Promise

Promises는 execute라는 콜백함수를 전달하며,
execute 콜백함수는 resolve와 reject 콜백함수를 각각 인자로 받는다.
주의! 새로운 Promise가 만들어질 때, 자동적으로 executor가 작동하여 바로 실행된다.

상태(state)
State : pending → fulfilled or rejected
- 대기(pending) : Promise 객체가 생성되어 대기중인 상태
- 이행(fulfilled) : resolve()를 실행시켰을때의 상태
- 거부(rejected) : reject()를 행 시켰을 때의 상태
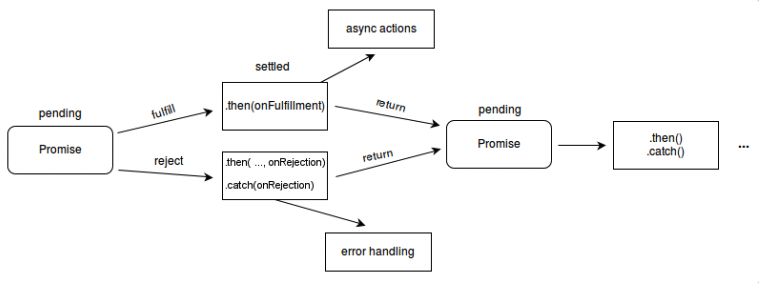
Promise 사용법
producer
//1. Producer
//주의 ! 새로운 promise가 만들어질때, 자동적으로 executor가 작동하여 바로 실행된다.
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//doing some heavy work (network, read file)
console.log("doing something....");
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("hyejin");
//reject(new Error('no network'));
}, 2000);
});Consumer / Promise 사용
//2. Promise 사용 : then, catch, finally
promise
.then((value) => {
// 값이 정상적으로 왔을 때
console.log(value);
})
.catch((error) => {
// 실패했을 때
console.log(error);
})
.finally(() => {
// 성공실패 상관없이 무조건
console.log("finally");
});콜백지옥 > 예시
const f1 = (callback) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("1번주문완료");
callback();
}, 1000);
};
const f2 = (callback) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("2번주문완료");
callback();
}, 3000);
};
const f3 = (callback) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("3번주문완료");
callback();
}, 2000);
};
// f1 -> f2 -> f3 순선대로 주문
console.log("시작");
f1(function () {
f2(function () {
f3(function () {
console.log("끝");
});
});
});callback -> promise 변경
const f1 = () => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("1번주문완료");
}, 1000);
});
};
const f2 = (message) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(message);
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("2번주문완료");
}, 3000);
});
};
const f3 = (message) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(message);
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("3번주문완료");
}, 2000);
});
};
console.log('시작');
f1()
.then((message) => f2(message)) // .then(f2)
.then((message) => f3(message)) // .then(f3)
.then((message) => console.log(message)) // .then(console.log)
.catch((e) => console.log(e))
.finally(() => console.log("끝"));promise.all
위 코드의 경우 총 6초가 걸리게 되는데, 아래의 경우는 3초가 걸림.
promise.all 을 쓰면 한꺼번에 진행해서 모두 이행되면 값을 사용할 수 있으므로 시간을 단축할 수 있다.
매개변수로 제공한 프로미스 각각의 이행 값을 모두 모아놓은 배열로 이행하며,
배열 요소의 순서는 매개변수에 지정한 프로미스의 순서를 유지한다.
promise.all([f1(),f2(),f3()]).then(res)=>}
console.log(res);
});
//['1번주문완료', '2번주문완료', '3번주문완료']>> 이 경우는 모두 다 성공해야지만 배열에 담아준다.
하나의 정보라도 누락되면 페이지 보여주지 않는 경우에 사용,
다보여주거나 아예안보여주거나 할 때 사용한다.
promise.race
promise.race([f1(),f2(),f3()]).then(res)=>}
console.log(res);
});
//1번주문완료all은 모든 작업이 완료될때까지 기다리지만,
race는 하나라도 1등으로 완료되면 끝냄으로 f1이 가장빠름으로 이것만 실행하고 뒤는 무시한다.
보통 용량이 큰 이미지를 로딩할 때 그 중에서 하나라도 완료되면 그것을 보여주는데에 사용.