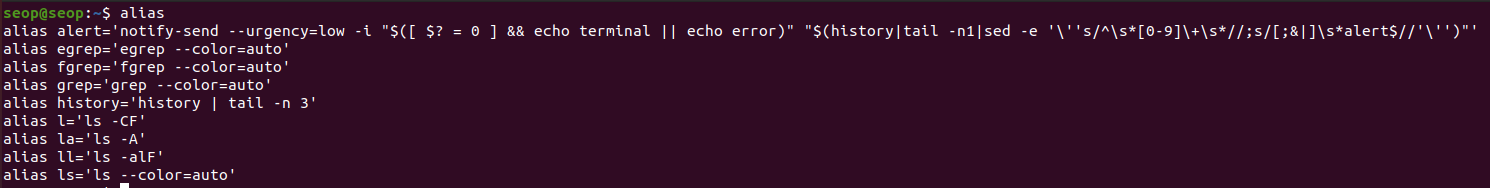
- example :
- 기존 alias 사용 :
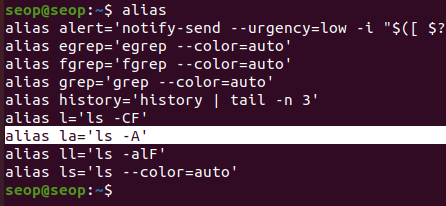
 (la와 'ls -A'가 똑같은 결과 ➡️ la는 'ls -A'의 alias임)
(la와 'ls -A'가 똑같은 결과 ➡️ la는 'ls -A'의 alias임) - 새로운 alias 추가 :

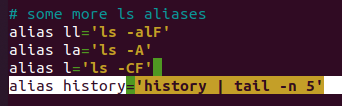
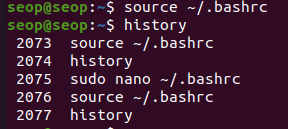 history 명령어를 실행했을 때, 마지막 5줄만 나오도록 ~/.bashrc 수정
history 명령어를 실행했을 때, 마지막 5줄만 나오도록 ~/.bashrc 수정
- 기존 alias 사용 :
Manipulating text
sed: Stream Editor = sed is used to modify the contents of a file or input streamawk: awk extracts and prints specific contents of a filesort: sortinggrep: Scans files for specific patterns; regular expression can be used.tee: tee takes output from any command, and send it to both a file and to standard output.wc: word count. (line, word, byte)
sed
-
sed: stream editor.
stream을 line 단위로 읽어서, 특정 패턴을 찾아 수정 가능.-
sed s/pattern/replace_string/ file.txt:
file을 읽어서, 발견한 첫번째에만 적용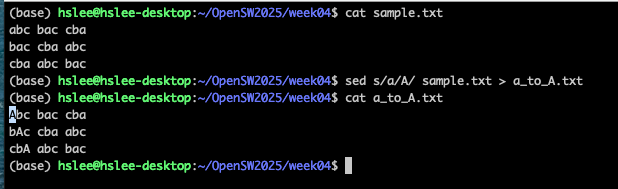
-
sed s/pattern/replace_string/
gfile.txt :
file을 읽어서, 발견한 모든 것에 적용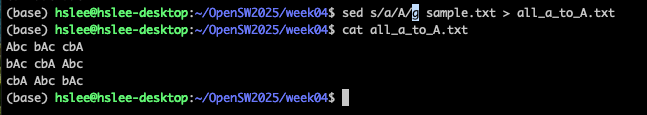
-
sed
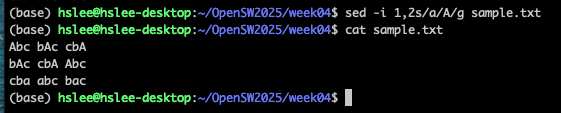
1,2s/pattern/replace_string/g file.txt :
file의 1~2번째 줄 사이만 읽어서 적용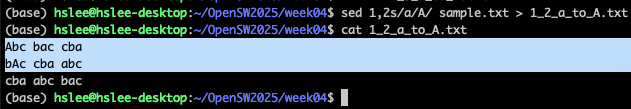
-
sed
-i
변경 사항을 inplace로 적용.
- MacOS에서는 -i 옵션 사용법이 살짝 다름.
sed-i [백업 파일의 확장자]~


백업파일을 만들고 싶지 않으면 그냥 sed-i ''~

- MacOS에서는 -i 옵션 사용법이 살짝 다름.
-
- sed
\error\dfile.txt :
file을 읽어서, 'error'가 포함된 라인을 delete
아래 예제는 'ab'가 포함된 라인을 delete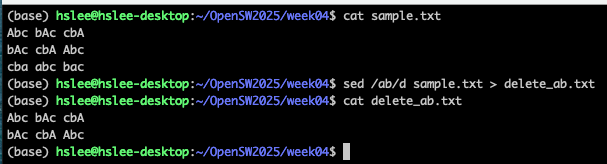
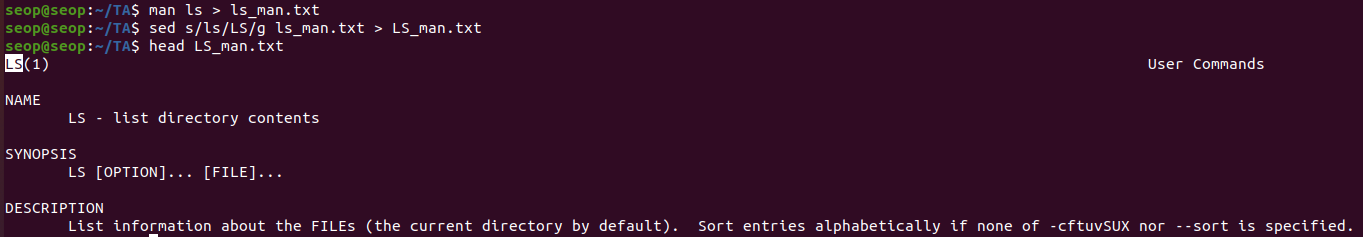
Quiz > ls_man.txt 파일에세 모든 ls를 대문자 LS로 변경하여 LS_man.txt로 저장하시오. (출력은 상위 10줄)
awk
-
awk: is used to extract and then print specific contents
column으로 된 file들에 적용하면 유용함. -
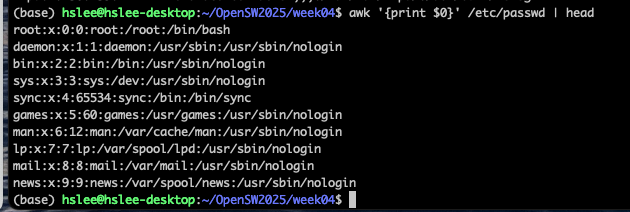
awk '{print $0}' file: print entire file ($0 : 파일 전체)
-
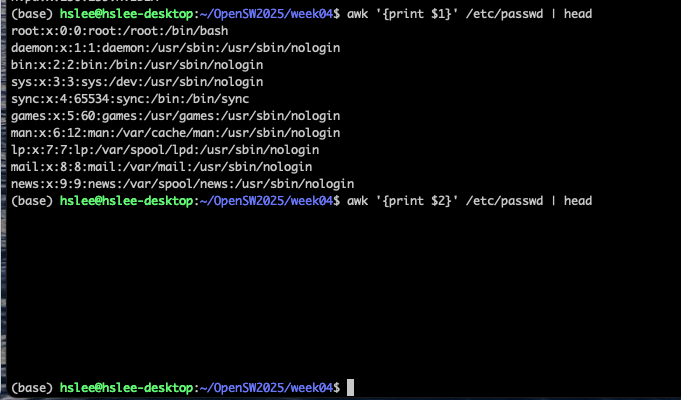
awk '{print
$1}' file: 1번째 column의 값들만 출력
아래 예제는 구분자 지정이 없으므로, 첫번째 column이 전체가 되어버림.
-
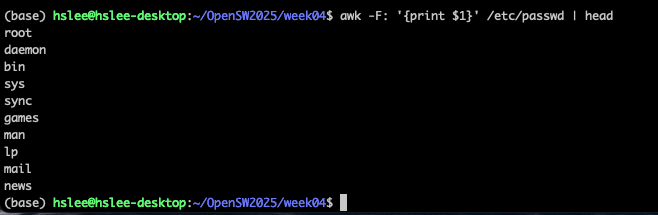
awk
-F:'{ print $1 }' file
-> ':'를 기준으로 구분했을 때, 1번째 column 값들을 출력
-
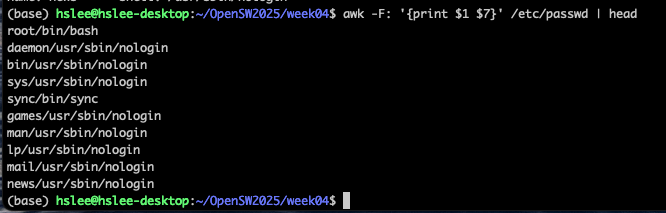
awk -F: '{ print $1 $7 }' file
-> ':'를 기준으로 구분했을 때, 1번째와 7번째 column 값들을 출력
 (아래처럼 "" 사이에 원하는 string을 출력할 수 있음/.)
(아래처럼 "" 사이에 원하는 string을 출력할 수 있음/.)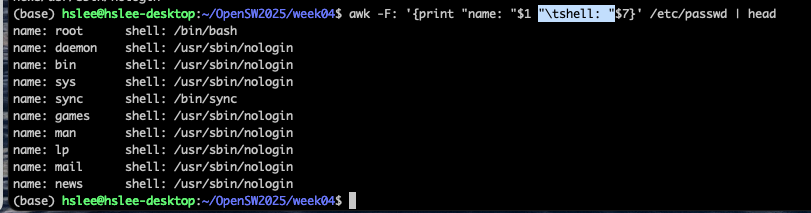
-
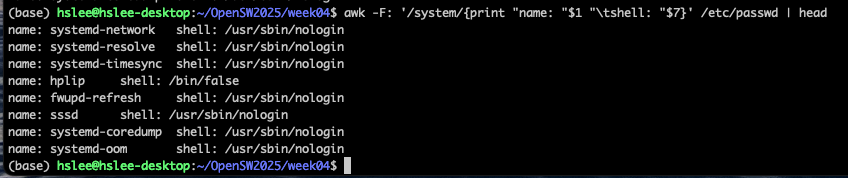
awk -F: '
/pattern/{"name: "$1 "\tshell: "$7}' file
-> /pattern/ 을 줘서 pattern이 찾아진 line들만 출력하도록 할 수 있다.
sort
-
sort file: file에 있는 line들을 사전순으로 sorting
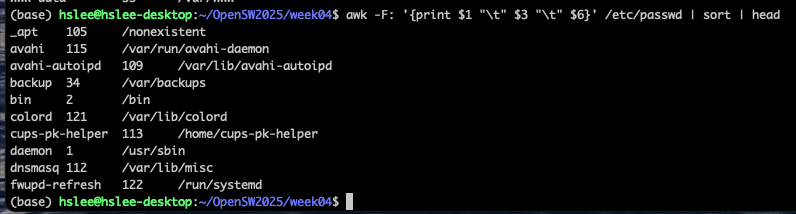
-
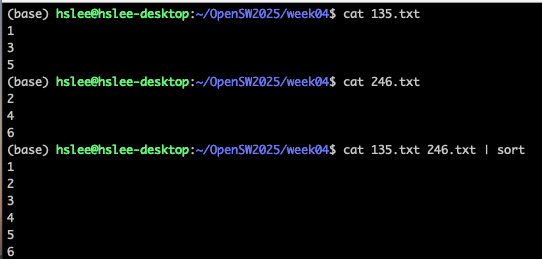
cat file1 file2 | sort: combined the two files, then sort the lines
-
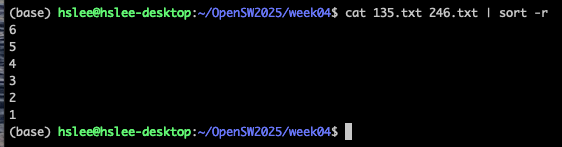
sort -r file: sort the lines in reverse order
-
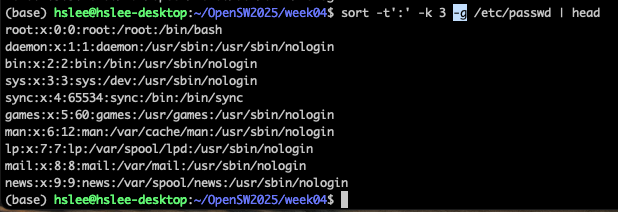
sort -k 3 file: sort the lines by the 3rd field on each line
(0, 1000, 1001 ...)
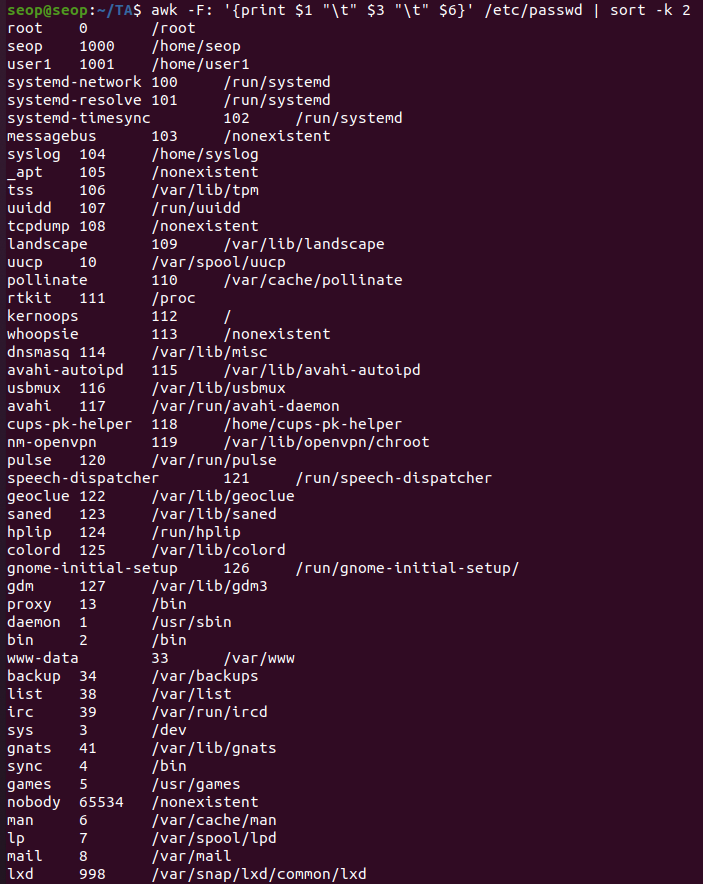
(진짜 숫자 크기로 정렬 하기 위해 -g option)
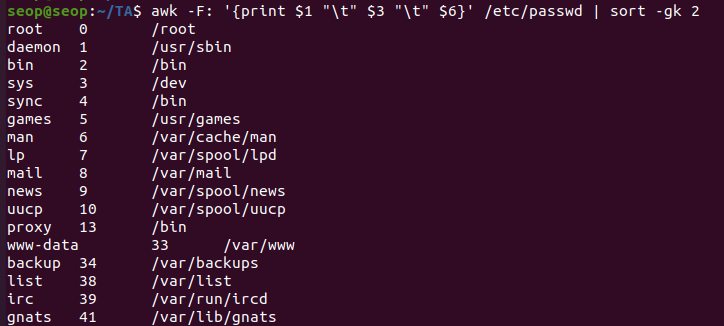
sort examples
-
sort, sort -r
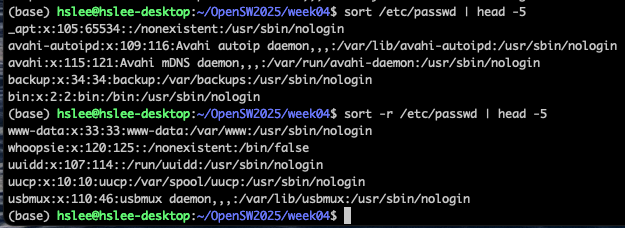
-
sort도 awk 명령어에서 -F
구분자옵션을 줬던 것 처럼, 유사하게구분자를 부여할 수 있다.
sort에서는 -t'구분자'로 한다.
또한 구분자에 의한 기준 column 번호도 지정할 수 있다.-k옵션 이용.
(아래 예제는:으로 구분하고, 3번째 column 기준으로 정렬하라.)
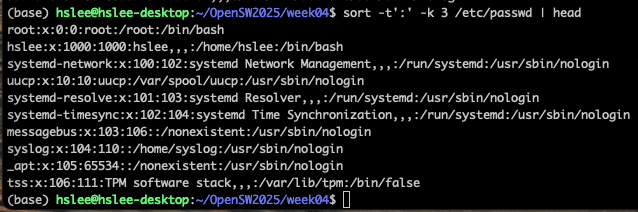
(3번째 column의 가장 앞에 숫자만 보고 정렬되었는데, 실제 숫자 크기대로 정렬하기 위해서 -n 또는 -g 옵션을 적용)
grep
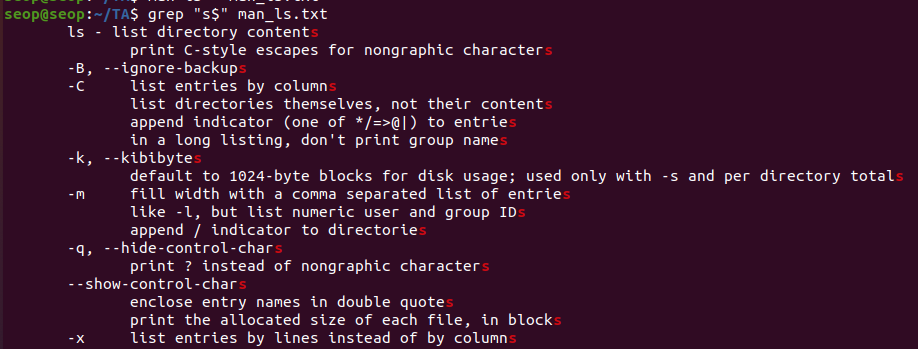
grep [pattern] <file>: 찾는 패턴이 있는 라인 출력
-
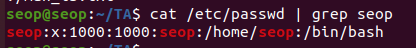
grep -v [pattern] <file>: 찾는 패턴이 없는 라인 출력 -
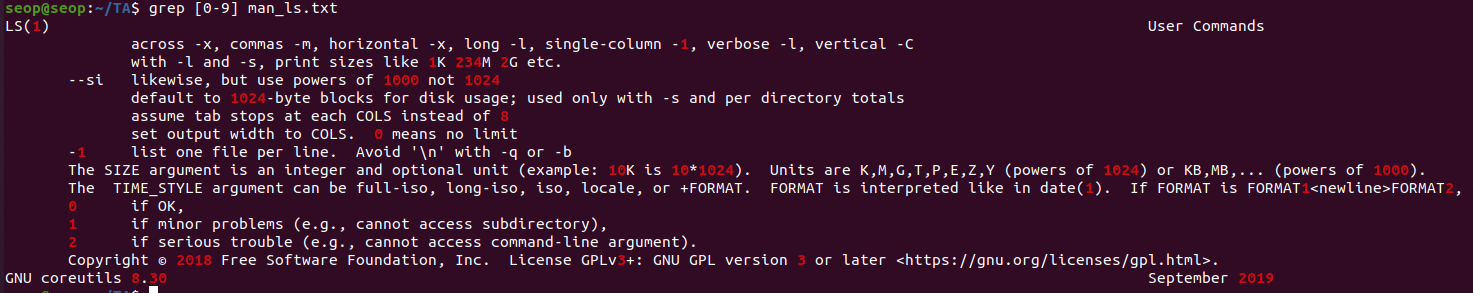
grep [0-9] <file>: print the lines that contain the number 0-9
-
grep -C 3 [pattern] <file>: pattern을 만족하는 line 기준 위, 아래 3줄. 총 7줄 출력.
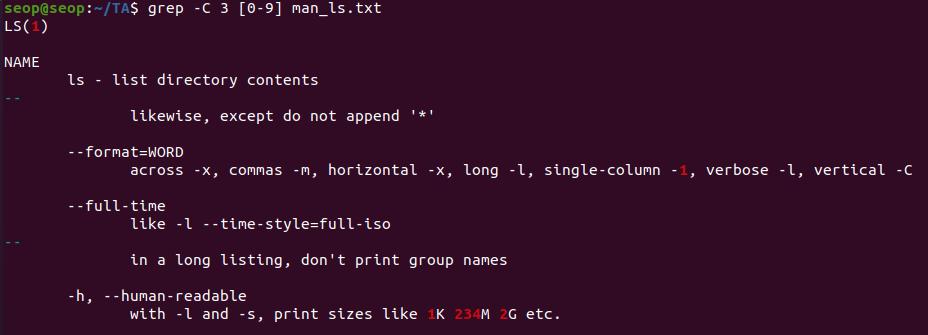
-
grep
-i[pattern] :
pattern의 대소문자 상관없이 있으면 출력 -
grep
-r[pattern] /dir:
/dir 밑에 있는 sub-dir와 파일들을 recursive하게 찾아서 출력
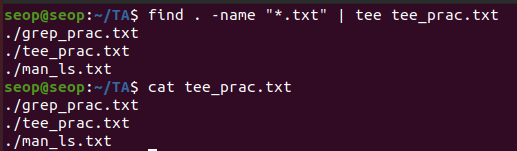
tee
tee: takes output from any command, and send it to both standard output, and to a file
Basic Regular expressions (BRE)
-
Consider sentence : "The quick brown fox jumped over the lazy dog"
-
.: 어떠한 character도 match
* a.. : azy

-
a | z: match a or z- b. | j. : br or ju
-
$: 라인의 끝 match- ..$ : og
-
^: 라인의 처음 match- ^... : 라인의 처음에서 그 뒤에 3개 item을 match
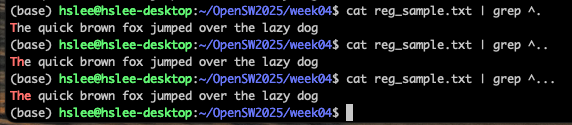
- ^... : 라인의 처음에서 그 뒤에 3개 item을 match
-
*: * 앞에 오는 item을 0번 또는 여러번 반복되는 것 match- l.* : l 뒤에 어떠한 character든 0번 또는 여러번 반복

- The.* : The 뒤에 어떠한 character가 오든 match
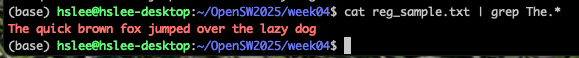
- l.* : l 뒤에 어떠한 character든 0번 또는 여러번 반복
-
[]: []안에 있는 어떠한 character든 match
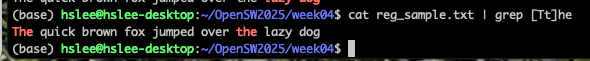
-
-
examples :
-
z로 시작하는 단어 찾기
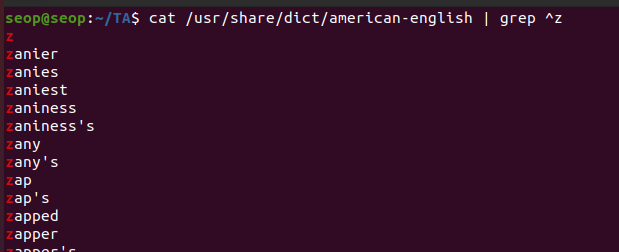
-
z로 시작해서 a로 끝나는 단어
-
'o', 'o' 사이에 0~n개 문자가 들어있는 단어 출력
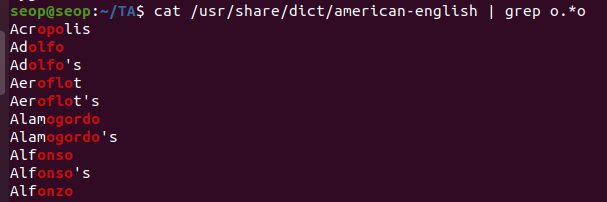
-
'a', 'a' 사이에 'a' or 'n' 들어있는 단어
-> a[an]a -
reg_ex1.txt에서 he로 시작하는 라인
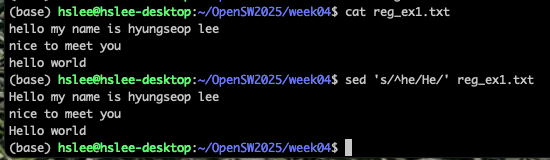
-
세글자인 단어

-
z로 시작해서 a로 끝나는 단어
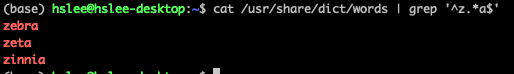
-
Extended Regular Expressions (ERE)
Basic Regular Expression은 오래된 linux tool들에서 기본적으로 동작했다면,
Extended Regular Expression은 더 확장된 기능을 제공.
grep에서 ERE를 쓰려면 -E option을 쓰거나,
egrep을 사용
+: + 앞에 오는 character가 1번 이상 반복

?: ? 앞에 오는 character가 0번 또는 1번 등장

(): ()로 그룹을 묶어서 처리. 반복하려면 뒤에 +, *, {} 붙임

|: OR

응용
-
/etc 디렉터리 밑에 있는 일반 파일 개수 세기 :
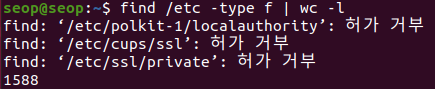

-
현재 디렉터리에 있는 모든 ".txt" file들의 접근 권한 변경하기
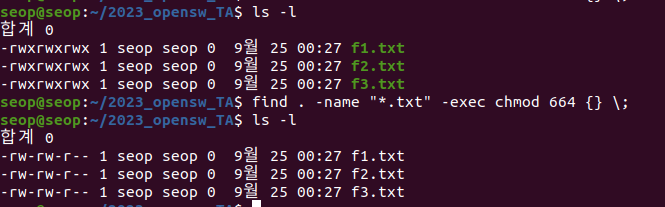
-
현재 디렉토리에 있는 모든 "week*"로 시작하는 디렉토리만 others에 대한 read 권한 해제하기.
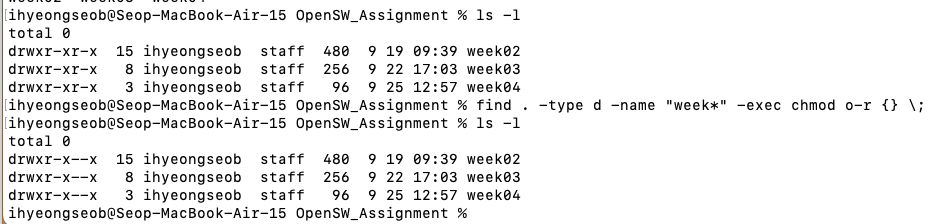
-
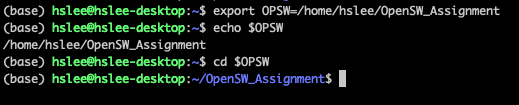
myhello 실행파일이 있는 디렉터리를 환경변수로 설정하여 ls처럼 사용하기
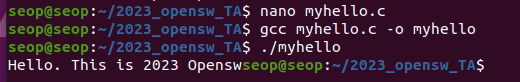
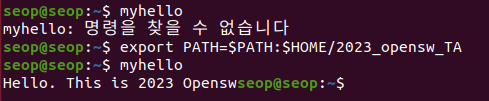
-
일시적인 환경변수 설정이 아닌 system을 재부팅했을 때도 계속해서 환경변수로 남게 만들기
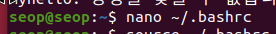

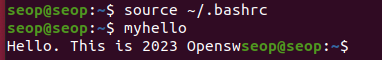 (이제 system 재부팅 후 다시 시도해도 될 것이다)
(이제 system 재부팅 후 다시 시도해도 될 것이다)
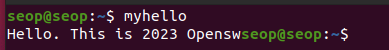
- myhello.c file에 있는 모든 int를 double로 바꾸기
(아래와 같이 하면 안된다. "printf"에 "int"가 있으니까 의도한 대로 바뀌지 않음)
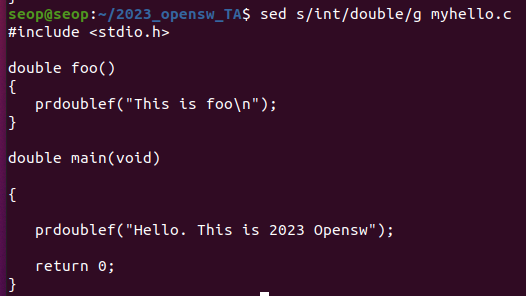
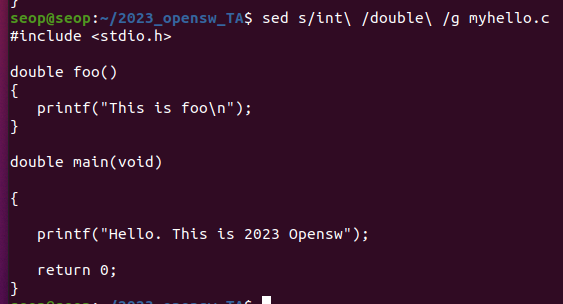
(아래와 같이 해야 한다. \(공백) : 공백)
-
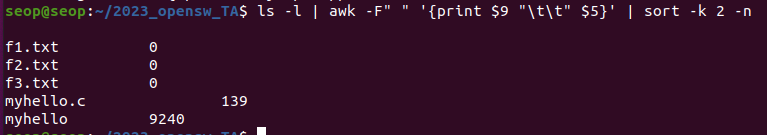
현재 디렉터리에 대하여, 파일/디렉터리명 \t\t 크기 순서로 나타내라
-
test1 user의 home directory에 others에 대해서 write 권한 부여하기
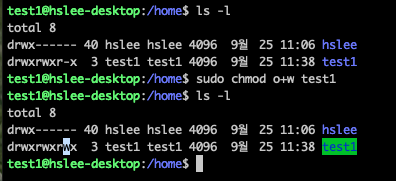
(위에서 others에 대해 write 권한을 줬기 때문에 아래에서 hslee user는 test1 user home directory에 파일을 생성할 수 있다.)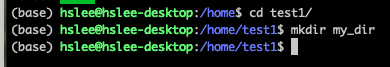
-
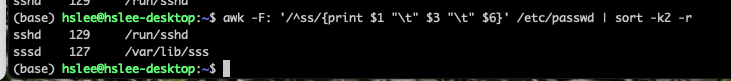
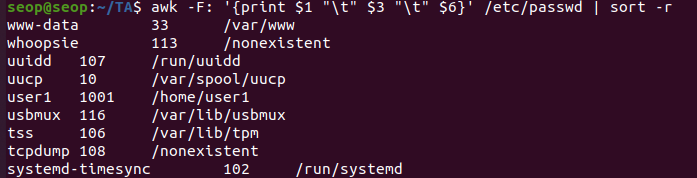
/etc/passwd에 'ss'로 시작하는 user에 대해서만,
uid, 사용 shell을 출력하시오.
단, uid에 대해서 내림차순 정렬해서 출력하시오.