특징
- Devide, Conquer의 원리를 활용한 정렬 방식
How to quick sort?
- pick a Pivot: usually last element.
- Partitioning with pointers: all numbers less than pivot will be moved to the left of the pivot, all numbers greater than pivot will be moved to the right of the pivot.
- if leftPointer is larger than the pivot, stop;
else lp++; - if rightPointer is less than the pivot, stop;
else rp--; - swap two numbers that pointers are pointing to.
- if lp and rp are pointing to the same number, than swap it with the pivot.
- if leftPointer is larger than the pivot, stop;
- Recursive Step: recursively quick sorts the subarrays. except the pivot.
장점
- 시간복잡도 O(nlog₂n)
- Sorting Algorithm 중 가장 빠른 속도, 불필요한 데이터의 이동을 줄이고 먼 거리의 데이터를 교환할 뿐만 아니라, 한 번 결정된 Pivot들이 추후 연산에서 제외되는 특성 때문
- Java의 Arrays.sort() 내부적으로도 Dual Pivot Quick Sort로 구현되어 있을 정도로 효율적인 알고리즘.
- Merge Sort와 달리 정렬하고자 하는 배열 안에서 교환하는 방식이므로, 다른 메모리 공간을 필요로 하지 않음.
단점
- 시간복잡도가 n^2 되는 경우가 발생: 이미 오름차순이나 내림차순으로 정렬되어있는 array에서는 pivot이 max값이나 min값이므로 partition 마다 비교횟수가 1개씩밖에 줄어들지 않기 때문
- unstable: 같은 위상을 가진 값이라면 어떤 순서도 가능
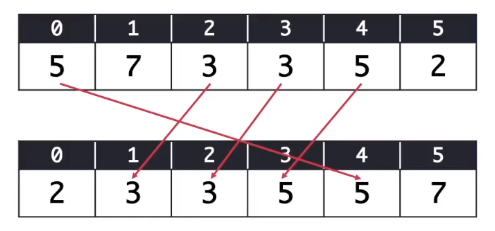
- sorting 이전에는 0번 index의 5가 먼저 -> 4번 index의 5 순서
- sorting 이후에는 4번 index의 5가 먼저오고 둘의 순서가 바뀜
import java.util.Arrays;
- 각 type에서 사용하는 sort 종류가 다르다
- DualPivotQuickSort
- faster than traditional(one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
boolean[], byte[], short[], int[], long[], float[], double[], char[]
- faster than traditional(one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
- ComparableTimSort
- based on the MergeSort.
- guaranteed to be stable equal elements will not be reordered as a result of the sort.
Integer[], Double[], String[], Object[]
How to Implement?
public class QuickSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {8, 2, 5, 3, 9, 4, 7, 6, 1};
System.out.println("Before QuickSort : " + Arrays.toString(array));
quickSort(array, 0, array.length-1);
System.out.println("After QuickSort : " + Arrays.toString(array));
}
public static void quickSort(int[] array, int lowIndex, int highIndex){
//0. when only one element left
if(lowIndex >= highIndex) return;
//1. pick a PIVOT.
int pivot = array[highIndex];
//2. PARTITIONING with pointers.
int leftPointer = lowIndex;
int rightPointer = highIndex;
while (leftPointer < rightPointer) {
while (array[leftPointer] <= pivot && leftPointer < rightPointer) {
leftPointer++;
}
while (array[rightPointer] >= pivot && leftPointer < rightPointer) {
rightPointer--;
}
swap(array, leftPointer, rightPointer);
}
//if lp and rp are pointing to the same number, than swap it with the pivot.
swap(array, leftPointer, highIndex);
//3. recursively quick sort
quickSort(array, lowIndex, leftPointer-1);
quickSort(array, leftPointer+1, highIndex);
}
private static void swap (int[] array, int index1, int index2){
int temp = array[index1];
array[index1] = array[index2];
array[index2] = temp;
}
}