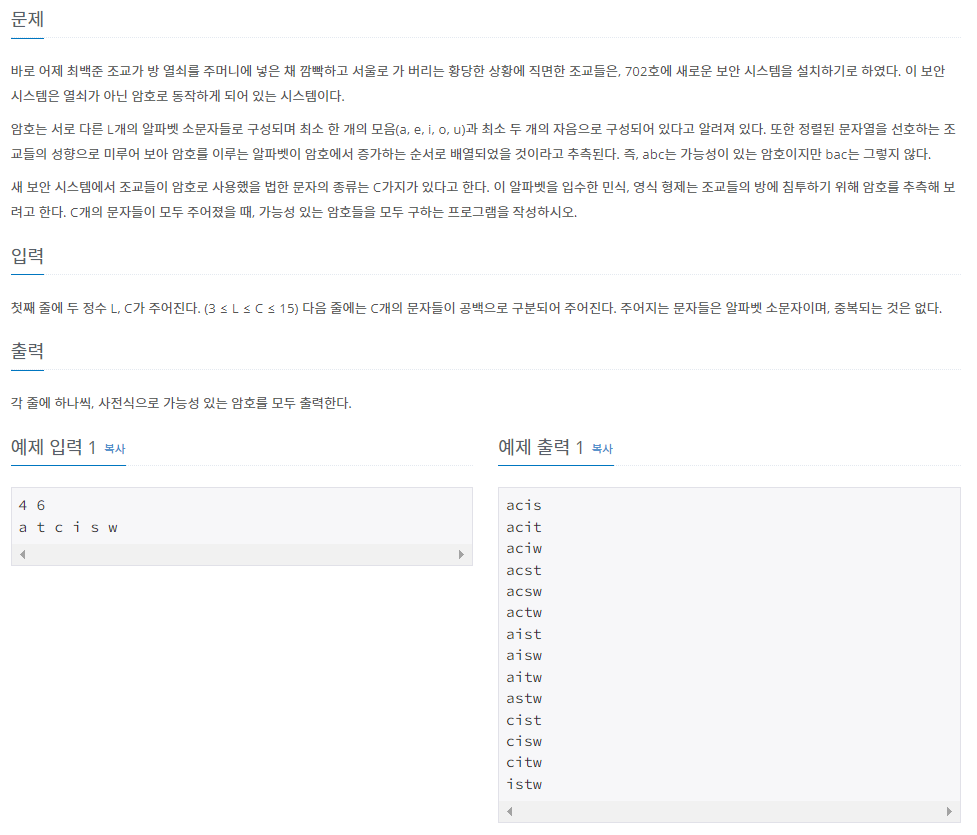
암호의 모든 경우의 수를 출력하면 된다.
다만, 제한조건으로는
- 최소 한개의 모음(a,e,i,o,u)과 두 개의 자음으로 구성 되어있다.
- 정렬된 문자를 선호하여, 순서대로 배열되어 있다.
만 기억하면 된다.
아래와 같이 코드를 구현했다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int L,C;
static String sum;
static boolean[] pos;
static String[] arr;
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
public static void dfs2(int idx, int start, String result) {
if (idx == L) {
int consonant = 0;
int vowel = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < result.length(); i++) {
if(result.charAt(i) == 'a'
|| result.charAt(i) == 'e'
|| result.charAt(i) == 'i'
|| result.charAt(i) == 'o'
|| result.charAt(i) == 'u'
) {
consonant++;
} else {
vowel++;
}
}
// 모음 하나이상, 자음 두개이상 일 때, 출력
if(consonant >= 1 && vowel >= 2) {
sb.append(result + "\n");
}
return;
}
for(int i = start ; i < C ; i++) {
if(!pos[i]) {
pos[i] = true;
dfs2(idx + 1, i + 1, sum = result + arr[i]);
pos[i] = false;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " ");
L = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
C = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
pos = new boolean[C];
arr = br.readLine().split(" ");
// 오름차순 정렬
Arrays.sort(arr);
// 탐색시작
dfs2(0,0,"");
System.out.print(sb);
}
}
