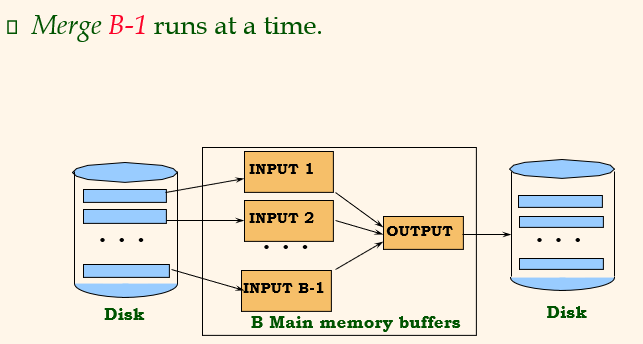
Pass 1, 2
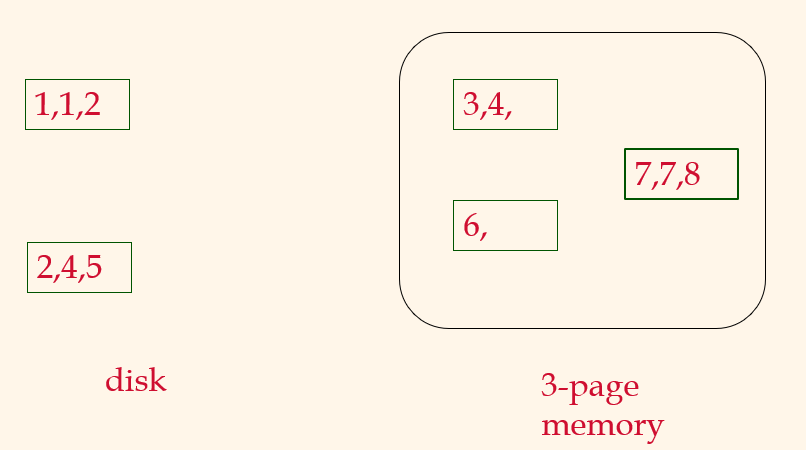
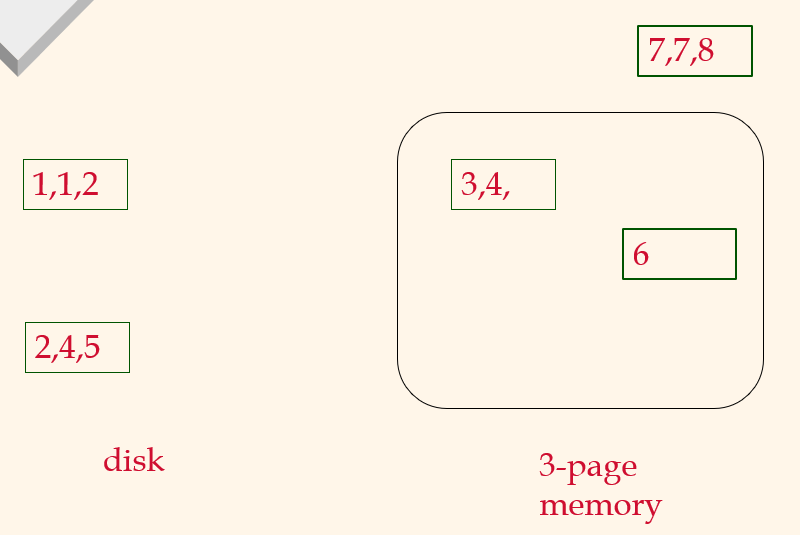
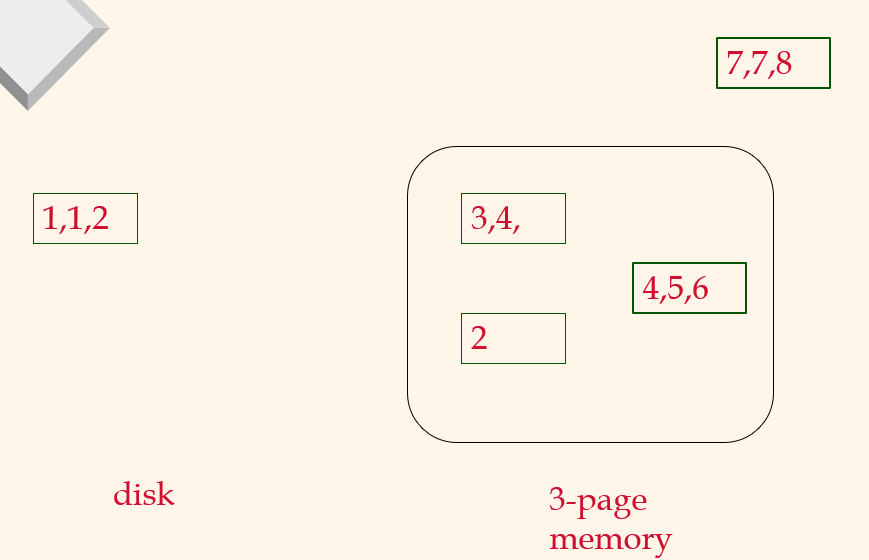
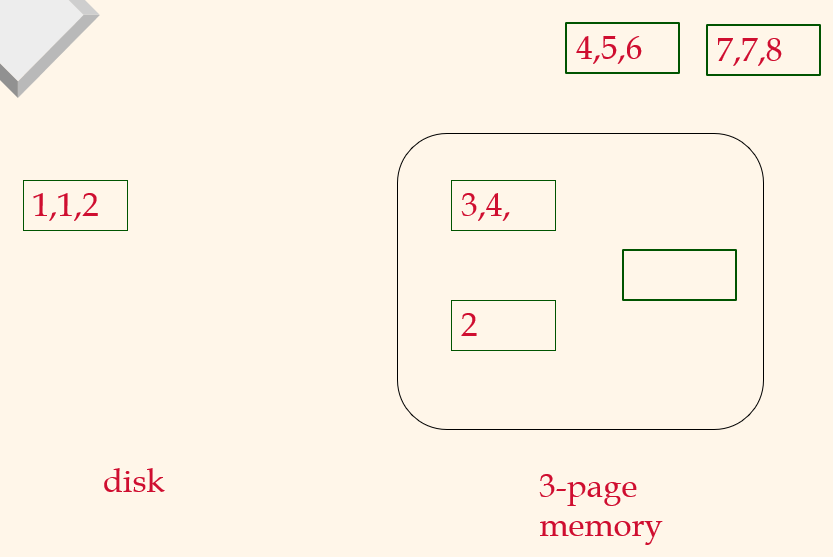
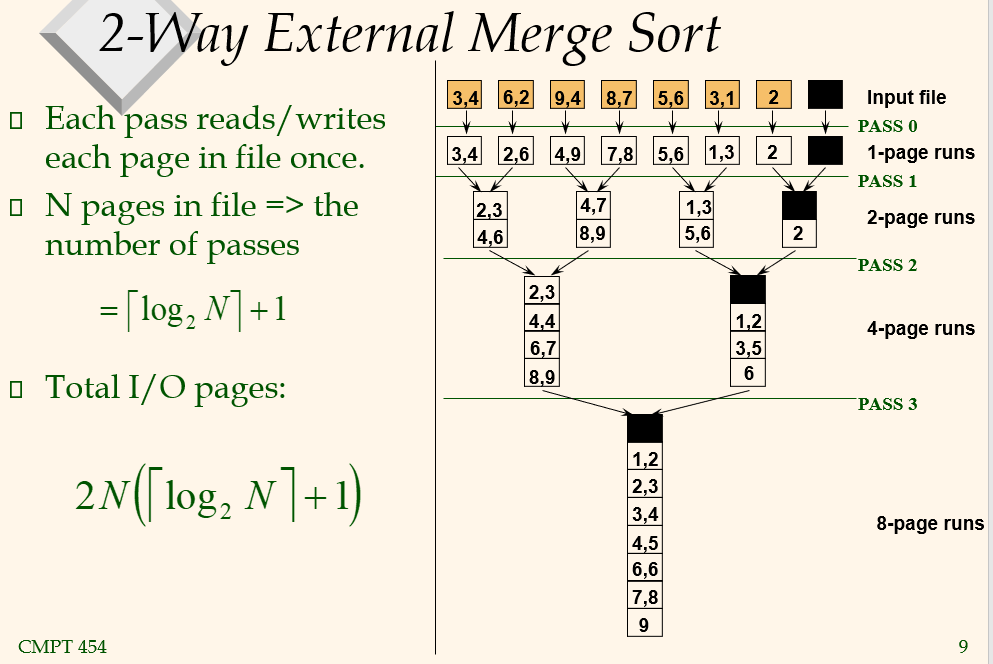
2-Way External Merge Sort
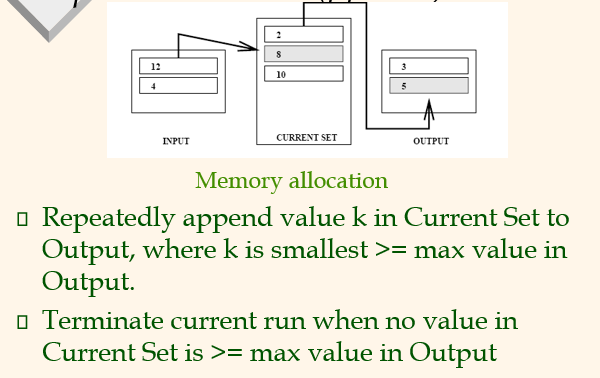
General External Merge Sort

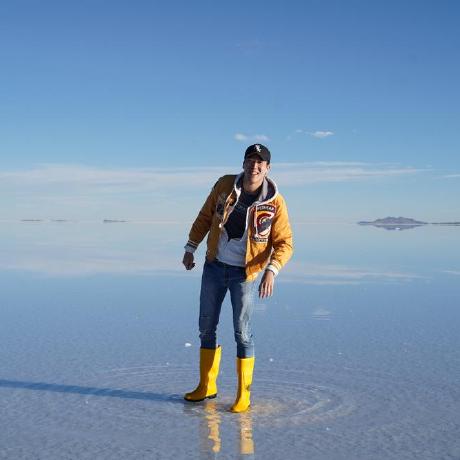
Pass 0
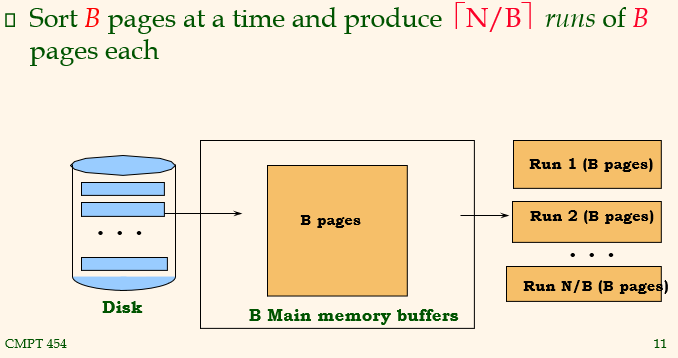
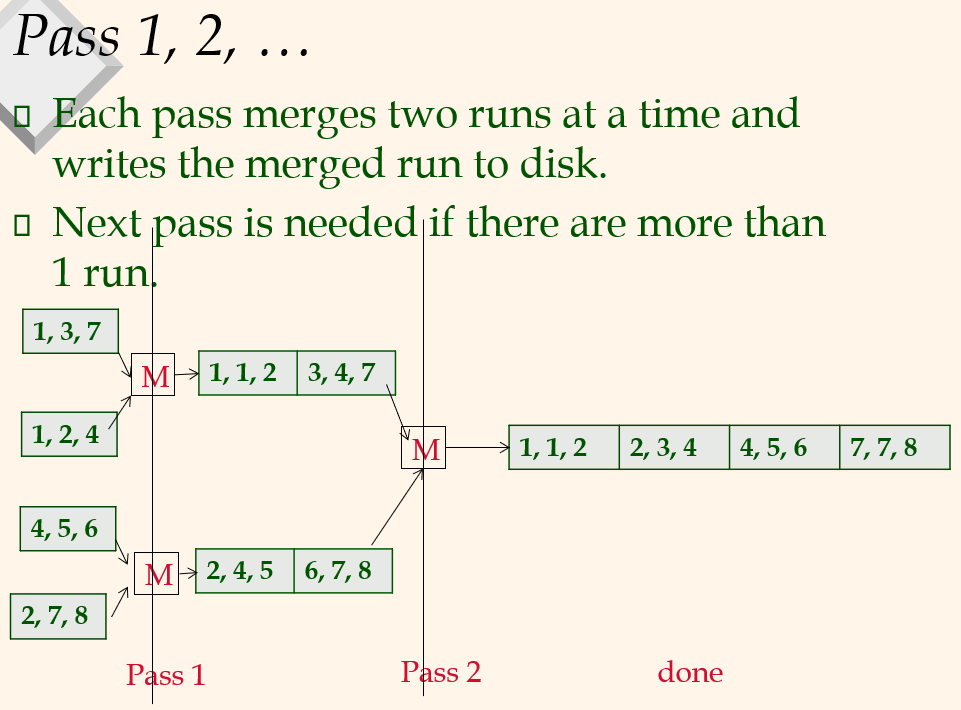
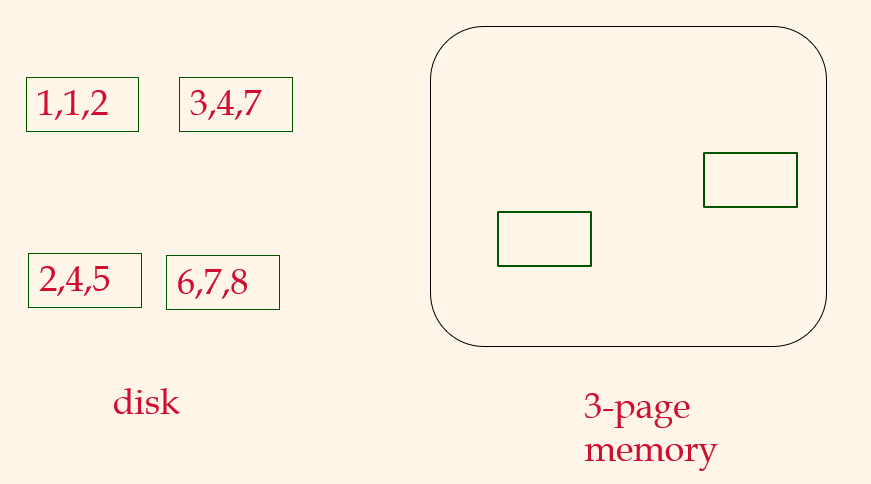
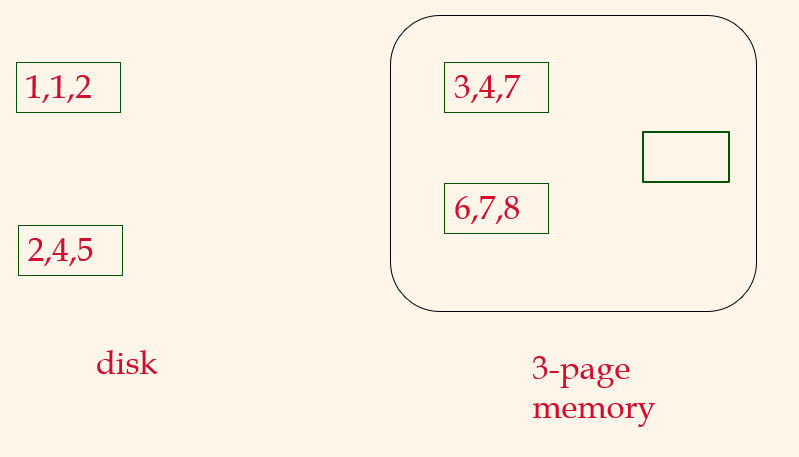
Pass 1, 2, ....
General External Merge Sort
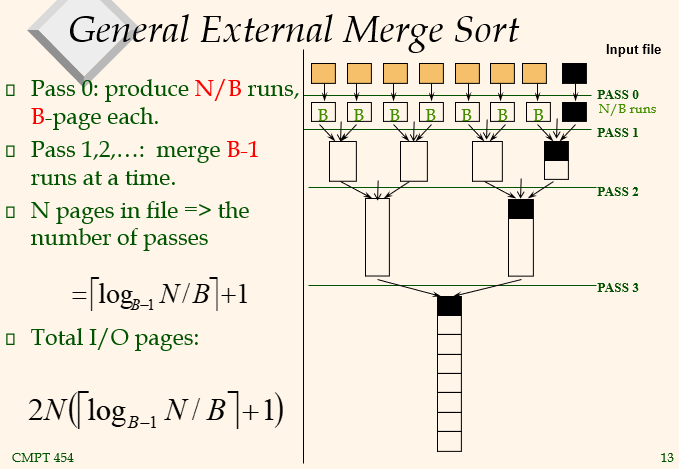
I/O Pages of External Merge Sort

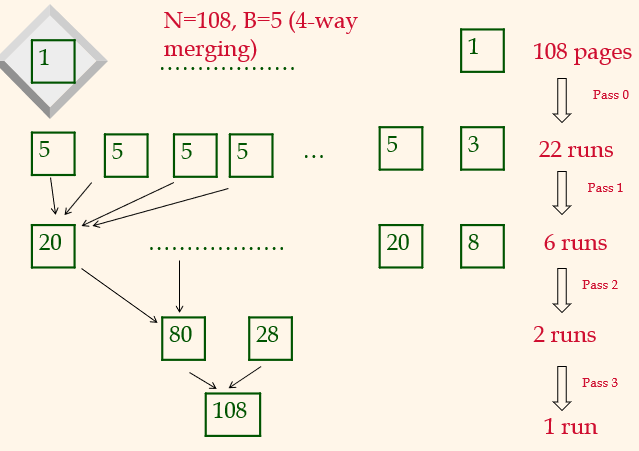
Number of Passes of External Sort
Blocked buffer: I/O pages vs I/O time
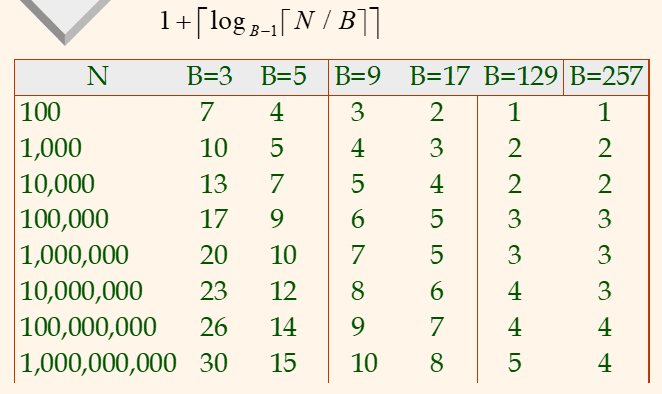
- If pages are sequentially stored on disk, I/O time per page can be reduced by having larger (b>1) input buffer.
- read b pages with 1 seek time and 1 rotational delay.
- (B-1)/b runs will be merged at a time, thus, more passes and more I/O pages.
2 Choices for 5-page Buffer (B=5)
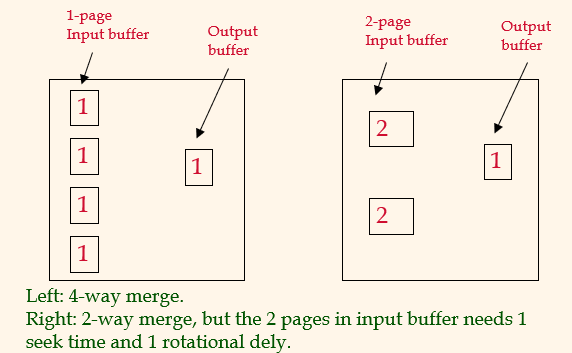
I/O cost in terms of number of page 는 오른쪽이 더 크다. more pass to merge because because each time can merge two. 하지만 오른쪽은 smaller I/O time per page이다. disk에 sequentially하게 저장되어있으면 1 seek time만 필요하기 때문이다.
Sorting cost for blocked buffers

Using B+ Trees for Sorting
- If the file to be sorted has B+ tree index on the sorting column(s), can retrieve records in order by traversing leaf pages.
- Is this a good idea?
- If B+ tree is clustered, very good idea!
- If B+ tree is not clustered, could be a very bad idea
B+ tree with searh key <A,B,C>. Can it be used to sort on A, on (A,B), on B, on (A,C)?
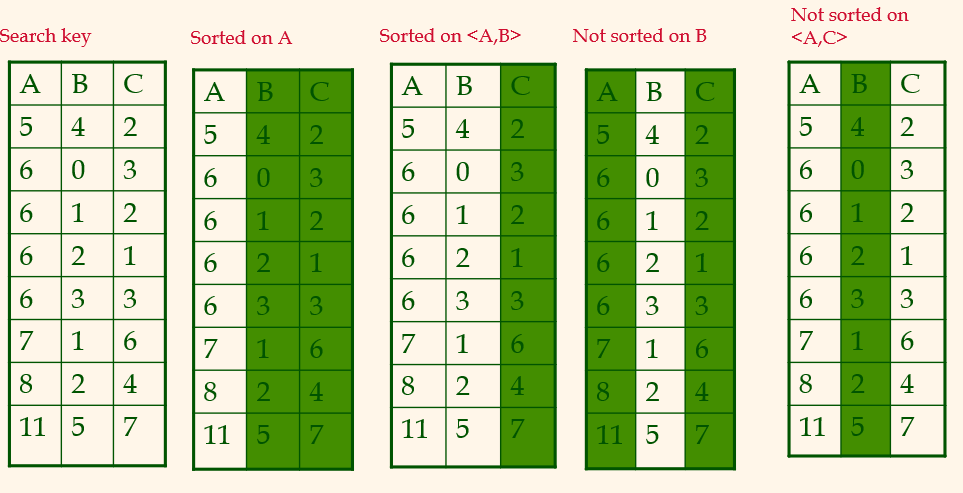
처음 두 개의 경우에는 B+트리 사용하기 좋고, 나머지는 좋은 경우가 아니다.
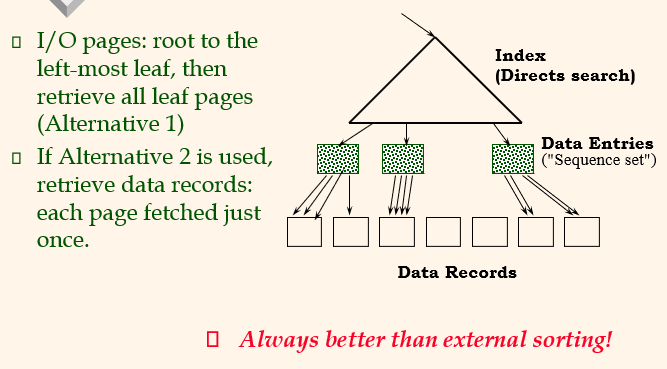
Clustered B+ Tree Used for Sorting
Unclustered B+ Tree Used for Sorting
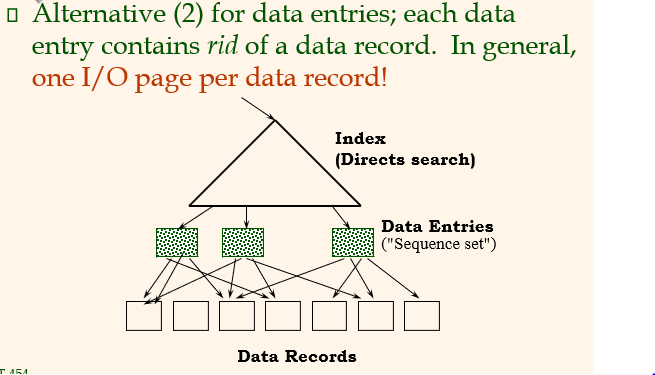

1*에서 p1 읽고,2*에서 p2 읽고3*에서 p3 읽고4*에서 p4 읽고5*에서 다시 p1 읽고 ...
-> 총 8 page를 읽는다.
External Sorting vs. Unclustered Index
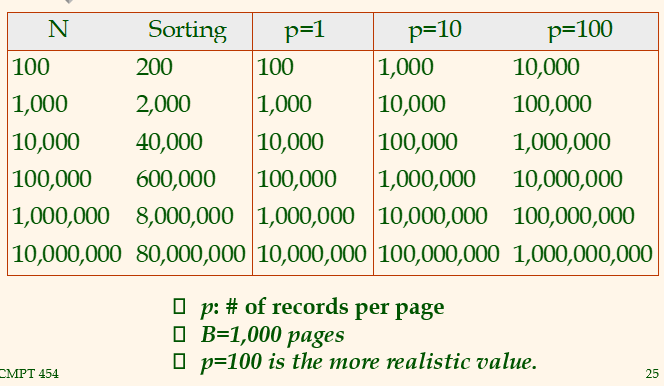
Summary


Replacement Sort (pp429)