Contents
- Types of Class Relationships in Class Diagram
Association Class
Whole-part relationship
Inheritence relationship
Association Class
연관 클래스
- 연관 관계에 속성이나 행위를 추가할 필요가 있을 때, 연관 관계를 클래스로 표현
한 학생(Student)은 다수의 강좌를 등록(Enrolls)할 수 있고 한 강좌(Course)에는 다수의 학생이 등록될 수 있음

- 이 상황에서 학점(grade)이라는 속성이 들어갈 수 있는 클래스는?
학점은 Student와 Course에 동시에 관련된 정보임
연관 관계에 속성이나 행위를 추가할 필요가 있을 때, 연관 관계를 클래스로 표현
Enrolls에 해당하는 association에 대해 클래스로 표현하고, 이 클래스에 grade를 추가 (이를 연관 클래스라고 함)
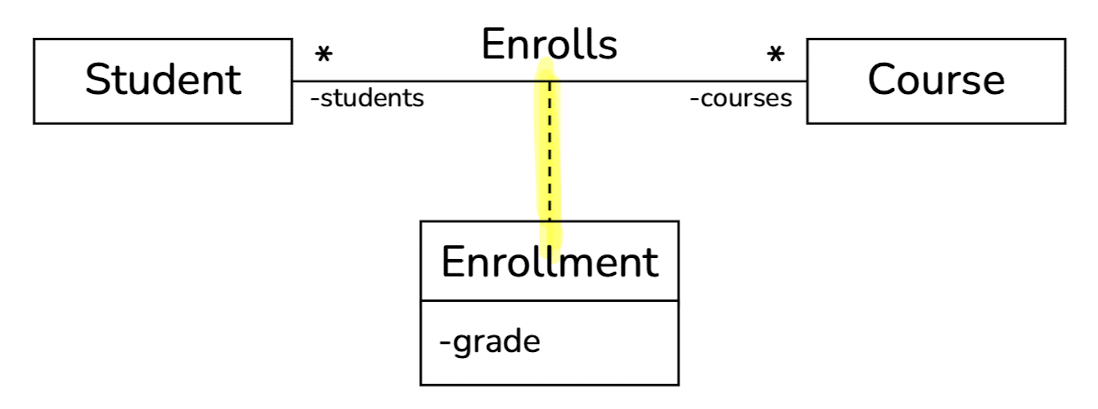
Association class to binary associations
- 연관 클래스를 풀어서 연관 관계로만 표현할 수도 있음
public class Enrollment {
private char grade;
private Student[] student;
private Course[] course;
}
public class Student {
private List<Enrollment> enrolls;
}
public class Course {
private List<Enrollment> enrolls;
}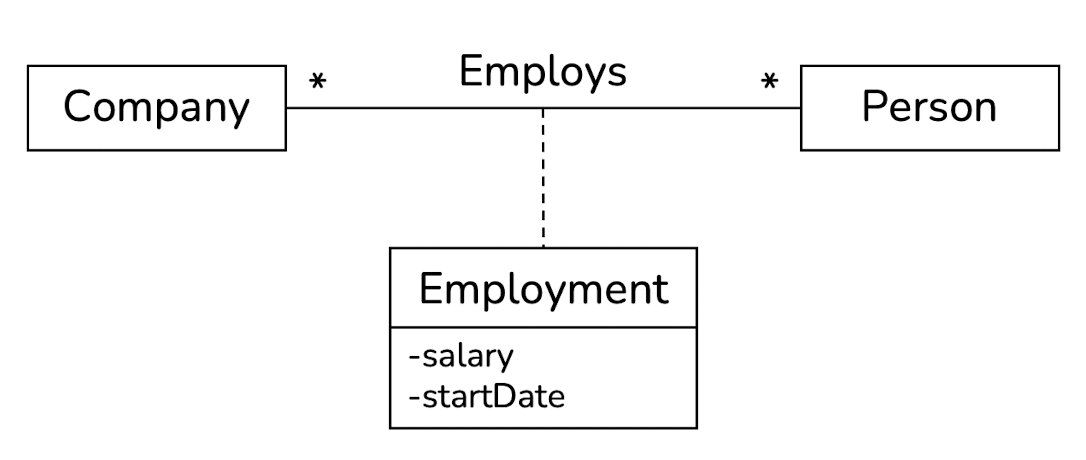
public class Employment {
private int salary;
private Date startDate;
private Company[] company;
private Person[] person;
}
public class Company {
private List<Employment> employments;
}
public class Person {
private List<Employment> employmentss;
}Aggregation and Composition
Whole-part Relationship
전체/부분 관계
-
전체 개념에 해당하는 클래스(Whole)와 이를 이루는 부품에 해당하는 클래스(Part)간의 관계
자동차와 바퀴는 자동차가 Whole이고 바퀴가 Part -
특별한 형태의 연관 관계라고 볼 수 있으며, 다음과 같은 상황에서 전체/부분 관계를 생각
부분 개념이 모여서 전체 개념을 이룰 때 (is part of)
어떤 클래스가 집합 개념을 가지며 구성하는 부분들을 소유하는 관계 (own)
전체/부분 관계의 특징
-
Transitive property
If A is part of B, and B is part of C, then A is also part of C -
Asymmetric property
It is not possible that "A is part of B" and "B is part of A" at the same time
전체/부분 관계의 종류
- Aggregation (집합)
- Composition (합성)
Aggregation Relationship
집합 관계
- 부분이 전체에 "약하게" 속하는 관계를 표현
전체라는 객체가 소멸되더라도 부분에 해당하는 객체는 사라지지 않음
집합 관계 예시
- Car와 Wheel의 관계
wheel은 car라는 개념에 상관 없이 독립적으로 존재할 수 있으며 다른 이동수단에도 쓰일 수 있음
집합 관계 다이어그램 표기법
- Empty Diamond를 Head로 가지는 화살표를 whole에 대응되는 클래스로 향하게 표기 (part -> whole)
Composition Relationship
합성 관계
- 부분이 전체에 "강하게" 연관되는 관계를 표현
전체라는 객체가 소멸되면 부분에 해당하는 객체도 사라짐
합성 관계 예시
- Building과 Room의 관계
건물이 없으면 방만으로는 의미가 없음 => 건물이 삭제되면 방도 같이 삭제
합성 관계 다이어그램 표기법
- Filled Diamond를 Head로 가지는 화살표를 whole에 대응되는 클래스로 향하게 표기 (part -> whole)

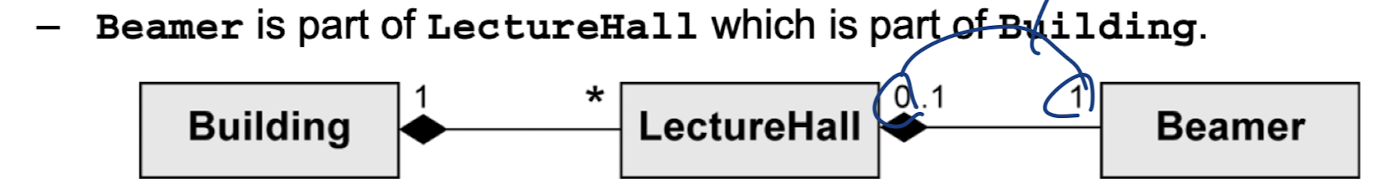
위 그림의 Multiplicity를 보면 LectureHall이 없어도(0) Beamer는 존재할 수 있다. 하지만, Lecturehall과 합성 관계이기 때문에 LectureHall 객체가 삭제되면 Beamer 객체 역시 사라진다.
Aggregation vs Composition
가장 큰 차이는 전체와 부분의 생명 주기
- 집합 : 전체 객체가 소멸되더라도 부분 객체는 사라지지 않음
- 합성 : 전체 객체가 소멸되면 부분 객체도 사라짐

### Composition Relationship
class Office:
def __init__(self, room_number, phone_number):
self.room_number = room_number
self.phone_number = phone_number
class Employee:
def __init__(self, room_number, phone_number):
self.office = Office(room_number, phone_number)

### Aggregation Relationship
class Office:
def __init__(self, room_number, phone_number):
self.room_number = room_number
self.phone_number = phone_number
class Employee:
def __init__(self, office):
self.office = office
class main:
office_100 = Office("100", "423-434")
e1 = Employee(office_100)
e2 = Employee(office_100)Inheritence Relationship
상속 관계(일반화 관계)
- 공통된 특성을 슈퍼 클래스로 일반화하는 관계를 표현
- Genralization is transitive
- Empty arrow from sub to super
Generalization - Abstract class
- 추상 클래스는 서브 클래스의 공통된 특성을 강조
슈퍼(추상) 클래스가 직접적으로 인스턴스화 되지는 않음(추상 메소드)
추상 클래스를 상속받는 non-abstract 서브 클래스만 인스턴스화 될 수 있음
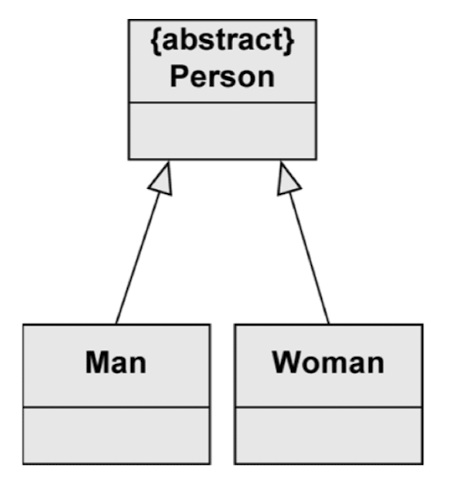
with Generalization
- attribute의 중복성을 방지할 수 있음
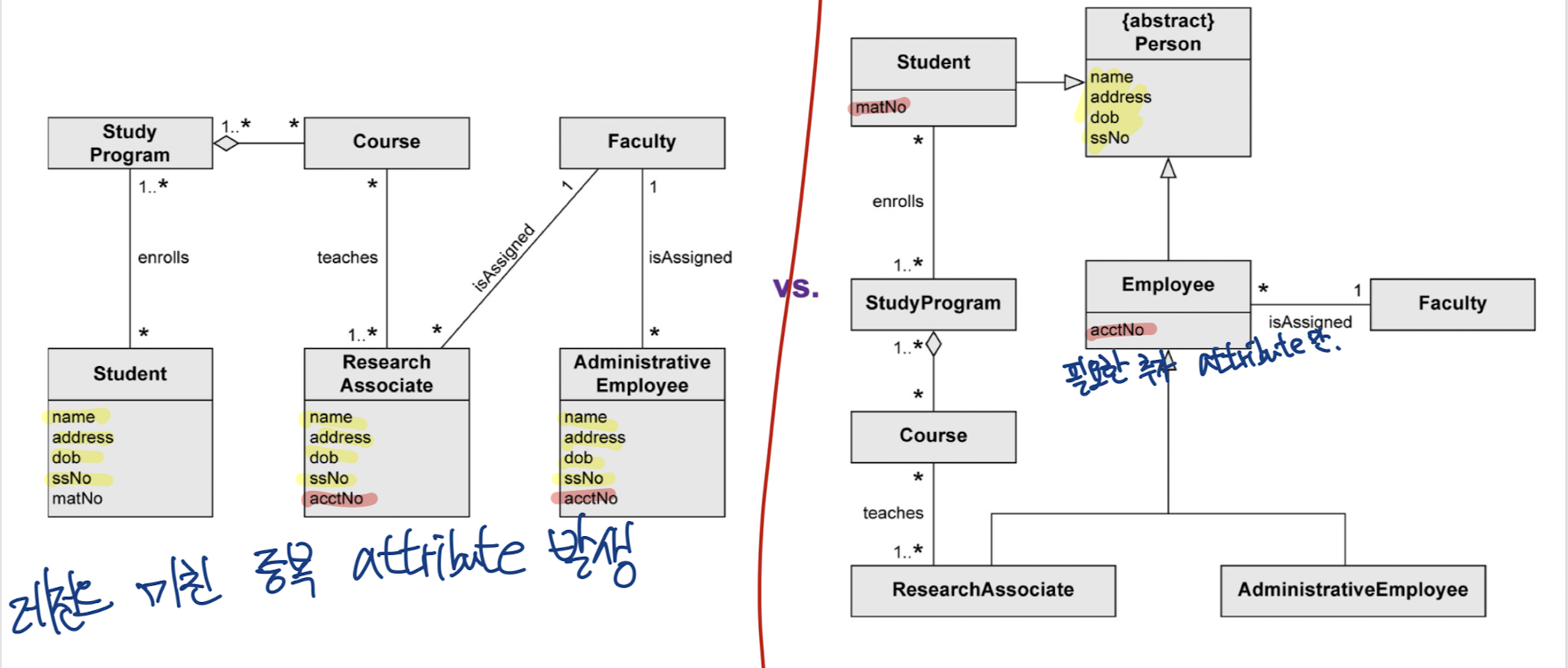
레전드 미친 중복 attribute 발생
