Compiler
- Definition of Compiler
- Translation, 소스코드에 대해서 같은 의미의 실행을 하는 프로그램으로 변환시켜줌.
- 이제는 언어에서 언어로 바꿔줌
- Characteristics of Compiler
- input language 구조를 이해하고 프로세스를 한다.
- 분석된 구조를 타겟 언어의 형태로 맵핑하는 알고리즘 사용한다. (복잡함)
- compiler : 타겟 코드 만드는데 중요한것은 efficiency이다.
/ interpreter : 즉시 만드는 것은 flexibility를 중요시함.
- A language-processing system
- (Idea) algorithm -> (Text editor) skeletal source program
-> (pre-processor) modified source program -> (Compiler) Assembly code
-> (Assembler) machine code(partial)
(머신코드를 바로 만들기 힘들어서 어셈블러 만들고 나머지는 다른 친구들한테 시킴.)
library, relocatable object files
-> (Linker) absolute machine code
- The Phases of A Compiler

- symbol-table manager 모든 모듈들이 공유하게 한다
- error handler 에러발생시 이를 보내서 핸들시킨다.
- Lexical Analysis Phase (필수)
- source program file에서 characters 읽기
- Grouping : lexemes or tokens라 불리는 chunks로 characters 묶기
- 토큰은 keyword, constant, operator, identifier, etc라는 logically cohesive sequence of character
- lexer(or scanner)에 의해 수행이 되고, 여기서는 efficiency가 가장 중요 관점
- Syntax Analysis Phase (필수)
- 그룹된 것을 계층적(hierarchically)으로 그룹화 시킴
- Intermediate repesentation 인 AST( Abstract Syntax tree)로 구성
- Performed by a parser
- Syntax Analysis Phase : Parse Tree
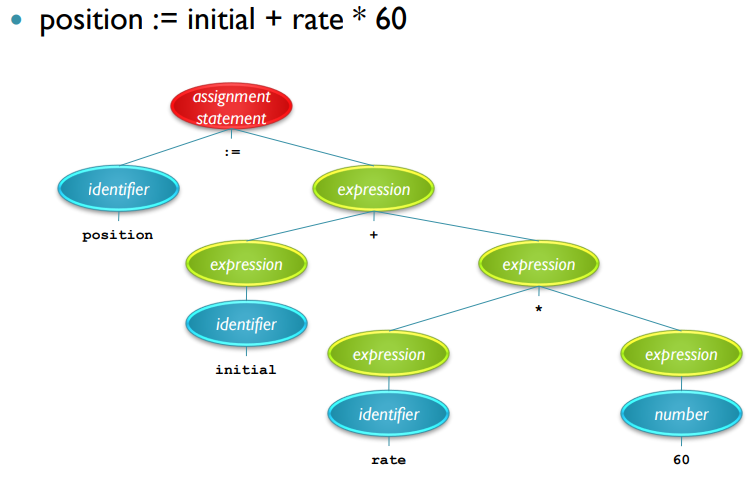
- Semantic Analysis Phase
- 잘 되어있는지 check
- 대부분은 parser가 하지만, 몇몇은 done by lexer or code generator
- 이 수행자 is called constrainer by pittman
- Type checking, uniqueness
-
Intermediate Representation
-
Code optimization
- Reducing execution time
- Saving memory space
- Reducing communication bandwidth
- Code Generation Phase (필수)
- 중간표현이나 어셈블리 코드를 마지막으로서 target code로 만드는 과정
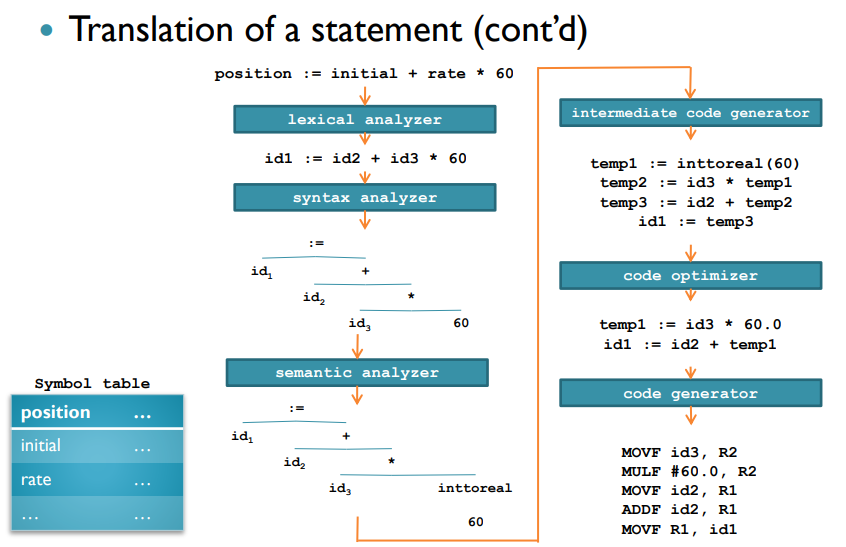
Grammar
- Basic concepts
- 정해진대로 써야함
- 4가지로 구성 되어있음 (∑, N, P, S)
- ∑ 변할 수 없는 terminal symbols
- nonterminal symbols는 변할 수 있고 이는 N안에 있음
- proguction rules P에 적혀있음 (알파가 베타로 변할 수 있다)
- goal symbol S is the start symbol
- 계산기 grammar
G = (∑, N, P, S) where
∑ = {n, +, \*, (, )}, // 이 5개만 쓸 수 있다.
N = {E, T, F}, // 다른것로 바꿀 수 있는 것들
P = {E → E + T, E → T, T →T * F, T → F, F → (E), F → n } // 바뀔 수 있다는 공식들 모음
S = E // 그 중에 E를 스타트 심볼로 정의하자- String
- terminal or zero로 이루어진 것
- Language
- A set of strings
- mathematically L(G) = { ω | ω ∈ ∑ and S => ω}
- if L(G1) = L(G2) -> G1 and G2 are equivalent
G1 = { {a, b, c}, / terminals /
{A, B} / non-terminals /
{A ➔ aB, A ➔ bB, A ➔ cB, B ➔ a, B ➔ b, B ➔ c},
S / start symbol / }
L(G1) = { aa, ab, ac, ba, bb, bc, ca, cb, cc}- Derivation
-
A -> bB -> bc (two immediate derivations)
could be summarized as A ->* bc -
Derive n + n * n using G2
답변이 yes면 만들 수 있다, no면 만들 수 없다.
If E ➔ n + n n is possible(at least one path to produce the string), then
we say that “string n + n * n can be derived from E using G2” or n + n *
n ∈ L(G2)

grammacty collectly 하다! -
Parse Tree from n+n*n using G2
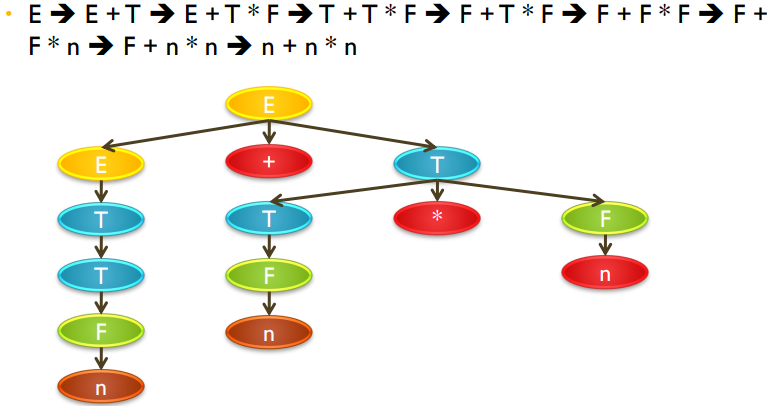
순차과정은 Top down, 역순은 Bottom up
- Terms for Grammar and Derivation Methods
- non terminal -> terminal로 만들어야함
- Rightmost derivation (Bottom up) vs. Leftmost derivation (Top down : start symbol 부터 시작함.)
Rigghtmost : 오른쪽부터 없애는 것 위 예시 그림 - Ambiguous grammar
왼쪽부터랑 오른쪽부터랑 결과가 다를때 쓸모가 없음 (트리가 달라지면)
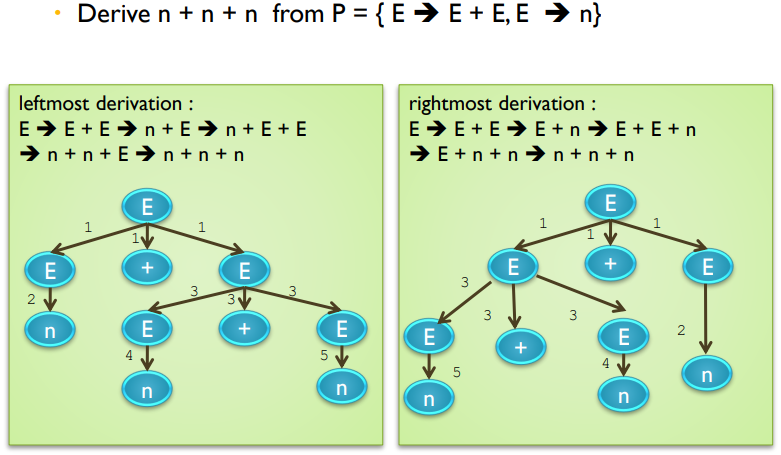
3-2-5 = 6 / 3-2-5=-4