자료구조 (Data Structure)란 무엇인가?
코딩 개발을 하는데 앞서 가장 기초적인 개념이 아마 자료 구조(Data Structure) 일거 같은데요. 컴퓨터 공학과 조금이라도 관련된 학과들은 아마도 모두 자료구조론이라는 수업이 커리큘럼에 포함되어 있을 거에요. 이는 좋은 알고리즘(Algorithm) 의 코드를 작성하는데 초석이 되는 개념들이기 때문에 꼭 숙지하고 있어야 할 개념이랍니다.
자료 구조 는 처리하고자 하는 대상 데이터의 표현방법과 이들을 메모리에 저장하기 위한 저장법 및 자료간의 관계와 자료의 응용을 쉽고 정확하고 빠르게 수행하기 위한 알고리즘 연구의 기본대상으로 여러 가지 형태로 정의할 수 있는 처리 관점의 데이터 형식 을 의미해요.
여기서 자료란 일종한 규칙에 의해 재정의될 수 있는 단순한 데이터로서 현실 세계로부터 단순한 관찰이나 측정 및 수집에 의해서 취할 수 있는 사실이나 개념의 값이나 값의 집합을 뜻해요. 정보는 단순한 자료를 정의된 규칙에 따라 컴퓨터에 의해 처리되어 결과로써 의미를 가지는 자료 형태를 말한답니다.
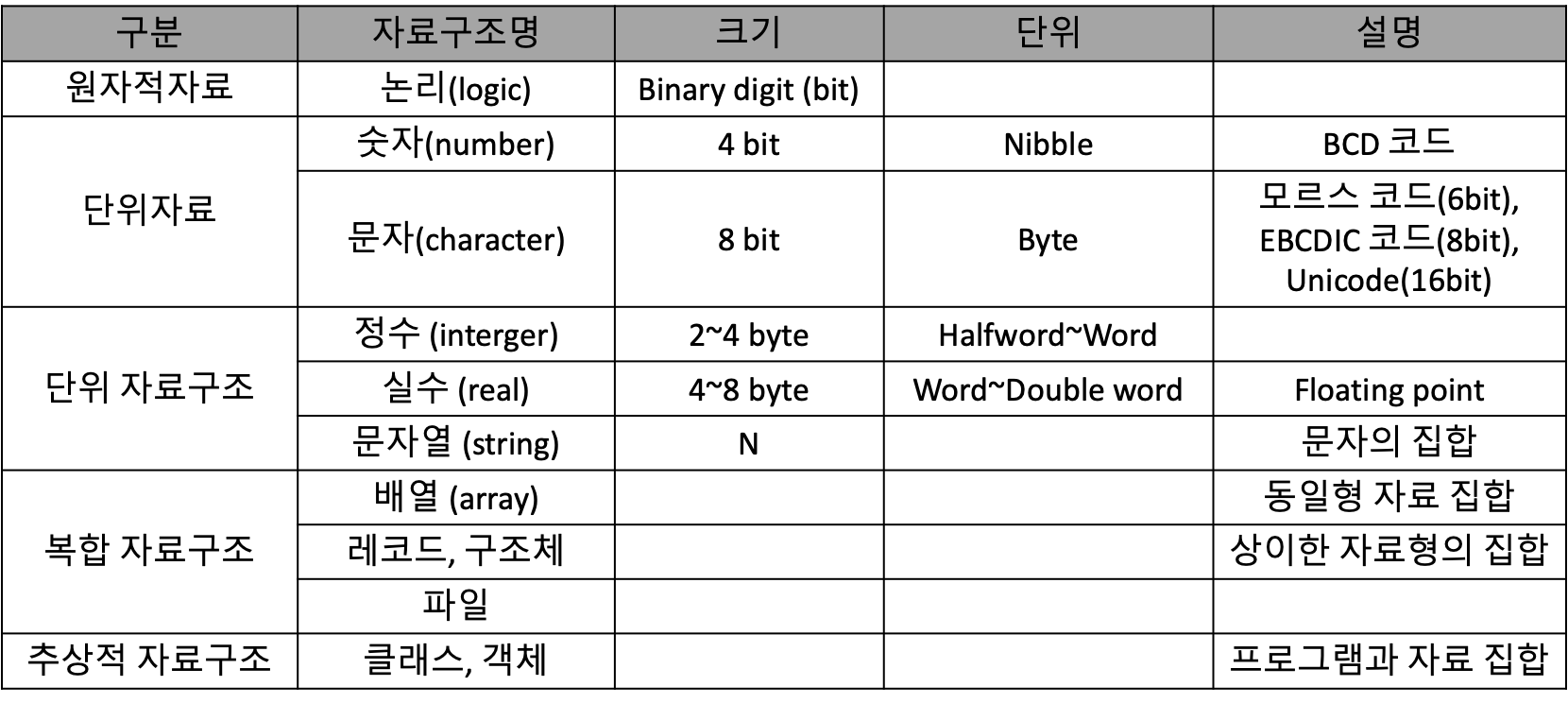
이러한 자료는 표현하고자 하는 대상 정보를 위해 내부의 전기적인 신호들이 어떻게 집합을 형성하는지의 형태에 따라 여러 종류의 명명단위로 구분돼요.
비트(bit: Binary Digit): 0(0V) 또는 1(+5V)로 표현되는 자료표현 및 저장의 최소 단위. n 비트에 대한 표현 가능한 정보의 개수는 2^n개이다.
니블(Nibble): 4bit로 구성되는 자료크기이며, 16진수 1자리 표현
바이트(Byte): 8bit로 구성되는 자료이며 ASCII(컴퓨터 내부의 표준 문자값) 문자 표현의 기본단위이며, 메모리 주소를 부여하는 기본단위
워드(Word): 기억장치별 사용정보의 단위이며 half word(2byte), full byte(4byte), double byte(8byte)가 있음
항목(field or item): 레코드를 구성하는 논리적 단위
레코드(record): 연관성 있는 자료 항목들의 집합이며 자료 처리의 단위. 응용 프로그램 에서 사용자가 정의한 논리적 레코드와 저장 매체에서 실제 입출력되는 기본 단위인 물리적 레코드가 있음
파일(file): 연관된 레코드의 집합
데이터베이스(database): 파일의 집합으로 중복된 데이터를 제거하여 다중의 목적을 위해 공유할 수 있도록 한 데이터 집합체
자료 구조 학습은 부과된 문제를 빠른 시간에 정확하고 효율적으로 해결하기 위해 프로그램에서 처리할 자료간의 논리적인 연관성을 분석하여 가장 적합한 기억장소 표현법과 접근 방법을 선택하는 것이며 선택된 자료를 빠르고 효율적으로 처리하기 위한 알고리즘을 개발하는데 목적이 있어요.
자료 구조 선택 기준
1. 프로그램에서 요구되는 기억 장소의 크기
2. 자료처리에 소요되는 처리 시간 (속도)
3. 프로그램 유지 및 보수의 용이성
4. 프로그램 구현의 용이성
5. 기억 장치 운영 방식
알고리즘
알고리즘 은 효과적인 업무수행을 위해 정의된 유한 집합과 운영형태를 말하며, 컴퓨터에 의한 자료처리 과정을 단계별로 기술한 것이에요. 이는 어떤 프로그램 언어를 선택하기에 앞서 원활한 프로그램 구현을 위한 정규형식의 운영형태를 의미하죠. 그리고 프로그램 은 이러한 알고리즘의 추상적 개념을 구체적으로 구현한 것이라 볼 수 있어요.
프로그램에 의한 해 도출과정
1단계: 시스템 분석
2단계: 입, 출력 결정
3단계: 알고리즘 설계
4단계: 코딩
5단계: 실행 및 테스트
6단계: 디버깅
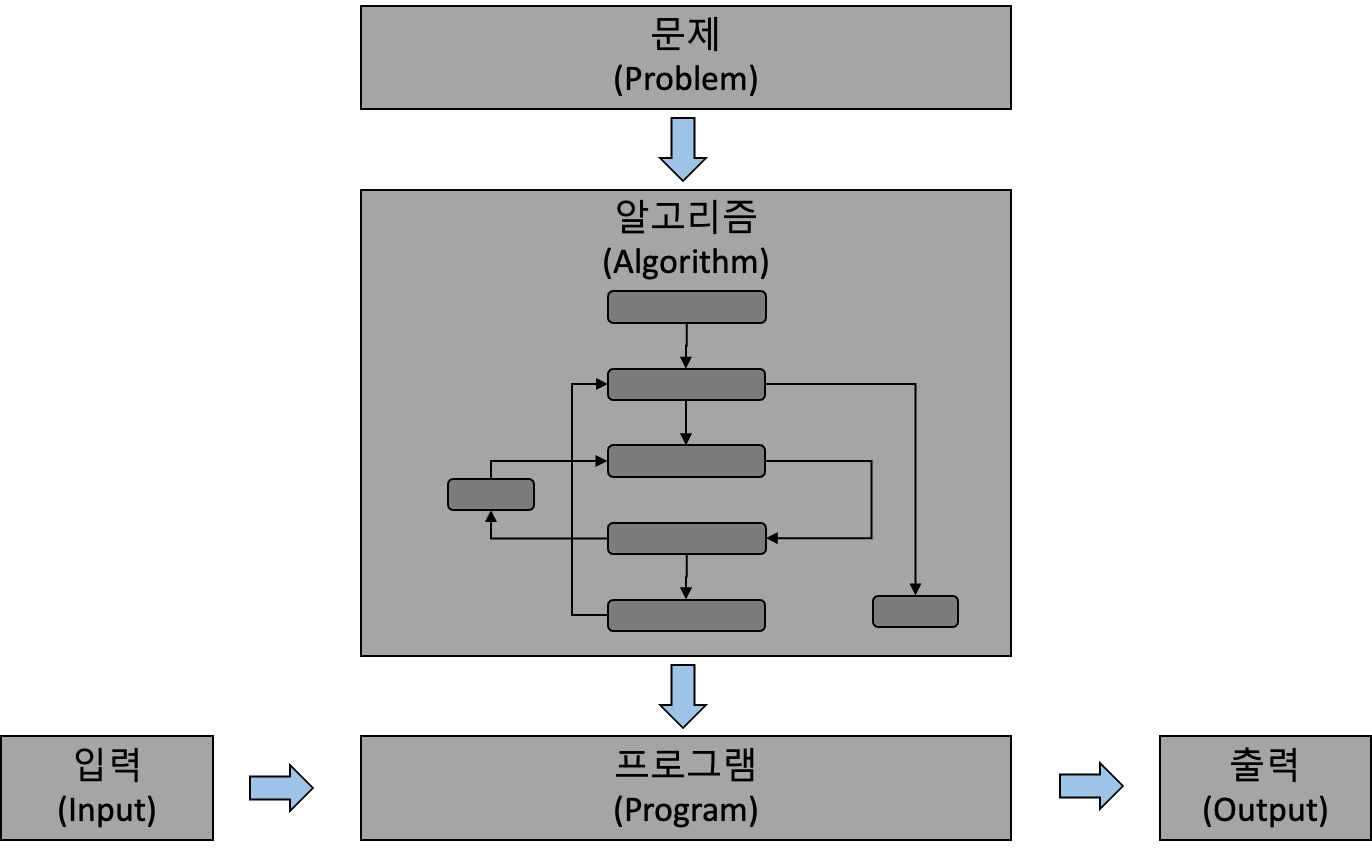
알고리즘에서 고려되어야 할 항목으로는 입력(Input), 출력(Output), 명확성(definiteness), 효과성(effectiveness), 종료성(termination)이 있어요.
알고리즘의 분석 및 복잡도 측정
효율적인 알고리즘 분석 기준
정확도(Correctness): 오류없이 정상적으로 동작하는지 정도를 분석하는 기준
단순성(Simplicity): 알고리즘의 가독성, 수정의 용이성 여부를 분석하는 기준
복잡도(Complexity): 결과 산출시점까지의 계싼 시간과 기억 장소 사용향을 분석하는 기준
복잡도 분석 방법
시간복잡도: 어떤 알고리즘이 얼마나 걸리느냐 (CPU 사용량)
공간복잡도: 어떤 알고리즘이 메모리를 얼마나 쓰느냐 (RAM 사용량)
시간 복잡도(time complexity)는 수행 속도(computation time) 측면의 복잡도이며 제어구문에 의해 알고리즘 속에 있는 각 문장이 반복 실행되는 비노수를 기준으로 측정해요.
시간 복잡도 중요 시간
1 (constant): 입력 자료의 수에 관계없이 일정한 실행시간
log N: 입력 자료의 수에 의해 실행시간 증가. 큰 문제를 일정한 크기로 반복적으로 줄여나가며 해를 찾는 방법에서 나타남
N (linear): 입력 자료의 수에 따라 선형적인 실행 시간이 소요. 각각의 입력 자료에 일정량의 시간이 할당되는 경우
N log N: 큰 문제를 일정한 크기를 갖는 문제로 분리하고(log N), 다시 하나로 모으는(N) 반복적인 방법에서 나타남
N^2: 이중의 중첩 루프에서 입력 자료를 처리할 때 발생
N^n: n중의 중첩 루프에서 입력 자료를 처리할 때 발생
시간 복잡도 표현
Big O - O(N) : 실행 시간 상한
Ω - Ω(N) : 실행 시간 하한 표현
θ - θ(N) : 실행 시간 평균 표련
// 복잡도 분석의 예
for (let i = 1; i < n i ++) { // (n - 1) 번
for (let j = 1; j <= n; j ++) { // n(n - 1) 번
...
}
}자료구조의 분류
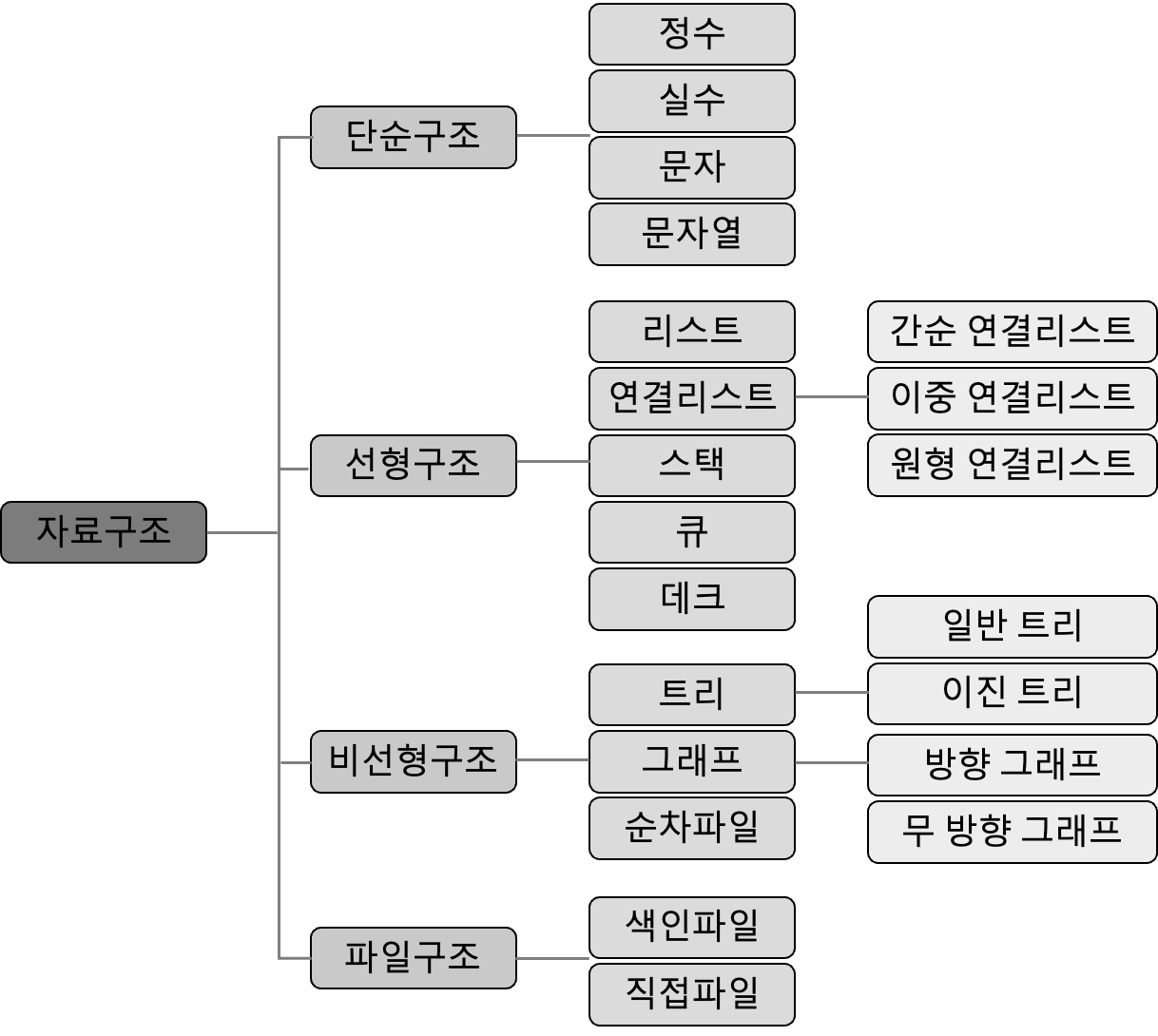
배열 (Array)과 레코드 (Record)
배열 과 레코드 는 여러 개의 데이터를 메모리에 연속적인 저장공간에 할당하는 자료형이에요. 배열은 같은 자료형을 가지는 원소로 구성되며 레코드는 서로 상이한 자료형의 집합에 의해 구성돼요. 레코드는 구성 항목, 필드의 이름으로 구성원을 접근하고, 배열은 배열의 첨자나 인덱스에 의해 자료를 접근한답니다.
배열은 같은 자료형을 갖는 여러 항목들을 하나의 식벽자(변수) 이름으로 구성하여 메모리에 연속적으로 저장하여 인덱스에 의해 접근하는 자료구조에요.
1차원 배열
1차원 배열 A의 표현
표현법: A(1:n)
배열의 i 번째 요소: A[i]
주소 계산: 첫번째 주소를 X, 원소의 길이를 length라 하면 i 번째 원소의 저장 장소 위치는 X + (i-1)length

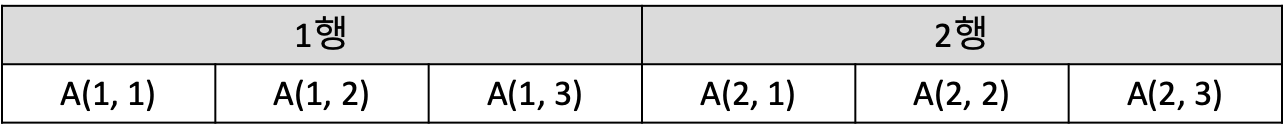
2차원 배열
표현법: A(1:u1, 1:u2)

행 우선 순서 - A(m, n)으로 정의된 2차원 배열
주소 계산: A = A(1, 1)의 주소라면 A(i, j)의 주소는 A + n(i - 1) + j
순서 위치: A(i, j)의 순서 위치는 n(i - 1) + j
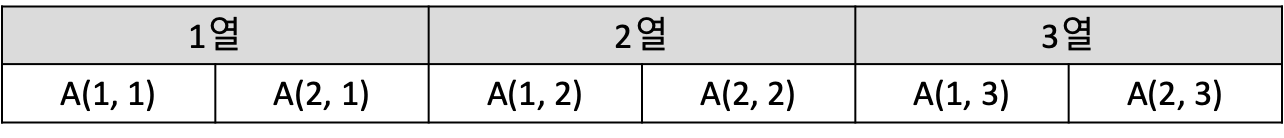
열 우선 순서 - A(m, n)으로 정의된 2차원 배열
주소 계산: A = A(1, 1)의 주소라면 A(i, j)의 주소는 A + m(j - 1) + i
순서 위치: A(i, j)의 순서 위치는 m(j - 1) + i
리스트 (List)
리스트는 원소의 집합을 말하여, 선형 리스트 와 연결 리스트 가 있어요.
선형 리스트 (Linear List)
선형 리스트 는 배열과 동일하므로 포인터가 없어도 리스트 시작으로부터 상대적인 위치를 계산하여 임의의 노드에 접근이 가능해요. 그리고 메모리에 연속적으로 저장이 되기 때문에 접근이 용이하고 연산 속도가 빠르죠. 또한 기억 공간에 대한 저장밀도가 높아서 낭비되는 기억 공간이 없어요.
다만 자료 저장시에 요구 크기 만큼의 연속적인 메모리 공간이 없을 경우, 저장이 불가능해요. 여기서 만약 배열에 존재하는 임의의 데이터를 삽입 또는 제거한다면, 자료의 메모리 이동횟수가 많아지죠. 밑에 그림을 예로 봅시다.
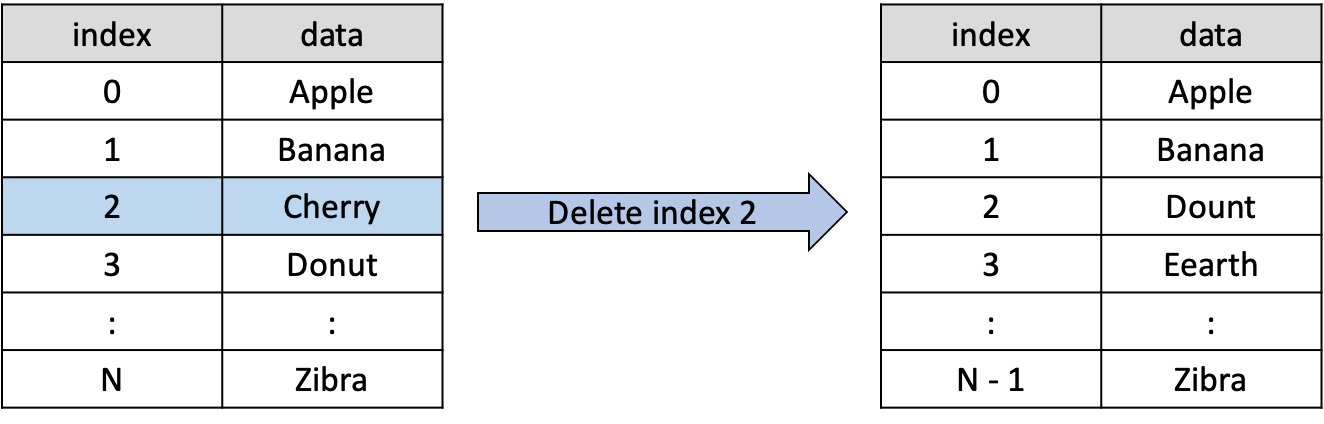
만약 위와 같은 리스트에서 인덱스 2의 'Cherry'를 삭제한다면, 그 뒤의 인덱스에 존재하는 'Donut'이 인덱스 2로 옮겨지고 나머지 노드들도 연속적으로 앞 인덱스로 이동해요.
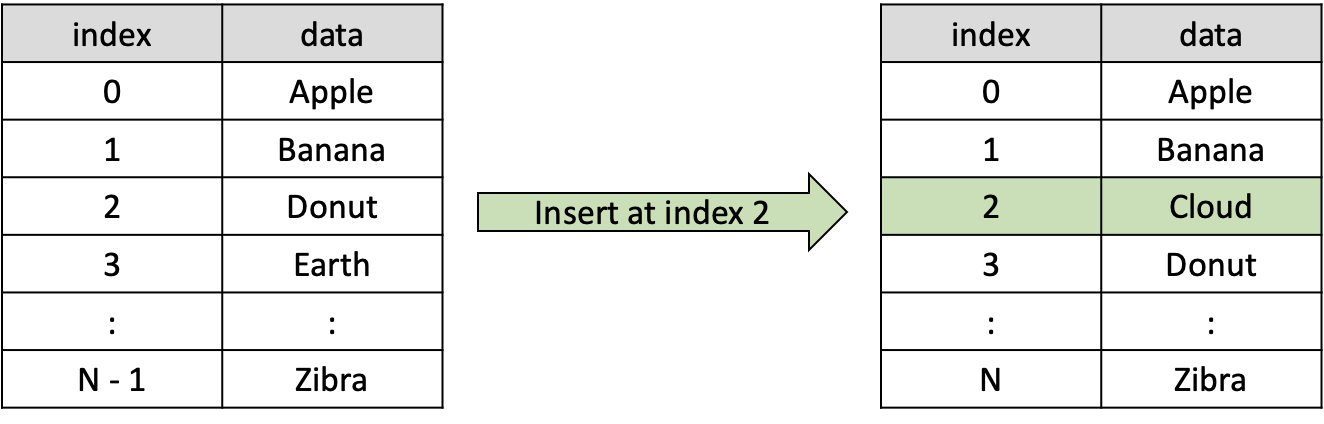
반대로 인덱스 2에 새로운 자료인 'Cloud'를 넣는다면, 'Donut'은 그 뒤의 인덱스로 이동하고 나머지 노드들도 한칸 씩 뒤로 이동하죠.
즉 선형 리스트에서 삽입과 삭제는 연산시간 을 회당 n만큼 소요하고, 노드의 개수가 많아질수록 큰 부담으로 작용하게 돼요. 또한 연산의 빈도수가 높을 경우 기존의 배열의 순열이 유지되어야 하기 때문에 메모리 내에서 배열을 구성하는 요소의 위치 이동이 많아지는 단점이 발생해요.
삽입 조작 후 자료의 평균 이동 횟수: (n + 1) / 2
삭제 조작 후 자료의 평균 이동 횟수: (n - 1) / 2
크기가 n인 배열에서 삽입, 삭제 조작의 연산 시간: x * (n)
연결 리스트 (Linked List)
연결 리스트 는 자료항목이 메모리의 연속적인 저장공간에 위치하지 않아도 되는 자료구조에요. 데이터의 논리적인 순서가 저장구조인 물리적인 순서와 상이할 수 있으며, 임의의 위치에 자료항목을 삽입 및 삭제할 수 있죠. 이를 위해서는 자료항목마다 다음 항목의 위치 지정을 위한 링크정보를 추가로 유지해야 해요. 때문에 링크정보(포인터) 를 위한 추가적인 기억 공간이 필요하고 포인터 해석을 위한 연산시간이 추가로 수반된답니다.
단순 연결 리스트 (Simple Linked List)
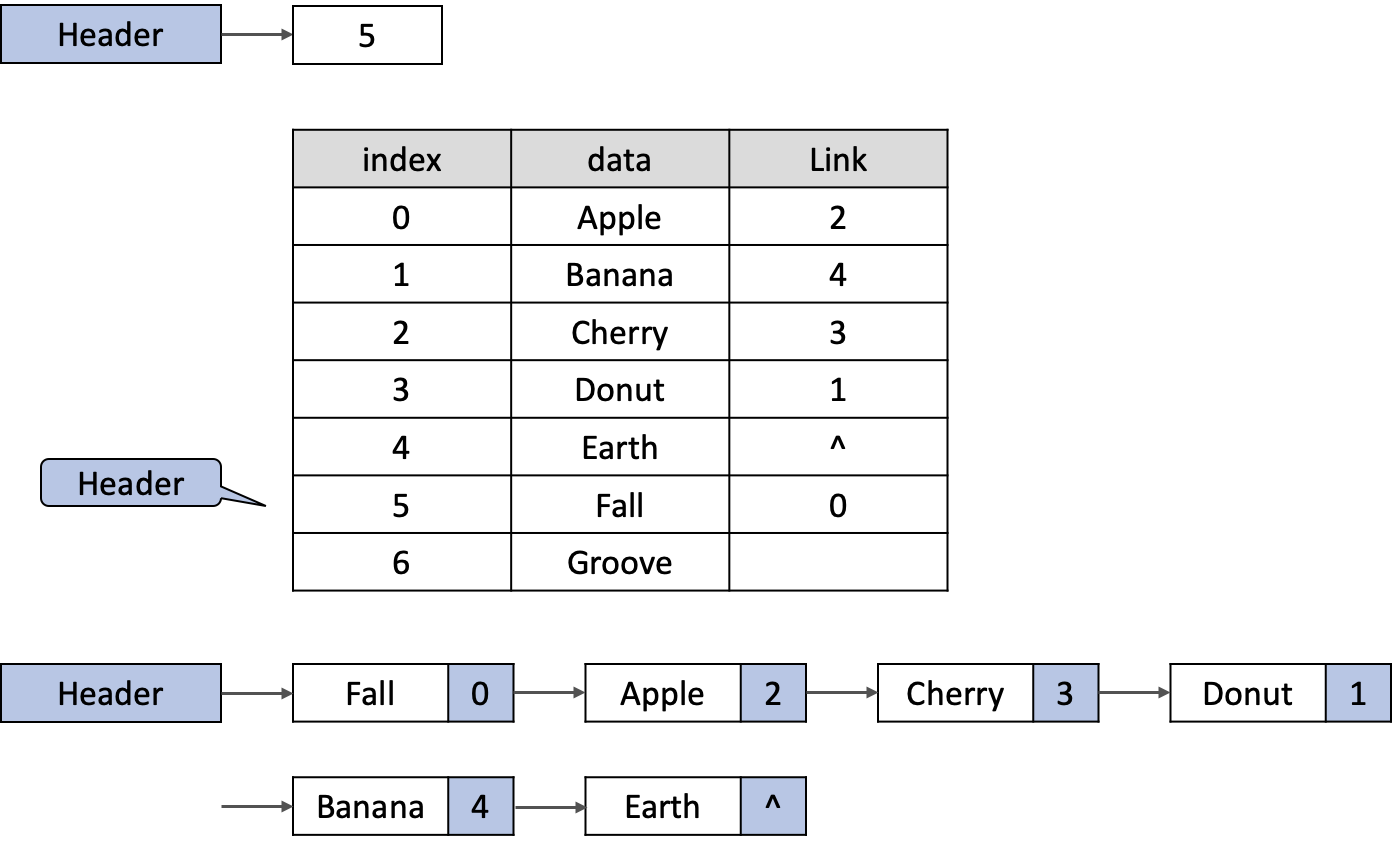
단순 연결 리스트 는 리스트를 구성하는 자료항목은 데이터 필드에 저장하고, 원소간의 순서를 나타내기 위해 연결 필드를 사용해요. 연결리스트의 시작번지를 header 정보로 유지하며 마지막 원소의 연결 부분은 null(^) 로써 리스트의 끝임을 명시합니다.
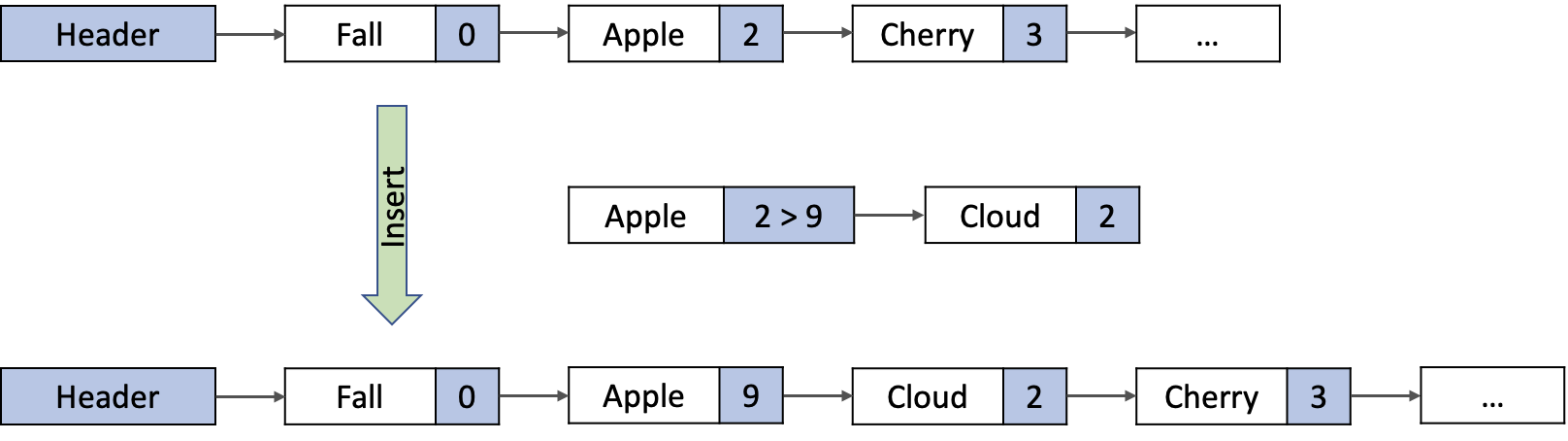
Apple 자료항목 이후에 Cloud를 추가하는 경우
1단계: 새 노드를 생성 new > Cloud(^)
2단계: 새 노드의 링크필드에 자신이 추가되는 이전항목의 링크필드를 복사한다.
3단계: 자신이 추가되는 이전항목의 링크필드에 자신이 위치한 메모리 주소를 복사한다.
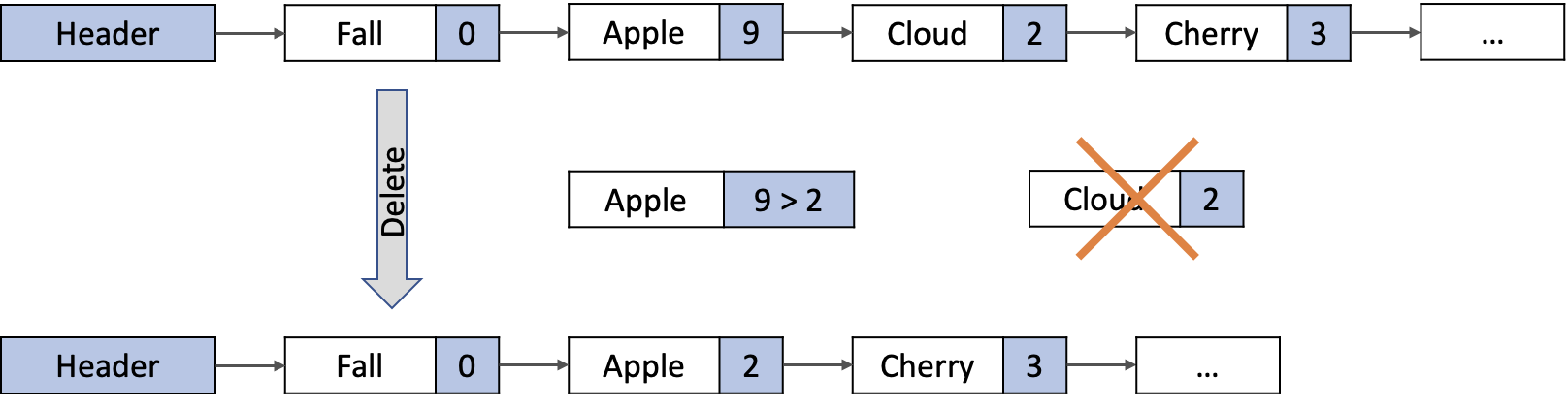
노드를 삭제하는 경우
1단계: 리스트에서 삭제할 노드를 선택한다.
2단계: 선행 노드의 링크필드에 삭제 대상 노드의 링크필드를 복사한다.
3단계: 삭제된 노드의 기억공간을 반환한다.
밑의 코드는 연결 리스트 를 자바스크립트 로 구현한 모습이에요.
// 단순 연결 리스트
function LinkedList() {
const Node = function(data, next) {
this.data = data; // 노드의 데이터
this.next = next;
}
let head = null; // 연결 리스트의 시작 노드 주소
let length = 0; // 연결 리스트의 데이터 수
// 연결 리스트의 front에 데이터 추가
this.insert = data => {
head = new Node(data, head); // Head 생성
length ++;
}
// 연결 리스트의 끝에 데이터 추가
this.append = data => {
if (head === null) {// 초기상태 자료 추가
this.insert(data);
} else { // 기존 자료 있을 경우 끝에 추가
let current = head;
while (current.next !== null) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = new Node(data, null);
length++;
}
}
// 연결 리스트의 특정위치(position)에 추가
this.insertAt = (position, data) => {
if (position > length || position < 0) {
console.log("Wrong place.");
return;
}
let count = 0, current = head;
const newNode = new Node(data, null) // 신규 노드 생성
if (position === 0) {
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
} else {
while (current !== null && count < (position - 1)) {
current = current.next;
count++;
}
newNode.next = current.next;
current.next = newNode;
}
length++;
}
// front의 항목 삭제
this.removeFromFront = () => {
if (this.isEmpty()) {// 연결 리스트가 비어 있는 경우
console.log("List is empty.");
return null;
} else {
const item = head.data;
head = head.next;
length--;
return item;
}
}
// 리스트의 끝에서 삭제
this.removeFromEnd = () => {
if (this.isEmpty()) { // 연결 리스트가 비어 있는 경우
console.log("List is empty");
return null;
} else { // 연결 리스트의 끝 요소 삭제
let prev = null, current = head;
while (current.next !== null) {
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
const item = current.data;
prev.next = null;
length--;
return item;
}
}
// 연결 리스트의 특정위치(position)에서 삭제
this.removeAt = position => {
if (position >= length || position < 0) {
console.log("Wrong place");
return null;
}
if (position === 0) { // 처음 노드 삭제
return this.removeFromFront();
} else {
let count = 0, prev = null, current = head;
while(current !== null && count < position) {
prev = current;
current = current.next;
count++;
}
const item = current.data;
prev.next = current.next;
length--;
return item;
}
}
this.remove = data => {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log("List is empty");
return null;
}
let prev = null, current = head;
while (current !== null) {
if (current.data === data) break;
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
if (current === null) {
console.log("Can't find data");
return null;
}
if (prev === null) { // 연결 리스트의 헤드에서 자료 찾음
return this.removeFromFront();
}
const item = current.data;
prev.next = current.next;
length--;
return item;
}
this.isEmpty = () => {
return head === null;
}
// 자료가 있으면 참, 없으면 거짓 변환
this.find = data => {
let node = head;
while (node !== null) { // 연결 리스트의 모든 노드 검색
if (node.data === data) {
return true;
}
node = node.next;
}
return false;
}
// 자료가 위치한 연결 리스트의 인덱스 반환
this.size = () => {
return length;
}
// 연결 리스틍 초기화
this.clear = () => {
head = null;
length = 0;
}
// 콘솔에 리스트의 모든 요소 출력
this.showAll = () => {
console.log("Data in linked list : ");
let node = head;
while (node !== null) {
console.log(node.data);
node = node.next;
}
console.log("--------------------");
}
}
// Test
const linkedList = new LinkedList(); // 리스트 생성
linkedList.insert(10); // front에 삽입
linkedList.insert(15); // front에 삽입
linkedList.showAll(); // 리스트 출력
linkedList.append(20); // end에 삽입
linkedList.append(50); // end에 삽입
linkedList.insert(5); // front에 삽입
linkedList.showAll(); // 리스트 출력
console.log("Number of list : " + linkedList.size());
linkedList.clear();
linkedList.insertAt(1, 10); // 리스트의 오류 위치에 삽입
linkedList.insertAt(0, 10); // front에 삽입
linkedList.showAll();
linkedList.insertAt(1, 2); // 리스트의 특정 위치에 삽입
linkedList.showAll();
linkedList.insertAt(1, 50); // 리스트의 특정 위치에 삽입
linkedList.showAll();
console.log(linkedList.find(2)); // 자료 검색
console.log(linkedList.find(100)); // 자료 검색
console.log("Removed Data : " + linkedList.removeFromFront()); // front에서 자료 삭제
linkedList.showAll();
console.log("Removed Data : " + linkedList.removeFromEnd()); // end에서 자료 삭제
linkedList.showAll();
console.log("Removed Data : " + linkedList.removeAt(1)); // end에서 자료 삭제
linkedList.showAll();
console.log("Removed Data : " + linkedList.remove(50)); // 특정 값의 요소를 삭제
linkedList.showAll();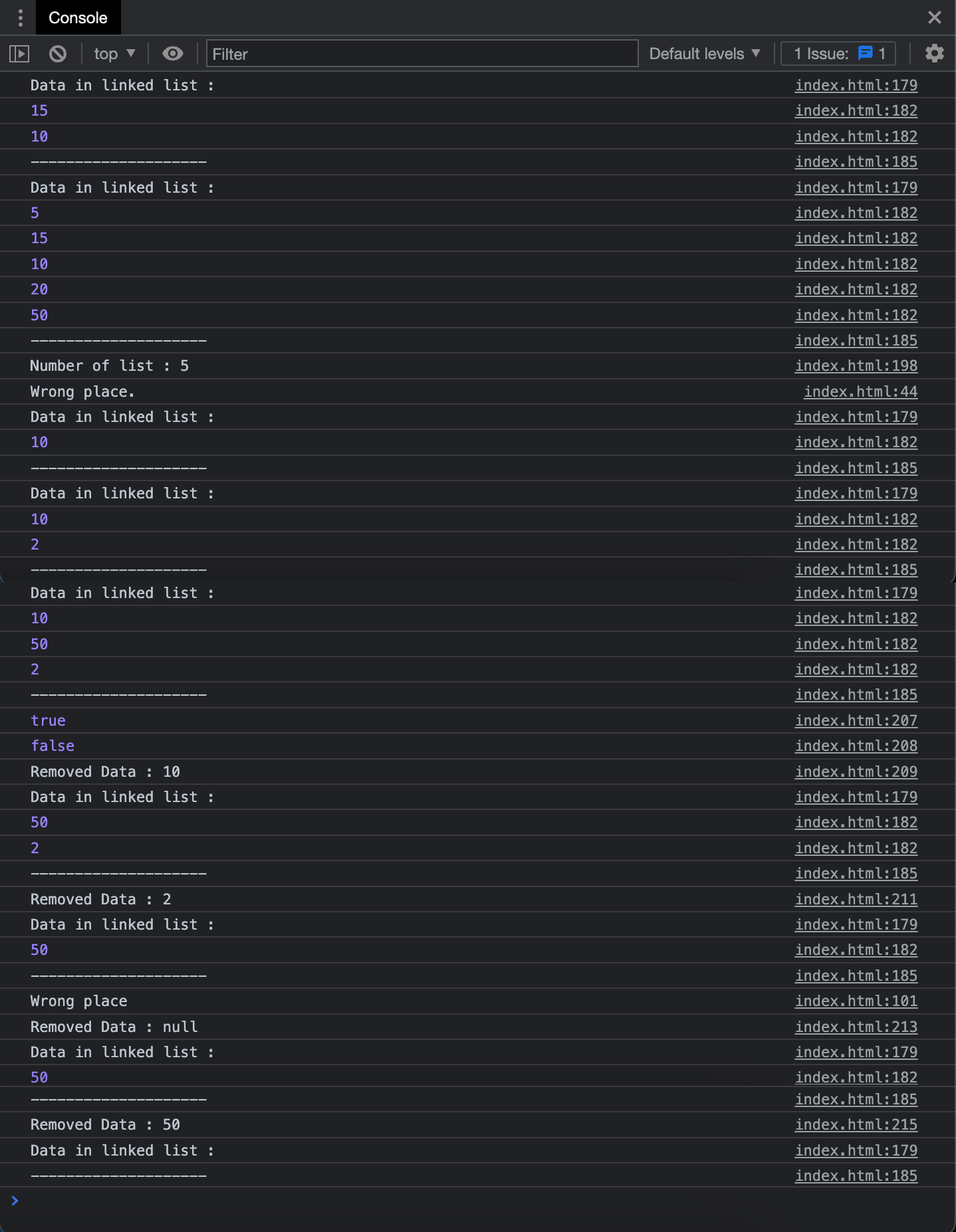
원형 연결 리스트 (Circular Linked List)
원형 연결 리스트 는 리스트의 마지막 항목의 링크 필드를 Null이 아닌 리스트의 Header 노드의 주소를 저장하도록 해요. 그래서 마지막 노드에서 검색을 종료하지 않고 다시 헤더 노드로부터 리스트 항목을 검사할 수 있도록 하죠.
// 원형 연결 리스트
function CircularLinkedList() {
const Node = function(data, next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
this.head = null;
this.length = 0;
this.insert = data => {
const newNode = new Node(data, null);
if (this.head === null) {
newNode.next = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next !== this.head) {
current = current.next;
}
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
current.next = this.head;
}
this.length++;
}
this.append = data => {
const newNode = new Node(data, null)
if (this.head === null) {
newNode.next = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next !== this.head) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
newNode.next = this.head;
}
this.length++;
}
this.insertAt = (position, data) => {
if (position > this.length || position < 0) {
console.log("Wrong place.");
return;
}
if (position === 0) {
this.insert(data);
} else if (position === this.length) {
this.append(data);
} else {
let count = 0, current = this.head;
const newNode = new Node(data, null);
while (count < (position - 1)) {
current = current.next;
count++;
}
newNode.next = current.next;
current.next = newNode;
this.length++;
}
}
this.removeFromFront = () => {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log("List is empty.")
return null;
} else {
const item = this.head.data;
if (this.length === 1) {
this.head = null;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next !== this.head) {
current = current.next;
}
this.head = this.head.next;
current.next = this.head;
}
this.length--;
return item;
}
}
this.removeFromEnd = () => {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log("List is empty.");
return null;
} else {
let item;
if (this.length === 1) {
item = this.head.data;
this.head = null;
} else {
let prev = null, current = this.head;
while (current.next !== this.head) {
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
item = current.data;
prev.next = this.head;
}
this.length--;
return item;
}
}
this.removeAt = position => {
if (position >= this.length || position < 0) {
console.log("Wrong place.");
return null;
}
if (position === 0) {
return this.removeFromFront();
} else if (position === this.length - 1) {
return this.removeFromEnd();
} else {
let count = 0, prev = null, current = this.head;
while (count < position) {
prev = current;
current = current.next;
count++;
}
const item = current.data;
prev.next = current.next;
this.length--;
return item;
}
}
this.isEmpty = () => {
return this.head === null;
}
this.find = data => {
let node = this.head, count = 0;
while (count < this.length) {
if (node.data === data) {
return true;
}
node = node.next;
count++;
}
return false;
}
this.size = () => {
return this.length;
}
this.clear = () => {
this.head = null;
this.length = 0;
}
this.showAll = () => {
console.log("Data in List : ");
let node = this.head, count = 0;
while (count < this.length) {
console.log(node.data);
node = node.next;
count++;
}
console.log("-------------")
}
}// Test
const linkedList = new CircularLinkedList();
linkedList.insert(10); // front에 삽입
linkedList.insert(15); // front에 삽입
linkedList.showAll(); // 리스트 출력
linkedList.append(20); // end에 삽입
linkedList.append(50); // end에 삽입
linkedList.insert(5); // front에 삽입
linkedList.showAll(); // 리스트 출력
console.log("Number of List : " + linkedList.size());
linkedList.clear();
linkedList.insertAt(1, 10); // 리스트의 오류 위치에 삽입
linkedList.insertAt(0, 10); // front에 삽입
linkedList.showAll();
linkedList.insertAt(1, 5); // end에 삽입
linkedList.showAll();
linkedList.insertAt(1, 2); // 리스트의 특정 위치에 삽입
linkedList.showAll();
linkedList.insertAt(1, 50); // 리스트의 특정 위치에 삽입
linkedList.showAll();
console.log(linkedList.find(2)); // 자료 검색
console.log(linkedList.find(100)); // 자료 검색
console.log("Removed Data : " + linkedList.removeFromFront()); // front에서 자료 삭제
linkedList.showAll();
console.log("Removed Data : " + linkedList.removeFromEnd()); // end에서 자료 삭제
linkedList.showAll();
console.log("Removed Data : " + linkedList.removeAt(1)); // back에서 자료 삭제
linkedList.showAll();
console.log("Removed Data : " + linkedList.removeAt(0)); // 0번 인덱스 요소 삭제
linkedList.showAll();
이중 연결 리스트
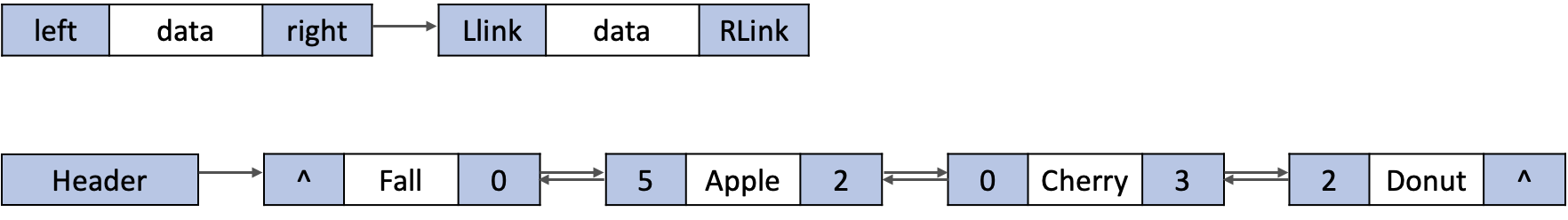
이중 연결 리스트 는 단순 연결 리스트에서 하나의 링크만을 사용함으로서 리스트를 한 쪽 방향으로만 탐색 가능하던 부분을 양방향 검색이 가능하도록 해줘요. 때문에 각 노드마다 선행 노드와 후행 노드의 주소를 모두 포함하므로 기억 장소가 추가로 요구하게 되죠. 각 노드는 선행 노드(left) 링크와 데이터 저장필드 후행 노드(right) 링크로 구성돼요.
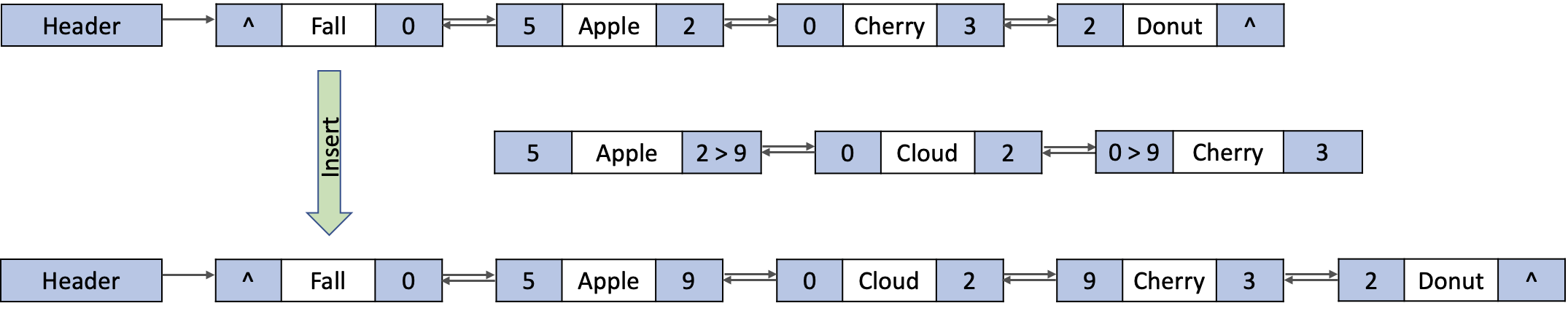
Apple 자료항목 이후에 Cloud를 추가하는 경우
1단계: 새로운 노드의 오른쪽 링크에 선행노드의 오른쪽 링크를 복사한다.
2단계: 새로운 노드의 왼쪽 링크에 선행노드의 오른쪽 링크가 가리키는 노드(후행노드)의 왼쪽 링크를 복사한다.
3단계: 후행노드의 왼쪽 링크에 노드 주소 new를 저장한다.
4단계: 선행노드의 오른쪽 링크에 새로운 노드 주소 new를 저장한다.
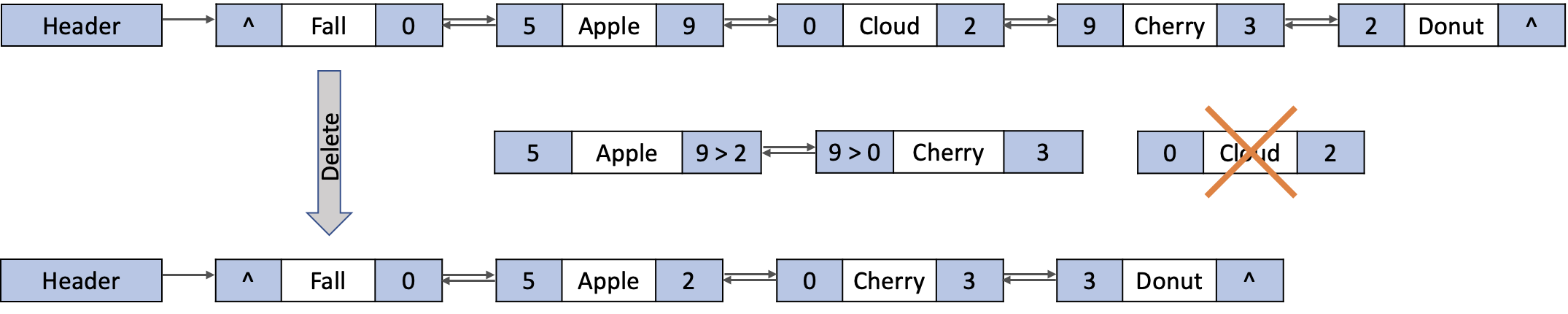
노드를 삭제하는 경우
1단계: 제거 대상 노드의 오른쪽 링크를 현재 제거대상 노드의 왼쪽 링크가 가리키고 있는 노드(선행노드)의 오른쪽 링크에 복사한다.
2단계: 제거 대상 노드의 왼쪽 링크를 현재 제거대상 노드의 오른쪽 링크가 가리키고 있는 노드(후행노드)의 왼쪽 링크에 복사한다.
3단계: 제거된 노드의 기억 공간을 반환한다.
function DoubleLinkedList() {
const Node = function(data, next, prev) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
this.head = null;
this.length = 0;
this.insert = data => {
const newNode= new Node(data, this.head, null);
if (this.head !== null) {
this.head.prev = newNode;
}
this.head = newNode;
this.length++;
}
this.append = data => {
if (this.head === null) {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next !== null) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = new Node(data, null, current);
this.length++;
}
}
this.insertAt = (position, data) => {
if (position > this.length || position < 0) {
console.log("Wrong place.");
return null;
}
let count = 0, current = this.head;
if (position === 0) {
this.insert(data);
} else {
while (current !== null && count < position - 1) {
current = current.next;
count++;
}
const newNode = new Node(data, current.next, current);
if (current.next !== null) {
current.next.prev = newNode;
}
current.next = newNode;
}
this.length++;
}
this.removeFromFront = () => {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log("List is empty");
return null;
} else {
const item = this.head.data;
this.head = this.head.next;
if (this.head !== null) {
this.head.prev = null;
}
this.length--;
return item;
}
}
this.removeFromEnd = () => {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log("List is empty");
return null;
} else {
let item;
if (this.length === 1) {
item = this.head.data;
this.head = null;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next !== null) {
current = current.next;
}
item = current.data;
const prev = current.prev;
current.prev.next = null;
}
this.length--;
return item;
}
}
this.removeAt = position => {
if (position >= this.length || position < 0) {
console.log("Wrong place.");
return null;
}
if (position === 0) {
return this.removeFromFront();
} else {
let count = 0, current = this.head;
while (current !== null && count < position) {
current = current.next;
count++;
}
const item = current.data;
const prev = current.prev;
prev.next = current.next;
if (current.next !== null) {
current.next.prev = prev;
}
this.length--;
return item;
}
}
this.remove = data => {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log("List is empty.");
return null;
}
let current = this.head;
while (current !== this.head) {
if (current.data === data) break;
current = current.next;
}
if (current === null) {
console.log("Data is not found.");
return null;
}
if (current.prev === null) {
return this.removeFromFront();
}
const item = current.data;
const prev = current.prev;
prev.next = current.next;
if (current.next !== null) {
current.next.prev = prev;
}
this.length--;
return item;
}
this.isEmpty = () => {
return this.head === null;
}
this.find = data => {
let node = this.head;
while (node !== null) {
if (node.data === data) {
return true;
}
node = node.next;
}
return false;
}
this.size = () => {
return this.length;
}
this.clear = () => {
this.head = null;
this.length = 0;
}
this.showAll = () => {
console.log("Data in List : ");
let node = this.head;
while (node !== null) {
console.log(node.data);
node = node.next;
}
console.log("------------");
}
}// Test
const linkedList = new DoubleLinkedList(); // 리스트 생성
linkedList.insert(10); // front에 삽입
linkedList.insert(15); // front에 삽입
linkedList.showAll(); // 리스트 출력
linkedList.append(20); // end에 삽입
linkedList.append(50); // end에 삽입
linkedList.insert(5); // front에 삽입
linkedList.showAll(); // 리스트 출력
console.log("Number of List : " + linkedList.size());
linkedList.clear();
linkedList.insertAt(1, 10); // 리스트의 오류 위치에 삽입
linkedList.insertAt(0, 10); // front에 삽입
linkedList.showAll();
linkedList.insertAt(1, 5); // end에 삽입
linkedList.showAll();
linkedList.insertAt(1, 2); // 리스트의 특정 위치에 삽입
linkedList.showAll();
linkedList.insertAt(1, 50); // 리스트의 특정 위치에 삽입
linkedList.showAll();
console.log(linkedList.find(2)); // 자료 검색
console.log(linkedList.find(100)); // 자료 검색
console.log("Removed Data : " + linkedList.removeFromFront()); // front에서 자료 삭제
linkedList.showAll();
console.log("Removed Data : " + linkedList.removeFromEnd()); // end에서 자료 삭제
linkedList.showAll();
console.log("Removed Data : " + linkedList.removeAt(1)); // back에서 자료 삭제
linkedList.showAll();
console.log("Removed Data : " + linkedList.remove(50)); // 특정 값의 요소 삭제
linkedList.showAll();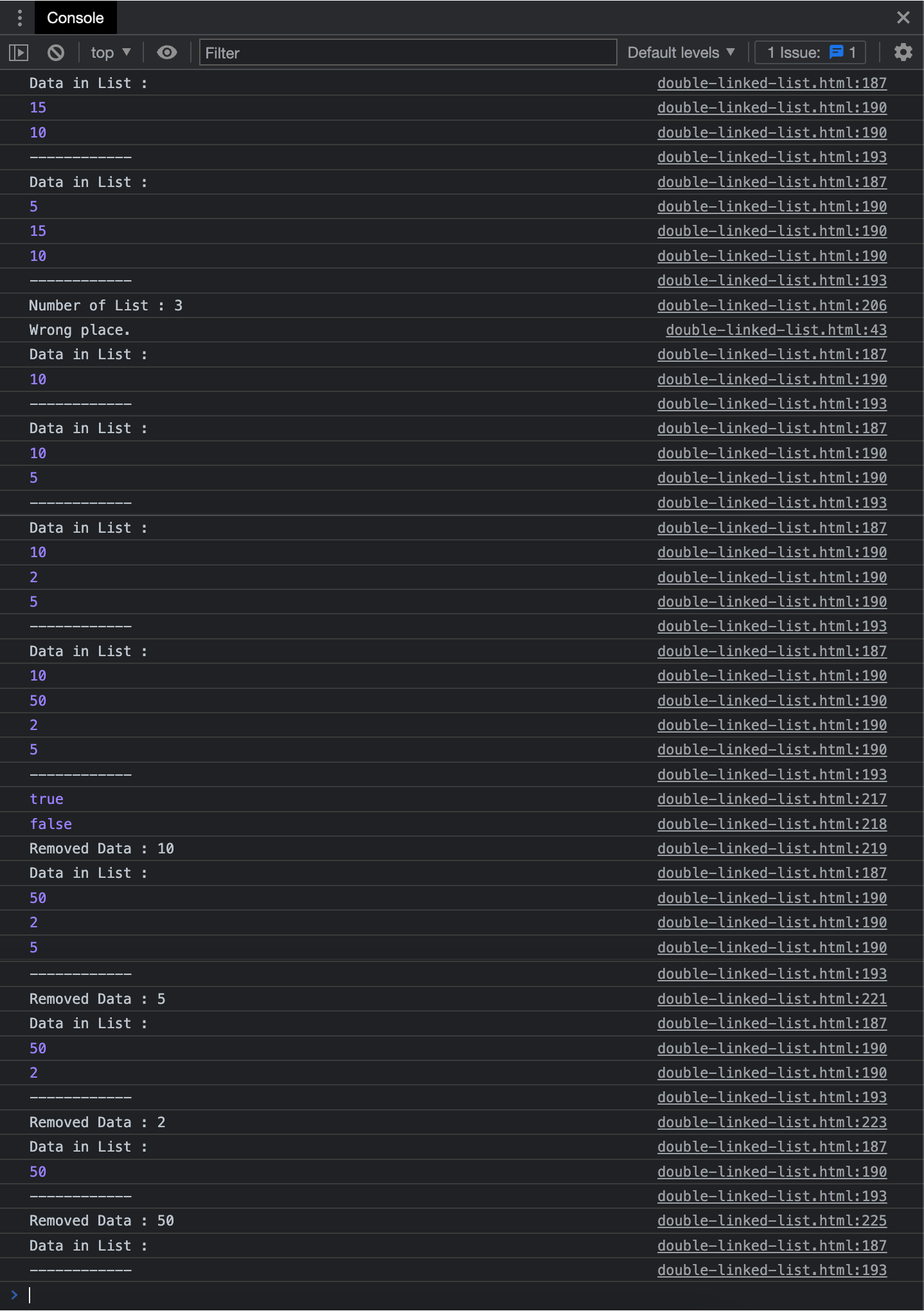
큐 (Queue)
큐(Queue) 는 선형구조로서 리스트의 특수한 형태이며 메모리 공간의 한쪽 끝에서 새로운 자료가 삽입되고 반대편에서 자료가 삭제되는 대기행렬과 같은 자료구조에요. 큐에서는 삭제가 발생하는 메모리 주소를 지시하기 위한 포인터를 Front(Head) , 삽입되는 메모리 주소를 반영하기 위한 포인터를 Rear(Tail) 라고 명명하고 유지하죠.
큐의 연산형태는 먼저 대기한 대상을 우선 처리하는 방식인 FIFO(First In First Out) , 다른 말로는 선입선출을 구현하는 자료구조에요. 이런 큐는 프로세스 스케줄링, 스풀링 등에 응용되기도 하죠.
큐는 간단하게 1차원 배열을 이용하여 구현할 수 있으며, 포인터 변수 front, rear를 사용해서 앞(삭제)과 뒤(삽입) 위치를 가리키면 돼요.
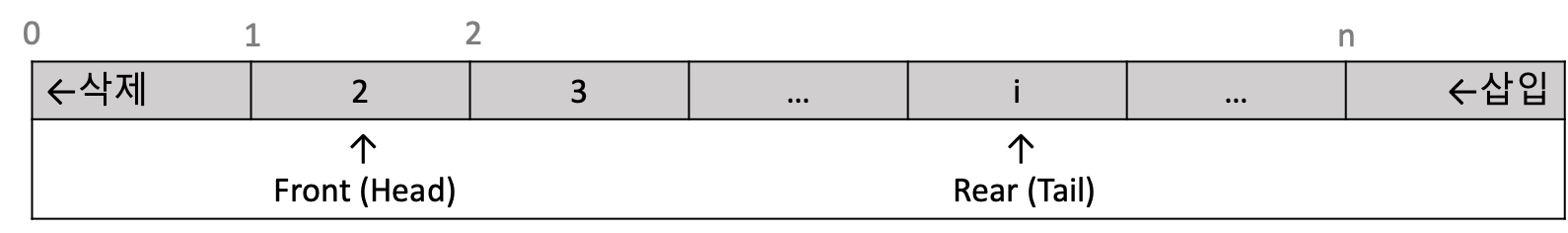
큐의 항목을 삽입할 때는 Rear의 포인터를 증가시켜 메모리 공간을 먼저 확보한 후에 데이터를 삽입하면 돼요. 반대로 항목을 삭제할 때는 현재 Front 포인터의 메모리 내용을 먼저 삭제한 후에 다음에 삭제할 위치 지정을 위해 포인터를 증가시키죠.
큐의 포인터 변화
삽입: Rear > Rear + 1 (삽입 이전에 포인터 증가)
삭제: Front > Front + 1 (삭제 후 포인터 증가)
// Queue
function Queue(array) {
let items = [];
if (array) items = array;
this.enqueue = element => {
items.push(element);
}
this.dequeue = () => {
return items.shift();
}
this.peek = () => {
return items[0];
}
this.isEmpty = () => {
return items.length === 0;
}
}// Test
const queue = new Queue();
queue.enqueue(10); // 항목 삽입
queue.enqueue(15); // 항목 삽입
console.log(queue.isEmpty()); // queue가 비어있는지 확인
console.log(queue.peek()); // 포인터가 가리키는 항목
console.log(queue.dequeue()); // 요소 삭제
console.log(queue.dequeue()); // 요소 삭제
console.log(queue.dequeue()); // 요소 삭제 (삭제할 항목이 존재하지 않음)
console.log(queue.isEmpty()); // queue가 비어있는지 확인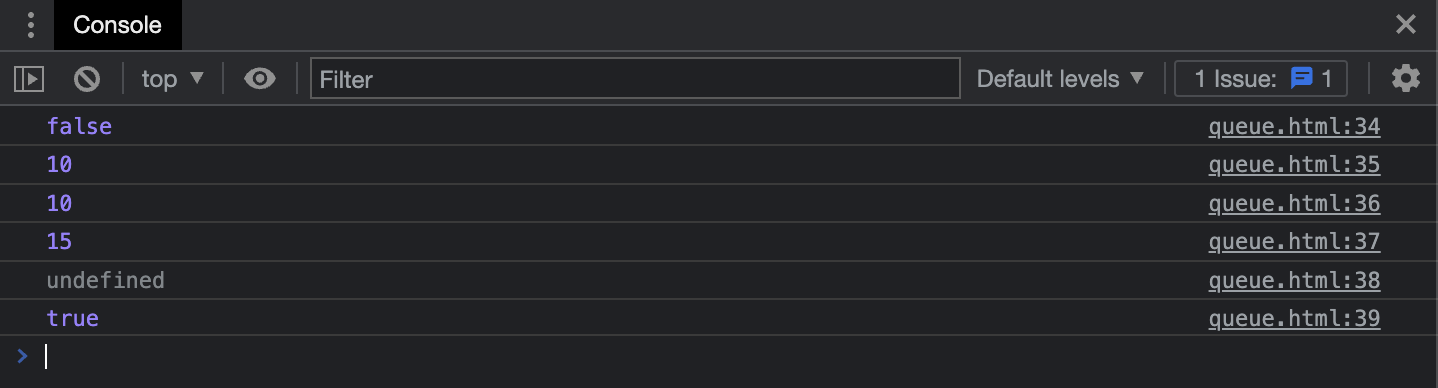
큐 자료 구조에서 특정 항목을 검색 하는 것도 중요한 연산이에요. 이를 위해 우선 shift가 버퍼 스택에 대해 호출 될 수 있도록 버퍼 큐 를 만들어야 해요. 이런 식으로 원래 큐로부터 어떤 항목도 제거되지 않도록 원래 큐는 건드리면 안돼요.
const queueSearch = (queue, element) => {
const bufferArray = queue.getBuffer
const bufferQueue = new Queue(bufferArray);
while (!bufferQueue.isEmpty()) {
if (bufferQueue.shift() === element) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}이동 큐 (Moving Queue)

고정 큐의 문제는 Front 포인터가 삭제하고 지나간 메모리의 앞부분이 빈 공간으로 남아 있음에도 알고리즘의 운영상 노드를 추가할 때 오버플로우 를 발생시킬 수 있다는 점이에요. 이동 큐 (Moving Queue) 는 Rear가 큐의 한쪽 끝을 포인팅하는 시점에서 반대쪽 공간이 비어 있을 때, 큐의 내용을 전체적으로 옮겨 공간이 있음에도 오버플로우가 발생하지 않도록 문제를 해결할 수 있죠.
우선순위 큐 (Priority Queue)
우선순위 큐 (Priority Queue) 는 이름에서 알 수 있듯이 항목이 우선순위를 포함하는 큐에요. 때문에 요소를 추가한 순서에 상관없이 각자의 우선순위에 따라 처리가 이루어지죠.
// Priority Queue
function PriorityQueue() {
const items = [];
function QueueElement(element, priority) {
this.element = element;
this.priority = priority;
}
this.enqueue = (element, priority) => {
const queueElement = new QueueElement(element, priority);
if (this.isEmpty()) {
items.push(queueElement);
} else {
let added = false;
for (let i = 0; i < items.length; i++) {
if (queueElement.priority < items[i].priority) {
items.splice(i, 0, queueElement);
added = true;
break;
}
}
if (!added) items.push(queueElement);
}
}
this.dequeue = () => {
return items.shift();
}
this.peek = () => {
return items[0];
}
this.isEmpty = () => {
return items.length === 0;
}
}// Test
const queue = new PriorityQueue();
queue.enqueue(10, 2); // 요소 삽입
queue.enqueue(15, 1); // 요소 삽입
queue.enqueue(50, 1); // 요소 삽입
console.log(queue.peek()); // 포인터가 가리키는 항목
console.log(queue.dequeue()); // 요소 삭제
console.log(queue.dequeue()); // 요소 삭제
console.log(queue.dequeue()); // 요소 삭제
console.log(queue.isEmpty()); // queue가 비어 있는지 확인스택 (Stack)
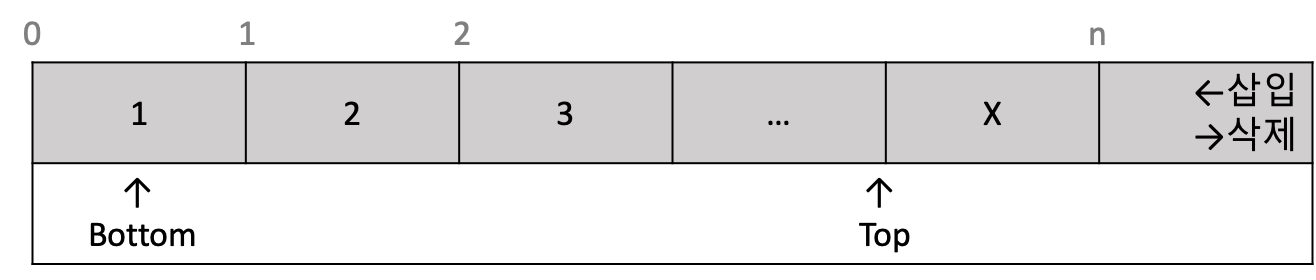
스택 (Stack) 이란 노드의 삽입이나 삭제가 자료공간의 최상위 주소인 Top 포인터 가 가리키는 스택의 한 쪽 끝에서만 이루어지는 자료구조에요. 스택의 가장 위에 있는 노드가 최상위 노드이며, 스택의 가장 아래에 있는 노드를 밑바닥 노드(Bottom node)라고 불러요. 스택의 최상위 주소에 새로운 노드 하나를 추가하는 연산을 PUSH라고 하며, 최상위에 있는 노드를 제거하는 연산을 POP이라고 해요.
PUSH와 POP 연산을 실행하기 위해 Top 포인터를 유지하며 자료의 삽입과 삭제는 Top 포인터가 지정하는 한쪽 방향으로만 진행돼요. 따라서, 스택은 LIFO(Last In First Out) , 즉 후입선출 자료구조에요. 스택은 인터럽트(interrupt) 또는 부프로그램(subprogram) 호출시의 반환되어야하는 복귀 주소값 저장 등에 활용돼요.
// Stack
function Stack(array) {
let items = [];
if (array) items = array;
this.push = element => {
items.push(element);
}
this.pop = element => {
return items.pop();
}
this.peek = () => {
return items[items.length - 1];
}
this.isEmpty = () => {
return items.length === 0;
}
}// Test
const stack = new Stack();
stack.push(10); // 요소 삽입
stack.push(15); // 요소 삽입
console.log(stack.isEmpty()); // stack이 비어 있는지 확인
console.log(stack.peek()); // 포인터가 가리키는 요소
console.log(stack.pop()); // 요소 삭제
console.log(stack.pop()); // 요소 삭제
console.log(stack.pop()); // 요소 삭제
console.log(stack.isEmpty()); // stack이 비어 있는지 확인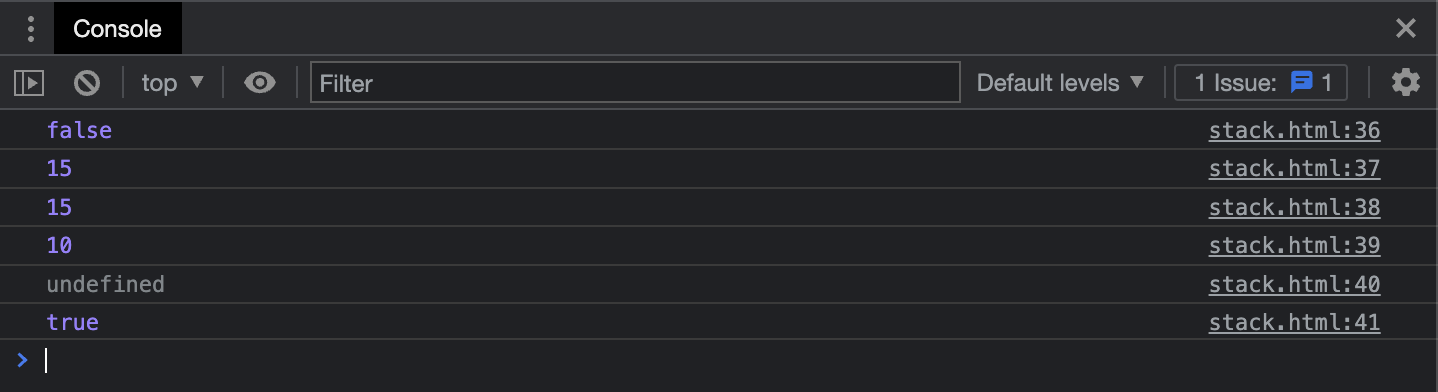
스택에서 어떤 항목이 존재하는지 확인하기 위해서는 큐를 검색해야 해요. 검색 역시 원래 스택에 변경이 생기지 않도록 버퍼 스택을 우선 생성 해야해요.
const stackSearsh = (stack, element) => {
const bufferArray = stack.getBuffer();
const bufferStack = new Stack(bufferArray);
while (!bufferStack.isEmpty()) {
if (bufferStack.pop() === element) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}스택의 응용 (수식의 연산)
수식을 표기하는 방법은 연산자와 피연산자의 위치에 따라 세 가지 방법으로 나뉘어요. 이 때, 사람 중심의 중위 표기법을 후위 표기법으로 변환한 후에 스택을 이용하여 연산합니다.
수식의 연산
연산자(Root), 왼쪽 연산자(Left), 우측 연산자(Right)
중위 표기법 (infix): a + b // Left - Root - Right
전위 표기법 (prefix): + ab // Root - Left - Right
후위 표기법 (postfix): ab + // Left - Right - Root
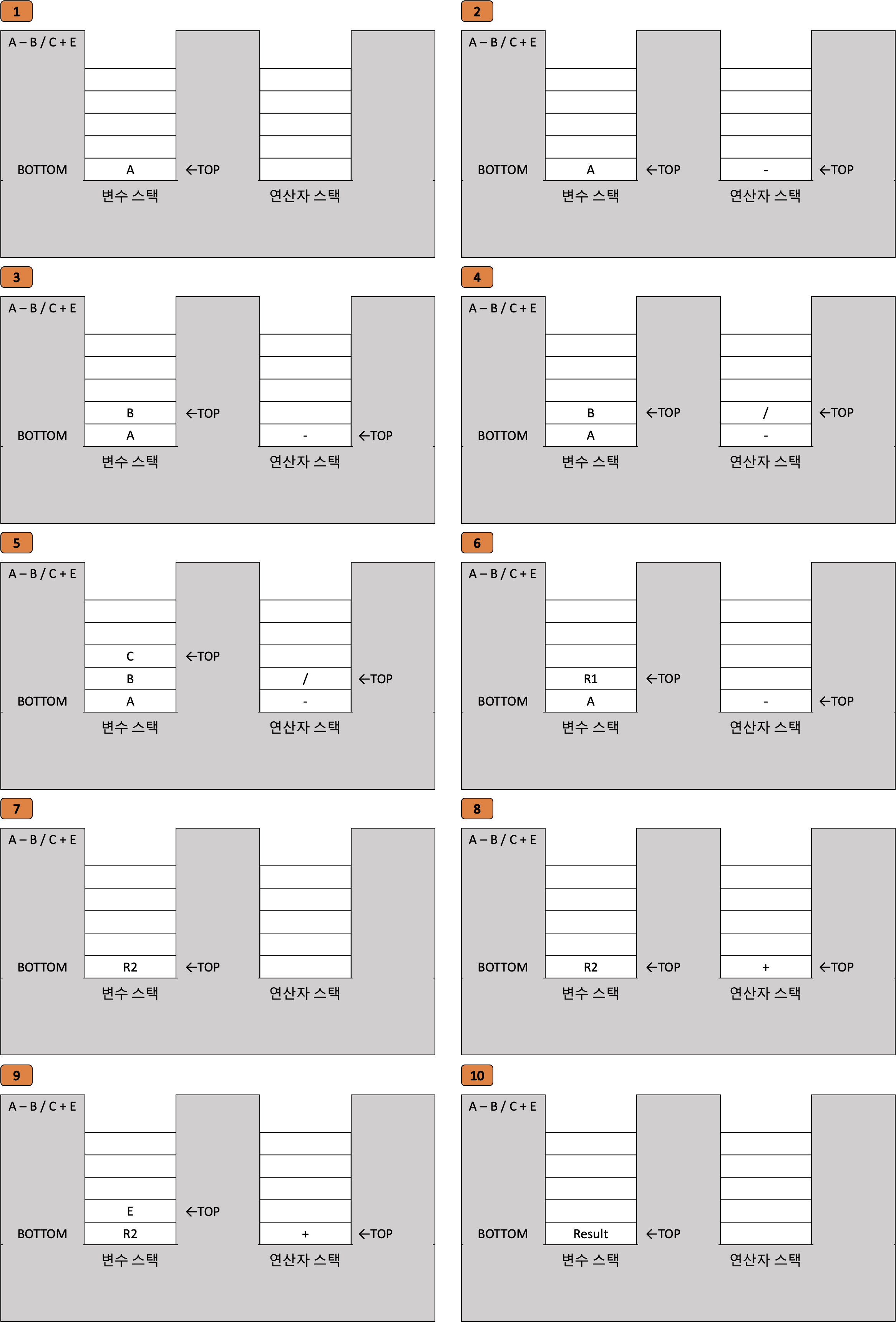
스택의 응용 (재귀호출의 복귀시점 제어)
스택을 이용하면 재귀함수를 호출할 때 복귀시점을 제어하기가 용이해져요.
// Factorial
const factorial = n => {
let fact = 1;
while (n) {
fact *= n;
n--;
}
return fact;
}
const recursiveFactorial = n => {
if (n === 0) return 1;
return n * recursiveFactorial(n - 1);
}
const memoizedFunction = fn => {
const cache = {};
return n => {
if (n in cache) return cache[n];
cache[n] = fn(n);
return cache[n];
}
}
const memoizedFactorial = memoizedFunction(x => {
if (x === 0) {
return 1;
} else {
return x * memoizedFactorial(x - 1);
}
});// Test
console.log(factorial(1));
console.log(factorial(2));
console.log(factorial(3));
console.log(factorial(10));
console.log(factorial(20));
console.log(recursiveFactorial(20));
console.log(memoizedFactorial(20));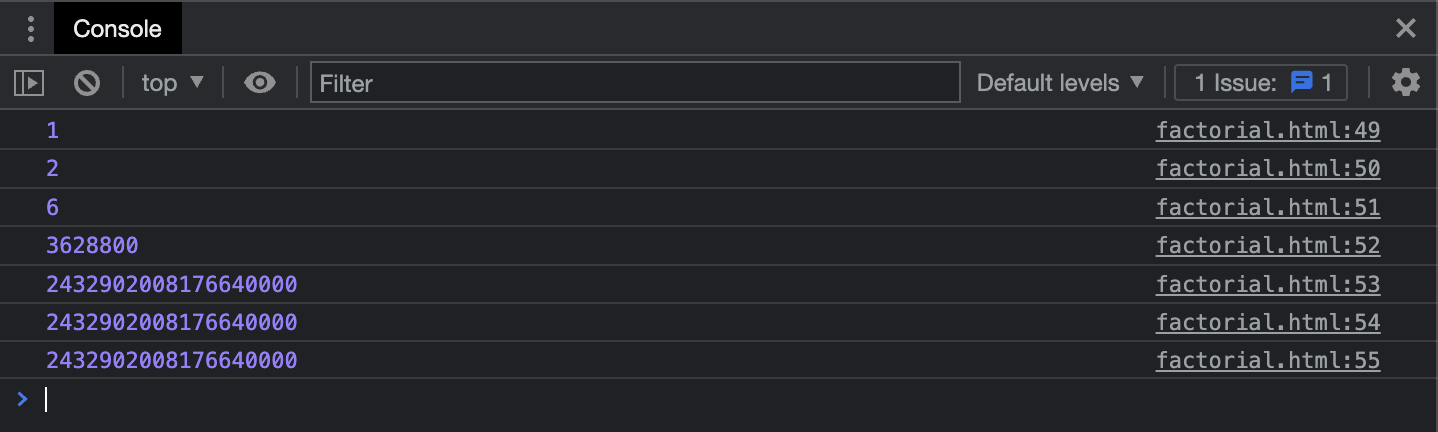
데크 (Deque, Double Ended Queue)
데크 (Deque)는 스택과 큐의 동작 방식의 복합 형태 로 수행되는 선형 자료구조이에요. 리스트의 양쪽 끝에서 삽입과 삭제가 가능한 구조이죠.
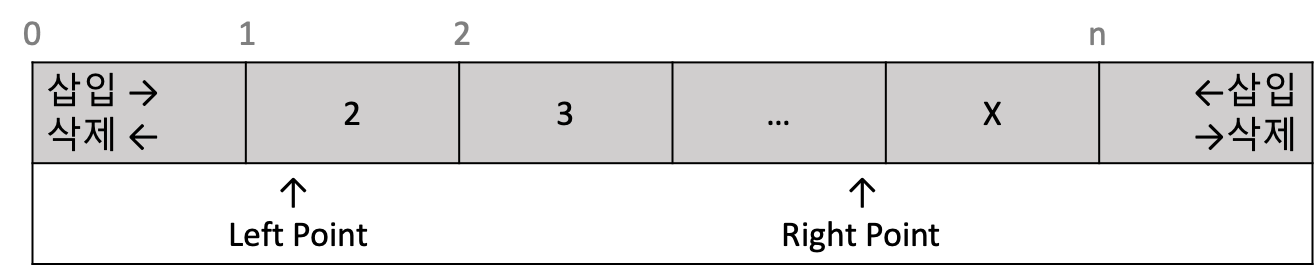
데크의 종류
스크롤 (Scroll): 일력 제한 데크로써 삽입은 리스트의 한쪽 끝에서 이루어지고, 삭제는 리스트의 양쪽 끝에서 이루어진다.
셸프 (Shelf): 출력 제한 데크로써 삽입은 리스트의 양쪽 끝에서 이루어지고, 삭제는 리스트의 한쪽 끝에서 이루어진다.
참고 자료
- 오주영, 『(Javascript로 배우는) 자료구조』, 에듀컨텐츠휴피아(2019)
- 배세민, 『자바스크립트로 하는 자료 구조와 알고리즘 : 핵심 자료구조 및 알고리즘을 이해하고 구현하기 위한 입문서』, 에이콘(2019)
