디버깅.
버그를 찾아내고 없애는 팁을 살펴본다.
첫 번째는 문제를 머릿속에 그려본다.
def my_function():
for i in range(1, 20):
if i == 20:
print("You got it")
my_function()i == 20이 되면, if문에 있는 문구가 출력되어야 한다. 하지만 출력되지 않는 버그가 발생한다.
이유는range의 상한선이 20이므로, 19까지만 i가 올라가기 때문에 버그가 발생한다는 것이다.
range(1, 20)을 range(1, 21)으로 바꾸면 문제가 해결된다.
def my_function():
for i in range(1, 21):
if i == 20:
print("You got it")
my_function()버그 재현하기.
다음에 버그가 발생 했을 때를 대비해여, 버그를 재현하여 보고, 어떤 조건에서 버그가 발생하는지 알아본다.
from random import randint
dice_imgs[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
dice_num = randint(1, 6)
print(dice_imgs[dice_num])dice_imgs는 순서가 0부터 시작해서 5로 끝난다. 하지만 6번째 원소는 존재하지 않으므로 오류가 나는 것이다.
from random import randint
dice_num = randint(0, 5)
print(dice_imgs[dice_num])컴퓨터의 입장에서 생각해보기
year = int(input("What's your year of birth?"))
if year > 1980 and year < 1994:
print("You are a millenial.")
elif year > 1994:
print("You are a Gen Z.")1994를 입력하였을 때, 아무런 것도 출력되지 않는다.
그 이유는 범위에서 벗어나기 떄문이다. 1994가 포함되도록 범위를 고치면 해결이 된다.
year = int(input("What's your year of birth?"))
if year > 1980 and year 1994:
print("You are a millenial.")
elif year >= 1994:
print("You are a Gen Z.")오류 수정하기 - 빨간 줄을 주목하세요.
편집기에서 오류가 나거나, 콘솔이 오류가 나올 때 해결 하는 방법
age = input("How old are you?")
if age > 18:
print("You can drive at age {age}.")if 다음 print는 들여쓰기를 해야 한다.
또한, input의 타입이 정해져 있지 않는다.
다음과 같이 고치면 된다.
또한, 에러가 발생 했을 때, 문구를 복사하여 구글에 검색하면 어떠한 부분에서 에러가 나는지 알 수 있다. (TypeError 부분)
그리고, 관찰되지 않는 error가 발생했는데, 이 부분은 코드를 만드는 사람의 경험에 의해 발견될 수 밖에 없다. fstring입력을 빼먹었다.
age = int(input("How old are you?"_
if age > 18;
print(f"You cann drive at age {age}.")print구문으로 버그를 해결하기
pages = 0
word_per_page = 0
pages = int(input("Number of pages: "))
word_per_page == int(input("Number of words per page: "))
total_words = pages * word_per_page
print(total_words)print구문으로 버그를 해결해 본다.
print(f"pages = {pages}")
print(f"word_per_page = {word_per_page_"}위에 구문을 대입하여 보면, word_per_page 가 대입이 아니라, 검증인 == 로 오타다 들어있는 것을 알 수 있다. (False가 된다.)
pages = 0
word_per_page = 0
pages = int (input("Number of pages: "))
word_per_page = int(input("Number of words per page: "))
total_words = pages * word_per_page
print(total_words)디버거 활용
PythonTutor을 활용하여 디버거를 써보자.
def mutate(a_list):
b_list = []
for item in a_list:
new_item = item * 2
b_list.append(new_item)
print(b_list)
mutate([1,2,3,5,8,13]) 위에 코드를 실행하면, [2, 4, 6, 10, 13, 26]이 출력되어야 하지만, 실제로는 26밖에 출력되지 않는다. 디버거를 사용하여 한 줄 한 줄 단계별로 실행하여 어떤 것이 잘못되었는지 살펴본다.
(tip. 라인 숫자를 클릭하면, 중단점 설정이 가능하다.)
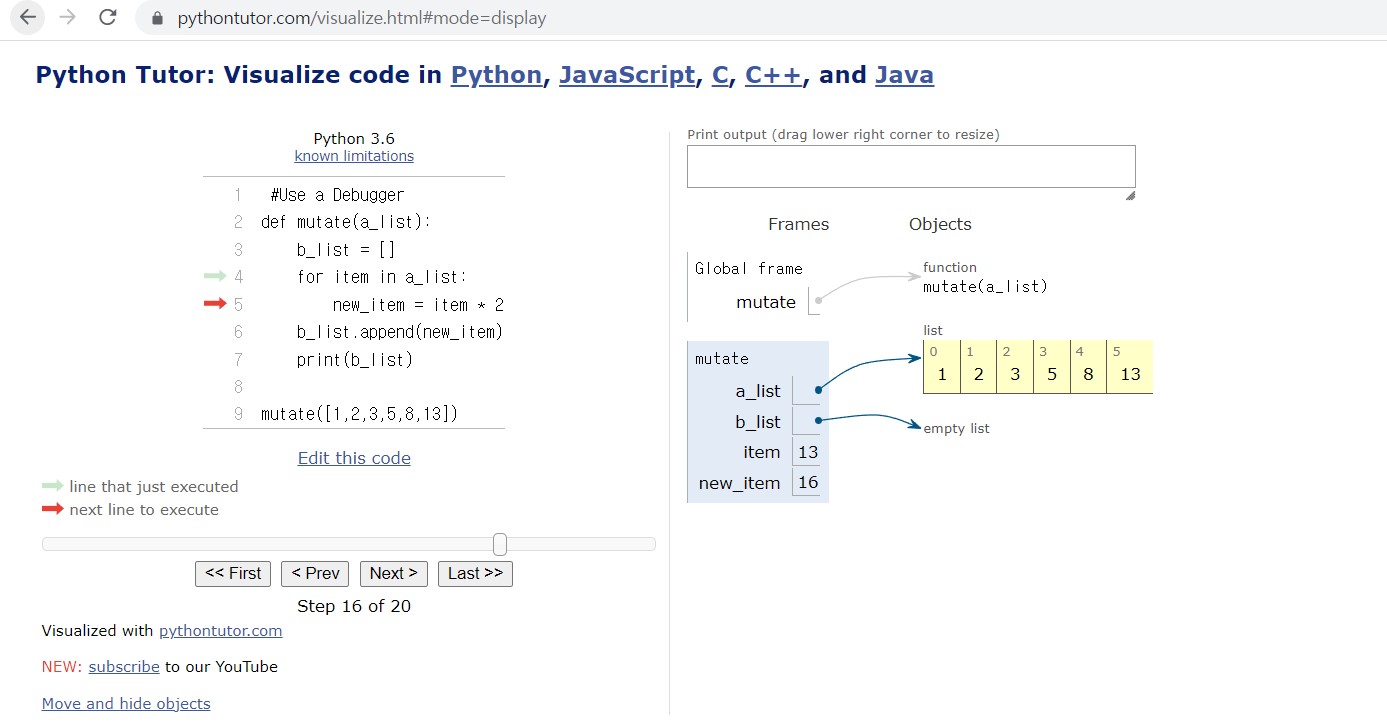
b_list.append가 for문 밖에 나와있어, new_item이 리스트에 들어가지 않았기 때문에 일어나는 문제였다. 다음과 같이 수정한다.
def mutate(a_list):
b_list = []
for item in a_list:
new_item = item * 2
b_list.append(new_item)
print(b_list)
mutate([1,2,3,5,8,13]) 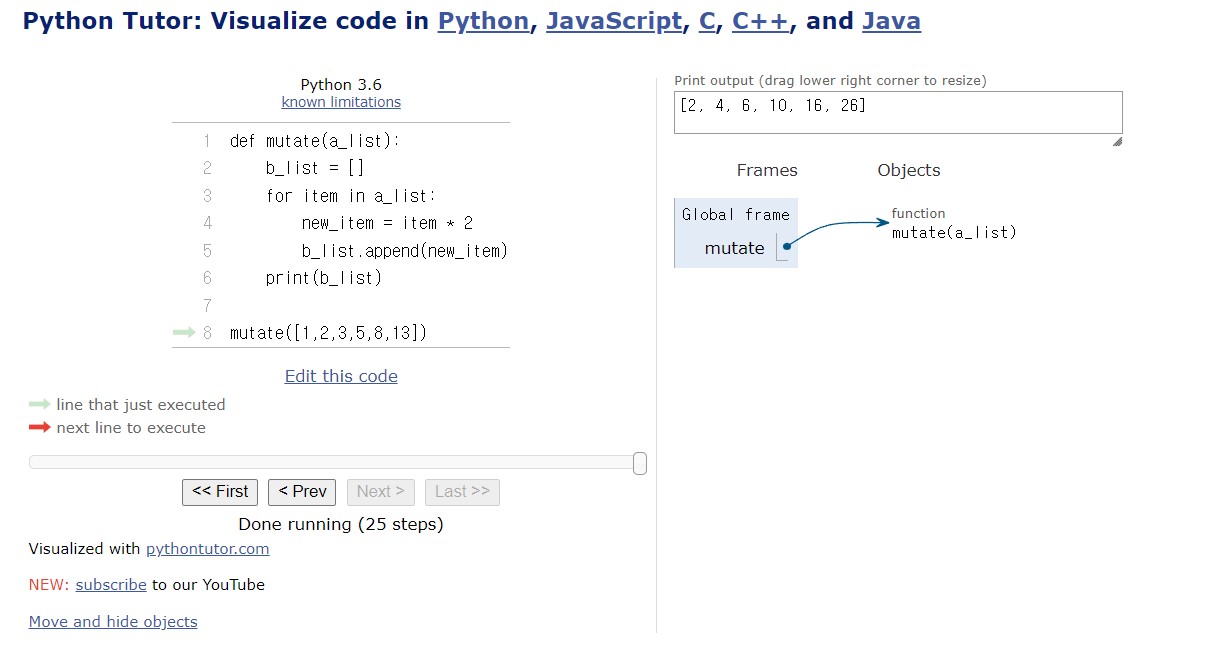
정상적으로 잘 작동함을 볼 수 있다.
유용한 디버깅 팁
코딩을 할 때에는, 한번에 많이 작성하는 것 보다, 자주 실행해 보는것이 좋다.
마지막에 실행을 하면, 한꺼번에 많은 버그가 터져서 해결이 안되는 경우도 많기 때문이다.
[인터렉티브 코딩 예제] 홀수와 짝수
number = int(input("Which number do you want to check?"))
if number % 2 = 0:
print("This is an even number.")
else:
print("This is an odd number.")위 코드에선, if문에서 대입 대신에 관계 연산자인 == 를 넣어야 한다.
해당 코드를 수정하면 다음과 같다.
number = int(input("Which number do you want to check?"))
if number % 2 == 0:
print("This is an even number.")
else:
print("This is an odd number.")[인터렉티브 코딩 예제] 윤년 문제
year = input("Which year do you want to check?")
if year % 4 == 0:
if year % 100 == 0:
if year % 400 == 0:
print("Leap year.")
else:
print("Not leap year.")
else:
print("Leap year.")
else:
print("Not leap year.")위의 코드는, input의 데이터 타입을 정의하지 않았다. 그러면 year의 입력값의 데이터 타입이 str이 된다.
올바른 데이터 타입을 지정해서 코드를 수정하면 다음과 같다.
year = int(input("Which year do you want to check?"))
if year % 4 == 0:
if year % 100 == 0:
if year % 400 == 0:
print("Leap year.")
else:
print("Not leap year.")
else:
print("Leap year.")
else:
print("Not leap year.")[인터렉티브 코딩 예제] 피즈-버즈 디버깅
for number in range(1, 101):
if number % 3 == 0 or number % 5 == 0:
print("FizzBuzz")
if number % 3 == 0:
print("Fizz")
if number % 5 == 0:
print("Buzz")
else:
print([number])코드를 실행해도 잘 출력이 되지만, 몇가지 실행 에러가 존재한다.
숫자가 전부 대괄호에 갖혀서 출력된다는 것.
FizzBuzz출력 이후에, Fizz혹은 Buzz가 같이 출력되는 것.
3과 5로 동시에 나뉘면 FizzBuzz가 출력되고, 3으로 나뉠 때는 Fizz가 출력되고, 5로 나뉘면 Buzz가 출력되기 위해서는 다음과 같이 코드를 수정한다.
for number in range(1, 101):
if number % 3 == 0 and number % 5 == 0:
print("FizzBuzz")
elif number % 3 == 0:
print("Fizz")
elif number % 5 == 0:
print("Buzz")
else:
print(number)if와 elif, else로 제작하여, 한 가지 조건이 발동하면, 다른 조건이 발동하지 않게 제작하였다.
대괄호를 삭제하여 숫자가 대괄호 안에 출력되지 않게 했다.
