파이프라인
1. 파이프라인
📌 1. 파이프라인
- 여러 개의 데이터 처리 과정을 하나의 처리과정(pipneline, sequence)으로 만들어 데이터를 일괄 처리해주는 기능
- 더 짧은 코드로 가시성 있게 효율적으로 처리 가능
- 다양한 패키지에서 파이프라인 지원 중
- 데이터 프레임 : Pandas, Polars
- 머신러닝 : Scikit-Learn
- 딥러닝 : Tensorflow, Pytorch
📌 2. Scikit-Learn의 파이프라인
- Pipeline 클래스를 통해 파이프라인 구현 가능
- 사용 목적
- 편의성과 캡슐화 : 전체 데이터 처리 시퀀스에서 fit과 predict 한 번만 적용하면 됨
- 통합된 하이퍼 파라미터 최적화 : grid search를 이용해 한 번에 하이퍼 파라미터 최적화 가능
- 안전성 강화 : 교차검증(cross-validation) 시 랜덤성에 의한 데이터의 통계적 특성이 변경되는 것 방지
📌 3. 파이프라인 이용하기
- 라이브러리 불러오기
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest, f_classif
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris- 파이프라인 사용하지 않을 경우
#데이터셋 로드
x_data, y_data = load_iris(return_X_y=True)
#피쳐 셀렉팅
feat_sel = SelectKBest(f_classif, k =2)
X_selected = feat_sel.fit_transform(x_data, y_data)
print('Selected Feautures :', feat_sel.get_feature_names_out())
#표준화
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaler.fit(X_selected)
X_transformed = scaler.transform(X_selected)
print('Standard Scaled : \n', X_transformed[:5, :])
#모델학습
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth = 3)
clf.fit(X_transformed, y_data)
print('Estimate : ', clf.predict(X_transformed)[:3])
print('Accuracy :', clf.score(X_transformed, y_data))Selected Feautures : ['x2' 'x3']
Standard Scaled :
[[-1.34022653 -1.3154443 ]
[-1.34022653 -1.3154443 ]
[-1.39706395 -1.3154443 ]
[-1.2833891 -1.3154443 ]
[-1.34022653 -1.3154443 ]]
Estimate : [0 0 0]
Accuracy : 0.9733333333333334- 파이프라인 사용할 경우
: 파이프라인은 (key, value)의 리스트 구성하여 만듦
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline#데이터셋 로드
x_data, y_data = load_iris(return_X_y = True)
#pipeline 구축
pipeline = Pipeline([
('Feature Selection', SelectKBest(f_classif, k = 2)),
('Standardization', StandardScaler()),
('Decision Tree', DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth = 3))
])
display(pipeline)
# 모형학습
pipeline.fit(x_data, y_data)
#예측과 성능 평가
print('Estimate : ', pipeline.predict(x_data)[:3])
print('Accuracy : ', pipeline.score(x_data, y_data))
Estimate : [0 0 0]
Accuracy : 0.9733333333333334- make_pipeline() 함수를 통해 파이프라인 생성 가능
: 파이프라인 이름 자동으로 만들어 줌
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
pipeline_auto = make_pipeline(SelectKBest(f_classif, k = 2),
StandardScaler(),
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth = 3))
display(pipeline_auto)
2. 파이프라인의 결합
📌 1. 수치형 데이터 파이프라인 처리
- 라이브러리 불러오기
import seaborn as sns
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputerdf = sns.load_dataset('diamonds')
print(df.info())
x_data = df.drop('price', axis = 1)
y_data = df['price']
numeric_col = list(x_data.select_dtypes(exclude = 'category').columns)
category_col = list(x_data.select_dtypes(exclude = 'category').columns)
print(f'numeric_col : {numeric_col}')
print(f'category_col : {category_col}')<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 53940 entries, 0 to 53939
Data columns (total 10 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 carat 53940 non-null float64
1 cut 53940 non-null category
2 color 53940 non-null category
3 clarity 53940 non-null category
4 depth 53940 non-null float64
5 table 53940 non-null float64
6 price 53940 non-null int64
7 x 53940 non-null float64
8 y 53940 non-null float64
9 z 53940 non-null float64
dtypes: category(3), float64(6), int64(1)
memory usage: 3.0 MB
None
numeric_col : ['carat', 'depth', 'table', 'x', 'y', 'z']
category_col : ['carat', 'depth', 'table', 'x', 'y', 'z']- 파이프라인 만들기
numeric_pipl = Pipeline(
steps = [
('imputer', SimpleImputer(strategy = 'mean')),
('scaler' , StandardScaler())
])
display(numeric_pipl)
#파이프라인 학습
numerical_data_piped = numeric_pipl.fit_transform(x_data[numeric_col])
pd.DataFrame(numerical_data_piped, columns = numeric_col).head()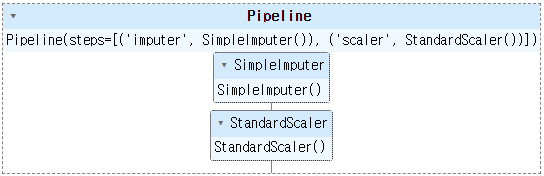
carat depth table x y z
0 -1.198168 -0.174092 -1.099672 -1.587837 -1.536196 -1.571129
1 -1.240361 -1.360738 1.585529 -1.641325 -1.658774 -1.741175
2 -1.198168 -3.385019 3.375663 -1.498691 -1.457395 -1.741175
3 -1.071587 0.454133 0.242928 -1.364971 -1.317305 -1.287720
4 -1.029394 1.082358 0.242928 -1.240167 -1.212238 -1.117674📌 2. 범주형 데이터 파이프라인 처리
- 라이브러리 불러오기
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder- 파이프라인 만들기
categ_pipl = Pipeline(
steps = [
('Imputer', SimpleImputer(strategy = 'constant')),
('onehot' , OneHotEncoder(sparse_output = False))
])
display(categ_pipl)
#파이프라인 학습
category_data_piped = categ_pipl.fit_transform(x_data[category_col])
#onehotencoder의 컬럼명 확인
category_colnames = categ_pipl[1].get_feature_names_out(category_col)
#파이프라인 이후 데이터(array -> dataframe)
pd.DataFrame(category_data_piped, columns = category_colnames).head()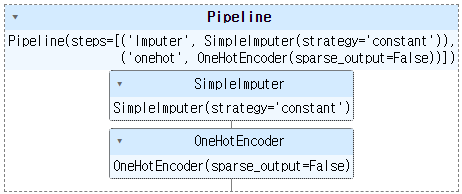
📌 3. 수치형 + 범주형 데이터 파이프라인 처리
- ColumnTransformer 클래스를 사용해 수치형과 범주형 데이터 파이프라인 결합 가능
- 필요한 라이브러리 불러오기
from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline- 파이프라인 결합
preprocessor = ColumnTransformer(
transformers = [
('numeric' , numeric_pipl, numeric_col),
('category', categ_pipl, category_col)
])
pipeln = make_pipeline(preprocessor, LinearRegression())
display(pipeln)
pipeln.fit(x_data, y_data)
print('Estimate : ', pipeln.predict(x_data))
print('Accuracy : ', pipeln.score(x_data, y_data))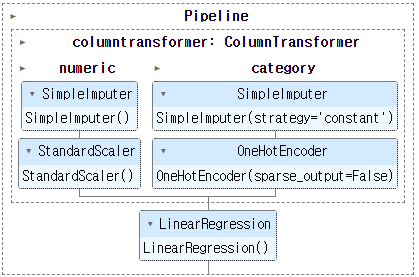
Estimate : [ 737.67578125 451.25585938 56.00585938 ... 2429.54882812 3297.50585938
3108.93359375]
Accuracy : 0.8938158297402341📌 4. ColumnTransformer
: 컬럼 기준으로 데이터 복합하여 처리해주는 함수
- 라이브러리 불러오기
from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np- ColumnTransformer 사용하기
: SimpleImputer을 사용해 height의 null 값들은 평균으로 출력하고 나머지 column은 통과
data_df = pd.DataFrame({
'height' : [165, np.nan, 182],
'weight' : [70, 62, np.nan],
'age' : [np.nan, 18, 15]
})
# SimpleImputer을 사용해 height의 null 값들은 평균으로 출력하고 나머지 column은 통과
col_transform = ColumnTransformer([
('Impute_mean', SimpleImputer(strategy = 'mean'), ['height'])],
remainder = 'passthrough')
display(col_transform)
print(data_df)
print(col_transform.fit_transform(data_df))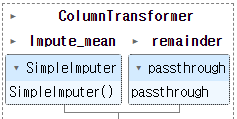
height weight age
0 165.0 70.0 NaN
1 NaN 62.0 18.0
2 182.0 NaN 15.0
[[165. 70. nan]
[173.5 62. 18. ]
[182. nan 15. ]]- ColumnTransformer 사용하기
: SimpleImputer을 사용해 mean과 median값을 null에 넣고 나머지 column에 대한 값은 상수로 -1값을 넣어줌
col_transform2 = ColumnTransformer([
('Impute_mean' , SimpleImputer(strategy = 'mean'), ['height']),
('Impute_median', SimpleImputer(strategy = 'median'), ['weight'])],
remainder = SimpleImputer(strategy = 'constant', fill_value = 1))
display(col_transform2)
print(data_df)
print(col_transform2.fit_transform(data_df))
height weight age
0 165.0 70.0 NaN
1 NaN 62.0 18.0
2 182.0 NaN 15.0
[[165. 70. 1. ]
[173.5 62. 18. ]
[182. 66. 15. ]]