Contents
- Static Modeling
- Notations in Class Diagram
- Dependency
- Association
Static Modeling
Static Modeling
정적 모델링
- 시스템의 구조와 구성 요소 간의 관계를 정적인(Static)측면에서 표현
- Structure diagram을 통해서 표현
Class diagram
- 시스템을 구성하는 클래스와 클래스 간의 관계를 도식화 함
From Sequence Diagram
Sequence diagram and class diagram
- Sequence diagram을 그리다 보면, 클래스들과 메소드들이 등장함
- Dynamic & static view를 동시에 그리고 반복적으로 그림
Design Class Diagram
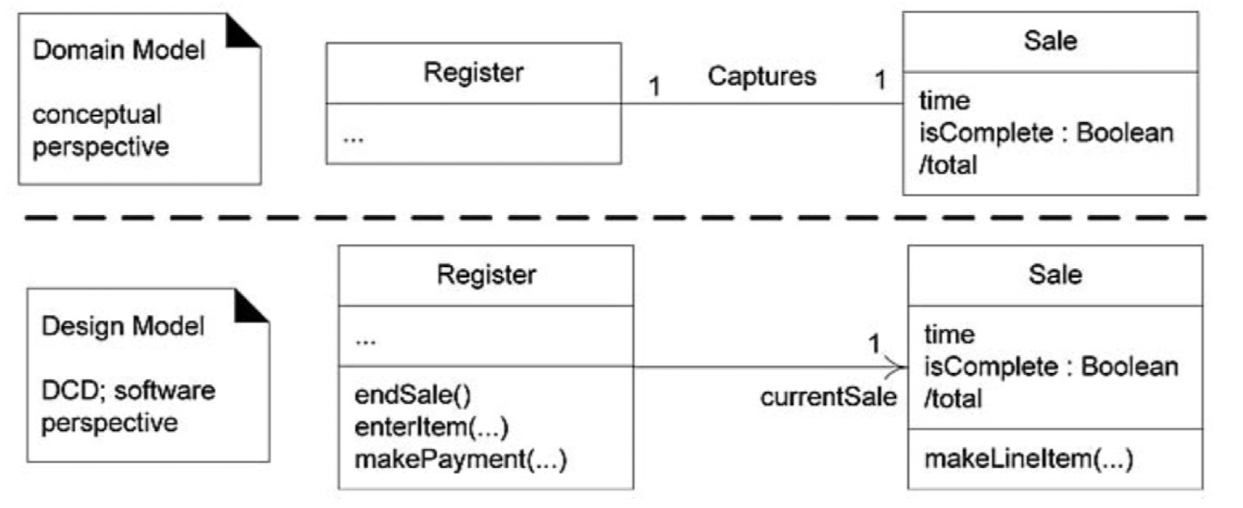
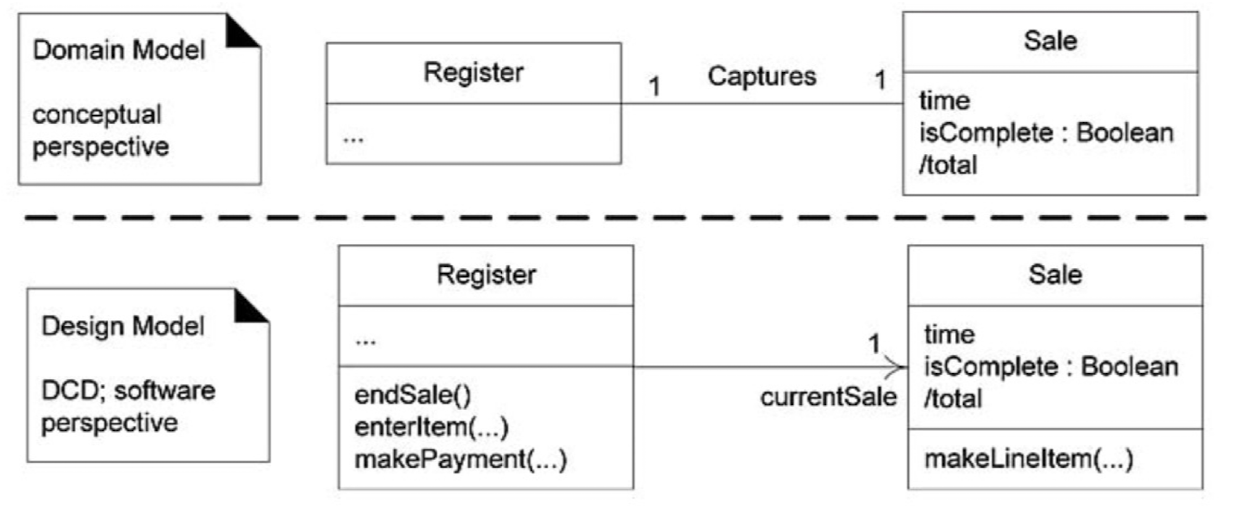
Domain model과 design class disgram의 차이점
- 둘 다 class diagram의 표기를 차용하지만,
- Domain model은 개념적인 (Conceptual) 관점에서 시스템을 이루는 도메인 객체 간의 관계를 표현
- Design class diagram은 소프트웨어 관점에서 시스템 내부의 클래스와 관계를 세부적으로 표현
Notaions in Class Diagram
Notations
클래스 (Class)
- Attribute와 Operations의 집합체 (데이터 타입)
- 클래스의 instance를 object라고 함
- Attribute는 클래스의 구조적 특징을 설명하는 데이터
- Operation은 클래스의 행위(Behavior)를 나타냄
Attribute syntax - 가시성(visibility)
- 클래스 안의 속성을 누가 접근할 수 있는지 명시
- 접근 지정자를 표기하는 것
+ : public - 외부 누구나 접근 할 수 있음
- : private - 해당 클래스 내에서만 접근 가능
# : protected - 클래스 자기 자신과 상속 받는 서브 클래스에서만 접근 가능

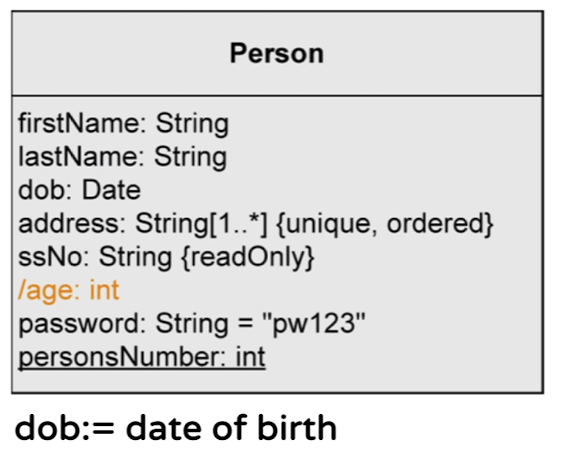
Attribute syntax - derived attribute
- Derived attribute는 다른 정보로부터 해당 attribute의 값이 계산되는 attribute를 말함
/name 과 같이 /(slash)를 이용하여 표기
관례적으로 {readOnly}를 붙이기도 함(다른 attribute로 부터 값이 결정되기 때문에 직접적인 수정을 허용하지 않는 것)
Attribute syntax - name and type
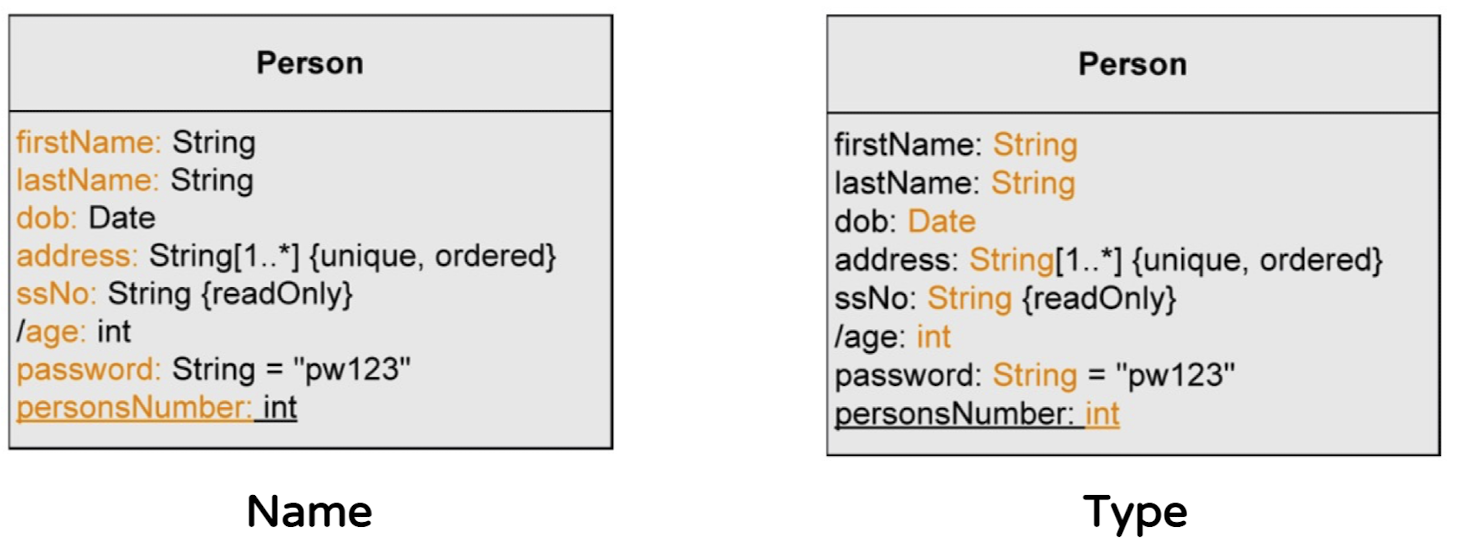
- Name : Type과 같이 속성의 이름과 타입을 명시
- Data type : primitive data type or user-defined class
Attribute syntax - Multiplicity
- 한 attribute가 가지는 값의 개수 (default는 1)
- Notation: [min...max]
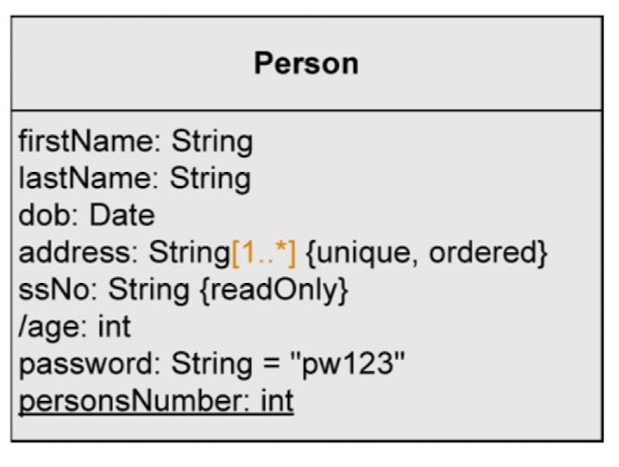
Attribute syntax - default value
- Attribute가 가지는 기본 값

Attribute syntax - properties
-
Pre-defined properties
{readOnly} = value cannot be changed (= final)
{unique} = no duplicates permitted
{non-unique} = duplicates permitted
{oredered} = fixed order of the values
{unordered} = no fixed order of the values -
Attribute specifications
Set : {unordered, unique}
Multi-set : {unordered, non-unique}
Ordered set : {ordered, unique}
List : {ordered, non-unique}

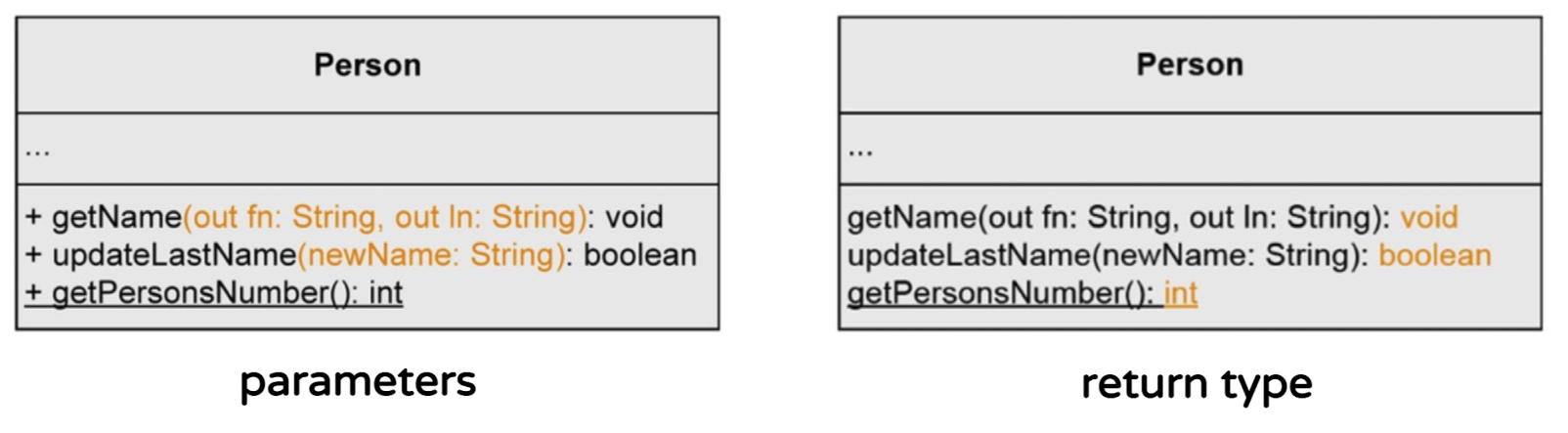
Operation syntax
- Visibility가 생략된 경우는 기본적으로 Public이라고 가정
- Parameter's direction
in : input parameter
out : output parameter
inout : combined input/output parameter
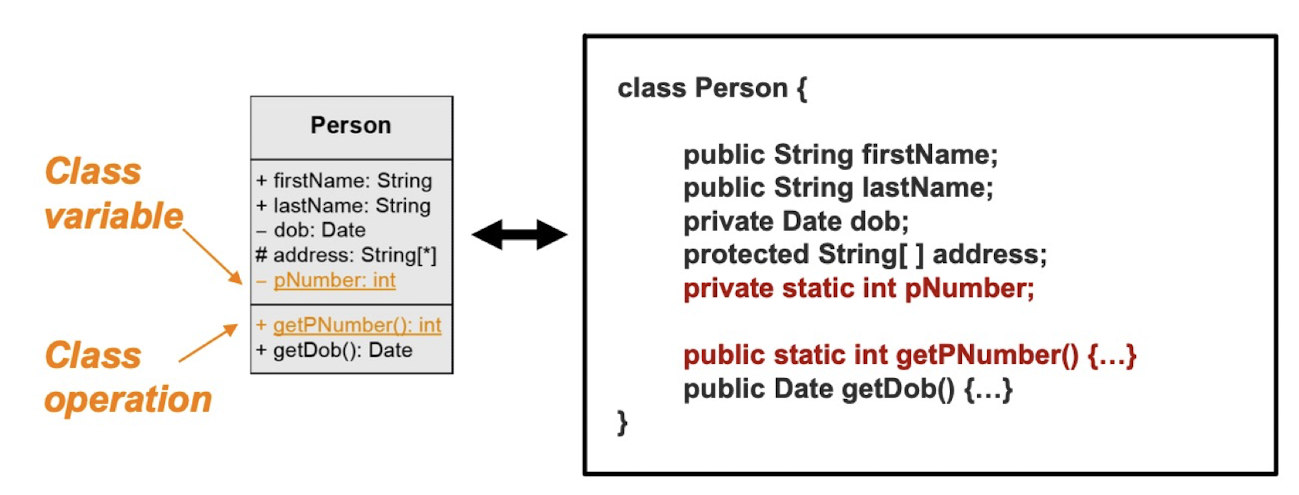
Class variable and class operation
- Class variable (= class attribute, static attribute)
클래스에서 한 번만 정의되면 모든 인스턴스에서 공유되는 속성 - Class operation (= static operation)
객체 생성 없이도 호출 될 수 있는 오퍼레이션 - static은 underline(밑줄)로 표시한다
Getter and Setter
- 일반적으로 (Private) 속성의 값을 읽어올 때는 getter, 값을 설정할 때는 setter를 통해서 수행함 (Information Hiding)
- 모든 속성에 대해서 getter/setter를 다 표시 하는 것은 장황해질 수 있기 때문에 종종 생략함
Abstract operation and abstract class
-
추상 오퍼레이션 : 구현체를 정의할 필요가 없는 오퍼레이션
-
추상 클래스 : 추상 오퍼레이션을 가지는 클래스
상속 구조에서 빈번히 등장 -
표현법
1) Italic 글씨체로 표현
2) {abstract} property를 붙여서 표현
3) class의 경우 << abstract >>로 표현하기도 함

Different level of class details
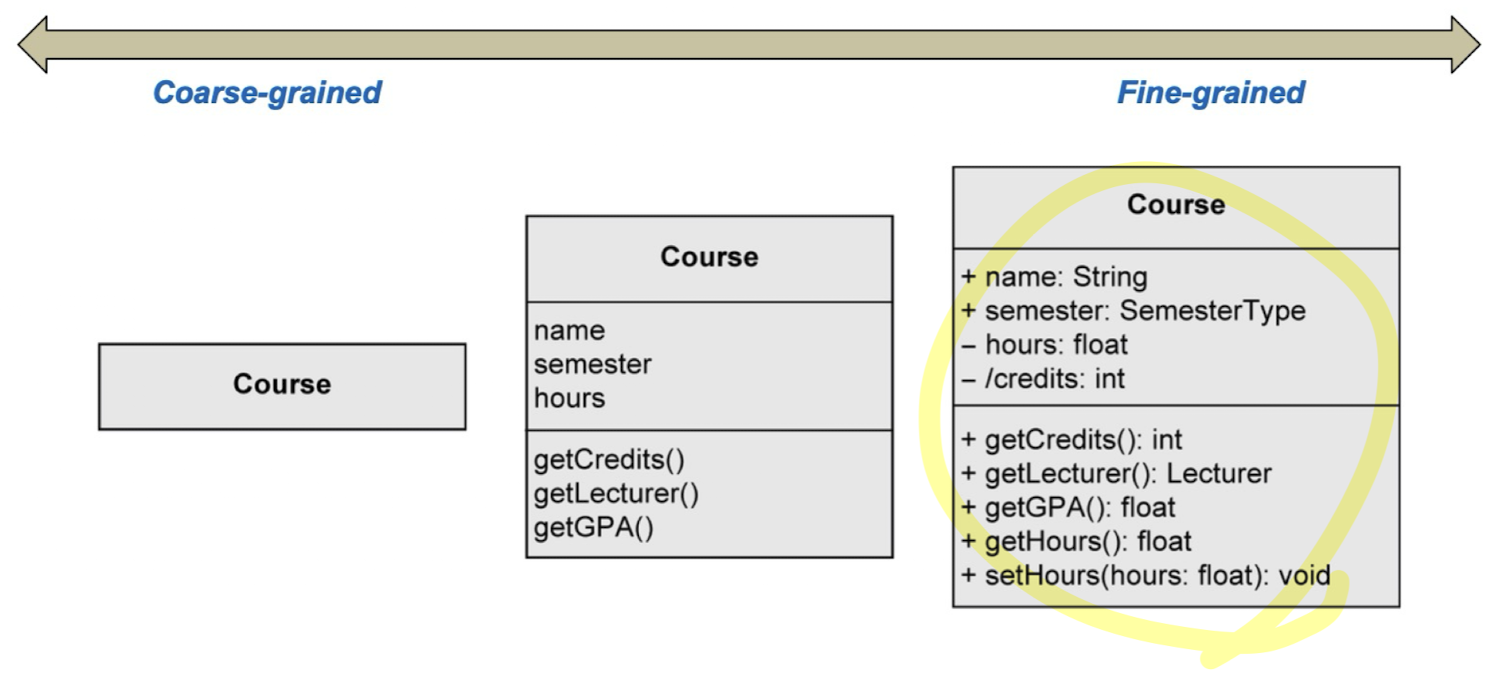
상황 및 목적에 맞는 detail level을 유연성 있게 선택
Dependency
Types of Class Relationship
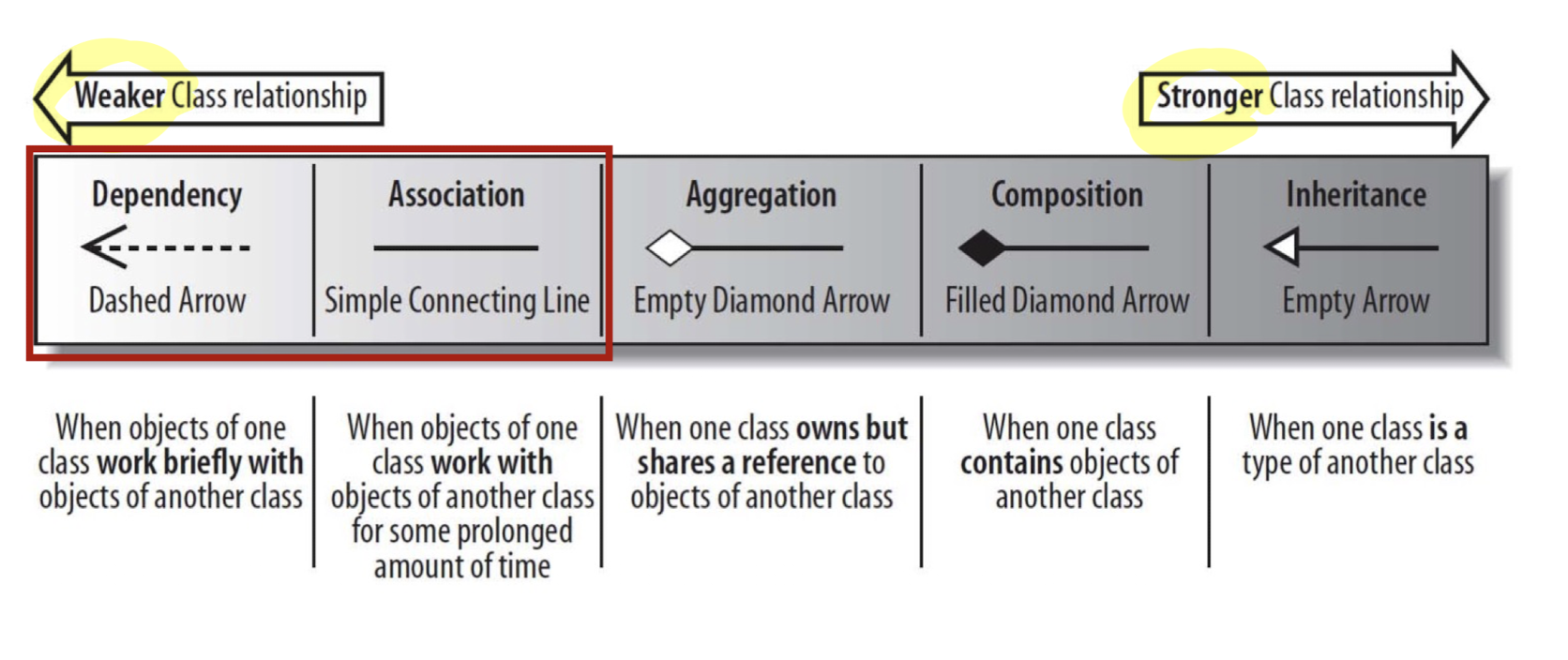
의존 관계(Dependency)
- 한 element(client)가 다른 element(supplier)를 의존하는 관계
Supplier가 수정되면 Client에도 영향이 생김 - 클래스 다이어그램에서는 한 클래스의 객체에서 다른 클래스의 객체를 잠시/간단하게 사용하는 상황을 의존 관계로 표현
메소드의 파라미터/반환 값으로 사용되거나, 지역 변수로 사용될 때(temporarily)
Association
연관 관계
- 객체 간의 연결 및 상호작용의 관계를 나타냄
- 어떤 클래스의 객체가 다른 클래스의 객체와 "장기간" 연관되어 동작할 때 연관 관계에 있다고 함
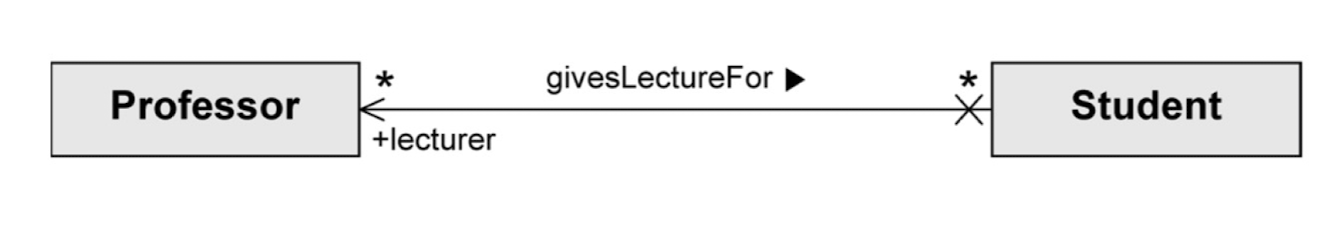
Navigability
- 한 객체가 다른 객체를 안다 = 그 객체의 visible 정보를 쓸 수 있다.

직선으로만 있다면 양방향으로 Navigability가 있음을 의미
Binary Association as Attribute
참조하는 객체에서 참조 대상 객체를 attribute로 가짐
- role name 이 attribute의 이름이 됨
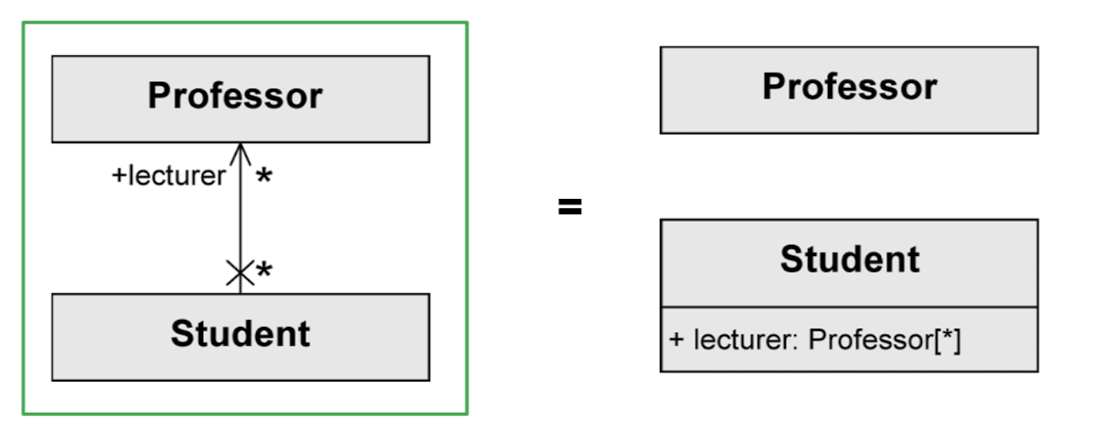
public class Professor {...}
public class Student {
public Professor[] lecturer;
...ex)

class Professor {
private List<Book> textbook;
}
class Book {
private List<Professor> author;
}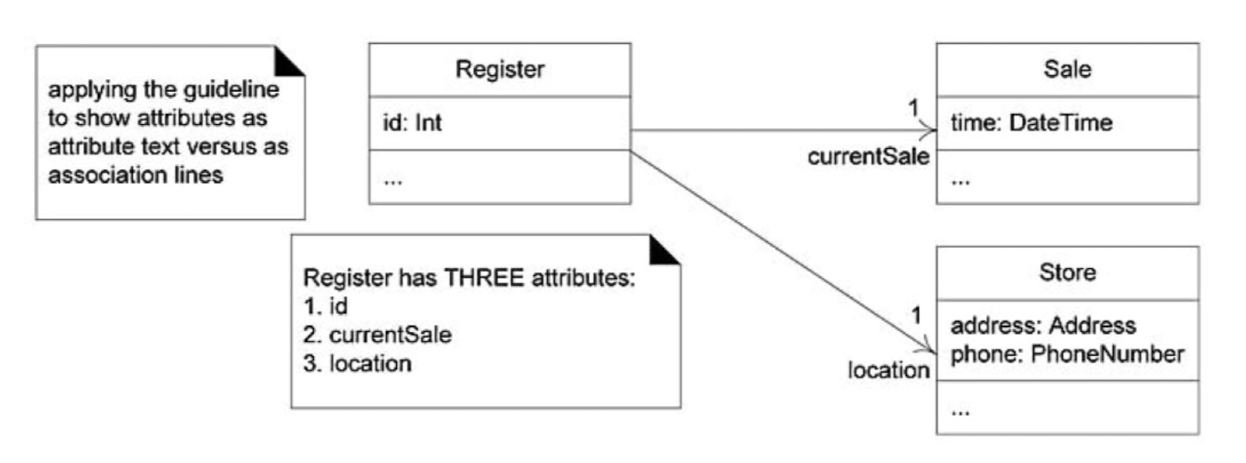
public class Register {
private int id;
private Sale currentSale;
private Store location;