객체지향(Object Oriented)
: 하나의 모델이 되는 청사진(Blueprint)를 만들고( = Class ),
이 청사진을 바탕으로 여러 객체(Object)를 만드는 프로그래밍 패턴( = Instance )
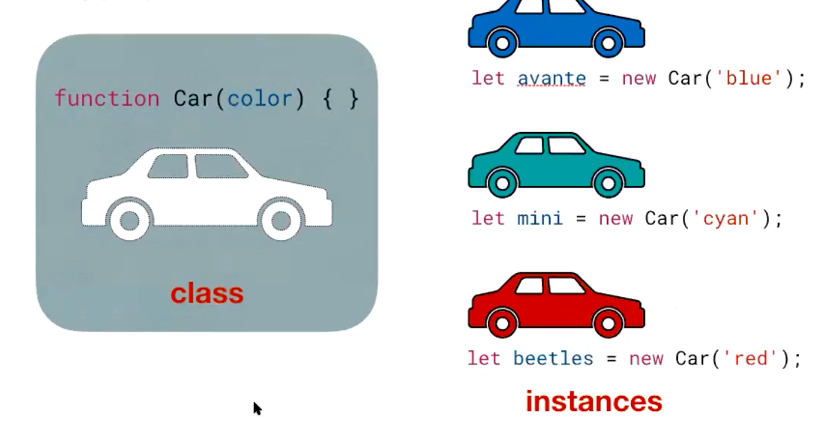
클래스(Class)를 만드는 방법
in ES5
function Car(brand, model, color){ this.brand = brand; this.model = model; this.color = color; }
in ES6
class Car{ constructor(brand, model, color){ this.brand = brand; this.model = model; this.color = color; } }
- 위 처럼 클래스를 만들때, 주의해야할 점은 클래스의 첫글자를 대문자로 써야한다.
ex) Car()
인스턴스(Instance) 만들기
: new 라는 키워드를 사용하여 만들 수 있습니다.
새로운 변수 (ex> avante,mini,...)에 새로운(new) 클래스(Car)를
담는다고 생각하면 좋을거 같다.
class Car{ constructor(brand, model, color){ this.brand = brand; this.model = model; this.color = color; } } let avante = new Car('Hyundai','avante','grey'); let mini = new Car('BMW','mini','red'); let avante = new Car('KIA','K5','black');

Car()라는 클래스에 새로운 메소드 또는 속성 만들기
//1. drive라는 메소드 추가 Car.prototype.drive() = function (){ console.log(this.model + '출발'); }
Primitive vs Reference
자바 스크립트에서 변수는 두가지의 value 타입을 가지고 있습니다. 하나는 primitive 이고 다른 하나는 reference 입니다. 우리가 변수에 값을 할당하면 자바스크립트에서는 이 변수가 어떤 value 타입을 가지고 있는지 결정합니다.
우선 primitive 타입은 여섯가지입니다.
1. undefined
2. null
3. boolean
4. number
5. string
6. symbol
reference 타입은 한가지입니다.
1. object (ex> object , array)
Primitive와 Reference 차이점
만약에 value 가 primitive라면, 그 값은 독립적으로 움직일 것입니다. 간단하게 예를 보겠습니다.
ex ) let value1 = 10; let value2 = value1; console.log(value1); // 10 console.log(value2); // 10 // value2 = 'hello world' console.log(value1); // 10 console.log(value2); // 'hello world'
위에 처럼 변수 value1를 선언하고 값을 할당했습니다.
value2 라는 변수를 선언 후 value1의 값을 할당했습니다.
value1와 value2를 출력했을때, 같은 값을 가지고 있는것을 확인했습니다.
그리고 나서 value2에 새로운 값 'hello world'를 할당했습니다.
다시 출력을 하니, value1와 value2는 다른 값을 가지게 되었습니다.
그러나 reference value는 조금 다릅니다.
reference 타입인 객체나 배열은 reference를 가지고 있습니다.
아래 예를 보시면 차이점을 확일 할 수 있습니다.
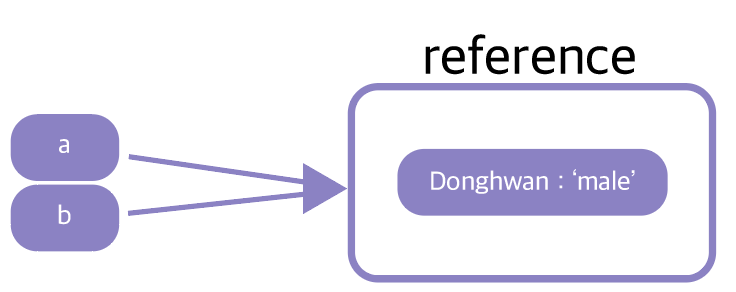
ex) let a = { Donghwan : 'male'}; let b = a; console.log(a.Donghwan); // 'male' console.log(b.Donghwan); // 'male'
여기 까지는 primitive 와 같은 방식으로 작동되었습니다.
let b.Donghwan = 28; console.log(a.Donghwan); // 28 console.log(b.Donghwan); // 28
위에서는 객체 b 의 key인 Donghwan을 재할당했습니다. 그리고 a와 b를 출력했더니, a와 b의 키 값이 둘다 28로 재할당 된것을 볼 수 있었습니다.
그림으로 예를 들어보면, 아래처럼 보일 것입니다.
같은 레퍼런스 안에 a 와 b가 들어있고 같은 값을 가리키고 있다.
그렇기 때문에 그 값을 바꾸면 둘 다 바뀐값을 가리키게 됩니다.