"Sorting" shows the biggest difference in efficiency by algorithm.
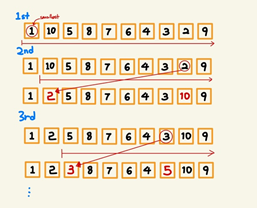
Because this is the first time we study algorithm, let's see the intuitive one though it is not effective.
Send the smallest number to the front.
[tips]
Using your hand and writing on the paper is the best way to study algorithms.
Wrong Answer
At first, I wrote the wrong codes that didn't satisfy the word "selection".
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
int Array[8] = {10, 5, 2, 4, 3, 9, 1, 7};
int len = 8;
int i, j, min, temp;
for(i=0 ; i<len-1 ; i++){
min = Array[i];
for(j=i ; j<len ; j++){
if(min>Array[j]){
temp = min;
min = Array[j];
Array[j] = temp;
}
}
}
for(int i=0 ; i<8 ; i++)
printf("%d", Array[i]);
return 0;
}This is more like "bubble" sorting.
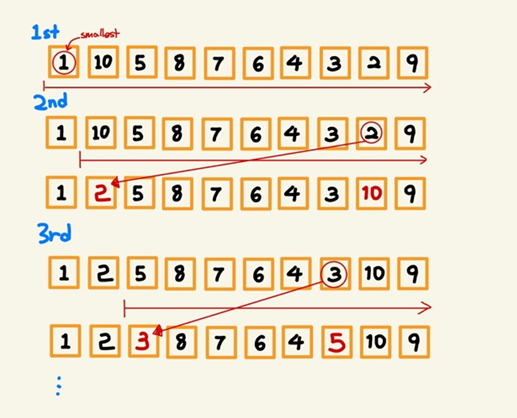
Let's see the right one.
Right Answer
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
int i, j, min, index, temp;
int array[10]={1, 10, 5, 8, 7, 6, 4, 3, 2, 9};
for(i=0 ; i<10 ; i++){
min = 9999; //the number that bigger than the number in array
for(j=i ; j<10 ; j++){
if(min>array[j]){
min = array[j];
index = j;
}
}
//swap
temp = array[i];
array[i]= array[index];
array[index]=temp;
}
for(i=0 ; i<10 ; i++){
printf("%d", array[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Time Complexity
10 + 9 + 8 + 7 + … + 1 → arithmetical sequence
= 10(10+1)/2
= n(n+1)/2 = O(n^2)
참고: 유튜브 동빈나