
이번 장은 간단하게 Entity-Relationship(ER) 모델에서 관계형 데이터베이스 설계로의 매핑 또는 변환하는 방법을 알고 넘어갑니다.
더 자세한 이론을 보고 싶다면 [DB #04]를 참고해주세요.
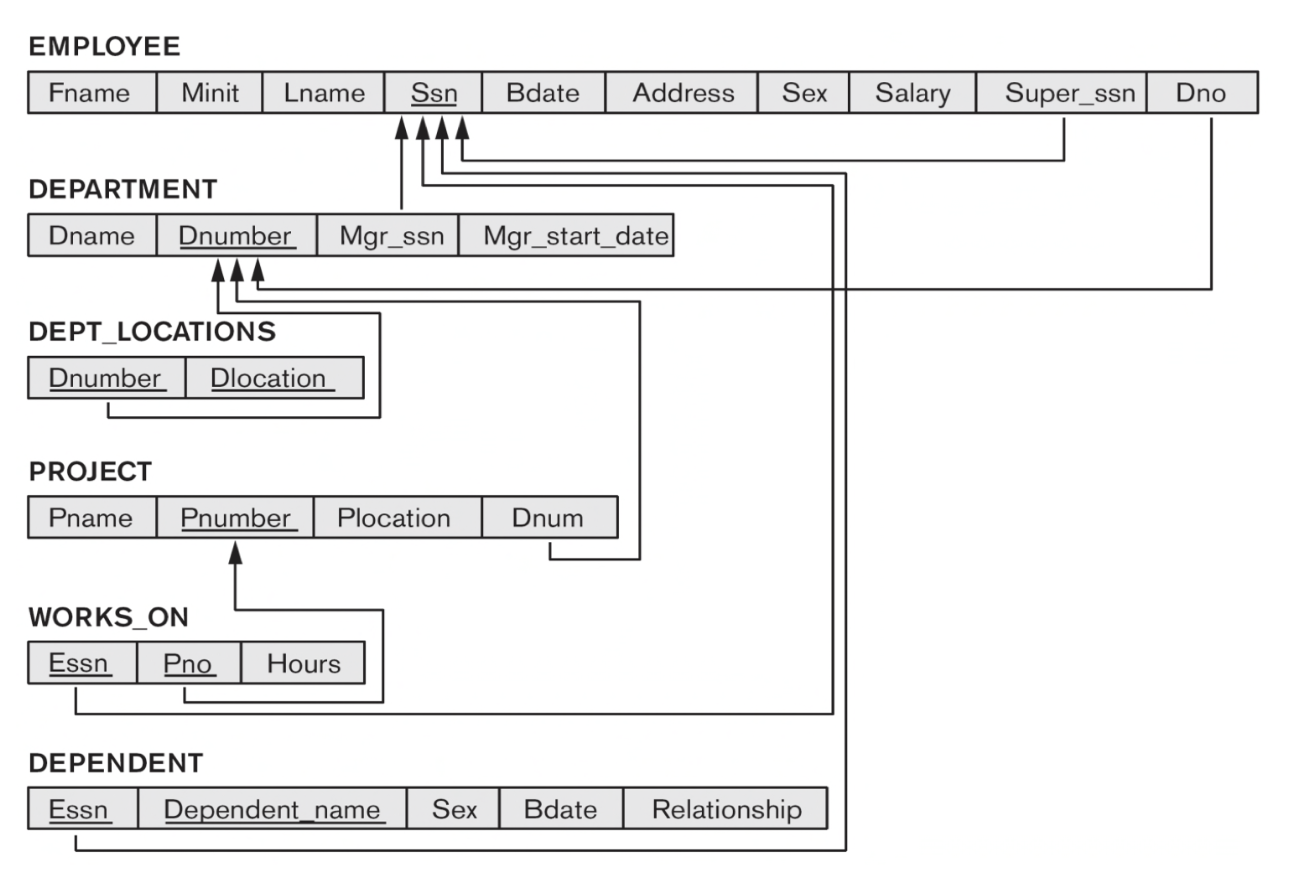
1. An ER Schema for COMPANY
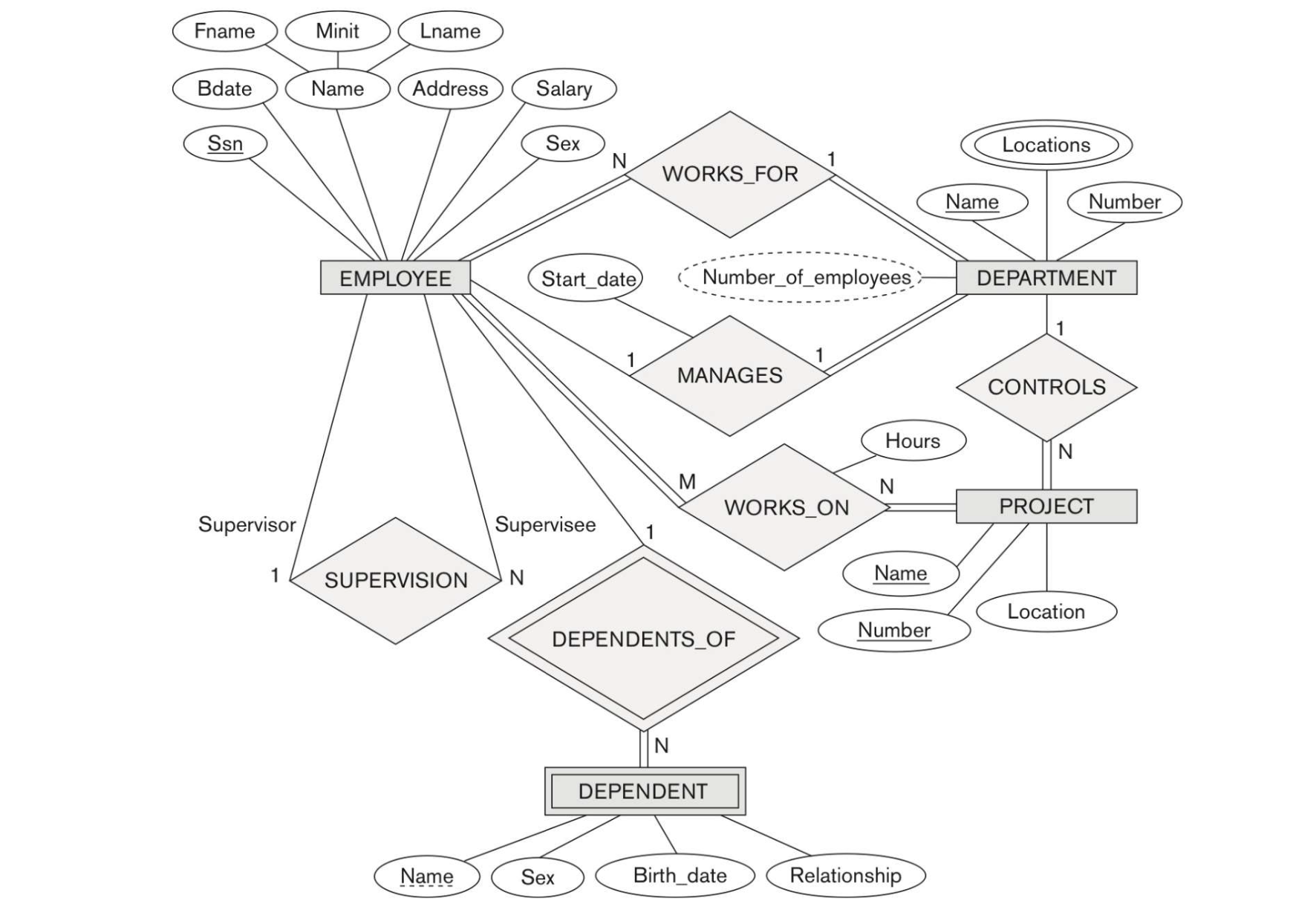
2. The Relational Schema for COMPANY
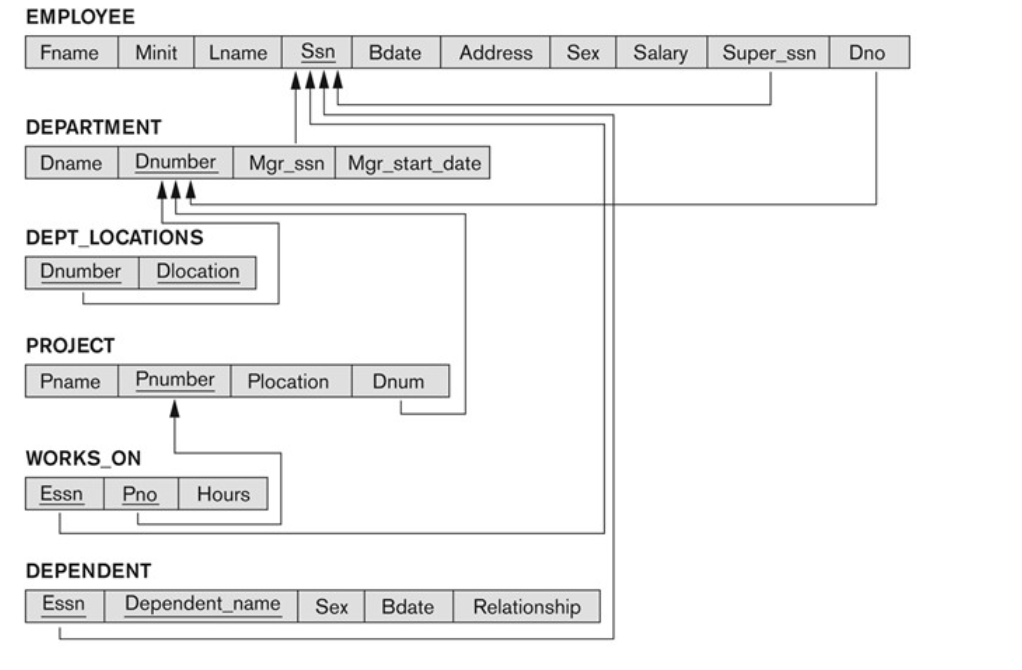
3. Goals During ER-to-Relational Mapping
- xPreserve all information (that includes all attributes)
ER 모델에서 정의된 모든 엔티티와 속성은 관계형 데이터베이스에 유지되어야 한다.
어떤 정보든 유실되면 안 된다.- Maintain the constraints to the extent possible
ER 모델에서 정의된 제약 조건 중 관게형 데이트베이스에서도 유지할 수 있는 것은 최대한 유지해야 한다.
모든 제약 조건이 관계형 모델로 완벽하게 매핑되지 않을 수도 있다.
EX) ER 모델에서 표현된 cardinality ratio (1:10)은 관계형 모델로 정확하게 매핑되기 어렵다.- Minimize null values
NULL 값은 DB에서 부적절한 무효값으로 취급되므로, 사용을 최소화하고 실제로 필요한 경우에만 사용하는 것이 중요
이것은 데이터 무결성과 쿼리의 간결성에도 도움이 되며, logical에서 physical schema로 mapping하는 데 도움을 준다.
4. The ER-Relational Mapping Algorithm
- Step 1: Mapping of Regular Entity Types
- Step 2: Mapping of Weak Entity Types
- Step 3: Mapping of Binary 1:1 Relationship Types
- Step 4: Mapping of Binary 1:N Relationship Types
- Step 5: Mapping of Binary M:N Relationship Types
- Step 6: Mapping of Multivalued attributes
- Step 7: Mapping of N-ary Relationship Types
4-1. Step 1: Mapping of Regular Entity Types
- ER schema에서 각 Strong Entity E에 대해, E의 모든 attribute를 포함한 관계 R을 생성한다.
- R의 key attribute 중 하나를 PK로 선택한다.
- 나머지는 SK(Unique)
- 만약 E의 선택된 key가 composite인 경우, 선택한 key의 simple attributes의 set이 R의 PK를 구성한다.
- simple attribute : Composite key에 속한 모든 attribute
- [Example]
The EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT, and PROJECT relations (mapped from the regular entities in the ER schema)
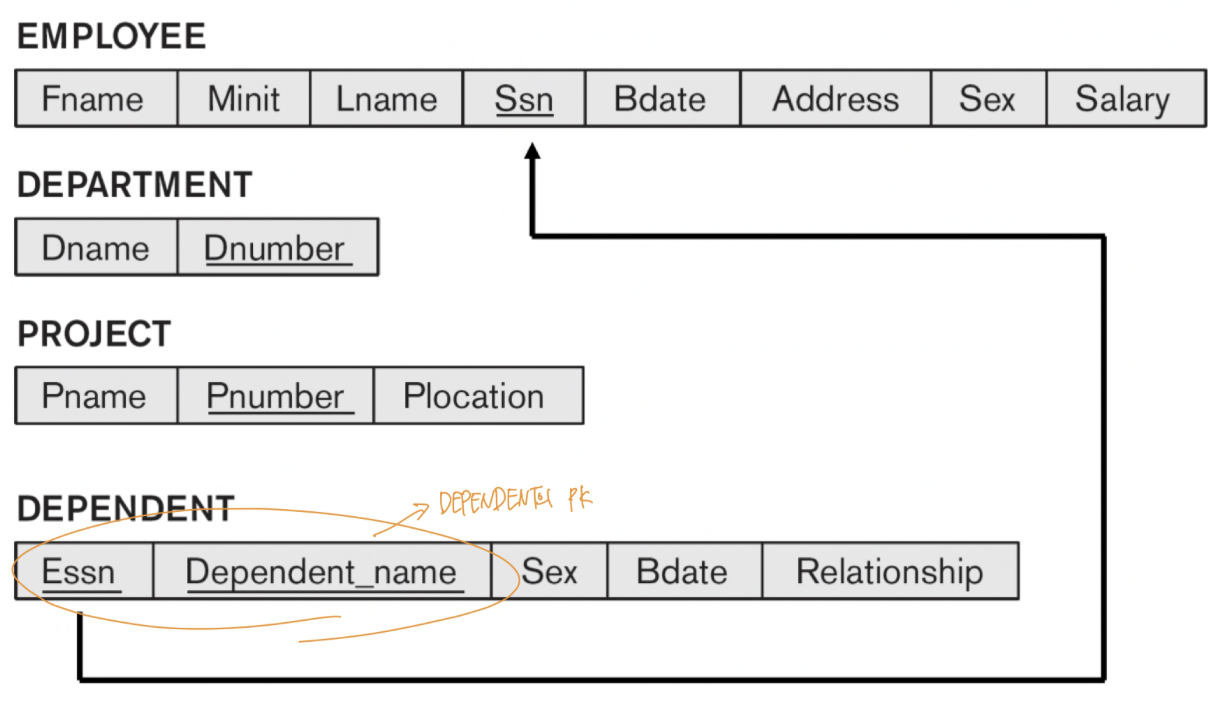
4-2. Step 2: Mapping of Weak Entity Types
- ER schema에서 각 weak entity type W에 대해, W의 모든 simple attribute를 R의 attribute로 포함시킨다.
- R에는 Owner Entity type E에 해당하는 PK를 FK로 포함시킨다.
- R의 PK는 Owner E의 PK와 weak entity W의 partial key의 조합으로 구성된다.
- [Example]
Example: The DEPENDENT relation
• PK: {Essn, Dependent_name}
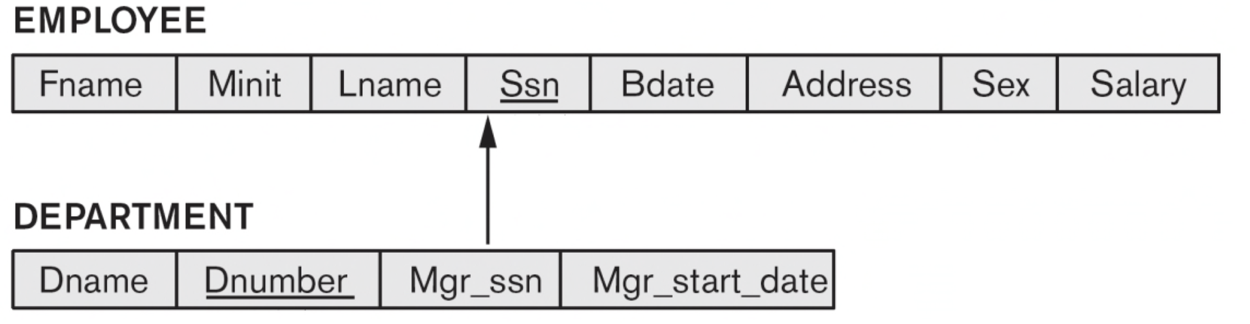
4-3. Step 3: Mapping of Binary 1:1 Relationship Types
ER schema에 있는 각 binary 1:1 relationship type R에 대해, R에 참여하는 엔티티 유형에 해당하는 관계 S와 T를 식별하는 세 가지 가능한 Option이 있다.
Foreign key approach(2 relations) option
- 관계 중 하나를 선택, 여기서는 S
- R에서 total participation으로 참여하고 있는 entity type을 선택하는 것이 더 좋다.)
- S에 FK에 T의 PK를 포함
[Example]
The MANAGES relationship type in the ER schema
- Relation S: The DEPARTMENT entity type (due to total participation).
- Relation T: The EMPLOYEE entity type
- The FK of S (e.g., the DEPARTMENT relation):
- Mgr_Ssn The PK (e.g., Ssn) of T (e.g., the EMPLOYEE relation)
- EMPLOYEE의 PK(Mgr_Ssn)을 DEPARTMENT의 FK로 가진다.
Merged relatuon (1 relation) option
- 1:1 관계를 대안적으로 나타내는 방법 중 하나, 두 엔티티 유형과 관계를 하나의 관계로 병합하는 것
- 양쪽의 참여가 모두 total participation인 경우에 적절하다.
Cross-reference or relationship relation(3 relations) option
- Relation S & T의 PK로부터 cross-referencing를 하기 위해 새로운 관계 U를 생성한다.
- U의 PK는 S & T로부터의 FK 중 하나
- 또 다른 FK는 U의 unique key
- 추가적인 join이 필요하다.
- 추가 정보를 얻기 위해 수행, overhead 발생
- [Example]
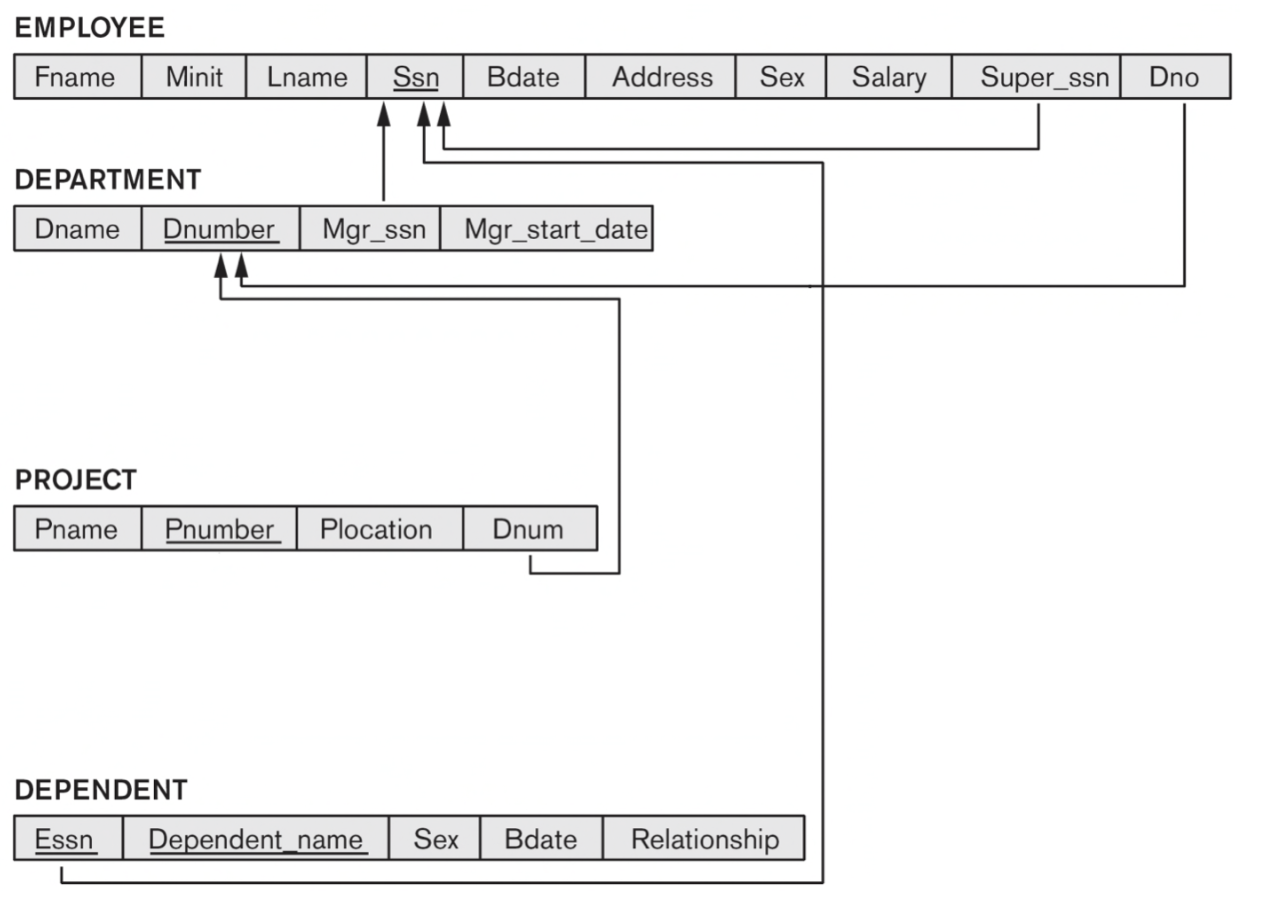
4-4. Step 4: Mapping of Binary 1:N Relationship Types
- 각 binary 1:N relationshp type R에 대해, Relation S는 N-side에 나타낸다.
- Relation T(R 관계에 참여하는 S의 반대)PK를 S의 FK로서 포함
- 1:N relation type의 simple attributes를 S의 attribute로 포함
- [Example]
- Relation S: The EMPLOYEE entity type (N-side)
- Relation T : The DEPARTMENT entity type (1-side)
- EMPLOYEE가 DEPARTMENT의 Dnumber(PK)를 참조하기 위해 Dno(FK)를 가진다.
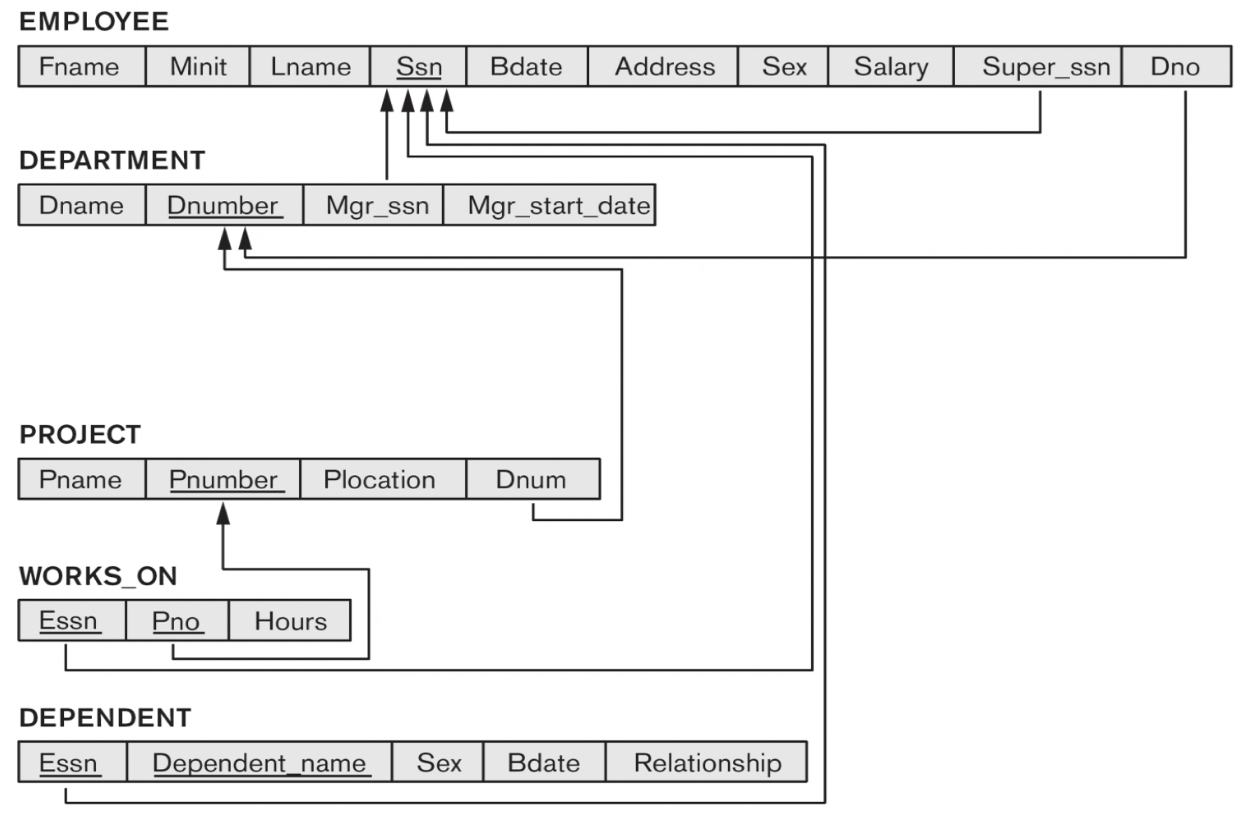
4-5. Step 5: Mapping of Binary M:N Relationship Types
- 각 일반적인 binary M:N 관계 R에 대해, 이를 표현할 수 있는 새로운 relation U를 생성한다.(relationship relation)
- relationship에 참여하는 entity types의 PK들을 U의 FK attributes로 포함하고, 포함한 FK들의 조합이 U의 PK를 구성한다.
- M:N 관계의 simple attribute를 U의 attribute로 포함한다.
- [Example]
- The WORKS_ON relationship type in ER
- Relation U: The WORKS_ON relationship type
- FKs (Essn and Pno): borrowed from the PKs (Ssn and Pnumber) of the EMPLOYEE and PROJECT relations, respectively
- PK: {Essn, Pno}
- One attribute: Hours, from Hours of WORKS_ON
4-6. Step 6: Mapping of Multivalued attributes
- 각 multivalued attribute A에 대해, 이를 표현할 새로운 relation U를 생성한다.
- This relation U will include
- A에 해당하는 attribute
- A를 attribute로서 가지는 entity의 PK를 FK로 가져온다.
- PK = {A, K}
- [Example]
- The Locations multi-valued attribute of Department
- Relation U: the DEPT_LOCATIONS relation
- A: Dlocation, from Locations of the DEPARTMENT entity type
- FK: Dnumber, from the PK of the DEPARTMENT entity type
- PK: {Dlocation, Dnumber}
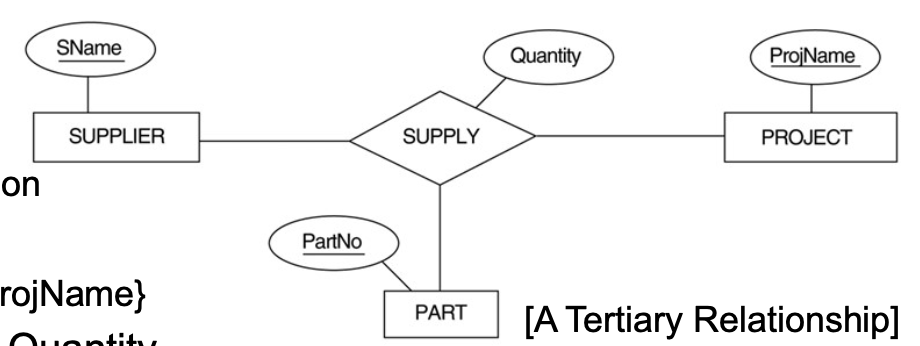
4-7. Step 7: Mapping of N-ary Relationship Types
- 각 n-ary(n>2) relation type R에 대해, 이를 표현할 새로운 relationship relation U를 생성한다.
- 참여하는 entity를 표현하는 relations의 PK를 U의 foreign key attributes로 가진다.
- n-ary 관계의 attribute를 U의 attribute로 포함시킨다.
- [Example]
- Relation U :
- The SUPPLY relation- PKs/FKs:
- {Sname, Partno, ProjName}- The other attribute: Quantity
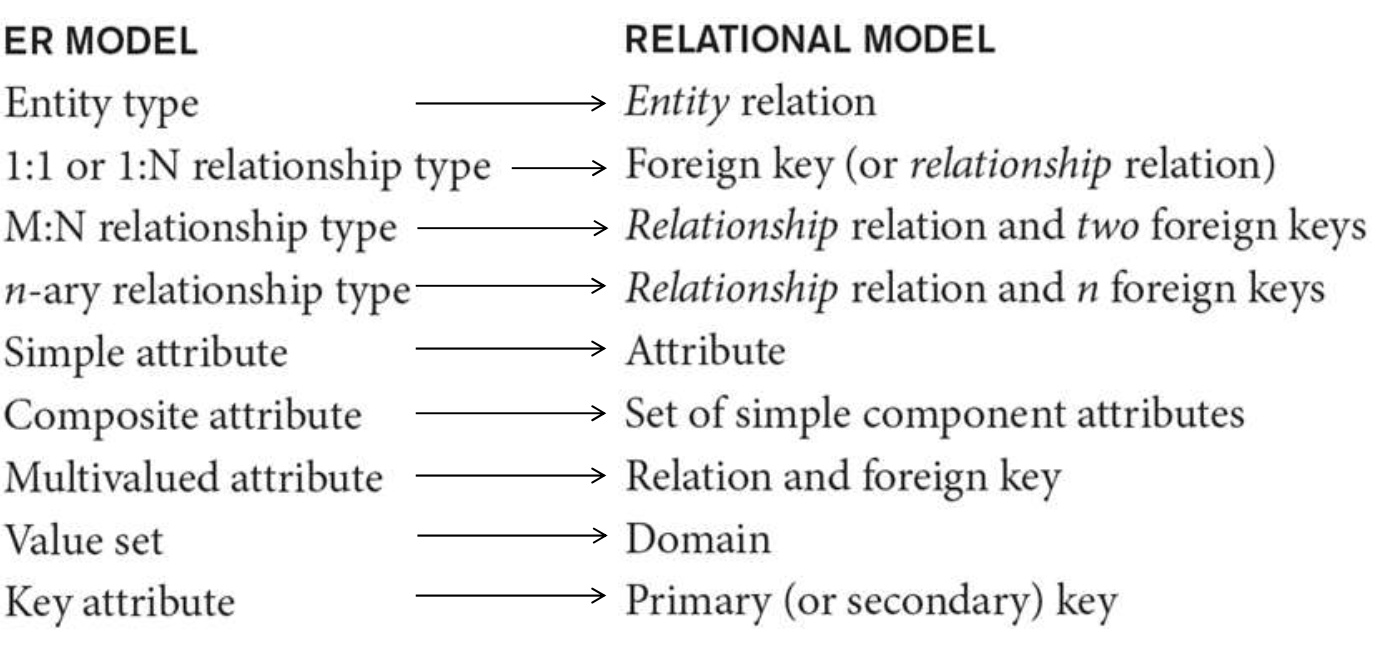
5. Correspondence between ER and Relational Models
Reference
Database System Concepts | Abraham Silberschatz
데이터베이스 시스템 7th edition

좋은 정보에요!
공유문화를 실천하는 당신이 진정 개발자 입니다.
오늘도 웃음꽃 피는 하루 되시기를^~^