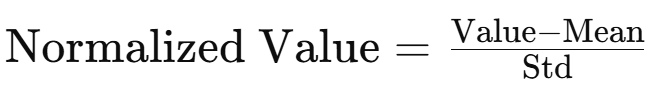- CNN을 이용해 CIFAR-10 데이터셋을 학습하고, 테스트 데이터를 분류하는 코드 작성.
- CIFAR-10은 10가지 클래스(예: 자동차, 개, 새 등)의 컬러 이미지를 포함한 데이터셋이다.
- 딥러닝에서 CNN은 이미지 데이터의 특성을 잘 학습하기 때문에 이미지 분류 문제에 자주 사용된다.
전체 코드
import torch
import torchvision.datasets as datasets
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tqdm import trange
transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]
)
trainset = datasets.CIFAR10(
root="./data", train=True, download=True, transform=transform
)
trainloader = DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
testset = datasets.CIFAR10(
root="./data", train=False, download=True, transform=transform
)
testloader = DataLoader(testset, batch_size=32, shuffle=False)
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f"{device} is available.")
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.feature_extraction = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(120, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.feature_extraction(x)
x = x.view(-1, 16 * 5 * 5)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
net = CNN().to(device)
print(net)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=1e-3, momentum=0.9)
loss_ = []
n = len(trainloader)
num_epochs = 10
pbar = trange(num_epochs)
for epoch in pbar:
running_loss = 0.0
for data in trainloader:
inputs, labels = data[0].to(device), data[1].to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
l = running_loss / n
loss_.append(l)
pbar.set_postfix({"epoch": epoch + 1, "loss": l})
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))
plt.plot(loss_, "-*")
plt.title("Training Loss")
plt.xlabel("epoch")
plt.show()
correct = 0
total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
net.eval()
for data in testloader:
images, labels = data[0].to(device), data[1].to(device)
outputs = net(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
print(
"Accuracy of the network on the 10000 test images: %d %%" % (100 * correct / total)
)데이터 전처리 및 로드
transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]
)
ToTensor()
이미지 데이터를 PyTorch 텐서(tensor)로 변환한다.
텐서는 다차원 배열 형태로 데이터를 표현하며, 딥러닝 모델의 입력으로 사용된다.원래 이미지는 0에서 255 사이의 값으로 표현된다(정수 값).
ToTensor()는 각 픽셀 값을 0.0에서 1.0 사이로 정규화된 실수 값으로 변환한다. 이는 픽셀 값을 255로 나누는 과정을 통해 이루어진다.
예를 들어, 픽셀 값이 128인 경우 128 / 255 = 0.50196으로 변환된다.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
Normalize(mean, std)는 각 채널(RGB)에 대해 평균(mean)과 표준편차(std)를 사용해 정규화한다.
CIFAR-10은 RGB 채널로 구성된 컬러 이미지로, 각 채널의 값을 별도로 정규화한다.
정규화의 이유
- 학습 안정성
신경망은 입력 데이터가 평균 0, 분산 1에 가까운 분포일 때 더 안정적으로 학습한다.
이를 통해 모델이 더 빠르게 수렴하고, 학습 속도를 개선할 수 있다.- 스케일 통일
데이터의 값이 일정한 범위(-1에서 1) 내에 존재하면, 특정 입력 값이 지나치게 크거나 작아지는 것을 방지한다.
이는 각 입력 값이 모델의 가중치 업데이트에 균등하게 영향을 미치도록 한다.- 채널 간 균형 유지
RGB 채널의 평균과 분산을 맞춤으로써 각 채널이 균등하게 학습에 기여하도록 한다.
만약 특정 채널의 값이 너무 크거나 작다면, 모델이 해당 채널에만 의존하게 되는 현상이 발생할 수 있다.
class CNN
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.feature_extraction = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5), nn.ReLU(), nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5), nn.ReLU(), nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(120, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.feature_extraction(x)
x = x.view(-1, 16 * 5 * 5)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x