개발 환경 구축하기
1. JDK 설치하기
OpenJDK 실행 경로 환경 변수 추가하기
Gradle 설치하기
https://gradle.org/install/#helpful-information
시스템 환경 변수 편집

IntelliJ IDEA 설치하기
JDK
JDK (Java Development Kit)는 Java 애플리케이션 개발에 필요한 도구 및 라이브러리 모음을 제공하는 소프트웨어 개발 환경입니다.
Gradle
Gradle은 빌드 자동화 도구입니다. Gradle 빌드 스크립트들은 Groovy 혹은 Kotlin DSL로 작성할 수 있습니다.
Gradle로 프로젝트 시작하기
$ mkdir demo
$ cd demo
$ gradle init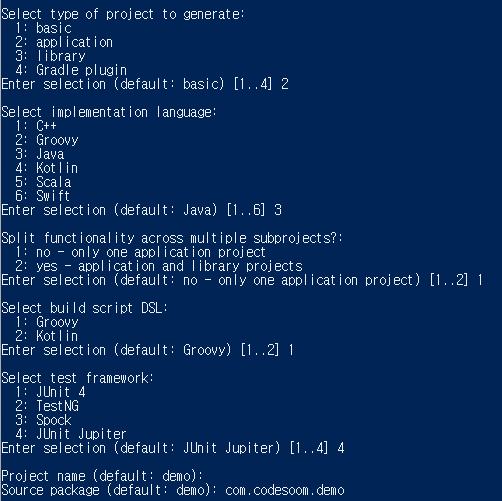
JUnit Jupiter가 Junit 5이다. 최근에는 다 이걸 사용한다.
idea.bat강의에는
idea .으로 intelliJ를 이 폴더에서 바로 실행하라고 하였지만, 32비트가 필요하다는 에러가 떴고, 검색 결과idea.bat을 사용하면 된다고 찾았다.
https://intellij-support.jetbrains.com/hc/en-us/community/posts/360005146240-Error-Launching-Idea-Java-Home-
gitignore
# Ignore Gradle project-specific cache directory
.gradle
# Ignore Gradle build output directory
build
# IDE
.ideaIDE인 .idea를 제외하게 했다.
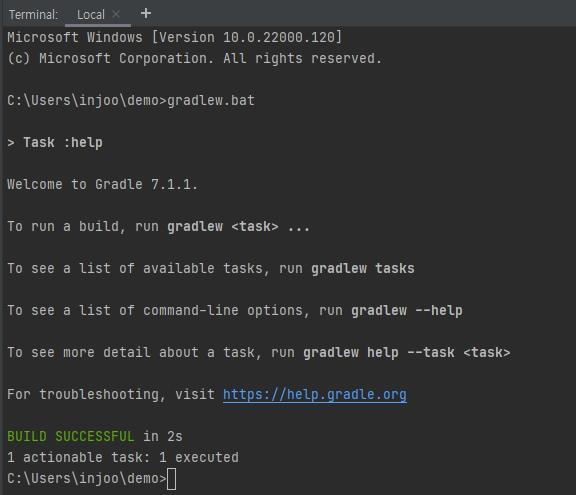
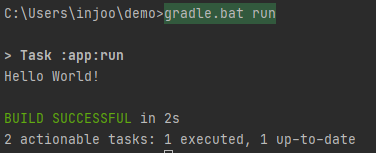
ide에서 gradle을 실행했다.
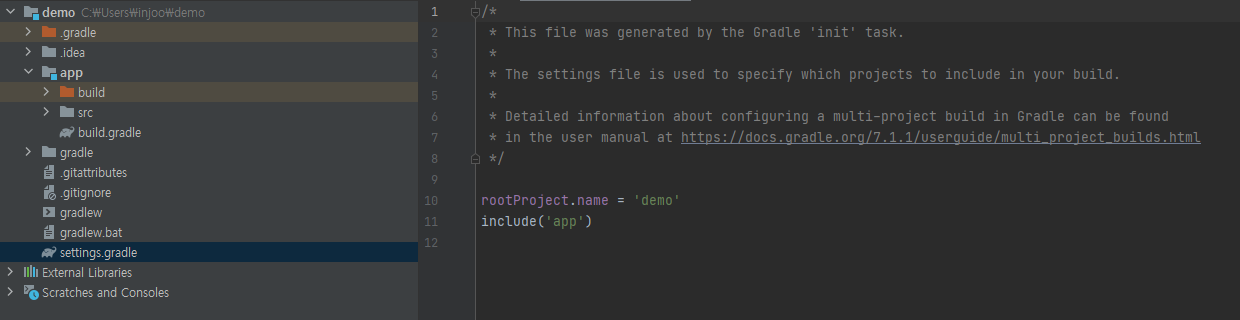
settings.gradle은 여러 개의 프로젝트들이 생길 수 있는데 그것들을 관리하는 것이다. 반대로 build.gradle은 각각의 어플리케이션에 대해 잡아주는 것이다.
REST API 만들기
Http란?
Hypertext Transfer Protocol(HTTP)은 하이퍼미디어 문서를 전송하기위핸 애플리케이션 레이어의 프로토콜입니다. HTTP는 클라이언트-서버 모델을 따르고 있습니다. 클라이언트가 연결을 요청하고 응답이 오길 기다립니다. HTTP는 stateless 프로토콜입니다. 서버는 요청간의 어떤 데이터도 유지하지 않습니다.
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP
리소스를 어떻게 식별할 수 있을까?
리소스는 어떤 문서나 사진, 영상 등 무엇이든 될 수 있는데 각 리소스는 URI(Uniform Resource Identifier)로 식별합니다. 대부분의 웹에서는 리소스의 경로로 리소스를 식별하는 URL(Uniform Resource Locator)로 식별합니다. 예를 들어 레스토랑의 목록이라는 리소스를 요청할 때는 https://codesoom.com/restaurants로 요청할 수 있습니다.
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Basics_of_HTTP/Identifying_resources_on_the_Web
REST API란?
REST(Representational state transfer)는 복수의 아키텍처 스타일을 조합하여 구축한 복합 아키텍처 스타일입니다.
- 클라이언트 / 서버 - 클라이언트가 서버에 요청을 보내면 서버는 응답을 돌려줍니다.
- Stateless 서버 - 클라이언트의 애플리케이션 상태를 서버에서 관리하지 않습니다.
- 유니폼 인터페이스 - 균일하게 인터페이스를 제약합니다.
- 계층화 시스템 - 시스템의 몇 개의 계층으로 분리할 수 있습니다. 클라이언트는 최종 서버에 직접 연결되어 있는지 중간에 연결되어 있는지를 알 수 없습니다.
- Code on demand - 프로그램 코드를 서버에서 다운로드해 클라이언트에서 실행합니다.
- 캐시 - 클라이언트와 중개자는 응답을 캐시 할 수 있습니다.
- Representational state transfer
Httpie 설치
https://httpie.io/docs#installation
# Make sure we have an up-to-date version of pip and setuptools:
python -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools
python -m pip install --upgrade httpie사용
http https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts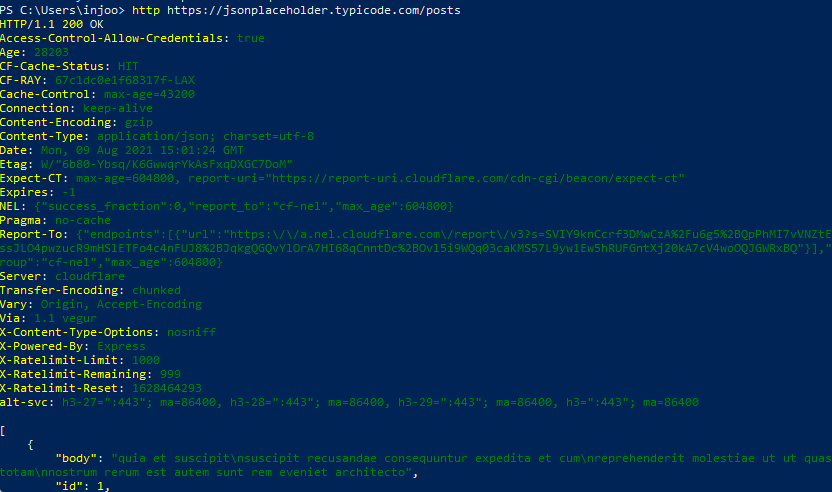
서버 구현
package com.codesoom.demo;
import com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpServer;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class App {
public String getGreeting() {
return "Hello World!";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new App().getGreeting());
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(8000);
try {
HttpServer httpServer = HttpServer.create(address, 0);
httpServer.start();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
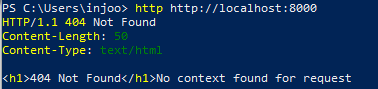
}
public class App {
public String getGreeting() {
return "Hello World!";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new App().getGreeting());
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(8000);
try {
HttpServer httpServer = HttpServer.create(address, 0);
httpServer.createContext("/");
httpServer.start();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}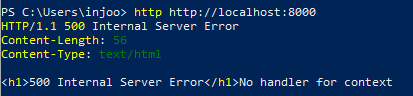
이번에는 handler가 없다고 나오고 있다. handler를 넣어주자.
public class App {
public String getGreeting() {
return "Hello World!";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new App().getGreeting());
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(8000);
try {
HttpServer httpServer = HttpServer.create(address, 0);
HttpHandler handler = new DemoHttpHandler();
httpServer.createContext("/", handler);
httpServer.start();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}DemoHttpHandler
package com.codesoom.demo;
import com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpExchange;
import com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpHandler;
import java.io.IOException;
public class DemoHttpHandler implements HttpHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpExchange exchange) throws IOException {
// 1. Method - GET, POST, PUT/PATCH, DELETE...
// 2. Path - "/", "/tasks", "/tasks/1", ..
// 3. Headers, Body(Content)
System.out.println("some request...");
}
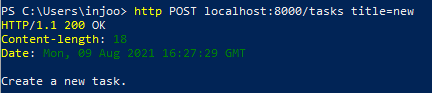
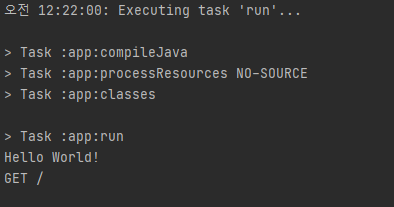
}PS C:\Users\injoo> http http://localhost:8000요청을 날리면
위와 같이 찍힌다.
public class DemoHttpHandler implements HttpHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpExchange exchange) throws IOException {
// 1. Method - GET, POST, PUT/PATCH, DELETE...
// 2. Path - "/", "/tasks", "/tasks/1", ..
// 3. Headers, Body(Content)
String method = exchange.getRequestMethod();
URI uri = exchange.getRequestURI();
String path = uri.getPath();
System.out.println(method + " " + path);
String content = "Hello, world!";
if (method.equals("GET") && path.equals("/tasks")) {
content = "We have no task.";
}
if (method.equals("POST") && path.equals("/tasks")) {
content = "Create a new task.";
}
exchange.sendResponseHeaders(200, content.getBytes().length);
OutputStream outputStream = exchange.getResponseBody();
outputStream.write(content.getBytes());
outputStream.flush();
outputStream.close();
}
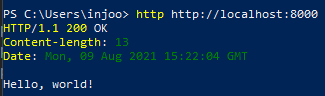
}
Jackson
JSON
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)이란 가벼운 데이터 교환 형식입니다. 클라이언트에서 서버로 데이터를 전송하거나 응답을 받을 때 JSON형식으로 전달합니다.
https://www.json.org/json-en.html
Jackson
Jackson은 Java에서 데이터를 처리하는 도구의 모음입니다. JSON뿐만 아니라 XML, YAML 등 여러 데이터 형식을 처리할 수 있습니다.
package com.codesoom.demo;
import com.codesoom.demo.models.Task;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpExchange;
import com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpHandler;
import com.sun.source.util.TaskListener;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.URI;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class DemoHttpHandler implements HttpHandler {
private List<Task> tasks = new ArrayList<>();
public DemoHttpHandler() {
Task task = new Task();
task.setId(1L);
task.setTitle("Do nothing...");
tasks.add(task);
}
@Override
public void handle(HttpExchange exchange) throws IOException {
// 1. Method - GET, POST, PUT/PATCH, DELETE...
// 2. Path - "/", "/tasks", "/tasks/1", ..
// 3. Headers, Body(Content)
String method = exchange.getRequestMethod();
URI uri = exchange.getRequestURI();
String path = uri.getPath();
System.out.println(method + " " + path);
String content = "Hello, world!";
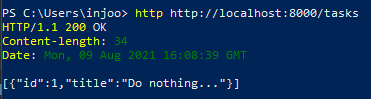
if (method.equals("GET") && path.equals("/tasks")) {
content = tasksToJSON();
}
if (method.equals("POST") && path.equals("/tasks")) {
content = "Create a new task.";
}
exchange.sendResponseHeaders(200, content.getBytes().length);
OutputStream outputStream = exchange.getResponseBody();
outputStream.write(content.getBytes());
outputStream.flush();
outputStream.close();
}
private String tasksToJSON() throws IOException {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
OutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
objectMapper.writeValue(outputStream, tasks);
return outputStream.toString();
}
}tasks
package com.codesoom.demo.models;
public class Task {
private Long id;
private String title;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
}
package com.codesoom.demo;
import com.codesoom.demo.models.Task;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpExchange;
import com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpHandler;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class DemoHttpHandler implements HttpHandler {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
private List<Task> tasks = new ArrayList<>();
public DemoHttpHandler() {
Task task = new Task();
task.setId(1L);
task.setTitle("Do nothing...");
tasks.add(task);
}
@Override
public void handle(HttpExchange exchange) throws IOException {
// 1. Method - GET, POST, PUT/PATCH, DELETE...
// 2. Path - "/", "/tasks", "/tasks/1", ..
// 3. Headers, Body(Content)
String method = exchange.getRequestMethod();
URI uri = exchange.getRequestURI();
String path = uri.getPath();
InputStream inputStream = exchange.getRequestBody();
String body = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream))
.lines()
.collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
System.out.println(method + " " + path);
if(!body.isBlank()) {
System.out.println(body);
Task task = toTask(body);
System.out.println(task);
}
String content = "Hello, world!";
if (method.equals("GET") && path.equals("/tasks")) {
content = tasksToJSON();
}
if (method.equals("POST") && path.equals("/tasks")) {
content = "Create a new task.";
}
exchange.sendResponseHeaders(200, content.getBytes().length);
OutputStream outputStream = exchange.getResponseBody();
outputStream.write(content.getBytes());
outputStream.flush();
outputStream.close();
}
private Task toTask(String content) throws JsonProcessingException {
return objectMapper.readValue(content, Task.class);
}
private String tasksToJSON() throws IOException {
OutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
objectMapper.writeValue(outputStream, tasks);
return outputStream.toString();
}
}