YOLO의 layer를 Pytorch를 이용해 구현하는 Chapter
Getting Started
-detector code가 위치할 폴더 만들기
- 나는 로컬에 programming/YOLOv3을 만듦
-darknet.py 파일 만들기 - 나는 VScode에서 YOLOv3을 들어가 파일 생성함
- YOLO network를 만드는 파일
-util.py파일 만들기 - YOLO network를 보충하는 파일. 여러 helper function이 포함돼 있음
Configuration File
-cfg file: network의 layout 기술
-official cfg파일을 사용할 것. YOLOv3/cfg폴더 안에 저장하기
- github에서 파일 다운받기: Raw버튼 클릭 후 Ctrl+S해서 원하는 폴더에 저장하기
-cfg파일을 살펴보면, YOLO에서 쓰이는 5가지 종류의 layer를 살펴볼 수 있다.
(1)Convolutional
(2)Shortcut
[shortcut]
from=-3
activation=linear -shortcut layer=skip connection
-skip connection: 어떤 layer의 output을 몇 개를 건너뛴 layer의 input으로 연결하는 것
-from: 이 input이 얼마나 뒤에서 온 output인지
(3)Upsample
-bilinear upsampling
(4)Route
[route]
layers = -4
[route]
layers = -1, 61-layers: 이 route layer를 위한 feature map output을 어느 index의 layer에서 뽑아낼 것인지
- layer가 2개의 값: 2개의 값 concatenate
(5)YOLO
-이 YOLO layer가 detection layer를 말한다.
Net
-input과 parameter에 대한 설명
Parsing the configuration file(parse_cfg())
-parsing: 파일을 단어단위로 분석하면서 어떤 정보인지를 알아낸 다음, 그 정보를 토대로 오브젝트를 실제로 만드는 것(파일은 오브젝트에 대한 명세일 뿐, 실제 그 오브젝트와 관련된 데이터를 직접적으로 담고 있지는 않음)
-darknet.py 상단에 다음 import문을 추가해 주자.
from __future__ import division
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
import numpy as np-parsing을 위해 parse_cfg 함수를 만들자.
- cfg파일을 parsing하고, 각 block을 dict로 저장하는 함수
- block의 attribute-value를 key-value로 저장
- 1)cfg file 내용을 string list로 저장
- 2)list를 loop
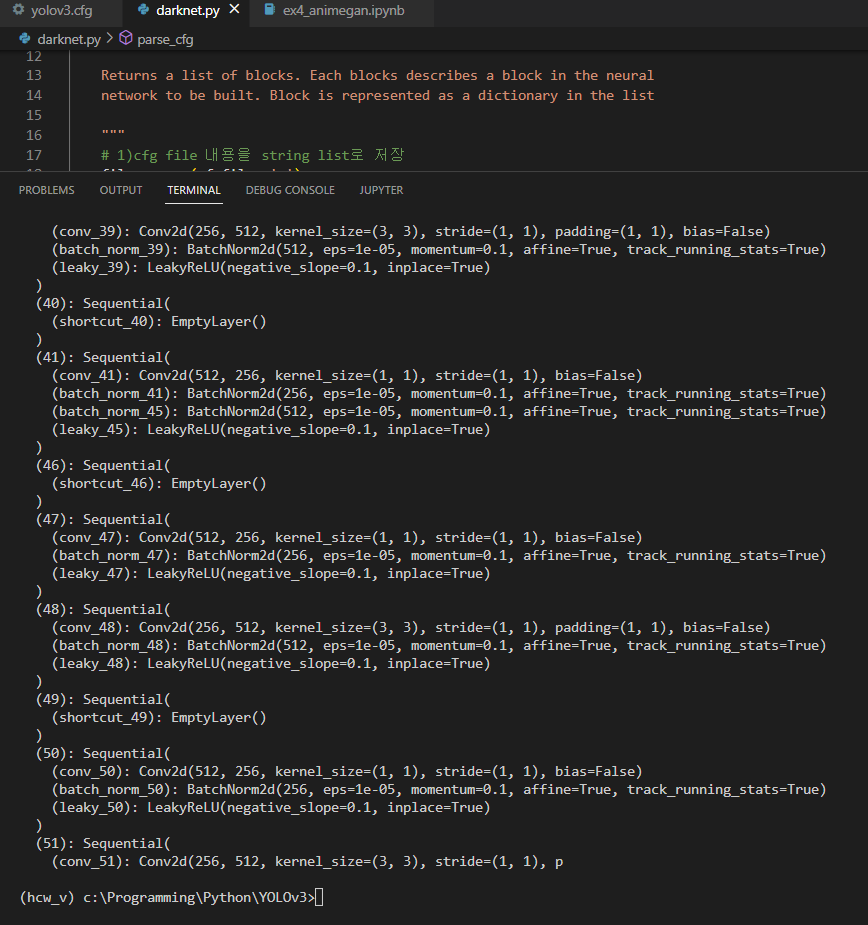
Creating the building blocks(create_modules())
parse_cfg file에서 return받은 list를 이용해 Pytorch module을 만든다.
Pytorch는 5개 종류의 layer중 convolutional과 upsample은 기본으로 제공한다.
나머지 3종류는 nn.Module class를 이용하여 우리가 구현해야 한다.
그 구현 함수가 create_module이다.
net_info: network information store
nn.ModuleList
-nn.Module(a)을 object로 가지고 있는 list이다.
-이 nn.ModuleList를 nn.Module(b)의 object로 넣으면, nn.ModuleList안에 있는 nn.Module(a)의 parameter가 nn.Module(b)의 object로 들어간다.
-새로운 CN을 만들 때, 그 kernel의 dimension을 정해야 함. kernel의 depth=filter개수. prev_filter: layer에 있는 filter개수를 계속 저장해 둔다.
-preceding layer의 filter개수도 필요하다. output_filters list에 output filter의 개수를 계속 저장해 둔다.
-convolutional, upsample 구현
- nn.Sequential, add_module통해 구현
Route Layer / Shortcut Layers
route, shortcut layer를 구현한다.
Wait, an empty layer?
-Pytorch에서 새로운 layer를 만들기: nn.Module object만들기-->forward function쓰기
-새로운 Route layer만들기: layers를 포함한 nn.Module object만들기-->forward function쓰기
YOLO Layer
Testing the code
VScode의 터미널에서 먼저
conda install pytorch torchvision torchaudio cpuonly -c pytorch
로 pytorch설치 후 Ctrl+F5
가상환경인 hcw_v에서 진행함.
터미널에서 conda activate hcw_v를 할 뿐만 아니라,
우측 하단에서 인터프리터를 hcw_v로 바꿔줘야지 원활하게 가상 환경에서 실행이 된다.
실행되는 것을 확인했다.