CH02 - 스프링 부트에서 테스트 코드를 작성하자
TDD
레드 그린 사이클
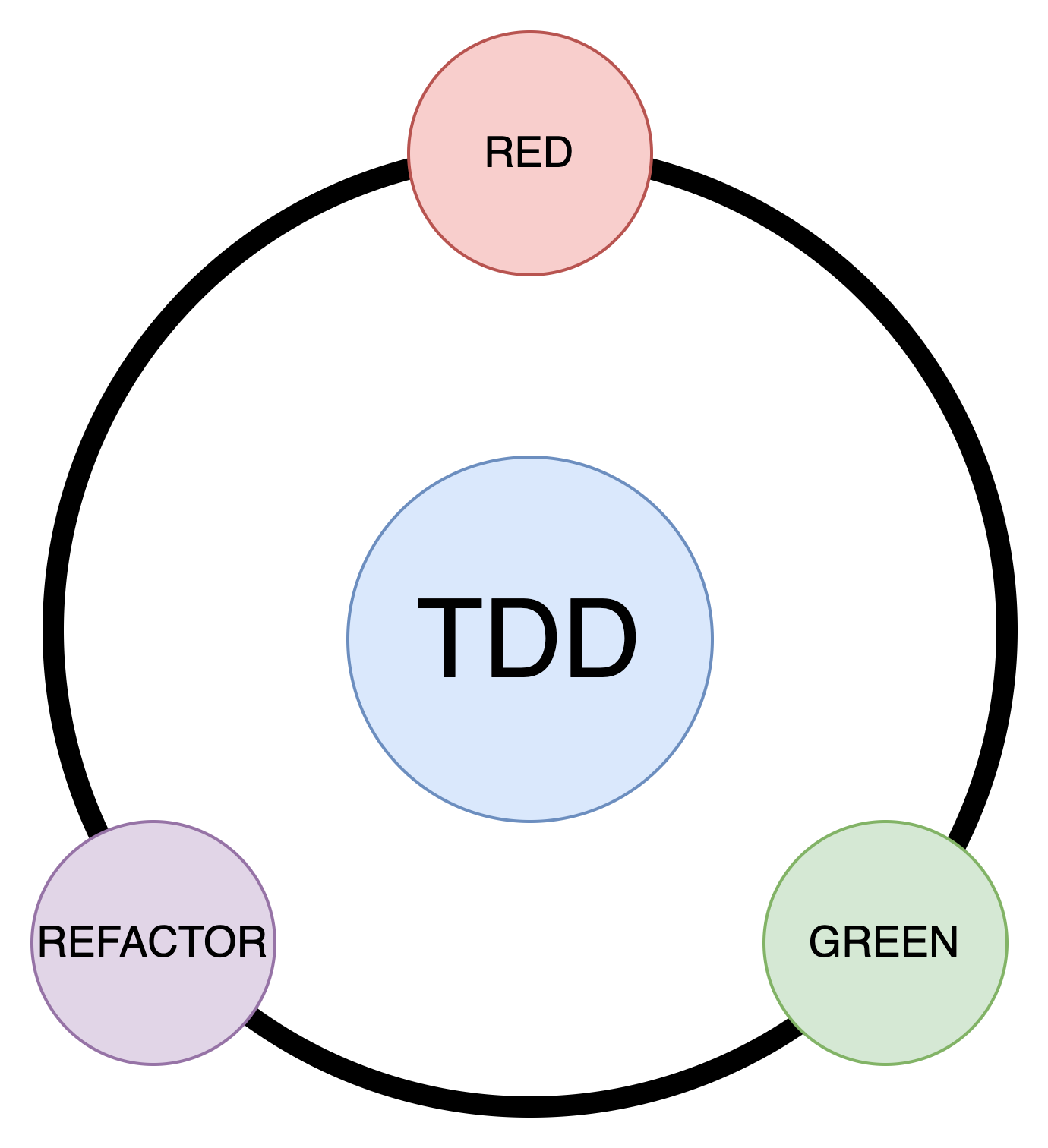
- 항상 실패하는 테스트를 먼저 작성 (RED)
- 테스트가 통과하는 프로덕션 코드를 작성 (GREEN)
- 테스트가 통과하면 프로덕션 코드를 리팩토링 (REFACTOR)
단위 테스트
- TDD 의 첫 번째 단계
- 기능 단위의 테스트 코드를 작성하는 것
- 작성 시점은 자유
- 리팩토링을 포함하지 않는다
단위 테스트의 이점
- 개발단계 초기에 문제를 발견할 수 있다
- 개발자가 나중에 코드를 리팩토링하거나 라이브러리 업그레이드 등에서 기존 기능이 올바르게 작동하지는 확인 가능
- 기능에 대한 불확실성을 감소
- 시스템에 대한 실제 문서를 제공
- 단위 테스트 자체를 문서로 사용 가능
- 톰캣을 재시작하지 않아도 된다
System.out.println()을 통해 눈으로 확인 하지 않아도 된다- 개발자가 만든 기능을 안전하게 보호
메인 클래스 작성
package com.pgrrr.book.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}@SpringBootApplication- 스프링 부트의 자동 설정
- 스프링 Bean 읽기와 생성 설정
- 이 위치부터 설정을 읽는다 → 프로젝트 최상단에 위치 시킨다
SpringApplication.run- main 메소드에서 실행
- 내장 WAS 를 실행
- 내장 WAS
- 스프링 부트에서 권장하는 방식
- 언제 어디서나 같은 환경에서 스프링 부트 배포 가능
API 작성
package com.pgrrr.book.springboot.web;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController // 1
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello") // 2
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
}@RestController- 컨트롤러를 JSON을 반환하는 컨트롤러로 만들어준다
@ResponseBody를 각 메소드마다 선언 했던 것을 한번에 사용
@GetMapping- HTTP Method 인 Get 의 요청을 받을 수 있는 API 를 만들어 줍니다.
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)대신 사용
WAS 대신 테스트 코드로 검증
package com.pgrrr.book.springboot.web;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.get;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) // 1
@WebMvcTest(controllers = HelloController.class) // 2
public class HelloControllerTest {
@Autowired // 3
private MockMvc mvc; // 4
@WithMockUser(roles = "USER")
@Test
public void hello가_리턴된다() throws Exception {
String hello = "hello";
mvc.perform(get("/hello")) // 5
.andExpect(status().isOk()) // 6
.andExpect(content().string(hello)); // 7
}
}@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)- 테스트를 진행할 때 JUnit 에 내장된 실행자 외에 다른 실행자를 실행
- SpringRunner 라는 스프링 실행자를 사용
- 스프링 부트 테스트와 JUnit 사이에 연결자 역할
@WebMvcTest- 여러 스프링 테스트 어노테이션 중 Web (Spring MVC) 에 집중할 수 있는 어노테이션
- 선언할 경우
@Controller,@ControllerAdvice사용 가능 @Service,@Component,@Repository사용 불가능- 컨트롤러만 사용하기 때문에 선언
@Autowired- 스프링이 관리하는 빈을 주입 받는다
private MockMvc mvc- 웹 API를 테스트할 때 사용
- 스프링 MVC 테스트의 시작점
- HTTP GET, POST 등에 대한 API 테스트 가능
mvc.perform(get(”/hello”))- MockMvc 를 통해 /hello 주소로 HTTP GET 요청을 한다
- 체이닝이 지원되어 여러 검증 기능을 이어서 선언 가능
.andExpect(status().isOk())mvc.perform의 결과를 검증- HTTP Header 의 Status 를 검증
- 200, 404, 500 등 상태 검증
- OK 는 200 여부 검증
.andExpect(content().string(hello))mvc.perform의 결과를 검증- 응답 본문의 내용을 검증
- Controller 에서 “hello” 를 리턴하는지 검증
@WithMockUser(roles = “USER”)@WithMockUser- UserDetail 생성
@WithAnonymousUser- 익명의 유저 생성
@WithUserDetails- UserDetails 조회
테스트 코드의 중요성
브라우저로 한 번씩 검증은 하되 테스트 코드는 꼭 작성
테스트 코드를 먼저 검증 후 필요하면 브라우저로 확인

