Characteriscis of an algorithm
Input: the algorithm receives input
Output: the algorithm produces output
Precision: the steps are precisely stated
Determinism: the intermediate results of each step of execution are unique and qre determined only by the inputs and the results of the preceding steps
Finiteness: the algorithm terminates; i.e., it stops after finitely many instructions have been executed
Generality: the algorithm applies to a sets of inputs
Analysis of Algorithms
Q. What is useless program?
A. time/space->too great
[Types of complexity]
- Best-case time: minimum time needed to execute the algorithm for inputs of size n
- Worst-case time: maximum time needed to execute the algorithm for inputs of size n
- Average-case time
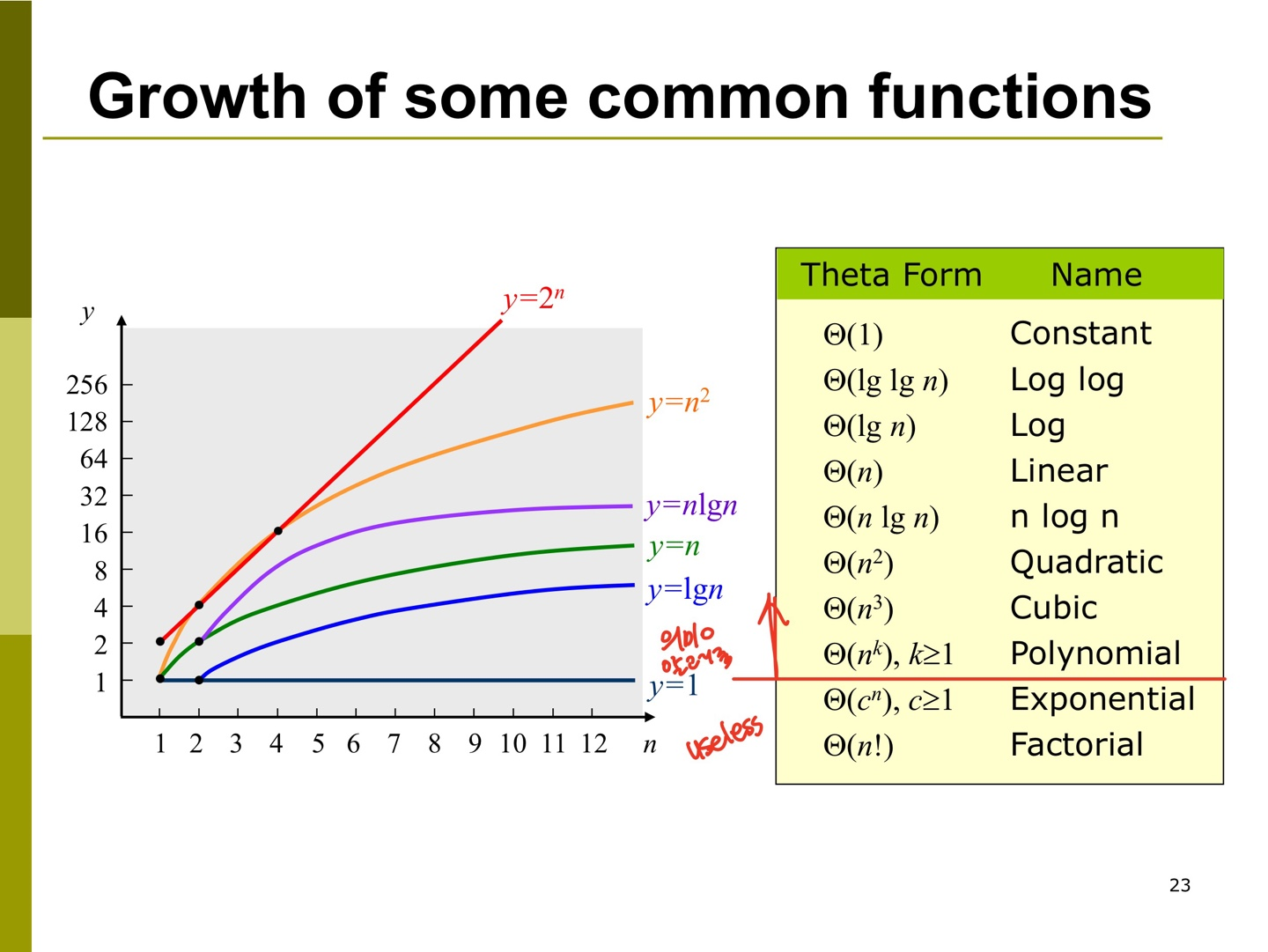
[Order of an algorithm]
1. f(n) = O(g(n))
:f(n) is of order at most g(n) or f(n) is big oh of g(n)
:asymptotic upper bound for f
2. f(n) = Ω(g(n))
:f(n) is of order at list g(n) or f(n) is omega of g(n)
:asymptotic lower bound for f
3. f(n) = Θ(g(n))
:f(n) is of order g(n) or f(n) is theta of g(n)
:asymptotic tight bound for f
출처) 이화여자대학교 이미정 교수님 이산수학 강의
