백준 11728번 배열 합치기
문제 - 배열 합치기
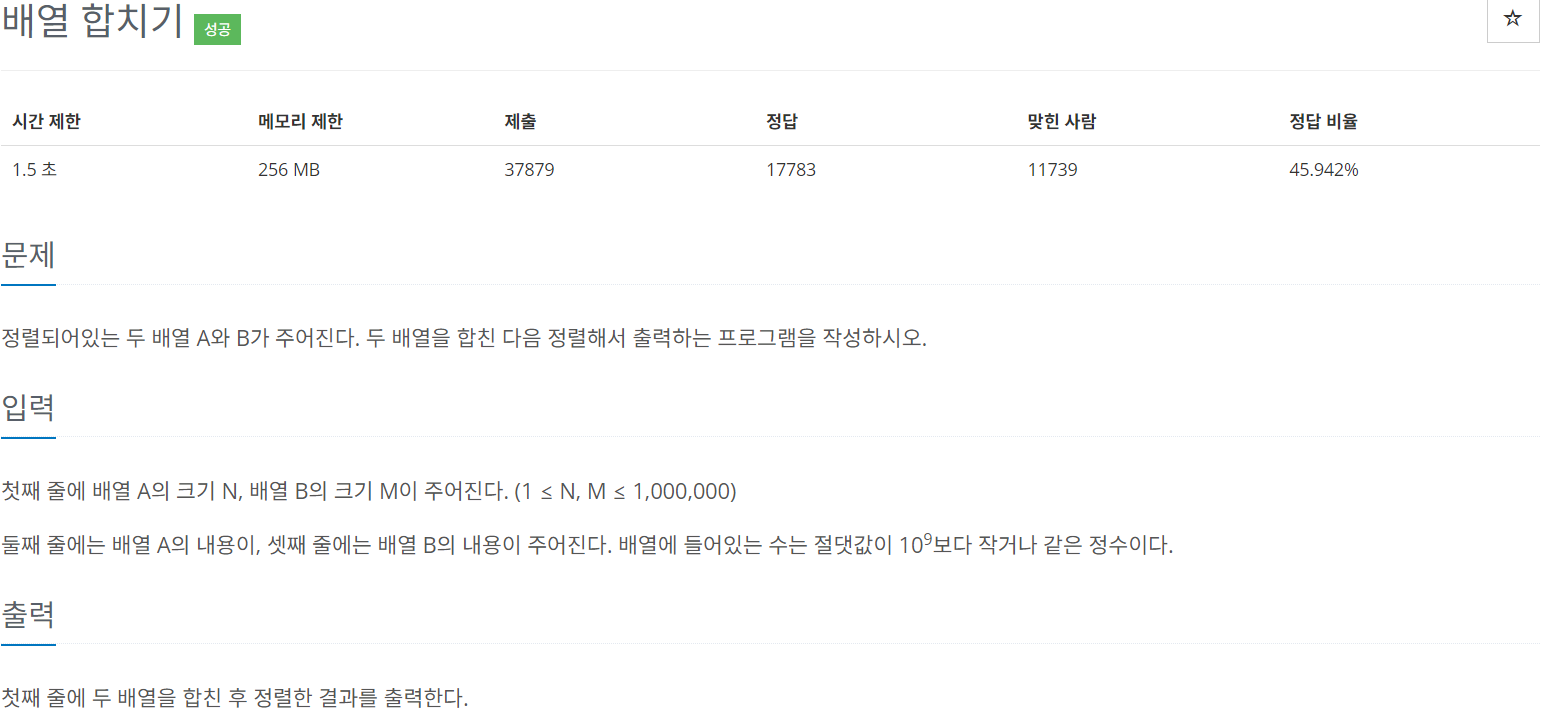
정렬되어있는 두 배열 A와 B가 주어진다. 두 배열을 합친 다음 정렬해서 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력
첫째 줄에 배열 A의 크기 N, 배열 B의 크기 M이 주어진다. (1 ≤ N, M ≤ 1,000,000)
둘째 줄에는 배열 A의 내용이, 셋째 줄에는 배열 B의 내용이 주어진다. 배열에 들어있는 수는 절댓값이 109보다 작거나 같은 정수이다.
출력
첫째 줄에 두 배열을 합친 후 정렬한 결과를 출력한다.
접근방법
두 배열을 1차원 배열로 입력받고
투포인터를 사용하여 두개의 배열을 비교하며 출력
투포인터를 활용할 줄 알면 쉽게 풀 수 있는 문제이다.
그래서 처음에는 투포인터를 활용하여 크기가 작은 값은 List에 추가하고 List를 출력하는 방법을 선택하였다.
잘못된 코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
static int N;
static int M;
public static List<Integer> solution(int[]arrA, int[]arrB){
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
int indexA = 0;
int indexB = 0;
while(indexA != N && indexB != M) {
if(arrA[indexA] < arrB[indexB]) {
result.add(arrA[indexA]);
indexA++;
}
else {
result.add(arrB[indexB]);
indexB++;
}
}
if(indexA !=N) {
for(;indexA<N;indexA++)
result.add(arrA[indexA]);
}
else if(indexB !=M) {
for(;indexB<M;indexB++)
result.add(arrB[indexB]);
}
return result;}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String [] strs = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = Integer.parseInt(strs[0]);
M = Integer.parseInt(strs[1]);
int [] arrA = new int[N];
int [] arrB = new int[M];
strs = br.readLine().split(" ");
for(int i =0; i<N;i++) {
arrA[i] = Integer.parseInt(strs[i]);
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrA));
strs = br.readLine().split(" ");
for(int i =0; i<M;i++) {
arrB[i] = Integer.parseInt(strs[i]);
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrB));
Arrays.sort(arrA);
Arrays.sort(arrB);
//크기 순서대로 정렬되어 있지 않은 경우를 대비하여 크기 순으로 배열 정렬
List<Integer> result = solution(arrA,arrB);
for(int data : result) {
System.out.print(data+ " ");
}
}
}
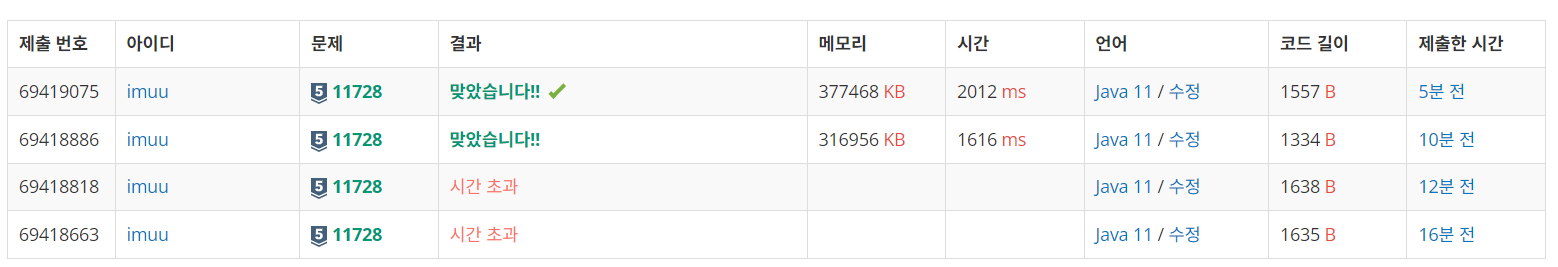
하지만 이 코드로 하면 시간초과가 나온다.
그래서 내가 투포인터를 잘못 써서 완전탐색이 된건가? 싶었고, 찾아보며 문제를 한차례 고쳐도 시간초과가 나왔다.
최종적으로 고쳐야 했던 부분은 System.out.print()를 얼마나 사용하는가?였다.
정답 코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
static int N;
static int M;
public static String solution(int[]arrA, int[]arrB){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int indexA = 0;
int indexB = 0;
while(indexA != N && indexB != M) {
if(arrA[indexA] < arrB[indexB]) {
sb.append(arrA[indexA]+" ");
indexA++;
}
else {
sb.append(arrB[indexB]+ " ");
indexB++;
}
}
if(indexA !=N) {
for(;indexA<N;indexA++)
sb.append(arrA[indexA]+ " ");
}
else if(indexB !=M) {
for(;indexB<M;indexB++)
sb.append(arrB[indexB]+ " ");
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String [] strs = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = Integer.parseInt(strs[0]);
M = Integer.parseInt(strs[1]);
int [] arrA = new int[N];
int [] arrB = new int[M];
strs = br.readLine().split(" ");
for(int i =0; i<N;i++) {
arrA[i] = Integer.parseInt(strs[i]);
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrA));
strs = br.readLine().split(" ");
for(int i =0; i<M;i++) {
arrB[i] = Integer.parseInt(strs[i]);
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrB));
Arrays.sort(arrA);
Arrays.sort(arrB);
//크기 순서대로 정렬되어 있지 않은 경우를 대비하여 크기 순으로 배열 정렬
String result = solution(arrA,arrB);
System.out.println(result);
}
}이전 코드와 고친 점은 StringBuilder를 이용하여
비교가 된 정렬된 수를 저장하고 한번에 출력한다는 점이었다.
이 문제를 풀면서 배운 점은
- 출력을 여러번 하면 시간 복잡도에 걸릴 수 있다는 것
- StringBuilder를 활용하여 결과를 저장해두고 한번만 출력하는 것
