이 포스트는 그래프에서 이어진다.
시작하며
DFS와 BFS는 그래프 탐색 기법이다.
1. 깊이 우선 탐색(depth-first search, DFS)
1.1 소개
DFS는 백트래킹 알고리즘 문제를 풀 때 쓰이며, 이는 코딩테스트에서 아주 빈번히 출제되는 유형이다.
백트래킹(backtracking) : 부모노드로 되돌아오는 과정
Depth-first search (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. The algorithm starts at the root node (selecting some arbitrary node as the root node in the case of a graph) and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking. Extra memory, usually a stack, is needed to keep track of the nodes discovered so far along a specified branch which helps in backtracking of the graph.
루트 노드(그래프의 경우 루트 노드로 임의 노드를 선택)에서 시작해서 백트래킹하기 전에 해당 분기에서 최대한 깊게 탐색한다.
1.2 구현
두 가지 구현 방식이 존재한다.
- recursive
재귀 호출하면서 visit flag를 사용하여 구현한다. - iterative
반복문과 visit flag, stack으로 구현한다.
구현할 때 iterative방식을 채택할 것이다.(교수님께서 그렇게 하라고 했기 때문에)
1.2.1 동작 과정
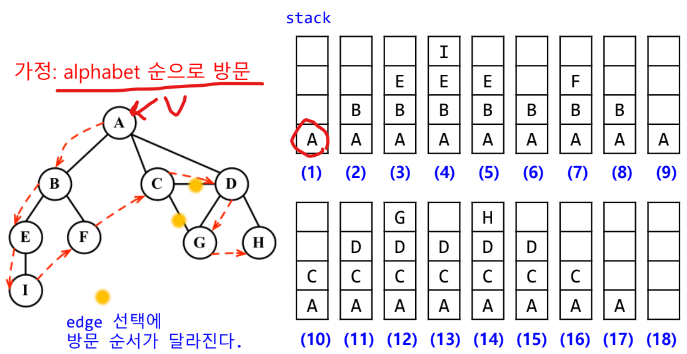
- 시작 정점 v를 결정:
visit mark & push(v) - 스택의 최상단 확인:
w = adjacent(top())
2-1. 방문하지 않은 정점 w 존재:push(w) & visiting mark
2-2. w가 없음:pop() - 2번 과정으로 돌아가 스택이 공백이 될 때까지 수행
1.2.2 알고리즘
DFS(G,v) ( v is the vertex where the search starts )
Stack S := {}; ( start with an empty stack )
for each vertex u, set visited[u] := false;
push S, v;
while (S is not empty) do
u := pop S;
if (not visited[u]) then
visited[u] := true;
for each unvisited neighbour w of u
push S, w;
end if
end while
END DFS()1.4 실행 시간
- 인접리스트(Adjacency List) 사용 시 :
O(V + E) - 인접행렬(Adjacency Matrix) 사용 시 :
- 인접 정점들을 찾는 시간 :
O(V) - 총 시간 :
O(V^2)
- 인접 정점들을 찾는 시간 :
1.5 깊이 제한
탐색 과정이 시작 노드에서 한없이 깊이 진행되는 것을 막기 위해 깊이 제한(depth bound)을 사용한다. 깊이 제한에 도달할 때까지 목표노드가 발견되지 않으면 최근에 첨가된 노드의 부모노드로 되돌아와서, 부모노드에 이전과는 다른 동작자를 적용하여 새로운 자식노드를 생성한다.
1.6 장단점
장점
- 저장공간 수요 적음.
- 목표노드가 깊은 단계에 있을 경우 해를 빨리 구할 수 있음.
단점
- 깊이 제한을 두지 않을 경우 해가 없는 경로에 깊이 빠질 수 있음.
- 도출한 해가 최단경로라는 보장이 없음.
=> 해가 여러 가지인 문제에 대해서는 적용할 수 없음. (해를 찾고 탐색을 끝내므로)
2. 너비 우선 탐색 (breath-first search, BFS)
2.1 소개
Breadth-first search (BFS) is an algorithm for searching a tree data structure for a node that satisfies a given property. It starts at the tree root and explores all nodes at the present depth prior to moving on to the nodes at the next depth level. Extra memory, usually a queue, is needed to keep track of the child nodes that were encountered but not yet explored.
루트노드부터 시작하여 다음 깊이로 넘어가기 전 현재 깊이에서 모든 노드를 탐색한다.
2.2 구현
DFS와 마찬가지로 두 가지 구현 방법이 존재한다.
- recursive
재귀 호출하면서 visit flag를 사용하여 구현한다. - iterative
반복문과 visit flag, queue로 구현한다.
2.2.1 동작 과정
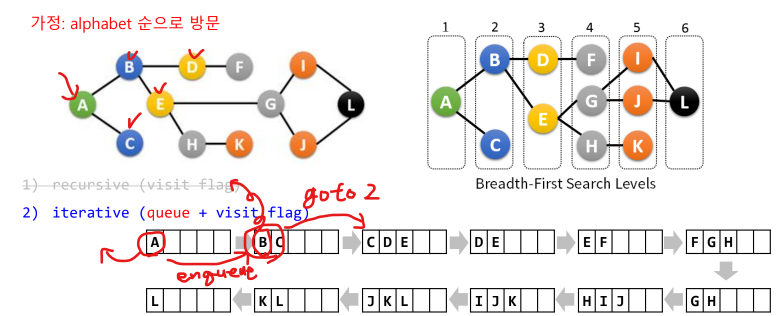
- 시작 정점 v를 방문 :
visit marking & enqueue() - 큐에서 최상단 dequue:
w = dequeue()
visit marking& 방문하지 않은 w의 인접노드 enqueue() - 2번 과정으로 돌아가 큐가 공백이 될 때까지 수행
2.2.2 알고리즘
1 procedure BFS(G, root) is
2 let Q be a queue
3 label root as explored
4 Q.enqueue(root)
5 while Q is not empty do
6 v := Q.dequeue()
7 if v is the goal then
8 return v
9 for all edges from v to w in G.adjacentEdges(v) do
10 if w is not labeled as explored then
11 label w as explored
12 Q.enqueue(w)2.4 실행 시간
- 인접리스트(Adjacency List) 사용 시 :
O(V + E) - 인접행렬(Adjacency Matrix) 사용 시 :
- 인접 정점들을 찾는 시간 :
O(V) - 총 시간 :
O(V^2)
- 인접 정점들을 찾는 시간 :
2.5 장단점
장점
- 출발노드에서 목표노드까지의 최단 길이 경로를 보장한다.
단점
- 경로가 매우 길 경우에는 탐색 가지가 급격히 증가함에 따라 보다 많은 기억 공간을 필요로 하게 된다.
- 해가 존재하지 않는다면 유한 그래프(finite graph)의 경우에는 모든 그래프를 탐색한 후에 실패로 끝난다.
- 무한 그래프(infinite graph)의 경우에는 결코 해를 찾지도 못하고, 끝내지도 못한다.
3. DFS & BFS in Python
from collections import deque, defaultdict
import sys
class Graph :
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.adj = defaultdict(list) #인접리스트
def addEdge(self, v, w):
self.adj[v].append(w)
self.adj[w].append(v)
def DFS(self, s):
visited = [False]*(self.V+1) #처음에는 모두 미방문
stack = [s] #현재 노드 추가
res = []
while stack :
s = stack.pop() #스택 최상단 팝
if visited[s] == 0: #미방문 노드일시 방문처리
visited[s] = True
res.append(s)
# 현재 노드 s의 모든 인접 노드 검사
# 방문하지 않았다면 스택에 push
for v in sorted(self.adj[s], reverse=True): #작은 노드부터 검사
if not visited[v]:
stack.append(v)
return res
def BFS(self, s):
visited = [False]*(self.V+1) #처음에는 모두 미방문
queue = deque()
queue.append(s)
visited[s] = True
res = []
while queue:
s = queue.popleft()
res.append(s)
# deque한 vertex의 모든 인접 노드들을 얻는다.
# 만약 탐색한 적이 없는 노드라면 방문처리하고 enqueue한다.
for v in sorted(self.adj[s]):
if not visited[v]:
queue.append(v)
visited[v] = True
return res
def printGraph(self):
for k, v in self.adj.items():
print(k, "=>", v)
N, M, V = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())
g = Graph(N) #N개의 vertex로 이루어진 그래프
for i in range(M): #간선생성
v1, v2 = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())
g.addEdge(v1, v2)
# g.printGraph()
print(*g.DFS(V))
print(*g.BFS(V))BFS, DFS알고리즘 관련 사이트, 블로그 등을 보면서 풀어낸 백준 1260번 코드이다.
- 230201) java 코드 추가
package silver2;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class B1260_DFS와_BFS {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int V = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int startNode = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
Graph g = new Graph(N);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int N1 = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int N2 = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
g.makeVertex(N1, N2);
}
g.DFS(startNode);
g.BFS(startNode);
}
}
class Graph {
public Map<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> adjList = new HashMap<>(); // 인접리스트(인접노드들)
boolean[] visited;
public Graph(int N) {
this.visited = new boolean[N + 1]; // 방문검사용 배열
}
// N1과 N2간의 Vertex추가
public void makeVertex(int N1, int N2) {
// N1 노드가 value로 가지고있는 리스트에 N2추가
ArrayList<Integer> temp = adjList.get(N1); // n1의 인접노드들
if (temp == null) // 만약에 비었으면 새로만들기
temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 간선만들기
temp.add(N2);
adjList.put(N1, temp);
// ==========================================
// N2노드가 value로 가지고있는 리스트에 N1추가
temp = adjList.get(N2); // n1의 인접노드들
if (temp == null) // 만약에 비었으면 새로만들기
temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 간선만들기
temp.add(N1);
adjList.put(N2, temp);
}
public void DFS(int startNode) {
// visited초기화 전처리
Arrays.fill(visited, false);
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); // DFS용 스택
// 시작 정점 결정
stack.add(startNode);
// ================노드 순회 시작=====================
while (stack.size() != 0) {
// 스택의 최상단 확인
int popedNode = stack.pop();
// 미방문 노드일시 방문처리 및 결과에 입력
if (!visited[popedNode]) {
visited[popedNode]=true;
System.out.print(popedNode+" ");
}
// 방문 노드의 인접 노드들 검사
ArrayList<Integer> popedList = adjList.get(popedNode);
if (popedList != null) {
Collections.sort(popedList);
// 방문노드에 인접한 노드들의 리스트를 내림차순 정렬해서 add해야
// stack에서 오름차순으로 pop할 수 있음
Collections.reverse(popedList);
// 인접한 노드 하나 검사
for (Integer node : popedList) {
// 방문하지 않은 정점 존재할 시
if (!visited[node])
stack.add(node);
} // 인접한 노드 하나 검사 끝
} //현재 방문노드의 인접노드 여부검사 끝
} // 노드 순회 끝 ==================================
System.out.println();
} // DFS 끝 ==========================================
public void BFS(int startNode) {
// visited초기화 전처리
Arrays.fill(visited, false);
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); //BFS용 큐
// 시작 정점 결정
queue.add(startNode);
visited[startNode] = true;
// ================노드 순회 시작=====================
while (queue.size() != 0) {
// 큐의 맨앞 노드 확인
int polledNode = queue.poll();
System.out.print(polledNode+" ");
// 현재 방문노드의 인접노드가 있는지 검사
ArrayList<Integer> polledList = adjList.get(polledNode);
if (polledList != null) {
// 오름차순으로 노드에 방문해야해서 인접노드 정렬
Collections.sort(polledList);
// 인접노드 순회
for (Integer node : polledList) {
if (!visited[node]) { //방문하지 않은 노드만 enqueue
queue.add(node);
visited[node]=true;
}
} //인접노드 순회 끝
} // 방문노드의 인접노드 유무 검사
} // ================노드 순회 끝 ===================
System.out.println();
}//BFS끝
}4. DFS vs BFS
| DFS | BFS | |
|---|---|---|
| 자료구조 | 스택 | 큐 |
| 실행 시간 | 인접리스트 - O(V + E) 인접행렬 - O(V^2) | 인접리스트 - O(V + E) 인접행렬 - O(V^2) |
| 백트래킹 | ⭕ | ❌ |
| 최단경로 탐색 | ❌ | ⭕ |
| 메모리 | 적음 | 많음 |
| 공간복잡도 | 루트노드부터 단말노드까지의 단일경로만 필요하므로 낮음 | 높음(시간복잡도보다 중요함) |
| 속도 | BFS보다 느림 | DFS보다 빠름 |
| 용도 | 수많은 경로를 탐색해야할 때 (게임, 퍼즐, 미로 등) | 최단경로를 구할 때 (가중치 없는 그래프에서) |
참고
DFS, BFS 개념 - https://devuna.tistory.com/32
DFS 개념, 장단점 - https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/깊이_우선_탐색
DFS 알고리즘 - http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~heap/270F02/node36.html
DFS 파이썬 코드 - https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/iterative-depth-first-traversal/
BFS 장단점 - https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/너비_우선_탐색
BFS 개념, 알고리즘 - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Breadth-first_search
BFS 파이썬 코드, 그래픽 이미지 - https://favtutor.com/blogs/breadth-first-search-python
DFS vs BFS - https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-bfs-and-dfs/

