1. 재현 가능성
동일한 연구나 실험을 반복했을 때 일관된 결과가 나오는지의 여부.
- 연구의 신뢰성을 높이는 중요한 요소
- 최근 p-value에 대한 논쟁이 두드러지고 있음
- 'p값을 사용하지 않는 것이 좋다'
- '유의수준을 0.05에서 다른 값으로 변경하는 것이 좋다'
- 가설 검정 원리 상의 문제나 가설 검정의 잘못된 사용이 낮은 재현성으로 이어진다는 문제 발생
- 논문을 재현해 실험을 하는데 똑같은 결과가 나오지 않는 사례가 많이 발생 재현성 위기
- 결과가 재현되지 않는다면 해당 가설의 신뢰도가 떨어짐
재현성 위기의 원인은?
- 실험 조건을 동일하게 조성하기 어려움
- 완전 동일하게 다시 실험을 수행하는 것은 쉽지 않은 문제
- 가설 검정 자체가 100%의 검정력을 가진 것이 아니기 때문에 오차가 발생할 수 있음
- 가설 검정 사용 방법에서의 잘못
- p-value가 0.05로 유도되게끔 조작 가능 (p-해킹)
- 실제로 통계적으로 아무 의미가 없음에도 의미가 있다고 해버리는 1종 오류 발생 가능
- 이를 유의수준으로 통제하는 것이 중요하나, 유의수준을 너무 낮추면 값 증가의 문제
- 잘못된 가설을 세우더라도 우연히 p-value가 0.05보다 낮아서 가설이 맞는 것처럼 보일 수도 있음
- 따라서 좋은 가설을 세우는 것도 중요
2. p-해킹
데이터 분석을 반복하여 p-value를 인위적으로 낮추는 행위
- 유의미한 결과를 위해 다양한 변수를 시도하거나, 데이터를 계속해서 분석하는 등의 방법 포함
- 데이터 분석 결과의 신뢰성을 저하시킴
언제 조심해야 하는가?
여러 가설 검정을 시도할 때
- 유의미한 p-value를 얻을 때까지 반복 분석하는 것 조심
- p-value가 0.05 이하인 결과만 선택적으로 보고하는 행위 조심
- 데이터 수를 늘리다가 특정 데이터 수에서 잠깐 p-value가 0.05 이하로 도출된 경우를 바탕으로 대립가설 채택하는 것 조심
- 즉, 결과를 보며 데이터 수를 늘려서는 안 됨
- 다양한 상황 중 p-value가 유리하게 나오는 상황만 선별적으로 보고하는 것 조심
- 다양한 변수를 건드리며 유리한 결과가 나올 때, 결과에 맞게 다시 처음부터 가설 세우는 것 조심
- 즉, 마음에 드는 상황만 골라서 보고하지 않아야 함. 모든 결과를 다 보고하거나 더 엄격한 추가실험 수행
- 가능한 가설을 미리 세우고 검증하는 가설검증형 방식으로 분석해야 하며, 탐색적으로 분석한 경우 모든 변수를 다 보고하고 본페로니 교정과 같은 방법 사용해야 함
3. 선택적 보고
유의미한 결과만 보고하고, 유의미하지 않은 결과는 보고하지 않는 행위
- 데이터 분석의 결과를 왜곡하고 신뢰성을 저하시킴
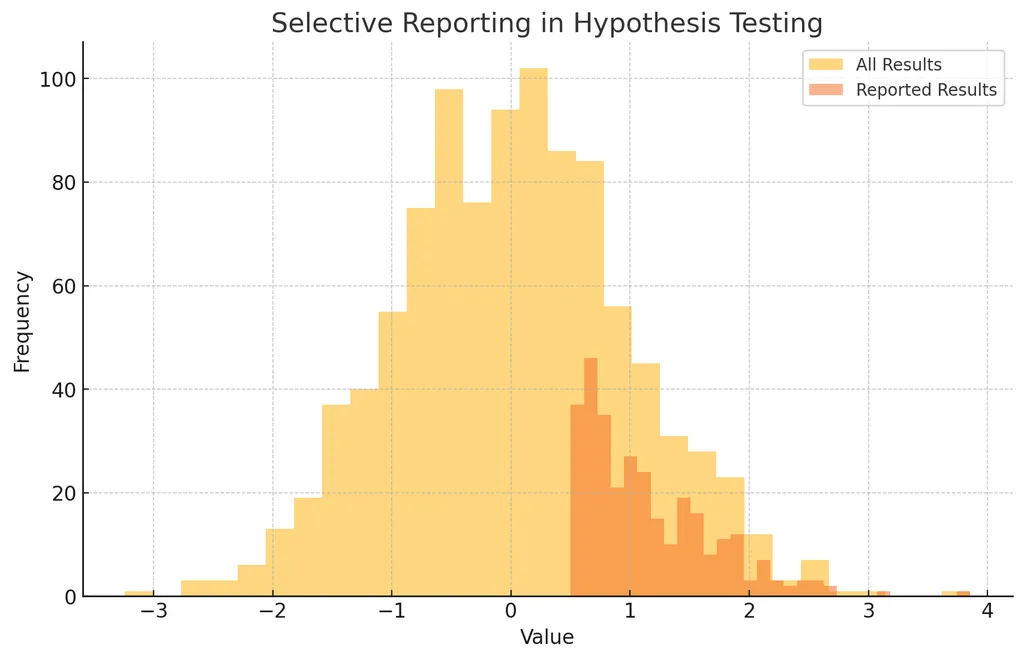
- 위 그림은 모든 결과와 선택적으로 보고된 결과를 히스토그램으로 나타냄
- 전체 결과와 보고된 결과의 분포가 다르면 선택적 보고의 가능성 시사
언제 조심해야 하는가?
- 유의미한 결과만 공개할 때
- 결과를 보면서 가설을 새로 설정했는데 마치 처음부터 설정한 가설인 것처럼 보고할 때
4. 자료수집 중단 시점 결정
원하는 결과가 나올 떄까지 자료를 수집하는 것 경계
- 데이터 수집을 시작하기 전에 언네 수집을 중단할지 명확하게 결정하지 않으면, 원하는 결과가 나올 때까지 데이터를 계속 수집할 수 있음. 이는 결과의 신뢰성을 저하시킴.

- 샘플 크기에 따른 평균값과 95% 신뢰구간을 나타낸 그래프
- 이상적으로는 사전에 정해진 계획에 따라 자료 수집을 중단해야 함
언제 조심해야 하는가?
- 결과를 이미 정해놓고 그에 맞추어 자료를 수집하고자 할 때
실습
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.stats as stats
# 데이터 수집 예시
np.random.seed(42)
data = np.random.normal(0, 1, 1000)
sample_sizes = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500]
p_values = []
for size in sample_sizes:
sample = np.random.choice(data, size)
_, p_value = stats.ttest_1samp(sample, 0)
p_values.append(p_value)
# p-값 시각화
plt.plot(sample_sizes, p_values, marker='o')
plt.axhline(y=0.05, color='red', linestyle='dashed', linewidth=1)
plt.title('p variation')
plt.xlabel('sample size')
plt.ylabel('p-value')
plt.show()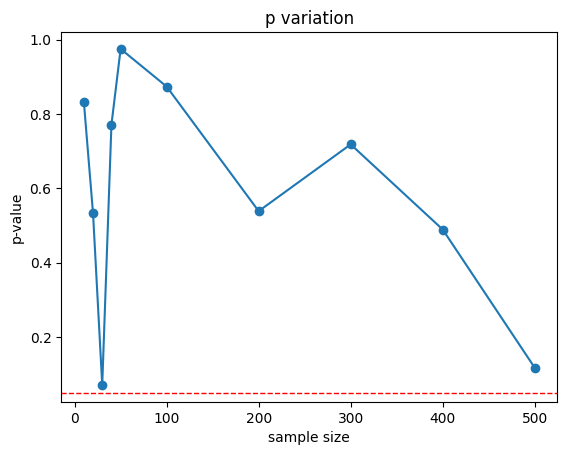
5. 데이터 탐색과 검증 분리
검증을 위한 데이터는 반드시 미리 따로 분리해 놓아야 함
- 데이터 탐색을 통해 가설을 설정하고, 이를 검증하기 위해 별도의 독립된 데이터셋 사용
- 이는 데이터의 과적합을 방지하고 결과의 신뢰성을 높임
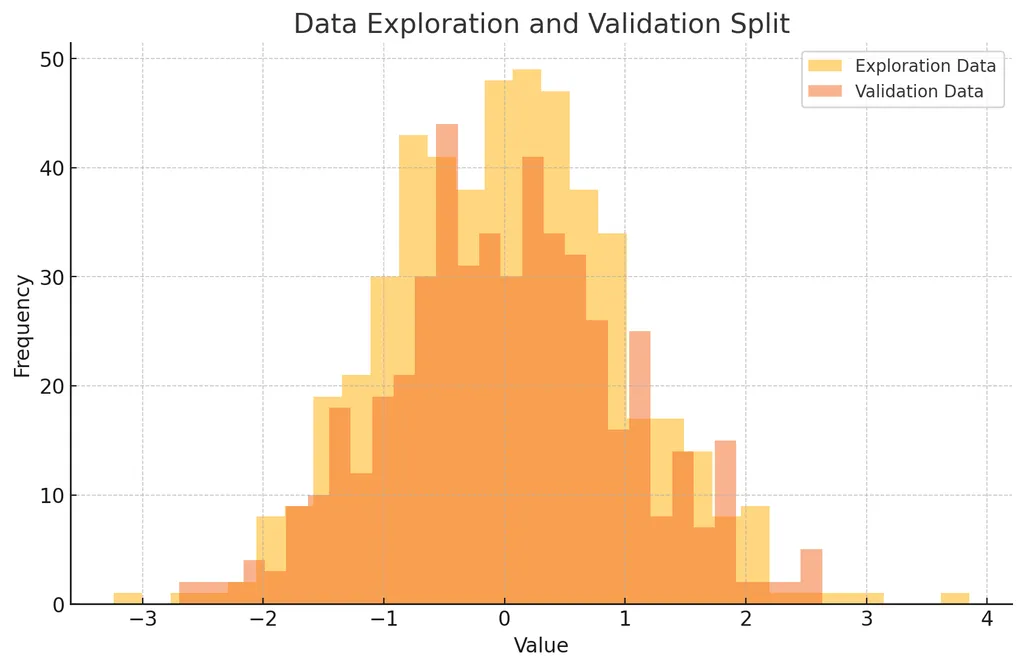
- 탐색 데이터와 검증 데이터를 히스토그램으로 표현
- 데이터 탐색과 검증을 분리하면 탐색 과정에서 발견된 패턴이 검증 데이터에도 유효한지 확인 가능
- 검증 데이터는 철저히 탐색 데이터와 구분되어야 함
실습
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import *
# 데이터 생성
np.random.seed(42)
X = 2 * np.random.rand(100, 1)
y = 4 + 3 * X + np.random.randn(100, 1)
# 데이터 분할 (탐색용 80%, 검증용 20%)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 모델 학습
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 탐색용 데이터로 예측
y_train_pred = model.predict(X_train)
# 검증용 데이터로 예측
y_test_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# 탐색용 데이터 평가
train_mse = mean_squared_error(y_train, y_train_pred)
train_r2 = r2_score(y_train, y_train_pred)
print(f"탐색용 데이터 - MSE: {train_mse}, R2: {train_r2}")
# 검증용 데이터 평가
test_mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_test_pred)
test_r2 = r2_score(y_test, y_test_pred)
print(f"검증용 데이터 - MSE: {test_mse}, R2: {test_r2}")결과:
탐색용 데이터 - MSE: 0.8476788564209705, R2: 0.7582381034538057
검증용 데이터 - MSE: 0.6536995137170021, R2: 0.8072059636181392
