[Paper Review] How Contextual are Contextualized Word Representations? Comparing the Geometry of BERT, ELMo, and GPT-2 Embeddings (Contextual Embedding)
1. Anisotropy
Contextualized representations are anisotropic in all non-input layers. If word representations from a particular layer were isotropic(i.e., directionally uniform), then the average cosine similarity between uniformly randomly sampled words would be 0(Arora et al., 2017). The closer this average is to 1, the more anistropic the representations.
-
isotropic: 등방성(좌), anisotropic: 이방성, 비등방성(우)
 -> 임베딩에서 isotropic은 주어진 vocab의 임베딩 벡터들이 사방으로 향함, anisotropic은 벡터가 주어진 공간에서 특정 방향으로 향해 일종의 cone 형태 이룸.
-> 임베딩에서 isotropic은 주어진 vocab의 임베딩 벡터들이 사방으로 향함, anisotropic은 벡터가 주어진 공간에서 특정 방향으로 향해 일종의 cone 형태 이룸. -
GPT-2의 마지막 층에서는 두 무작위 단어의 코사인 유사도가 거의 1에 가까울 정도로 극단적 anisotropy

In almost all layers of BERT, ELMo, and GPT-2, the word representations are anisotropic(i.e., not directionally uniform): the average cosine similarity between uniformly randomly sampled word is non-zero. The one exception is ELMo's input layer; this is not surprising given that it generates character-level embeddings without using context. Representations in higher layers are generally more anisotropic than those in lower ones.
2. 문맥에 따른 단어 표현(Context-Specificity)
(1) Self-Similarity
: 평균 코사인 유사도로 계산됨, 특정 레이어에서 단어 표현의 문맥 특이성 측정 지표
(1->0으로 값이 변할수록 문맥 특이성이 최대가 됨)
- 높은 레이어일수록 문맥 특이성 강해짐(self-similarity 감소로)
- GPT-2의 마지막 레이어는 거의 최대의 문맥 특이성
- ELMo의 입력 레이어는 self-similarity가 1(정적 임베딩을 사용하므로)
(2) stopwords
- ‘the’, ‘of’, ‘to’ 등의 stopwords-> 문맥 특이성이 가장 큼 (self-similarity가 낮음)
- 다의어 아니어도 문맥에 따라 다양한 표현적 특성 나타냄
(3) 문장 내 단어 유사도(Intra-Sentence Similarity)
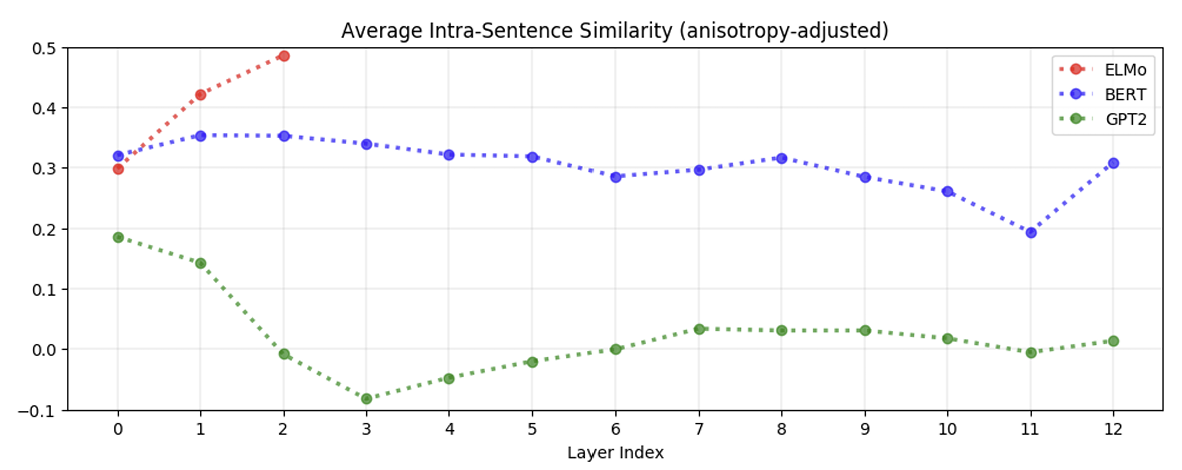
- 문장 내 단어 표현은 문맥화가 잘 되어 있더라도 서로 유사하지 않을 수 있음
3. 정적 vs. 문맥화된 표현
(1) Maximum Explainable Variance(MEV)
: 단어의 문맥화된 표현 중 정적 임베딩으로 설명 가능한 분산의 비율
- 정적 임베딩이 단어의 문맥화된 표현을 얼마나 잘 대체할 수 있는지에 대한 상한선 제공
- adjusted MEV
- 문맥화된 표현의 anisotropy 조정을 위해 무작위로 샘플링 된 단어 표현의 첫 번째 주성분으로 설명되는 분산 비율을 차감하여 계산
(2) 관찰 결과
- ELMo, BERT, 또는GPT-2의 어떤 레이어에서도 단어의 문맥 분산이 단어의 문맥적 표현에서 5% 이상의 분산을 평균적으로 정적 임베딩으로 설명할 수 없음-> 정적 임베딩이 문맥화된 표현을 대체하기에 매우 제한적(GPT-2의 2~11 레이어는 높은 anisotropy로 인해 raw MEV가 약 30%로 나타남)
- 단어 표현의 문맥화 모델은 단순히 한정된 개수의 단어 의미 표현 중 하나를 할당하지 않음(그렇지 않았다면 MEV 비율 더 높음)
(3) Principal Components
- 낮은 레이어(예: BERT Layer 1)의 문맥화된 표현은 GloVe 및 FastText보다 여러 벤치마크에서 더 우수한 성능이 나타남
Principal components of contextualized representations in lower layers outperform GloVe and FastText on many benchmarks.
