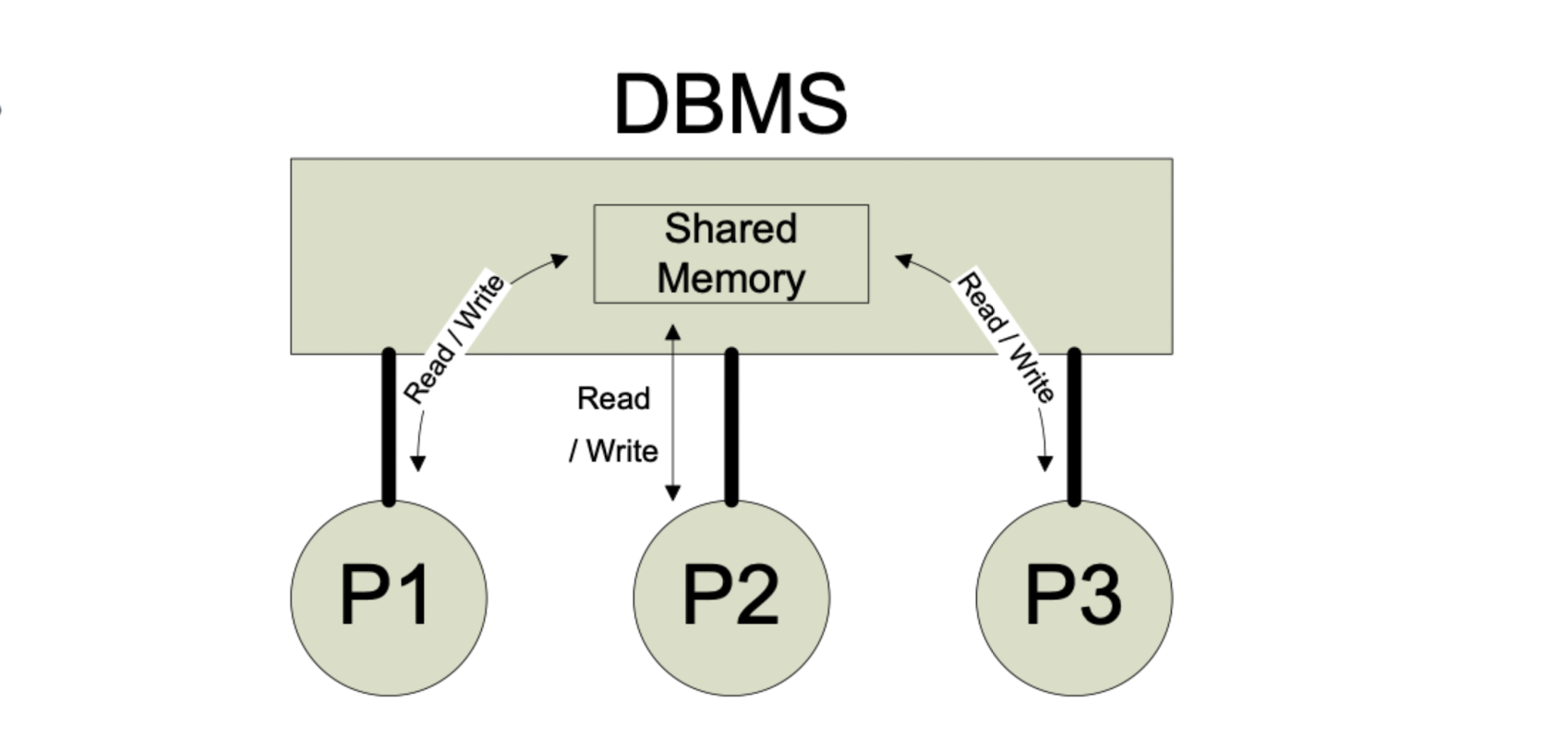
Process Management
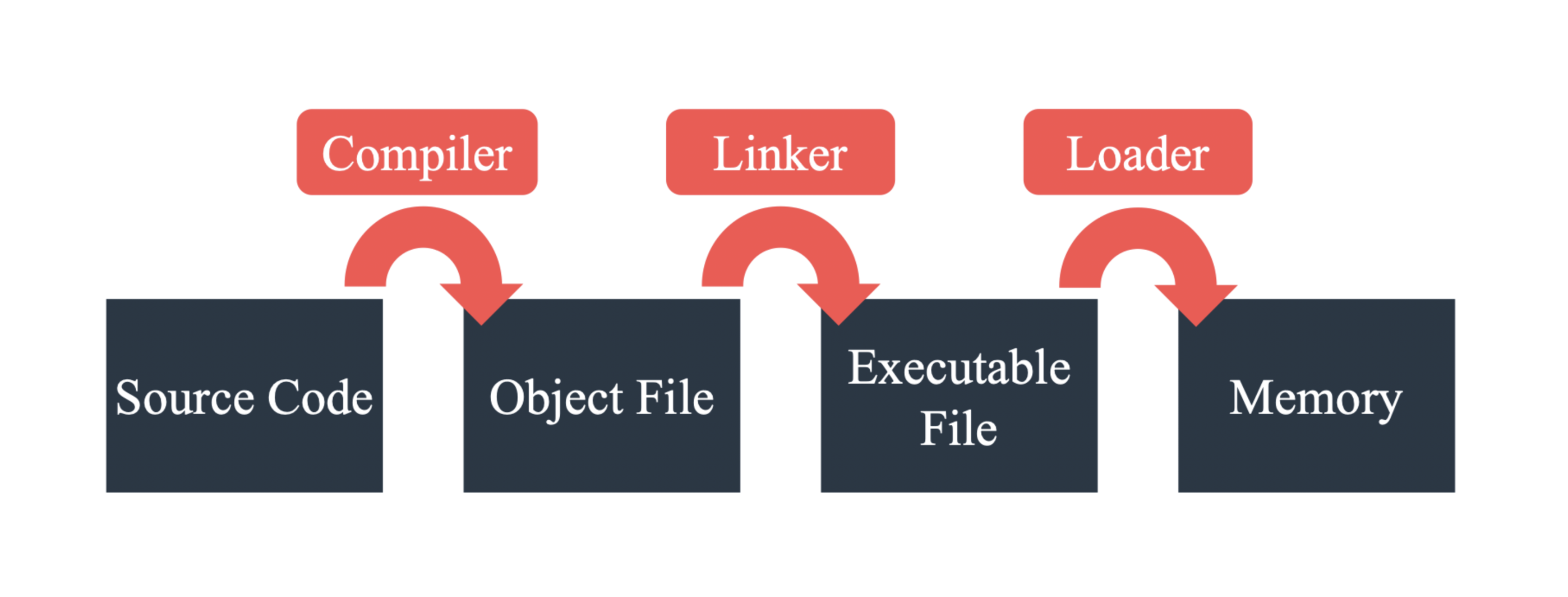
프로그램이 만들어지는 과정.
Compiler
역할
- 사람이 이해할 수 있는 프로그래밍 언어로 작성된 Source Code를 컴퓨터(CPU)가 이해할 수 있는 기계어로 표현된 Object파일로 변환
Source Code (e.g., C file)
- 프로그램이 수행하고자 하는 작업이 프로그래밍 언어로 표현되어 있다.
Object (e.g., O file)
-
컴퓨터(CPU)가 이해할 수 있는 기계어로 구성된 파일
자체로는 수행이 이루어지지 못함
프로세스로 변환되기 위한 정보가 삽입되어야 함 -
Relocatable Addresses(Relative Address)로 표현
심볼들의 주소가 상대적인 값으로 표현됨
(시작주소로부터 26바이트 지점)
Linker
역할
- 관련된 여러 Object파일들과 라이브러리들을 연결하여, 메모리로 로드 될 수 있는 하나의 Executable로 변환
Executable (e.g., exe file)
- 특정한 환경(OS)에서 수행될 수 있는 파일
- 프로세스로의 변환을 위한 Header, 작업 내용인 Text, 필요한 데이터인 Data를 포함한다.
- Absolute Address로 표현
심볼들의 주소가 절대값으로 표현됨
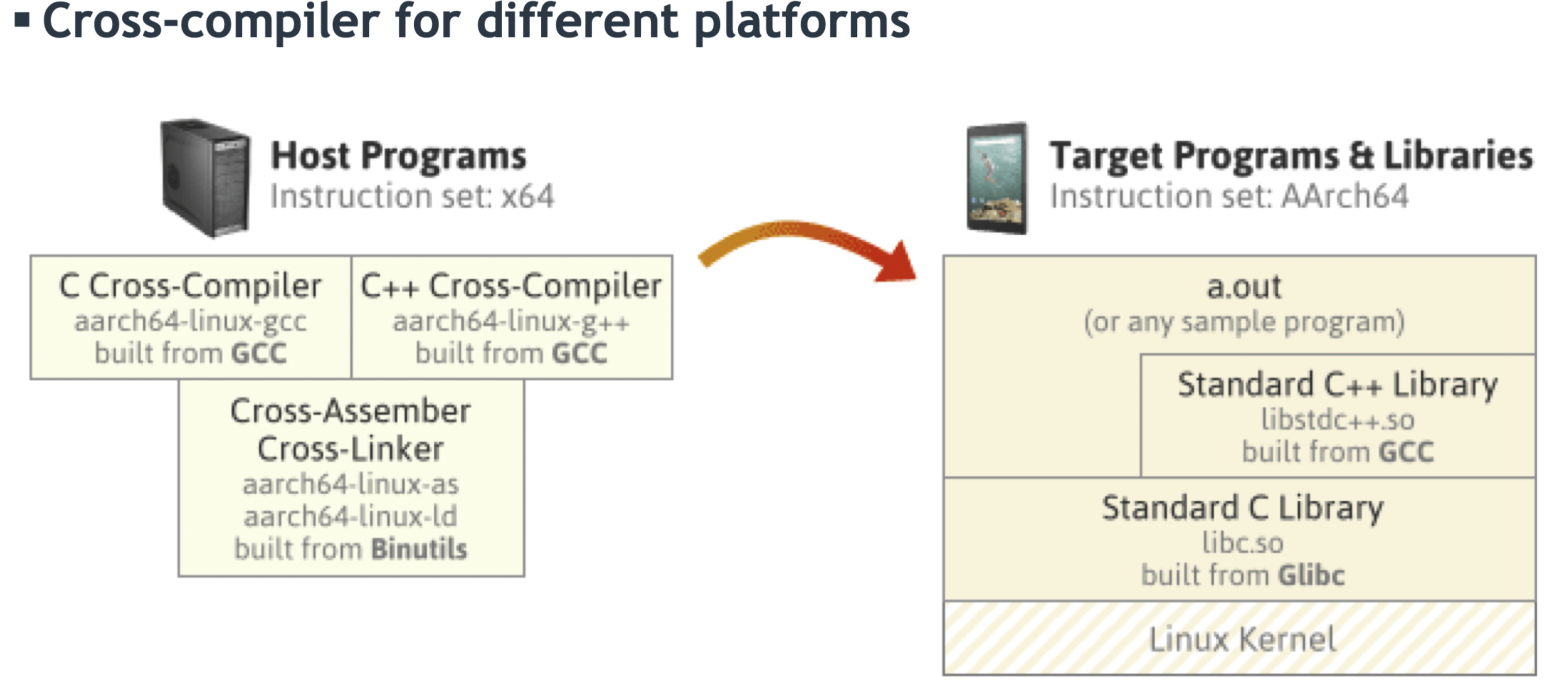
Compiler와 Linker는 결과물이 수행될 OS와 CPU에 따라 다른 형태의 파일을 만든다.
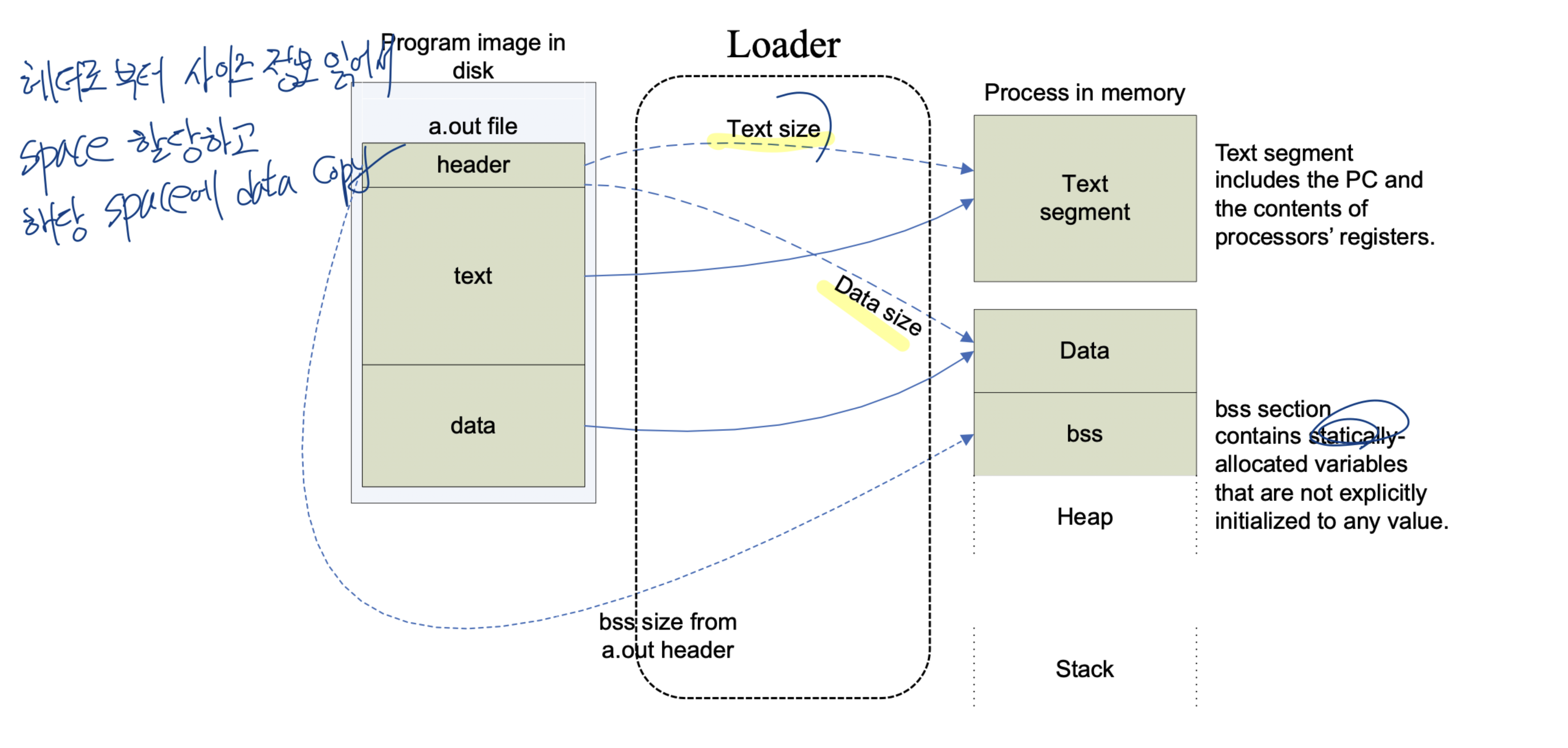
Loader
역할
- Executable을 실제 메모리에 올려주는 역할을 담당하는 운영체제의 일부
동작 과정
- Executable의 Header를 읽어, Text와 Data의 크기를 결정
- 프로그램을 위한 Address Space를 생성
- 실행 명령어와 Data들을 Executable로부터 생성한 Address Space로 복사
- 프로그램의 Argument들을 Stack으로 복사
- CPU내 Register를 초기화하고, Start-up Routine으로 Jump
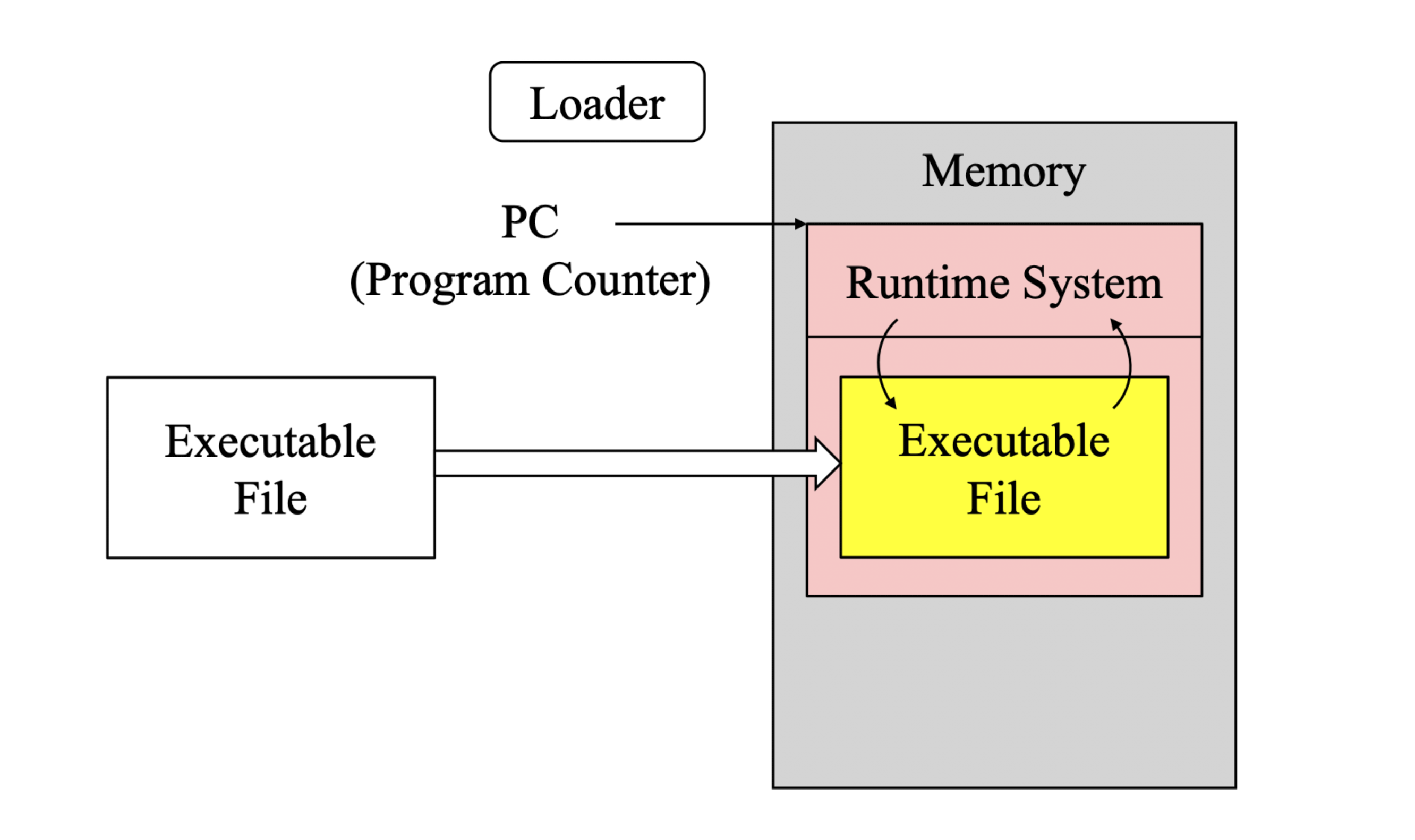
Runtime System
역할
- Runtime System은 응용 프로그램의 효율적인 실행을 지원하기 위해, 프로그램과 연결하여 상호 작용함
C Runtime System Program Execution
-
GCC는 Start-up Code Object 파일을 추가하여 프로그램을 컴파일 하며, 이 때 기본 라이브러리들도 동적으로 링크 된다.
-
Process를 시작하기 위해 커널은 PC(프로그램 카운터)를 _start함수의 주소로 지정한다.
-
_start함수는 동적으로 링크된 C 라이브러리 및 쓰레드 환경을 초기화하기 위해 _libc_start_main함수를 호출한다.
-
라이브러리 초기화를 진행한 이후, 프로그램의 main함수가 호출된다.
Process Concept
Process - Abstraction for
- Execution Unit : 스케줄링의 단위
- Protection Domain : 서로 침범하지 못함
Process - Implemented with
- Program Counter
- Stack
- Data Section
프로세스는 디스크에 저장된 프로그램으로부터 변환되어 메모리로 로딩된다.
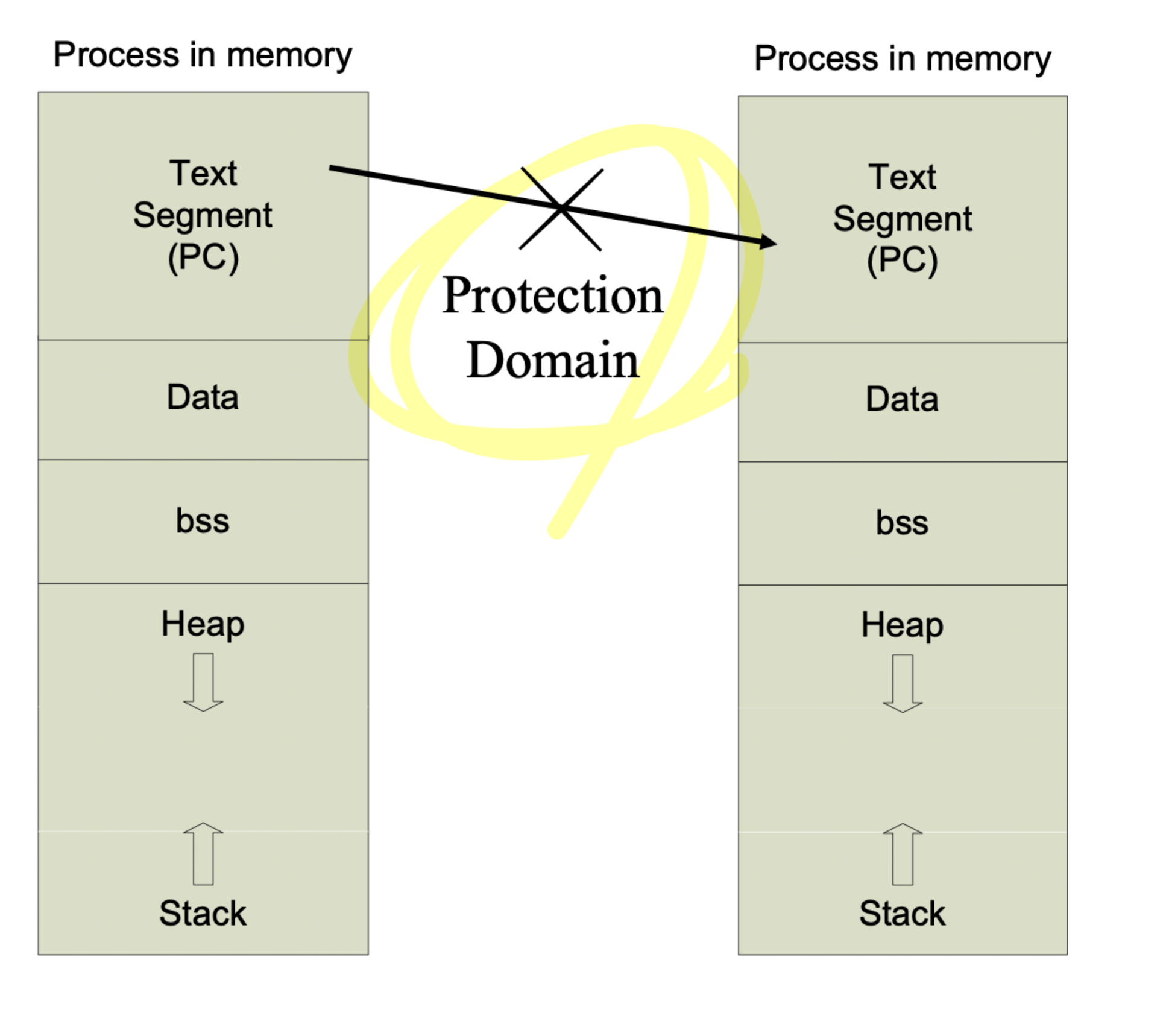
서로 다른 프로세스들간에는 침범하지 못한다. (Protection Domain)
Transition of Process State
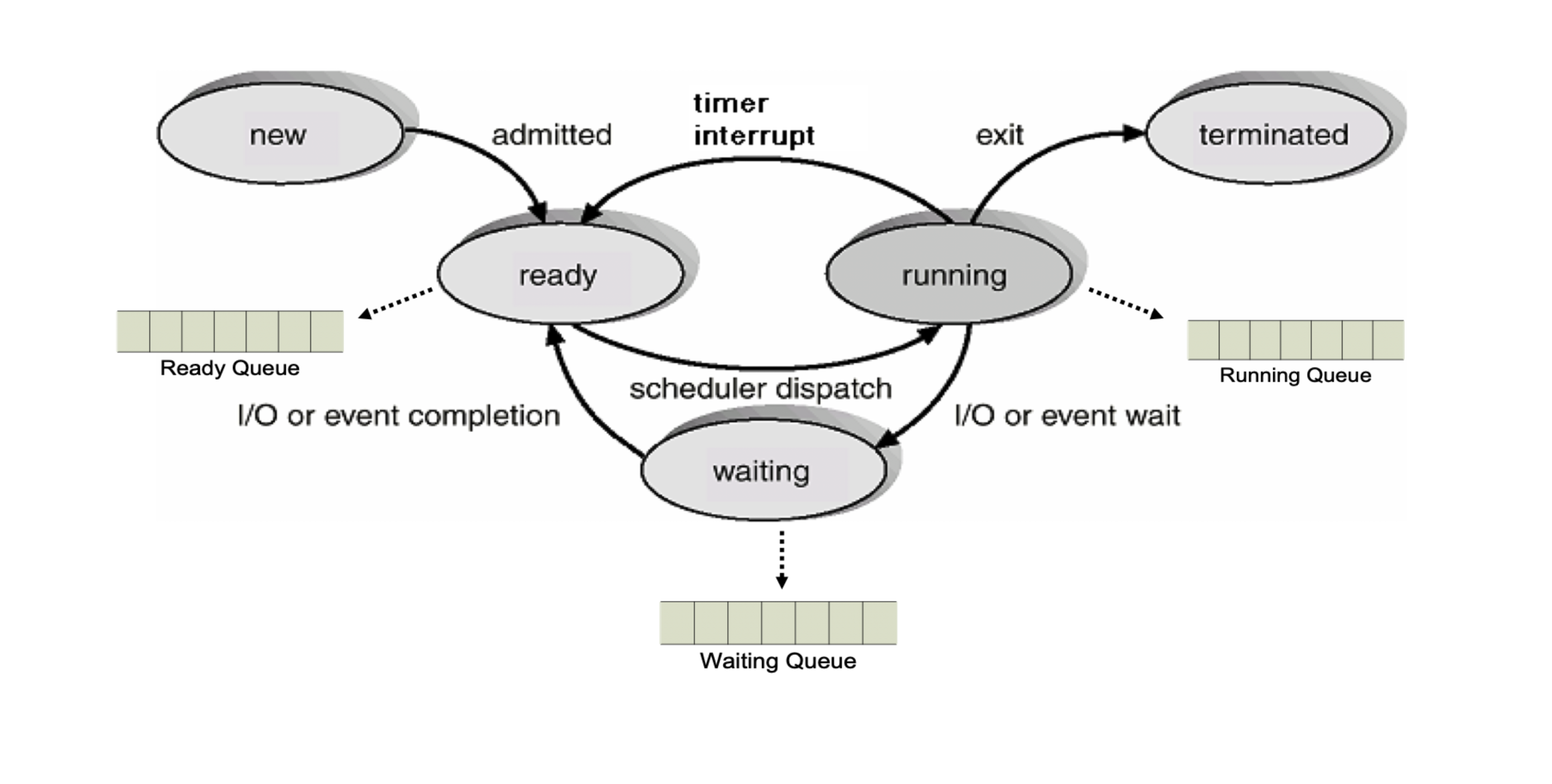
-
New : The Process is being created
-
Running : Instructions are being executed
-
Waiting : The process is waiting for some event to occur
-
Ready : The process is waiting to be assigned to a processor
-
Terminated : The process has finished execution
커널 내에 Ready Queue, Waiting Queue, Running Queue를 두고 프로세스들을 상태에 따라 관리한다.
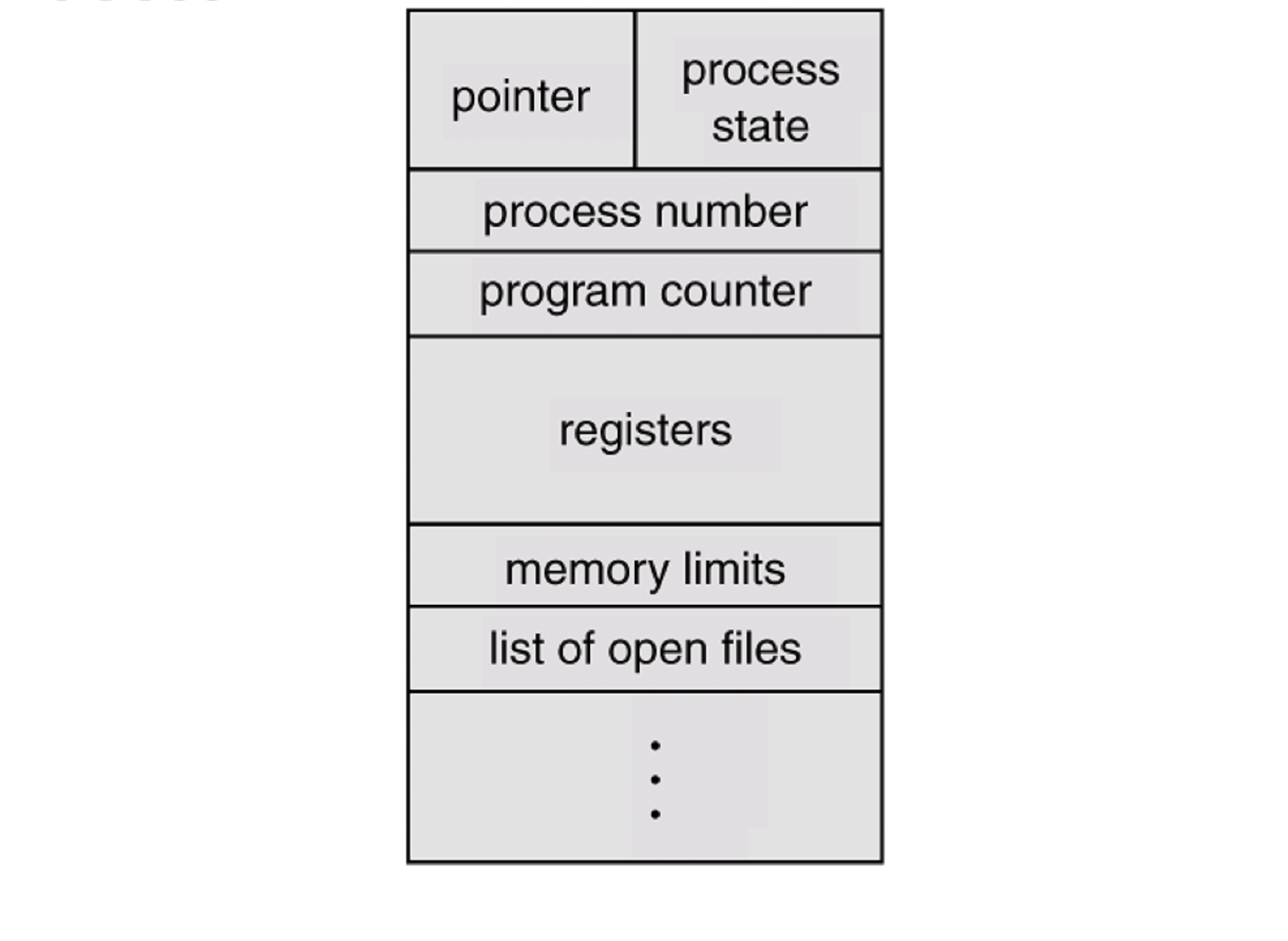
Process Control Block
PCB
- 각 프로세스는 PCB에 의해서 OS안에 나타나진다(represented)
Information associated with each process
- Process State
- Program Counter
- CPU Registers
- CPU Scheduling Information
- Memory Management Information
- Accounting Information
- I/O Status Information
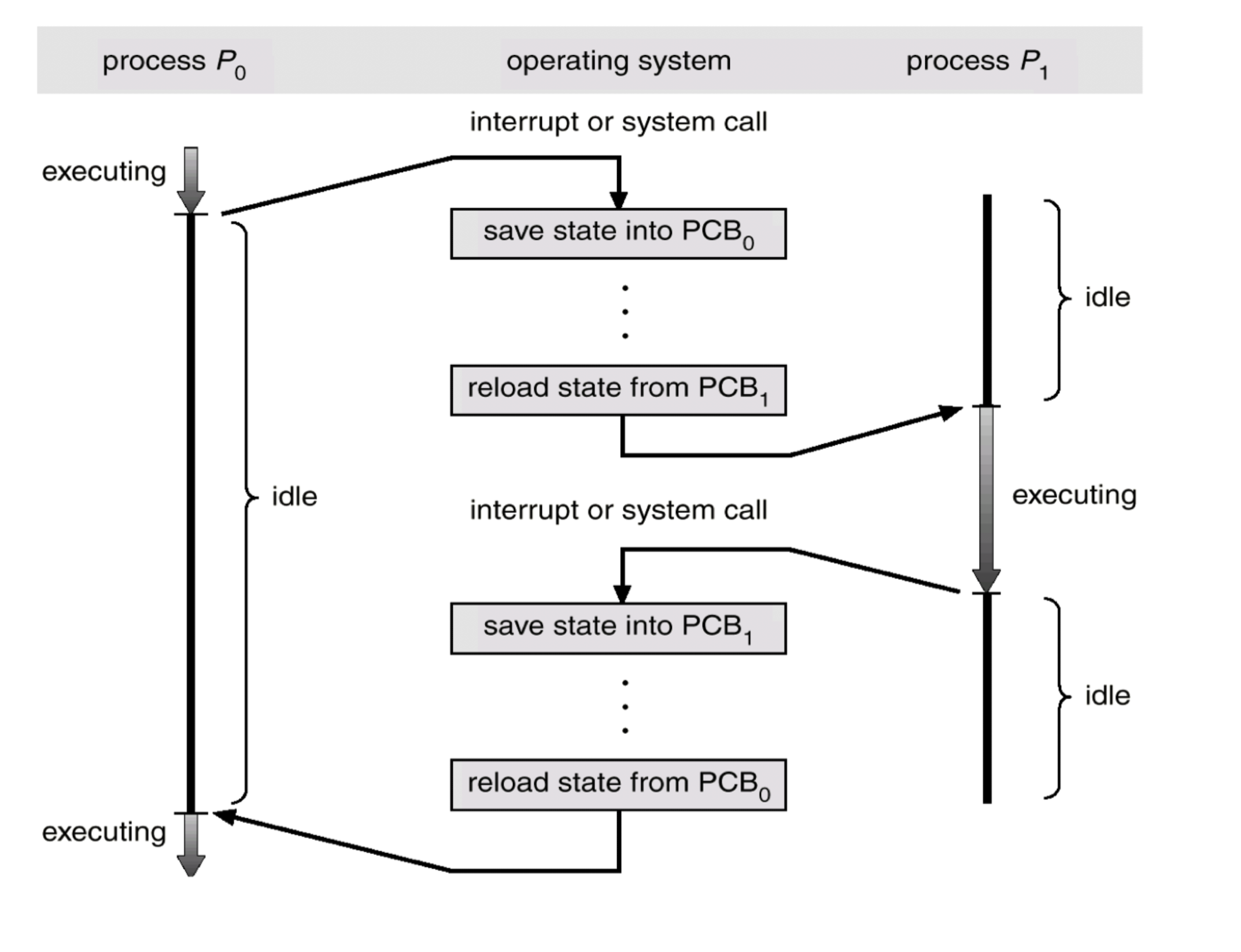
Context Switching
-
When CPU switches to a new process, kernel must save the state of the old(current) process(기존 프로세스 상태 저장) and load the saved state for the new process(새로운 프로세스 로드).
-
Context switching time is overhead
System can't do useful work while switching -
Context switching time depends on H/W support
프로세서 구조에 따른 Context Switch의 차이
CISC
- 복잡한 명령어 셋 구성 -> 효율 높임, 클럭 속도 저하
- 복잡한 회로 -> 물리적인 공간 차지 -> 레지스터 용량 저하
e.g., Intel Pentium Processor
RISC
-
간단한 명령어 셋 구성 -> 클럭 속도 높임 -> 빠른 수행 속도
-
절약된 물리적 공간에 보다 많은 레지스터 장착
Context Switch 시 레지스터 내용 변경에 보다 큰 오버헤드가 발생함.
e.g., ARM Processor -
Register Window (Berkeley RISC Design)
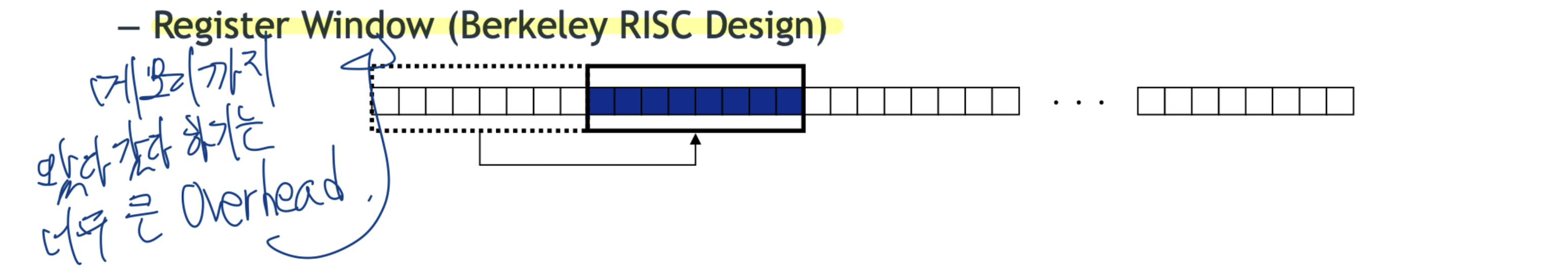
memory에 접근하는 수를 최대한 줄이고자 Register를 이용
참고
Context Switch Diagram
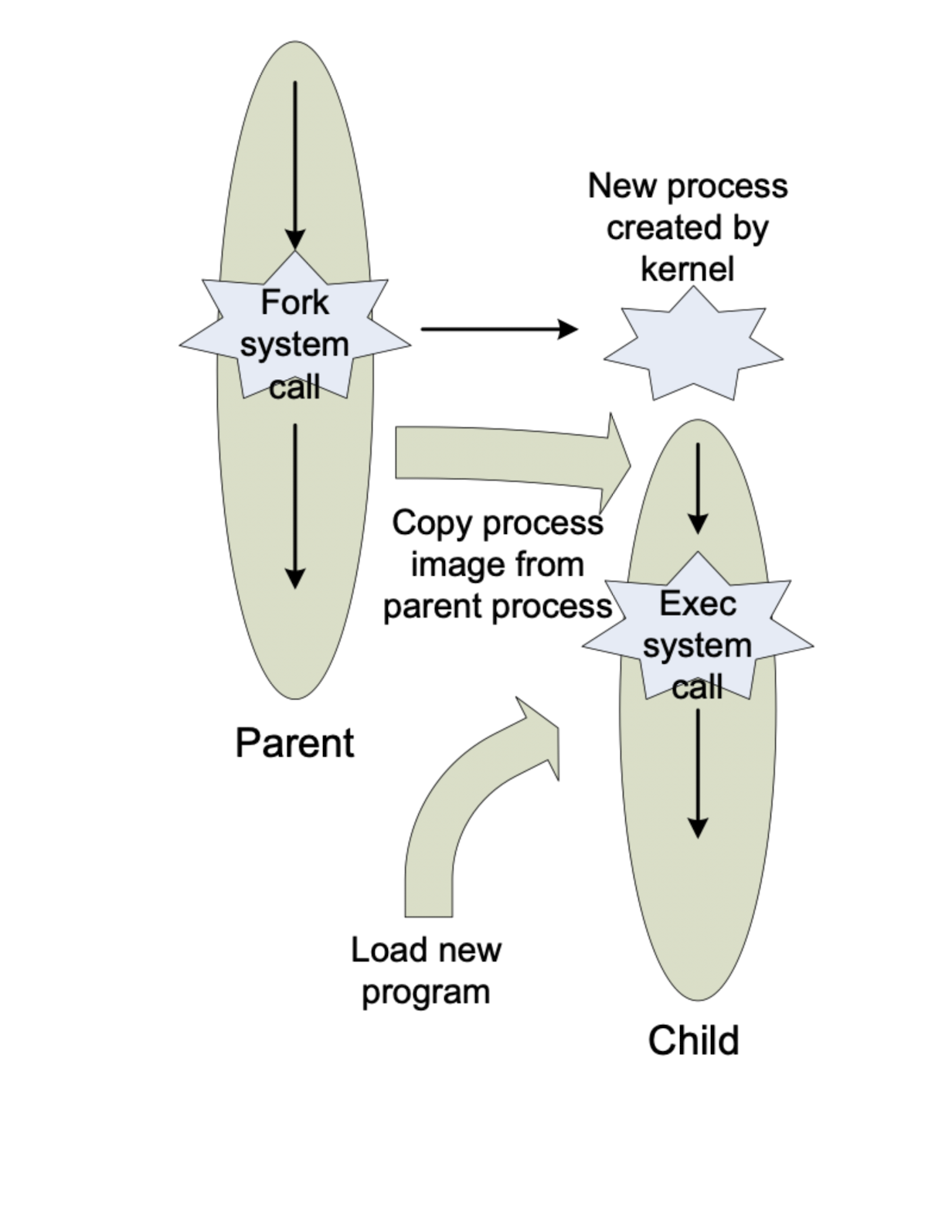
Process Creation
-
프로세스들은 Concurrently하게 실행될 수 있으며, 동적으로 생성/종료 된다.
-
OS provides process creation and process termination mechanisms
-
Process Creation (i.e., fork())

Process Creation in Memory View
Memory (Text and Data Section)
-
Child process is a duplicate of the parent process.
-
Child process has a program loaded into it
- Unix example
- A new process created by fork system call
- A new process (child process) consists of a copy of the memory of the original process (parent process)
- Exec(2): to replace the memory with a new program
Process Termination
Process Termination
-
A process terminates when it finished executing its final statement and asks the OS to delete it by using exit system call.
- Output data from child to parent (via wait())
- Process's resources are deallocated by OS
-
The abort function causes abnormal process termination to occur.
- The SIGABRT signal is sent to the calling process.
- Core dump is made.
Cooperating Processes
Independent process cannot affect or be affected by the execution of another process.
Advantages of process cooperation
-
Information sharing
-
Computation speed-up
-
Modularity
-
Convenience