문제
You are given an m x n grid rooms initialized with these three possible values.
- 1 A wall or an obstacle.
- 0 A gate.
- INF Infinity means an empty room. We use the value 231 - 1 = 2147483647 to represent INF
as you may assume that the distance to a gate is less than 2147483647.
Fill each empty room with the distance to its nearest gate.
If it is impossible to reach a gate, it should be filled with INF.m * n 크기의 2차원 배열에 세가지 값이 존재한다
- 1 : 벽 혹은 장애물
- 0 : 출입문
- INF < 2147483647 > : 빈 방
각각의 빈 방을 가장 가까운 출입문까지의 거리로 채우세요.
만약 출입문에 갈수 없는 방이면 INF로 채우십시오.
예시
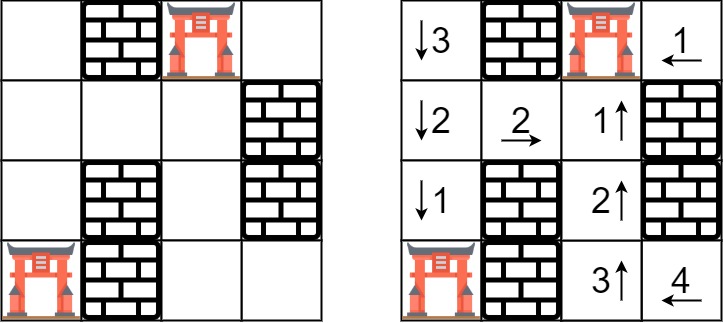
Input: rooms = [
[2147483647,-1,0,2147483647],
[2147483647,2147483647,2147483647,-1],
[2147483647,-1,2147483647,-1],
[0,-1,2147483647,2147483647]
]
Output: [[3,-1,0,1],[2,2,1,-1],[1,-1,2,-1],[0,-1,3,4]]제한
- m == rooms.length
- n == rooms[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 250
- rooms[i][j] 의 값은 -1, 0, 혹은 2^31 - 1
풀이법
IDEA
처음에는 각각의 방에서 시작한 BFS를 통해 출입구에 도달시 거리를 작성할까 했었는데
생각해보니까 애초에 게이트에서 BFS를 돌려서 INF였던 빈 방들의 값을 작성해주면 되는게 아닌가 싶어
해보았다.
풀이
맨 처음 출입구들의 위치를 전부 조사해 큐에 집어 넣고
BFS를 했다.
이때 중요한 점은 다른 출입문이나 벽에 닿으면 순회를 멈추어야 된다는 것이다.
다른 문에 도달했다는 것은 그 근처의 빈 방들은 어차피 그 문에 더 가까운 거리를 가질것이기에 의미가 없을것이다.
또한 빈 방에 적힌 거리를 수정 할 때에만 BFS에 추가 해야 하는데, 이를 통해 되돌아오는것을 방지할수도 있고
이미 다른 출입문에 가까운 경우에도 순회를 멈출수 있게 된다.
class Solution:
def wallsAndGates(self, rooms: List[List[int]]) -> None:
vertSize = len(rooms)
horiSize = len(rooms[0])
mv = [-1, 0, 1, 0]
mh = [0, -1, 0, 1]
gates = deque()
# 들어갈수 있는 Gate들 전부 조사함.
for v in range(vertSize):
for h in range(horiSize):
if rooms[v][h] == 0:
gates.append([v, h])
while len(gates) != 0:
# 순회 위해 빼옴
gate = gates.popleft()
for i in range(4):
tv = gate[0] + mv[i]
th = gate[1] + mh[i]
if tv < 0 or tv >= vertSize or th < 0 or th >= horiSize or rooms[tv][th] == 0 or rooms[tv][th] == -1: continue
# 적혀있는 거리보다 우리가 더 가까운 경우
if rooms[tv][th] > rooms[gate[0]][gate[1]] + 1:
rooms[tv][th] = rooms[gate[0]][gate[1]] + 1
gates.append([tv, th])
return rooms