리눅스 기본 명령어 - Processes, File operations
Processes
Process types
-
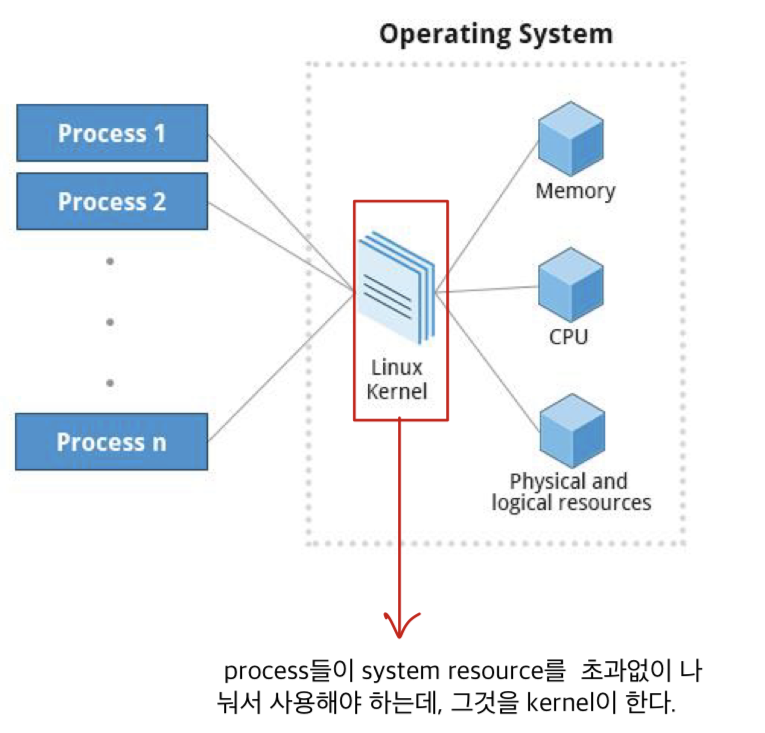
process:- an instance of one or more related tasks executing a program/command
- use system resources(CPU, IO devices, memory, ...)
- OS(특히 kernel이 관리)는 각 process에 resource를 할당해준다.
-
Process Types:Interactive process:
Started by a user and communicate with the user through command/graphical interface.
ex) bash, top, ls, findBatch process:
Automatic processes which are scheduled from and then disconnected from the terminal (순차적으로 실행된다)
ex) ldconfig, updatedbDaemon:
Server processes that run continuously.
ex) httpd, sshd, libvirtdThreads:
Lightweight process.
A process can have many threads sharing its memory space.
한 process에서 여러 일을 동시에 처리할 수 있도록 threads를 생성하여 programming할 수 있음.
ex) firefox(web browser)Kernel threads:
Kernel도 하나의 큰 process로 볼 수 있고, 그 안에서도 여러 job을 동시에 실행한다.
ps command를 통해 확인할 수 있다.
ex) Kthreadd, ksoftirqd
Process Scheduling and States
- Kernel choose a process to run on CPU according to their priority.
(Kernel에 scheduler라는 module이 어떤 process를 사용할지 결정한다) - 처리중인 process : running state
- 쉬고 있는 process : sleep state
- ex) writing to disk : CPU 입장에서 disk가 너무 느리기 때문에 disk가 file에 write하는 것을 기다리지 않고 sleep state로 바꾼다.
PID
Process ID = PID:
OS에서 부여한 Unique ID of a process
수행중인 process는 독립적인 Process ID를 가짐Parent Process ID = PPID: ID of a parent that started this process.- process는 다른 process가 생성한다.
system이 booting될 때,
가장 먼저 init process가 실행됨 (Linux는 systemd라는 daemon process)
init process인 systemd가 생성되면,
systemd가 process1, process2를 생성
process1이 process3, ...를 생성
➡️ p1, p2의 PPID = systemd의 PID
➡️ p3의 PPID = p1의 PID - 예를 들어, 'ls' 명령어 실행하면 그 parent process인 shell(bash, zsh)이 실행시킴
shell process는 사용자가 OS에게 명령을 전달하고, 그 결과를 출력해주는 program
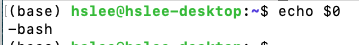
실행 중인 shell 종류 확인

- process는 다른 process가 생성한다.
Thread ID = TID: each thread has a unique TID.- 하나의 process 안에서도 여러 개의 thread가 있을 수 있는데,
thread들도 고유한 thread ID가 있다.
- 하나의 process 안에서도 여러 개의 thread가 있을 수 있는데,
ps, pstree, top, kill
ps
-
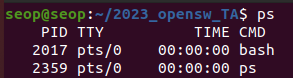
ps: provides information about running processes-
ps: displays all processes running
-
ps -ef: displays all process in the system
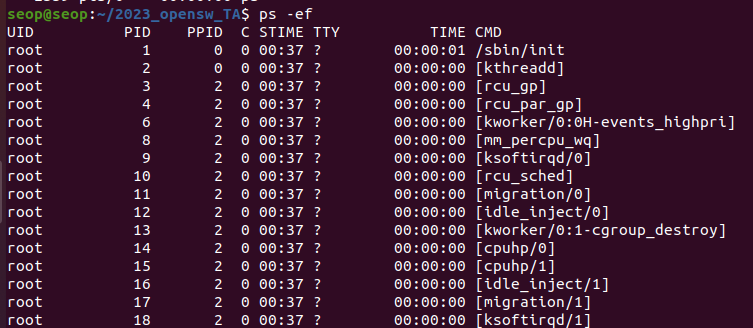
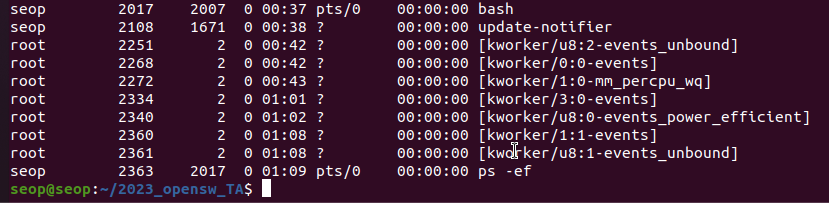
- "ps -ef"의 PPID = 2017.
PID=2017은 bash라는 process이다.
bash : born again shell
bash가 program을 읽어서 memory에 넣어서 실행시킴.
bash의 PPID를 따라가다 보면, init process가 생성한 것을 볼 수 있다. - [ksoftirqd/0] 처럼 *d로 끝나는 process들은 daemon process.
- "ps -ef"의 PPID = 2017.
-
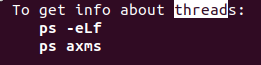
ps -eLf: more info about thread
-
-
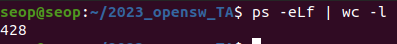
현재 몇개의 process가 실행되고 있는지 확인하기
pstree
-
pstree: displays the processes in the form of a tree diagram
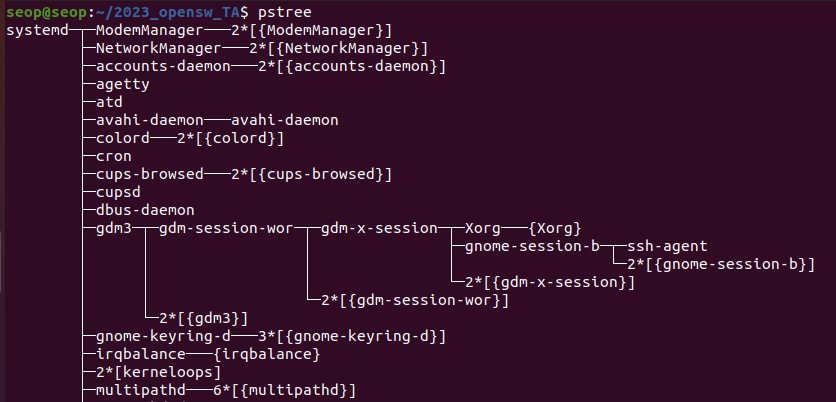 systemd가 init process임을 알 수 있다.
systemd가 init process임을 알 수 있다. -
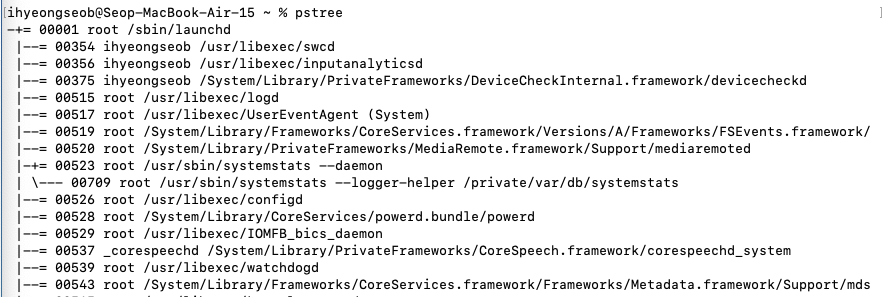
맥OS에서는
brew install pstree
맥OS에서 init process는 /sbin/launched임을 알 수 있다.
top
-
top update process status regulary
-
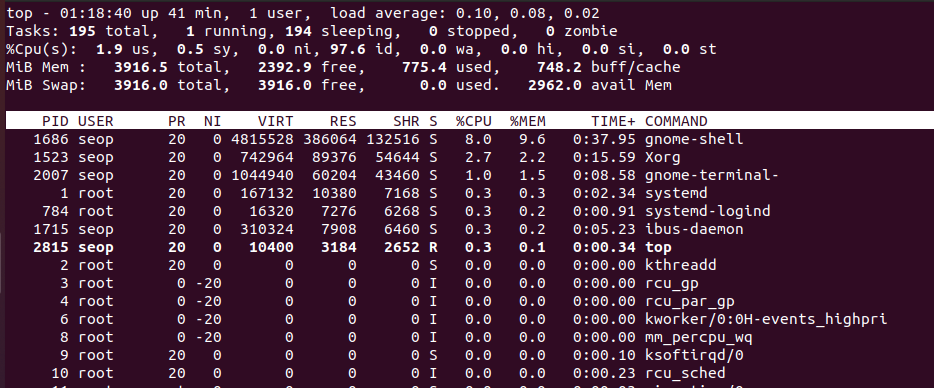
top:- update process status regularly
- CPU가 많이 점유하고 있는 process들을 위에 보여준다.
(computer의 resource를 많이 잡아먹는 process를 파악하는 데에 유리하다) - PR : Priority.
(값이 작을수록 우선순위가 높다. kernel이 실행시킨 것은 매우 중요한 process이기 때문에-가 붙음.) - NI : root user가 설정 가능한 Priority
- %CPU 100 : core 1개를 쓰고 있다.
%CPU 137.7 : core 2개를 쓰고 있다. - Total 195 : cpu가 20개 있는데 어떻게 195개가 실행되고 있는가?
OS의 kernel에 의해 scheduling된다.
그래서 실제로 running process는 1개. sleeping process는 194개인 것이다.
-
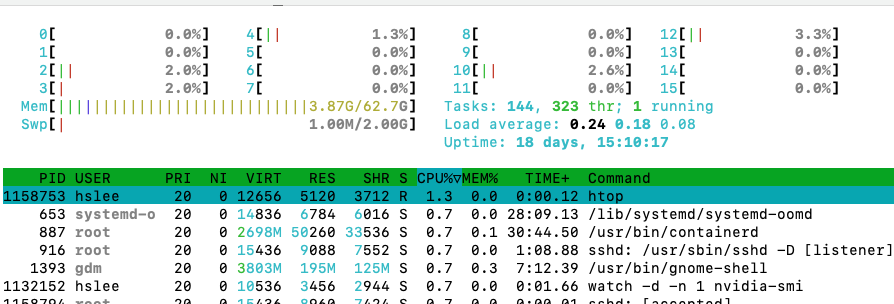
htop: top과 동일한 system process monitoring tool. (더 사용자 친화적, 직관적)
kill
-
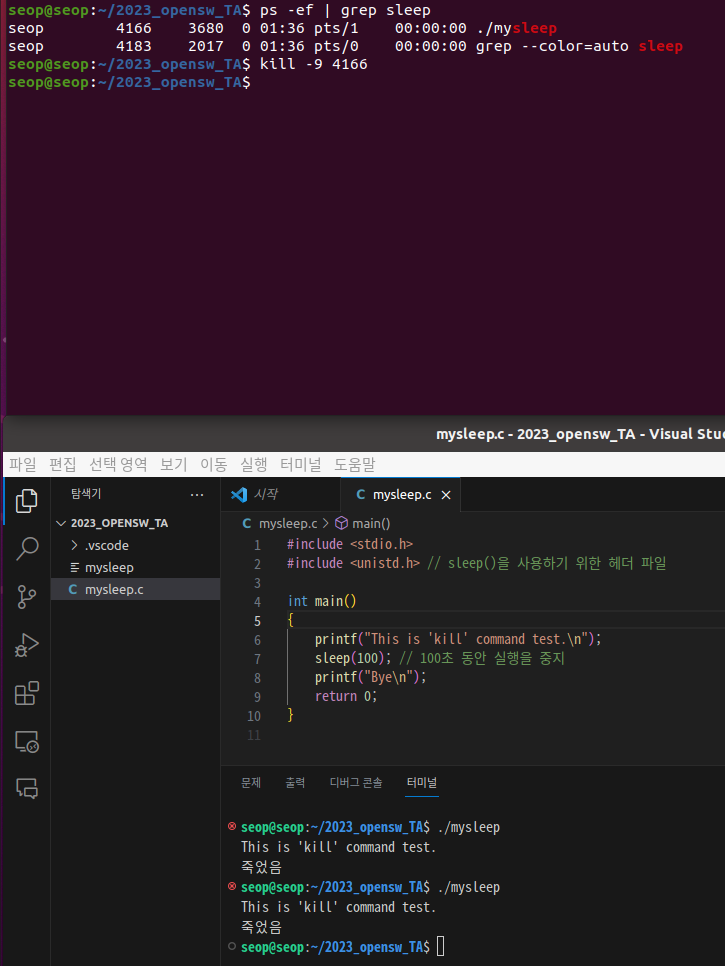
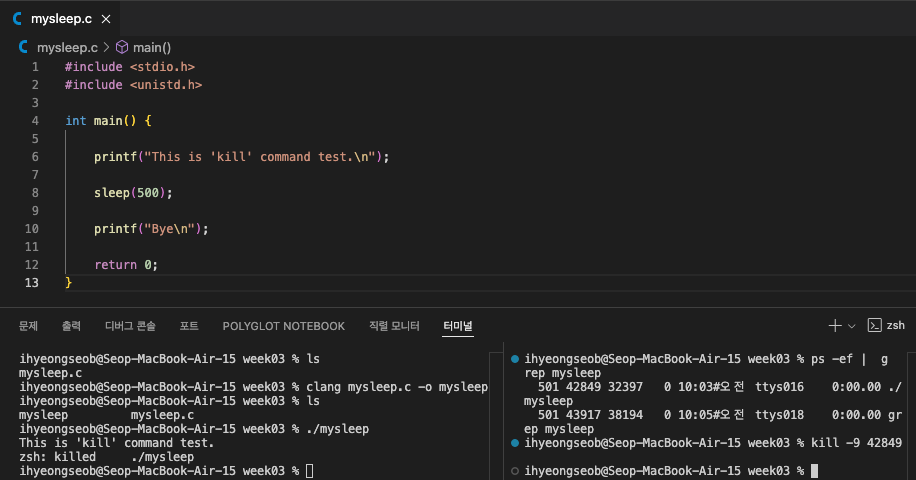
kill: to terminate a process -
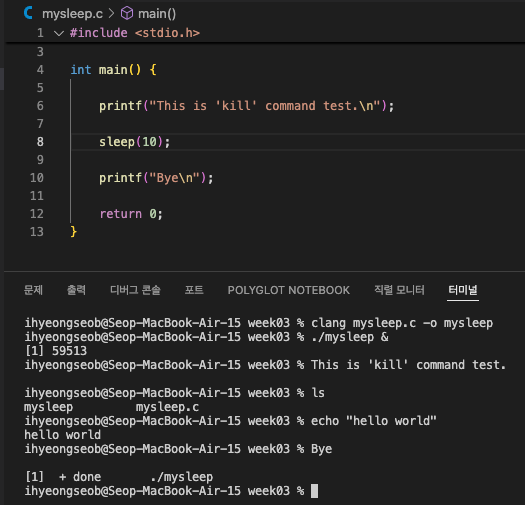
kill을 test해보기 위해, process 중간에 sleep을 하는 program을 생성하고
sleep하는 동안 kill로 해당 process를 종료시켜볼 것이다.- sleep 함수를 사용할 수 있도록 manual page 참고
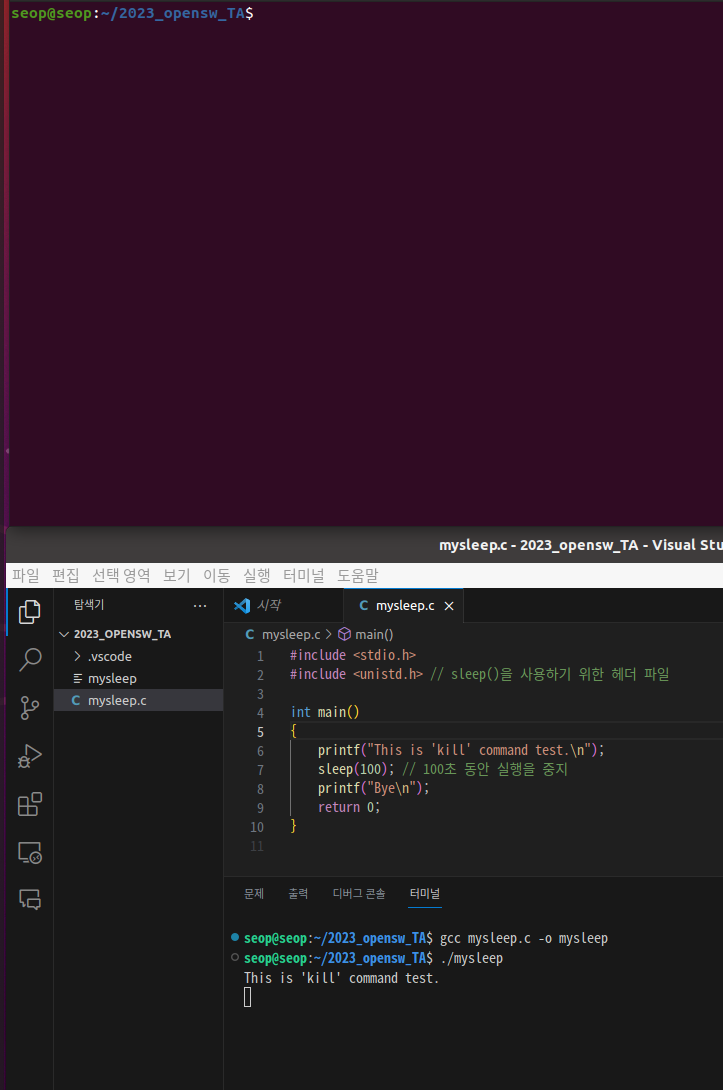
- mysleep 실행파일을 실행시키기
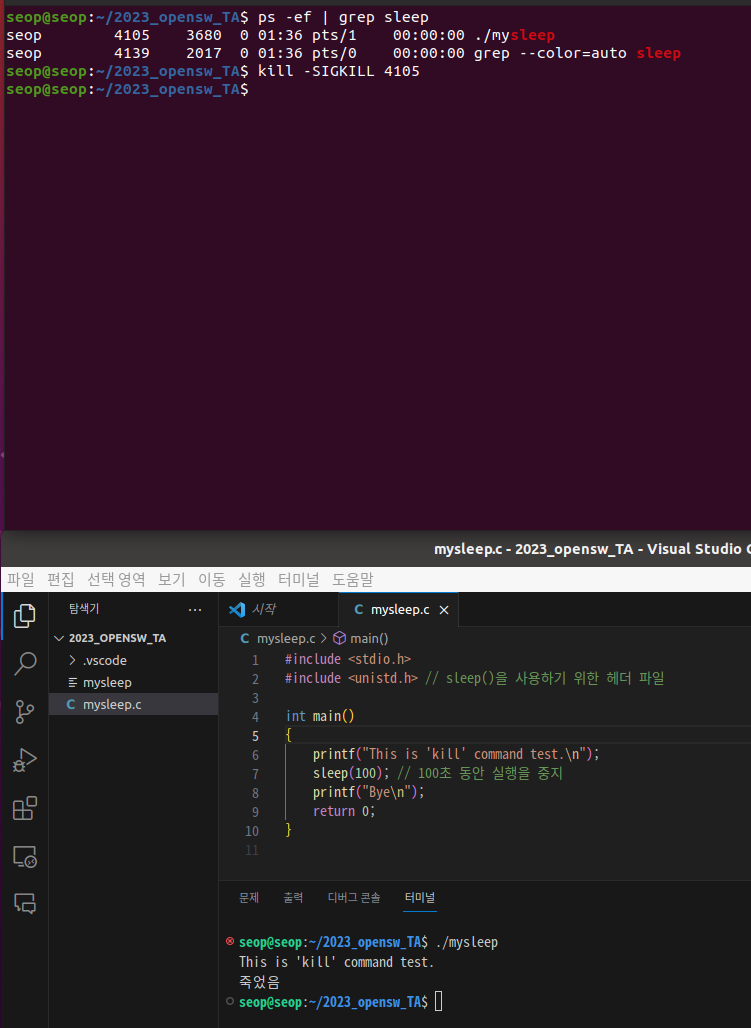
- ps로 mysleep process의 PID를 확인 후 kill
- sleep 함수를 사용할 수 있도록 manual page 참고
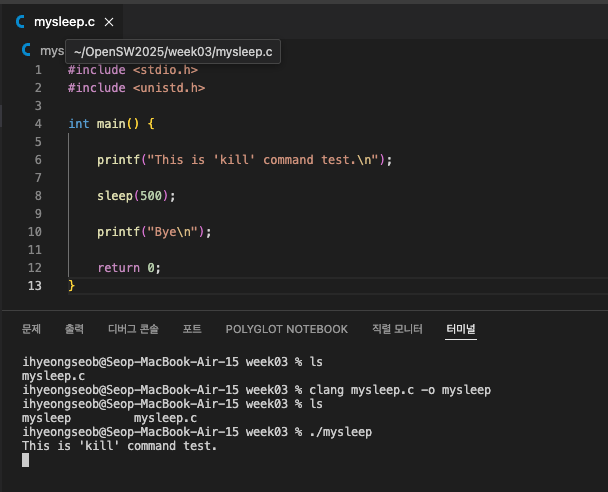
kill with clang(gcc) in MacOS
-
gcc는 GNU 프로젝트에서 만든 컴파일러 모음.
전통적으로 리눅스/유닉스 표준 C 컴파일러 역할.
최적화가 잘 되어 있고, GNU/Linux 배포판에서는 보통 gcc가 기본. -
LLVM 프로젝트의 C, C++, Objective-C 컴파일러 프론트엔드.
애플이 macOS와 iOS 개발을 위해 강하게 밀고 있는 컴파일러.
GCC보다 컴파일 속도가 빠르고 에러 메시지가 친절.
macOS에 기본 내장된 gcc는 사실 Clang을 가리키는 심볼릭 링크.
그래서 gcc --version 치면 Apple clang version이 나옴

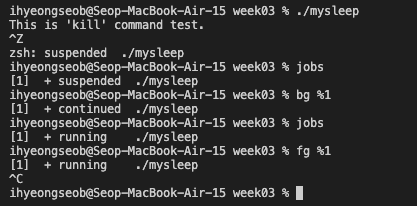
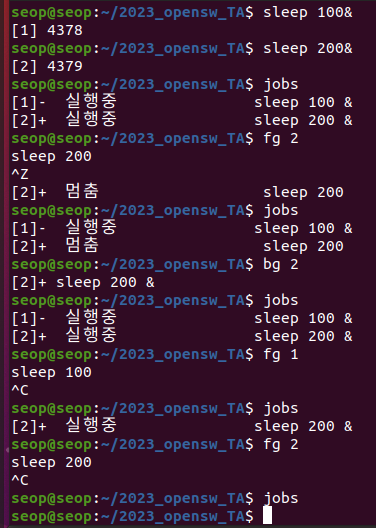
Background and Foreground jobs
-
In Linux, a
jobis a command launched from a terminal window(=shell) -
Foreground job: runs directly from the shell.- CTRL-Z : suspend a foreground job.
- CTRL-C : terminate a foreground job.
-
Background job:-
Use suffix '&' to launch a command in the background

-
forground job들은 실행이 완료되기 전까지 shell을 쓸 수가 없다.
ls, pwd와 같은 작은 job은 문제가 되지 않지만,
실행시간이 긴 job들은 shell을 쓸 수 없게 되어서 Background job이 만들어졌다.
example :
mysleep을 background job으로 실행되도록 했으니
ls, pwd와 같은 job들을 계속해서 사용할 수 있다.
-
jobs
-
jobs: displays all jobs running in the both foreground and background. -
fgandbg: command to run a job in the background and foreground, repectively. -
Managing jobs example :
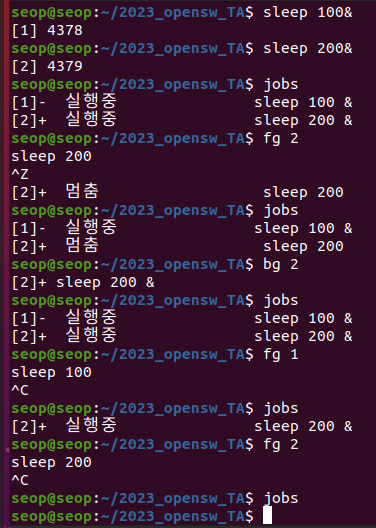
fg & bg in MacOS
- macOS는 zsh가 기본 shell인데, zsh에서 fg & bg 명령을 쓸 때 job을 지정하는 방식이 bash와 살짝 다름.
bash에서는 'fg 1'라 하면 [1] job이 foreground로 전환되었지만,
zsh에서는 표준 POSIX 방식을 엄격히 따라 'fg %1' 라고 해야 foreground로 전환됨.
(bash에서는 job control 문법에서 %을 붙이는 것을 편의상 생략해줬던 것임.)


ps vs. top vs. jobs
-
ps:- 현재 실행 중인 process의 상태를 보여줌
- 정적인 스냅샷을 제공 → 실행하는 순간의 프로세스 목록만 출력
-
top:- 실시간으로 프로세스 활동을 모니터링
- CPU, 메모리 사용량, 실행 시간 등을 지속적으로 갱신해서 보여줌
- ps가 사진 한 장이라면, top은 동영상 느낌
-
jobs:- 현재 shell session에서 실행 중인 bg/fg job을 보여줌
- 시스템 전체가 아니라 내 terminal에서 실행한 작업들만 관리
File operations
Partitions and filesystems
-
In Linux(Unix), "Everything is a file".
- Everything is treaded as a file
-
Filesystem is structured like a tree.
- The start of the tree is called "root directory"
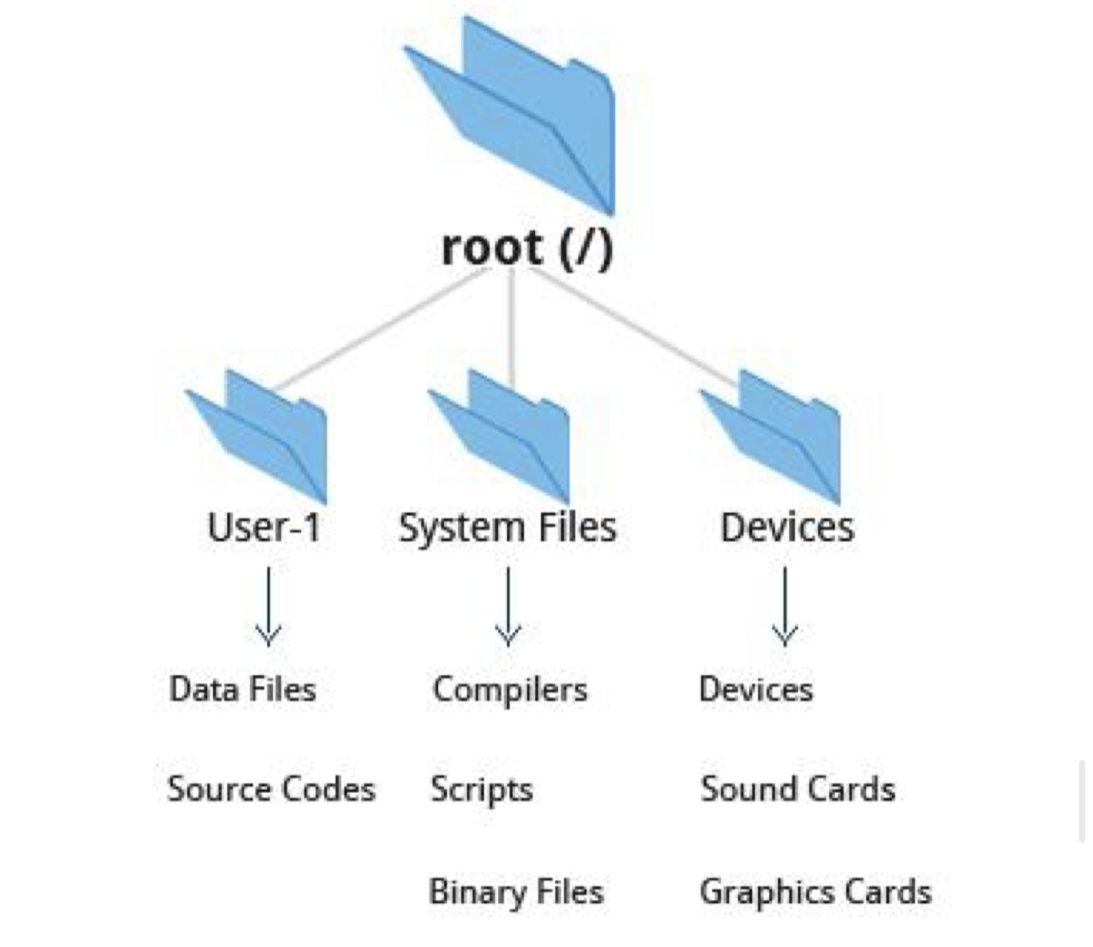
- The start of the tree is called "root directory"
Mount
-
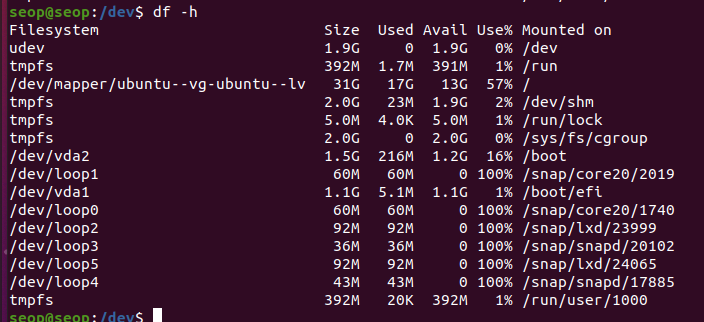
하나의 disk는 여러 partitions로 구분되어 있음
-
mount: command is used to attach a filesystem somewhere within the filesystem tree.-
왜 쓰는가?
- USB, 외장 하드, SD 카드와 같은 물리적 저장장치와 연결
/dev/sdb1 (실제 디스크 장치)를 /mnt/usb 폴더에서 접근 가능하게 함sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/usb - network file system 연결
NFS, SMB/CIFS를 이용해 다른 컴퓨터의 공유 폴더를 내 컴퓨터에 연결sudo mount -t cifs //192.168.0.10/shared /mnt/shared -o username=user - directory binding
original_dir 안의 파일들이 mount_point에서도 그대로 보임
실제 파일 복사 없이 “같은 파일을 두 곳에서 보이도록” 하는 느낌sudo mount --bind ~/original_dir ~/mount_point
- USB, 외장 하드, SD 카드와 같은 물리적 저장장치와 연결
-
'mount'
실제 partition이 출력되지만, 가상의 partition들도 존재하기 때문에 많이 출력됨.
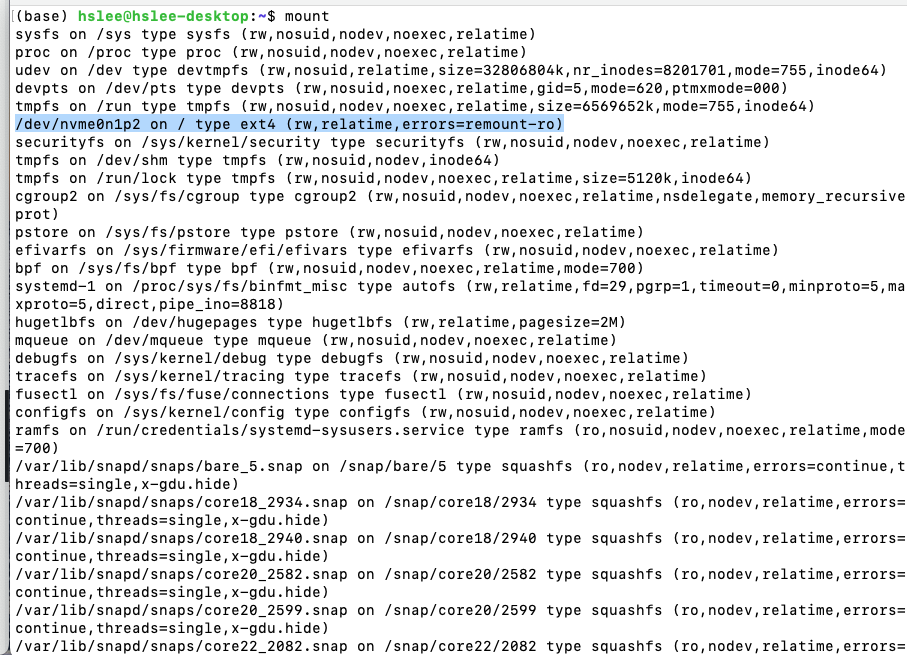 /dev/nvme0n1p2 partition은 /에 ext4 type으로 mount되어 있다.
/dev/nvme0n1p2 partition은 /에 ext4 type으로 mount되어 있다.
(아래와 같이 실제로 file system 상에 존재하는지 확인해볼 수 있음.)
(blkid로 UUID, 파일시스템 종류까지 확인 가능)


-
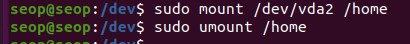
/dev/vda2를 /home에 마운트.
home directory에 작업한 것은 /dev/vda2에 작성됨
-
booting할 때, 어떤 partition을 어떤 directory에 mount할 것인지 정의할 수 있음 (/etc/fstab)
UUID는 disk partition 이름임. 그 partition을 /boot/efi에 vfat 타입으로 mount를 하겠다.

-
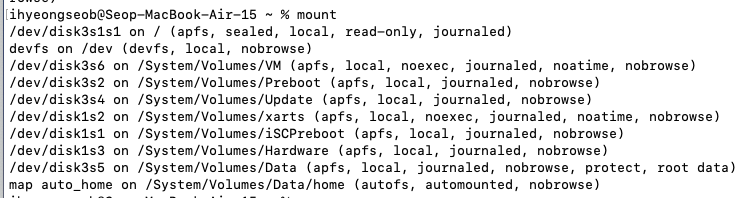
macOS에서는 /etc/fstab 파일이 존재할 수 있지만, 기본적으로는 비어 있거나 거의 사용되지 않는다고 함.
대부분의 마운트는 자동 마운트(autofs)로 관리되며, /etc/fstab에 직접 기록하는 경우는 드뭄
-
Comparing files
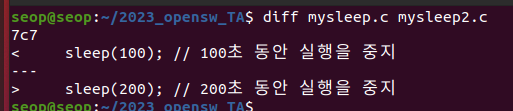
diff
diff: is used to compare files and directories
Backing up files
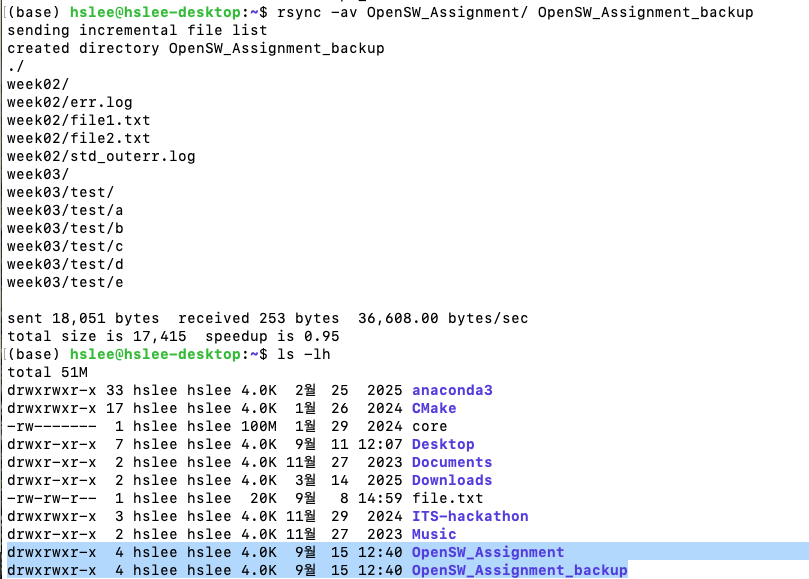
rsync:- copies files/directories to both local/remote locations
- is very useful to back up a project directory.
- 한 컴퓨터 안에서 copy하려면 cp 명령어를 이용하면 되는데,
원격의 컴퓨터에 backup을 위해 copy하려면 rsync 이용- 한 컴퓨터 안에서 rsync
(rsync -av src/ dest/)
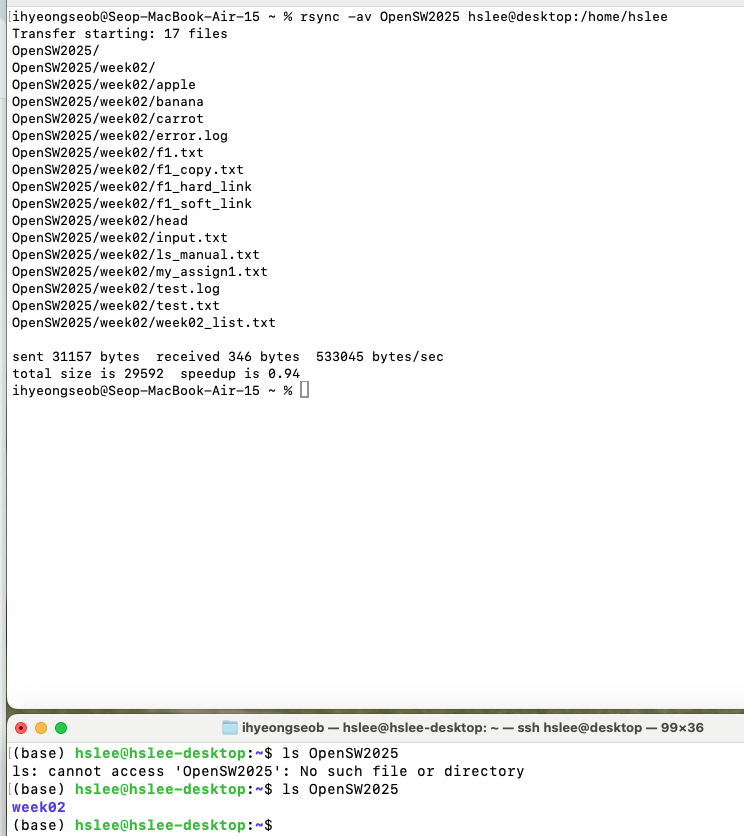
- 원격 컴퓨터에 backup
만약에 dest/에 해당 file이 존재한다면, 바뀐 내용을 update해줌.- rsync
-avsrc/ user@host:dest/
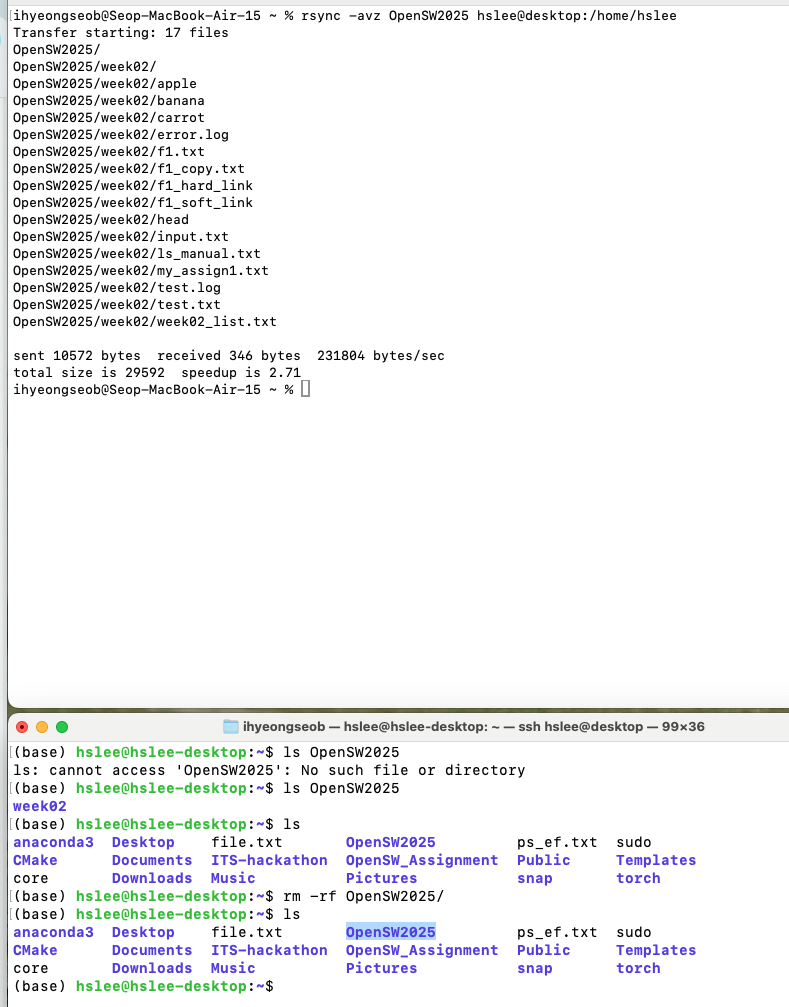
- rsync
-avzsrc/ user@host:dest/
송신 측에서 data를 gzip 방식으로 실시간 압축하여 전송,
(전송량이 줄어들어 속도가 빨라짐)
수신 측에서는 전송된 압축 데이터를 자동으로 해제하여 원래 파일 그대로 저장
- rsync
- 한 컴퓨터 안에서 rsync
Compressing files
1. 파일 하나를 압축
gzip: The most frequently used Linux compression utility- Uncompression : gzip -d or gunzip
bzip2: Produces files significantly smaller than those produced by gzip- Uncompression : bzip -d or bunzip2
zip: Often requried to decompress archives from Windows- Uncompression : unzip
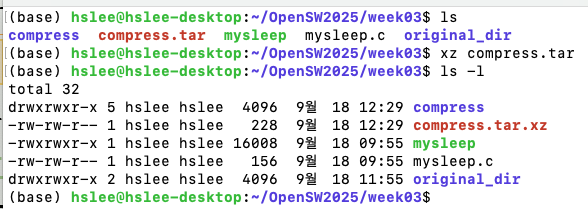
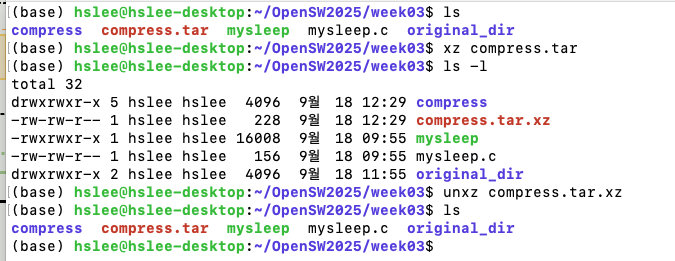
xz: Maximum compression, slowest compression- unxz
2. 여러 파일을 압축
-
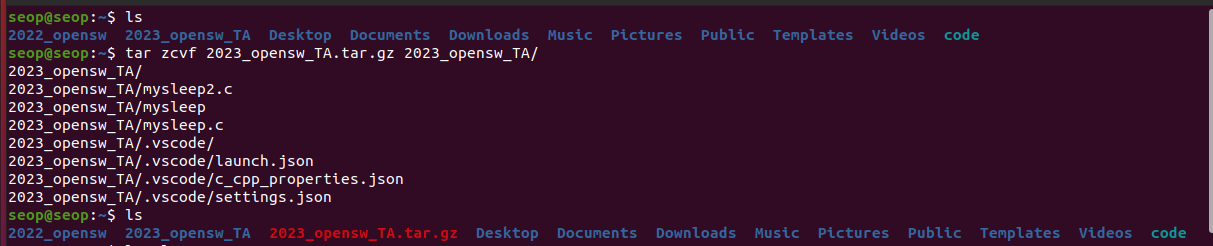
tar: is often used to group files in an archive and then compress the whole archive at once묶어만놓기(tar-cvf), 풀기(tar -xvf
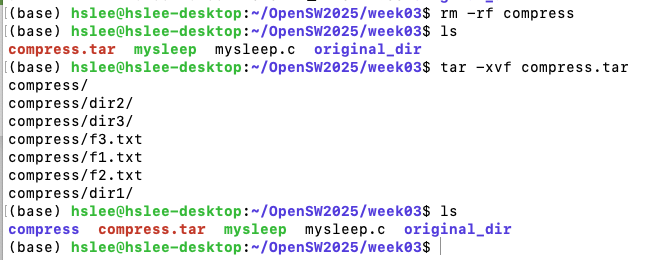
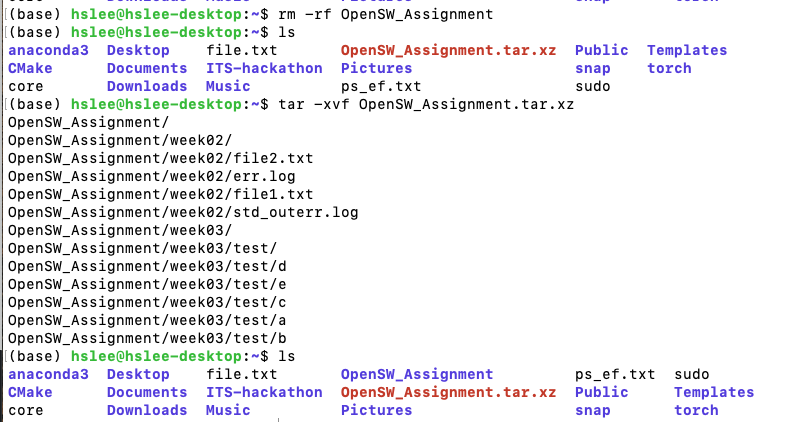
묶기: tar -cvf target source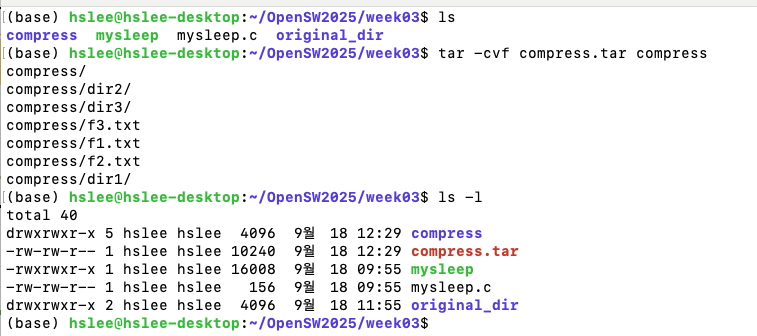
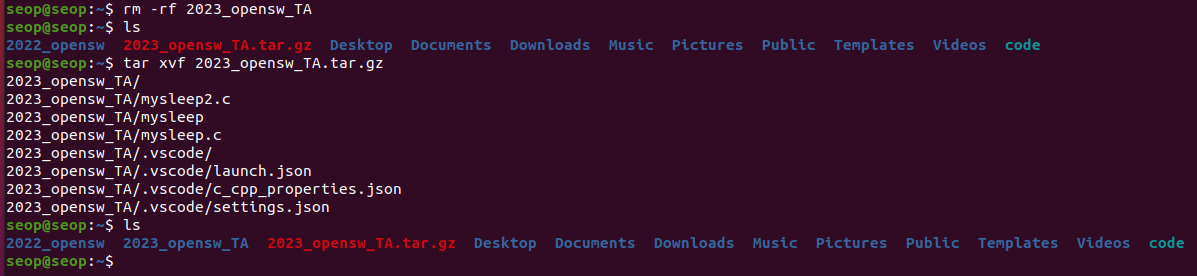
풀기: tar -xvf source
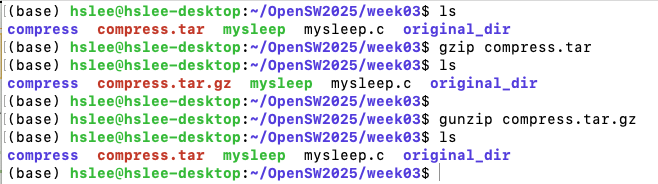
- 묶어만 놓은 파일을 gzip으로 압축, gunzip으로 압축해제
- 묶어만 놓은 파일을 bzip2으로 압축, bunzip2으로 압축해제

- 묶어만 놓은 파일을 zip으로 압축, unzip으로 압축해제
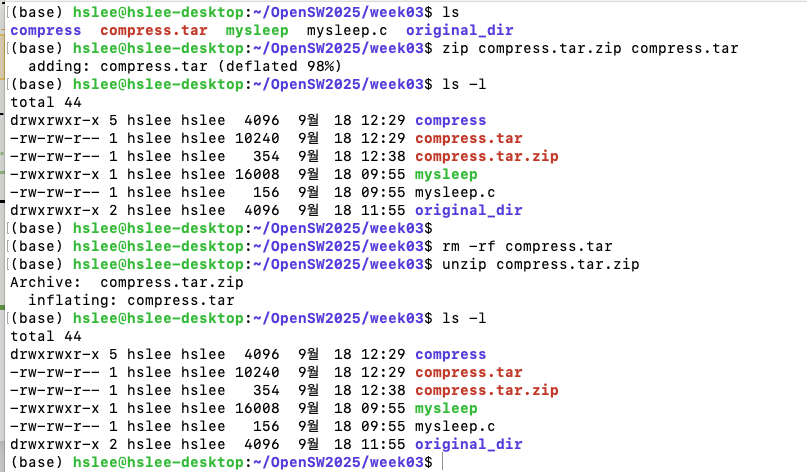 (zip 명령어는 아래처럼 묶고 압축을 동시에 가능)
(zip 명령어는 아래처럼 묶고 압축을 동시에 가능)

- 묶어만 놓은 파일을 xz으로 압축, unxz으로 압축해제
- 2 stages 걸리는 것을 한 번에 하는데(=묶음 & 압축을 한 번에), gzip 형식으로
tar-zcvf(모으고 나서gzip으로 압축)
tar -xvf (해제)
 )
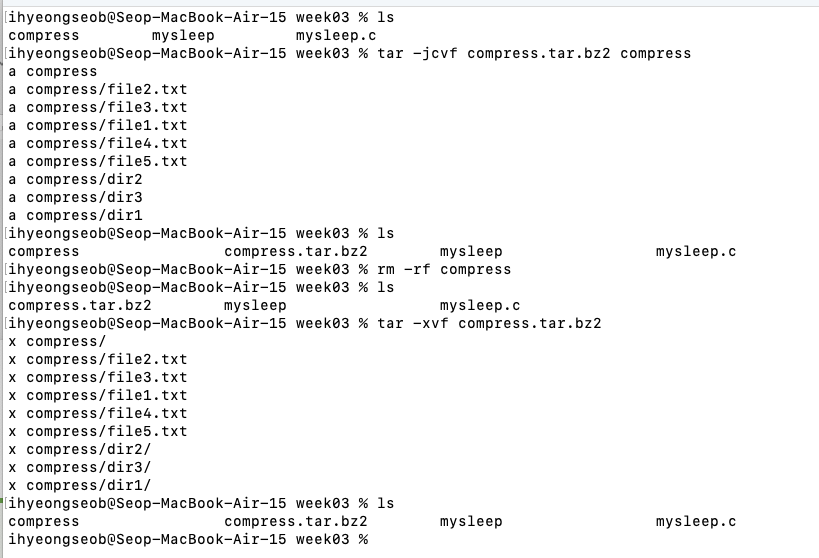
) - 2 stages 걸리는 것을 한 번에 하는데(=묶음 & 압축을 한 번에), bzip2 형식으로
tar-jcvf(모으고 나서bz2으로 압축)
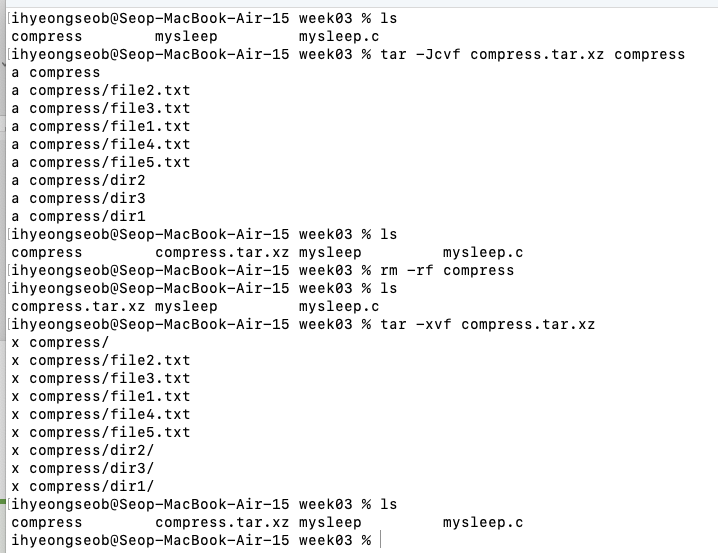
tar -xvf (해제) - 2 stages 걸리는 것을 한 번에 하는데(=묶음 & 압축을 한 번에), xz 형식으로
tar-Jcvf(모으고 나서xz형식으로 압축)
tar -xvf (해제)
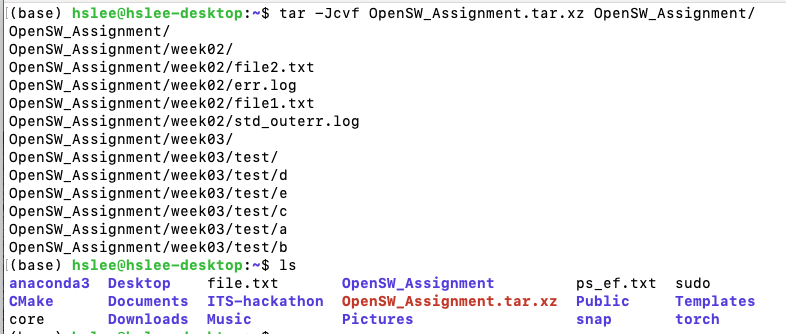
-
실제로
xz형식이 가장 압축률이 높은지 확인해보기
-zcvf*.tar.gz생성
-jcvf*.tar.bz2생성
-Jcvf*.tar.xz생성
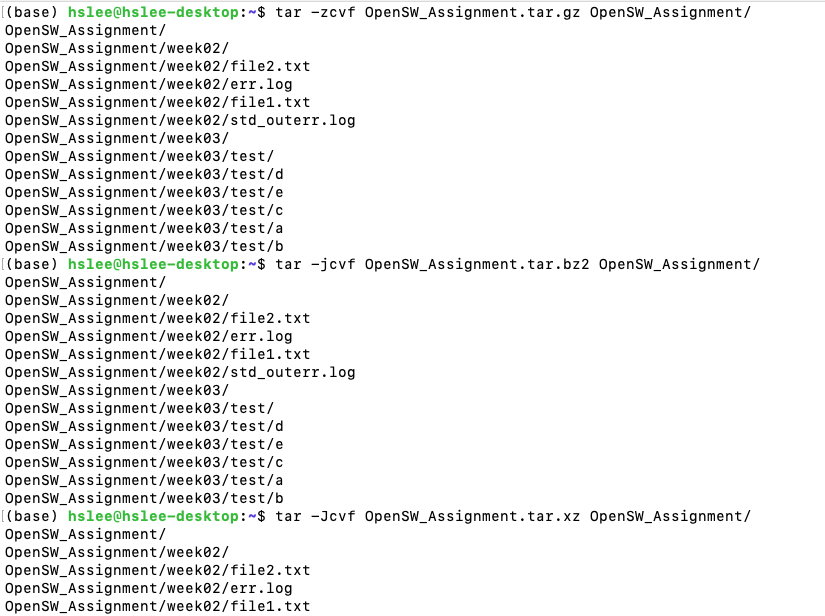 파일 사이즈 비교하기
파일 사이즈 비교하기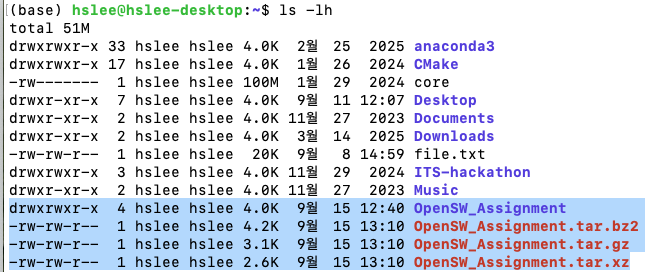
File Compressing in MacOS
- 2 stage ((1. tar -cvf + 2. 각 압축 명령)
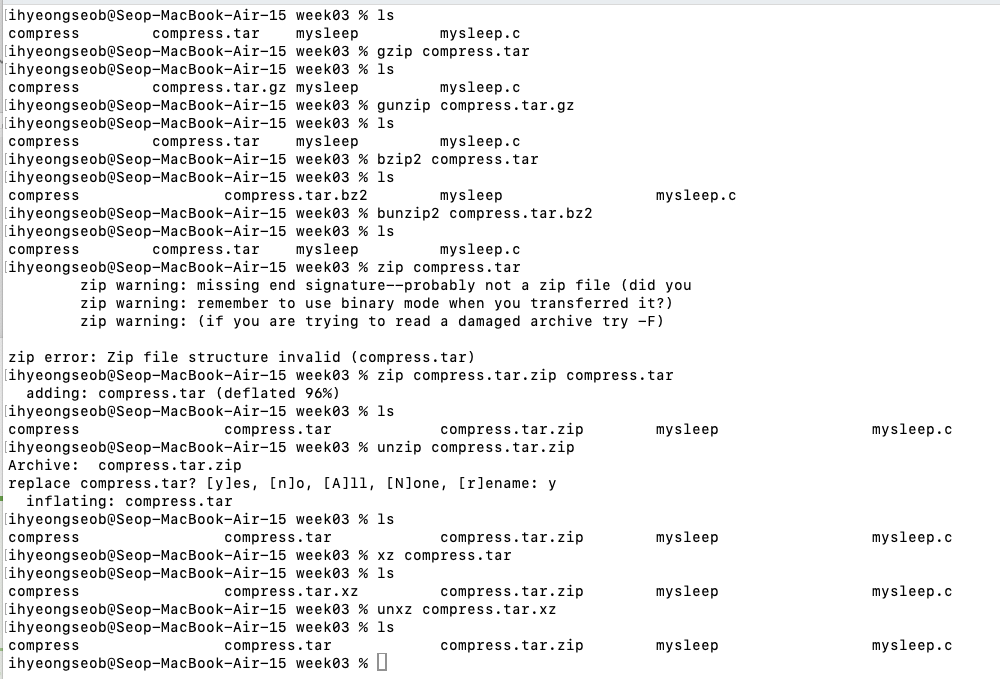
- 1 stage
- tar -zcvf

- tar -jcvf
- tar -Jcvf
- tar -zcvf