knative의 serving을 사용하면서 궁금증
-
이걸 찾아본거는 serverless 어플리케이션을 만들면 내부적으로 knative의 service에서는 어떤 server를 사용하는걸까?
-
Autoscaled은 어떤 순서로 되는것일까?
1. Knative Serving에서 내부 Server는 어떤걸 사용할까?
- 내부적으로 Opensource를 사용하여 개발되었을거라 생각하고 Github을 찾아봤다.
- 근데 knative에서 사용하는 activator, autoscaler에서도 server를 사용하기 때문에 어디에서 serverless server를 생성하는지 좀 더 찾아봐야 했다...
- http, grpc차이만 조금 있지 knative, servless에 사용되는 server도 go의 server로 개발하여 사용하는것을 확인했다.
- 그럼 어디에서 serverless server를 생성하는것일까?
- 일단!!! src/net/http/server.go를 사용하는 것을 찾았다.
- http server를 직접 생성하여, docker image를 만들어 knative service로 배포하는 코드기 있었다.
- https://github.com/knative/serving/blob/d5d489c0babd5c9ae9a37d707c06df92d70711f5/test/test_images/hellohttp2/service.yaml
- 이것은 serverless를 사용하는것이 아니라 knative의 주변기능들을 응용하는 방법이다. 주변기능이라하면 autoscale, canary등을 사용할 수 있을것 같다.
- kfserving도 이런식으로 구현이 되어 있는것같다.
- 예전에 kfserving 코드를 봤을때, tonado를 사용한 server구현이 되어 있었던 기억이 난다.
- 이것은 serverless를 구현하는 예제로 handler를 만들어서 serverless로 구성하는 코드로 따라가보니
- network package에서 server를 만드는게 있었다.
- 근데...이거는 예제일 뿐이다.
- https://github.com/knative/serving/blob/d5d489c0babd5c9ae9a37d707c06df92d70711f5/test/test_images/helloworld/helloworld.go
- http server를 직접 생성하여, docker image를 만들어 knative service로 배포하는 코드기 있었다.
- 근데 knative에서 사용하는 activator, autoscaler에서도 server를 사용하기 때문에 어디에서 serverless server를 생성하는지 좀 더 찾아봐야 했다...
1. func main() {
flag.Parse()
log.Print("Hello world app started.")
test.ListenAndServeGracefully(":8080", handler)
}
2. // ListenAndServeGracefully calls into ListenAndServeGracefullyWithPattern
// by passing handler to handle requests for "/"
func ListenAndServeGracefully(addr string, handler func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request)) {
ListenAndServeGracefullyWithHandler(addr, http.HandlerFunc(handler))
}
3.
// ListenAndServeGracefullyWithHandler creates an HTTP server, listens on the defined address
// and handles incoming requests with the given handler.
// It blocks until SIGTERM is received and the underlying server has shutdown gracefully.
func ListenAndServeGracefullyWithHandler(addr string, handler http.Handler) {
server := pkgnet.NewServer(addr, handler)
go server.ListenAndServe()
<-signals.SetupSignalHandler()
server.Shutdown(context.Background())
}
4.
// NewServer returns a new HTTP Server with HTTP2 handler.
func NewServer(addr string, h http.Handler) *http.Server {
h1s := &http.Server{
Addr: addr,
Handler: h2c.NewHandler(h, &http2.Server{}),
}
return h1s
}
5. $http.Server는 위에 설명한 go의 src/net/http/server.go를 사용하여 server를 만드는 것이였다.
-
실제로 activator, autoscaler, revision쯤에서 serverless에 사용되는 server를 생성하는게 있을거 같은데...
- 더이상 찾아 보진 않았다. 나중에 시간나면 찾아 보는걸로...
- 혹시 아시는분은 댓글과 코드 위치를 달아주시면 감사염~
-
그리고 statserver, profileserver등이 있었다.
-
참고로 위에 사용한 http server와 grpc server를 만들때 사용되는 기본코드 이다.
func NewServer(addr string, h http.Handler) *http.Server {
h1s := &http.Server{
Addr: addr,
Handler: h2c.NewHandler(h, &http2.Server{}),
}
return h1s
}- grpc server
// NewServer creates a gRPC server which has no service registered and has not
// started to accept requests yet.
func NewServer(opt ...ServerOption) *Server {
opts := defaultServerOptions
for _, o := range opt {
o.apply(&opts)
}
s := &Server{
lis: make(map[net.Listener]bool),
opts: opts,
conns: make(map[transport.ServerTransport]bool),
services: make(map[string]*serviceInfo),
quit: grpcsync.NewEvent(),
done: grpcsync.NewEvent(),
czData: new(channelzData),
}
chainUnaryServerInterceptors(s)
chainStreamServerInterceptors(s)
s.cv = sync.NewCond(&s.mu)
if EnableTracing {
_, file, line, _ := runtime.Caller(1)
s.events = trace.NewEventLog("grpc.Server", fmt.Sprintf("%s:%d", file, line))
}
if s.opts.numServerWorkers > 0 {
s.initServerWorkers()
}
if channelz.IsOn() {
s.channelzID = channelz.RegisterServer(&channelzServer{s}, "")
}
return s
}
2. Autoscale 순서
- 전체 흐름도는 아래와 같다.
- 너무 복잡하다....
- 아래는 요청 Data plane을 굵은 선으로 표시되어 있으며 나머지는 실제 아래 그림처럼 구성이 되기위해서 모듈간 Control plane이라고 볼수 있다.
- 대충 데이터 흐름은 Ingress -> public service ->Pod로 전송되는 것이지만 내부적으로 istio Ingressgateway -> virtual service (destination) -> service -> pod 등의 절차로 볼수 있으며, pod로의 traffic결정은 configuration, revision, route등의 값으로 정해지는것이다.
- Control plane은 더 아래서 설명하겠다.
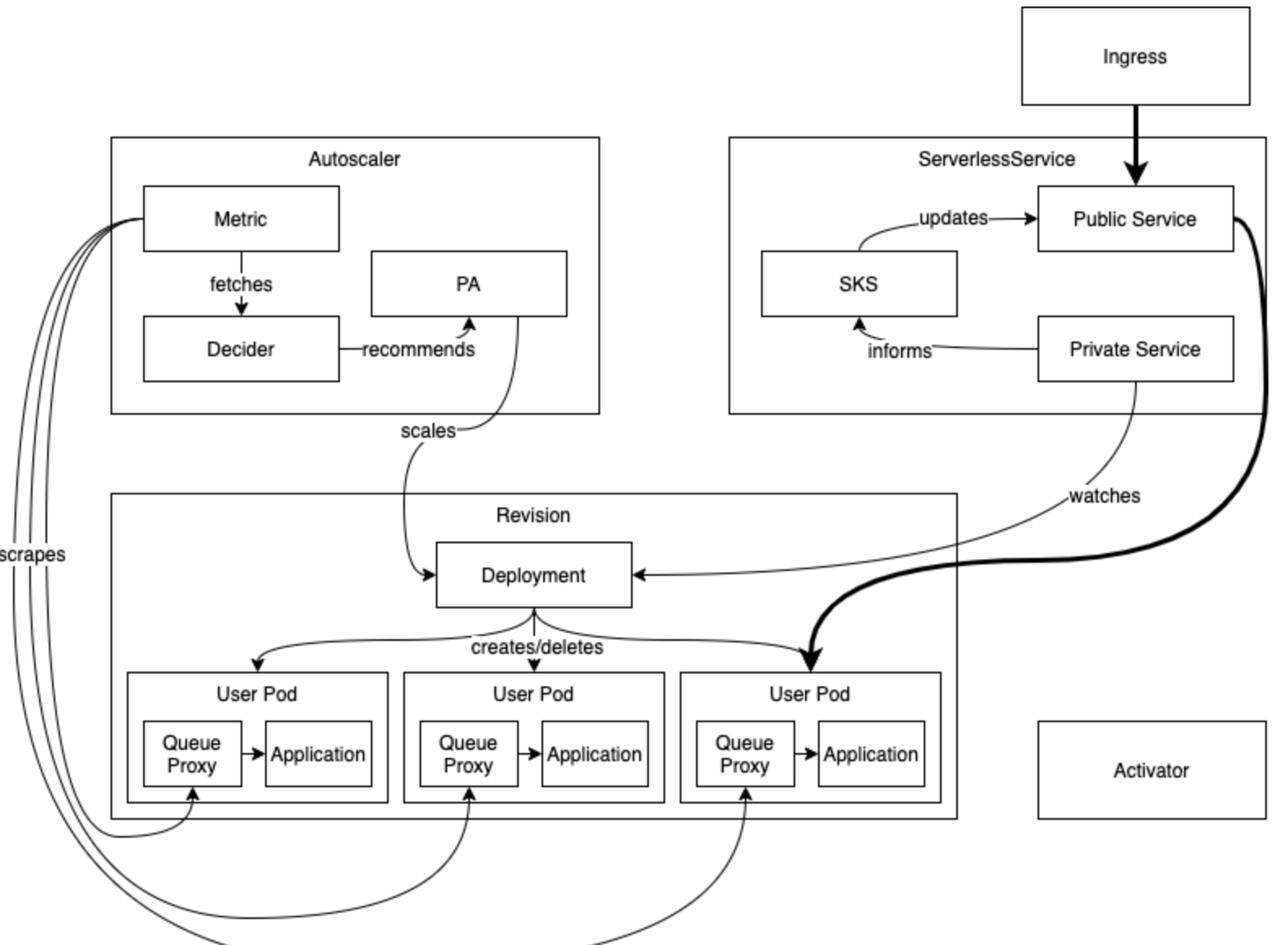
- pod가 0에서 autoscale이 되어 생성되면서 요청을 받는 과정
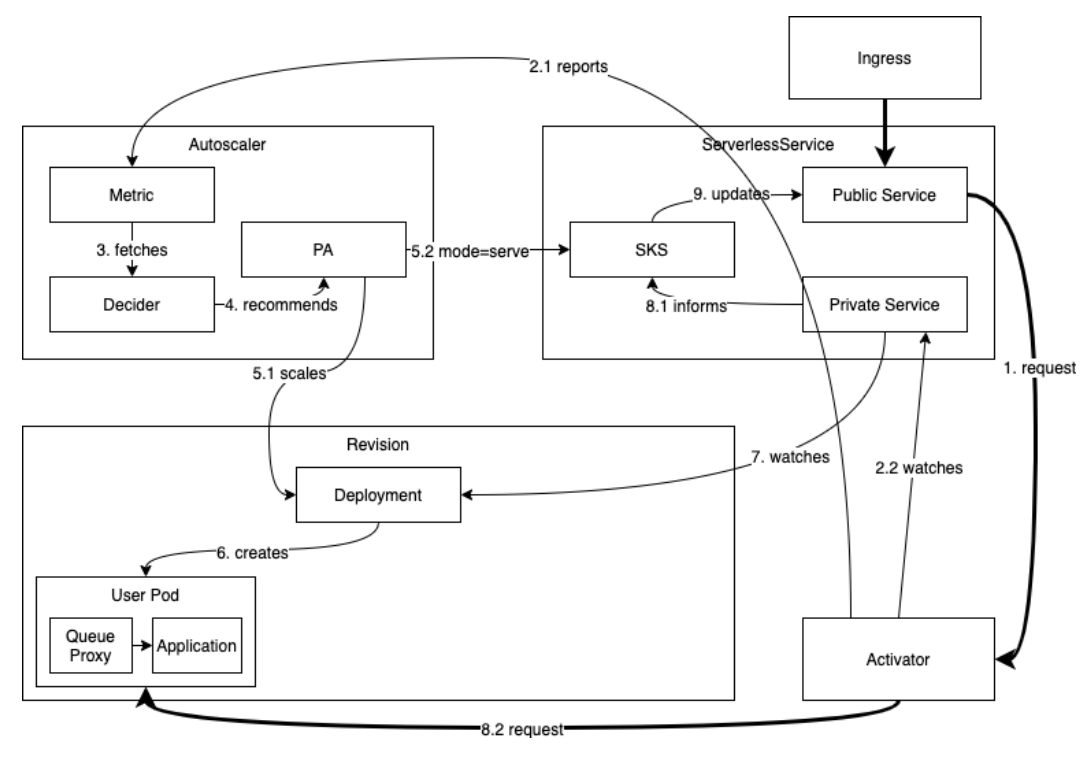
- 전제 상태로 보면, SKS는 proxy모드에 있다.
- Ingress로 요청이 들어온다. - 그림 0
- 요청은 Activator로 전달된다. - 그림 1
- 요청의 수가 Autoscaler로 리포팅된다. - 그림 2.1
- 요청은 Activator의 buffer에 담겨 있고, SKS의 private service를 watch하여 Endpoint가 생성되는것을 지쳐보고 있다. - 그림 2.2
- Autoscaler는 Activator에서 온 count를 보고 Decider와 PA(Pod Autoscale)를 사용하여 Revision Deployment를 생성하고(scale up N>0), SKS의 mode를 serve로 변경한다. - 그림 3,4,5.1,5.2
- Deployment는 Pod를 생성한다. - 그림 6
- Deployment, Pod가 생성되면 내부적으로 Endpoint가 생성되는데, SKS Private service는 Deployment를 watch하고 있어서, Endpoint가 생성된것을 알수 있다. 이를 확인하여 SKS에게 알려준다. - 그림 7, 8-1
- Activator는 SKS의 private service를 watch(5)하고 있었기때문에 Endpoint가 생성된것을 확인하고, probe(liveness, readiness) healthy를 테스트해본다.그리고 buffer에 있던 요청을 해당 pod로 보낸다.
- pod에 요청이 없을때, Scaling이 0이 되는 과정
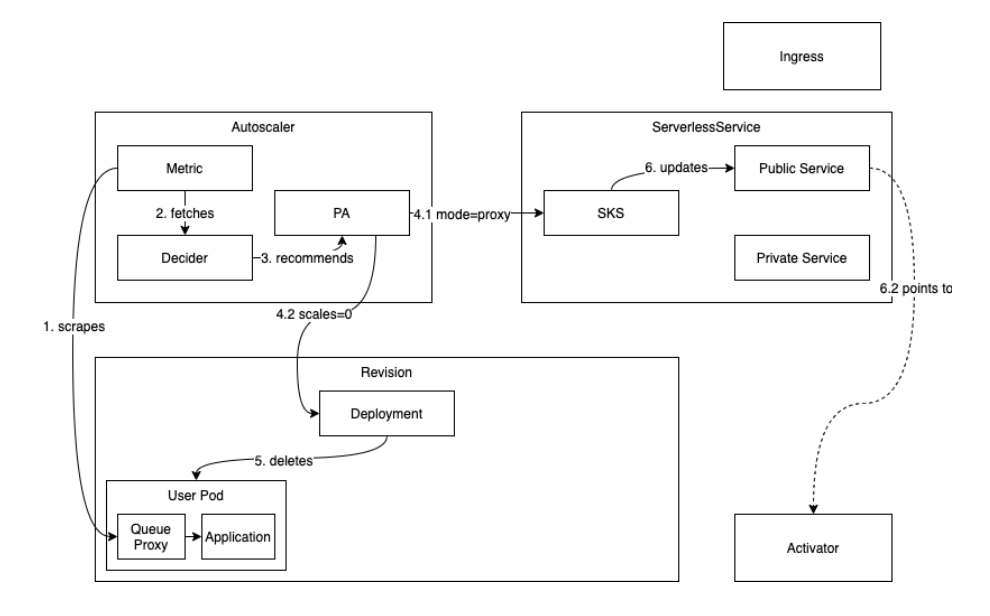
- 요청이 일정시간 발생하지 않으면 클러스터 리소스사용을 없애기위해서 이런처리를할 수 있다.
- pod안에는 Queue proxy컨테이너가 있는데 여기서 현재 요청받는게 없다는 것을 Autoscaler의 metric에 알려준다. - 그림 1
- Metric은 Decider를 통해 PA(Pod Autoscaler)에 이 상황을 알려준다. - 그림 2, 3
- PA에서는 SKS의 mode를 proxy로 변경을 알려주고, Revision의 Deployment Scale을 0으로 변경한다. - 그림 4.1, 4.2
- Revision의 Deployment는 Pod를 모두 삭제한다. - 그림 5
- 그리고 SKS의 Public Service는 Activator를 바라보며, 새로운 요청이들어오면 Activator로 보낼수 있는 상태를 만든다.
