Embeddings
- Embeddings are numerical representations of text concepts converted to number sequences.
- They make it easy for computers to understand the relationships between those concepts.
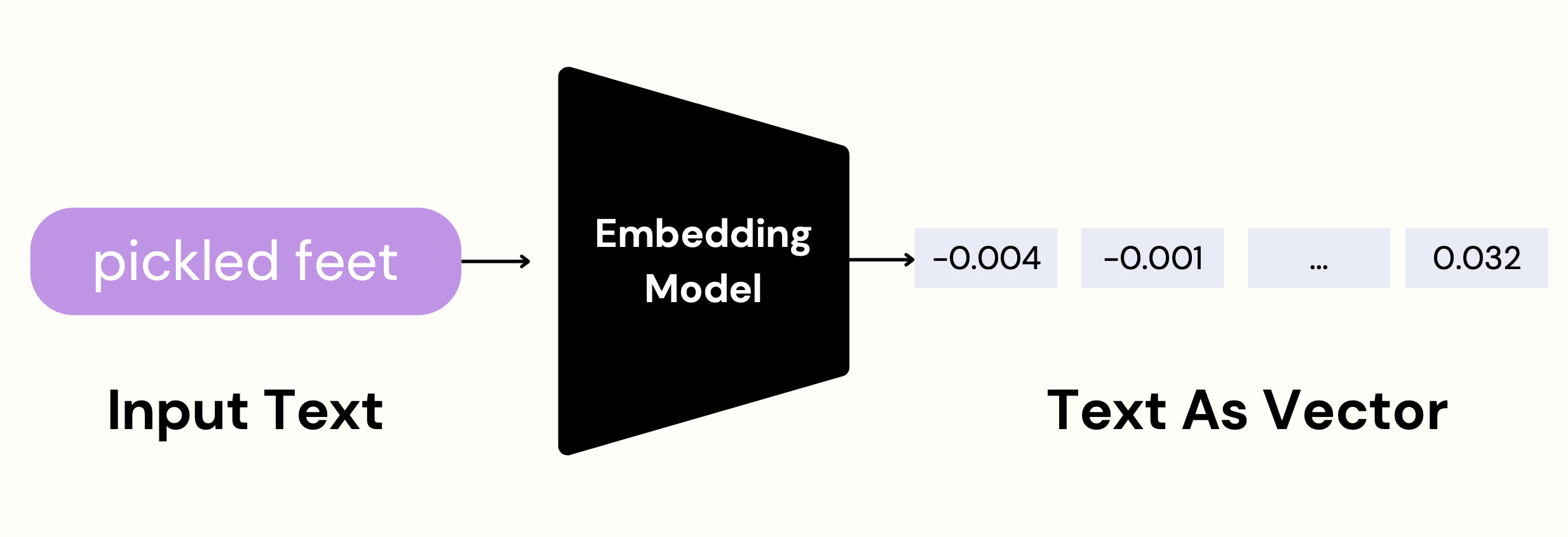
- Input Text를 받아서 Embedding model을 통과하면 Text를 Vector의 형태로 변경할 수 있다.
- OpenAI has an embedding model called text-embedding-ada-002
- Given some input text, it returns an embedding as a 1536 dimension vector
- We can store these embeddings and then use them to perform searches, recommendations, and more
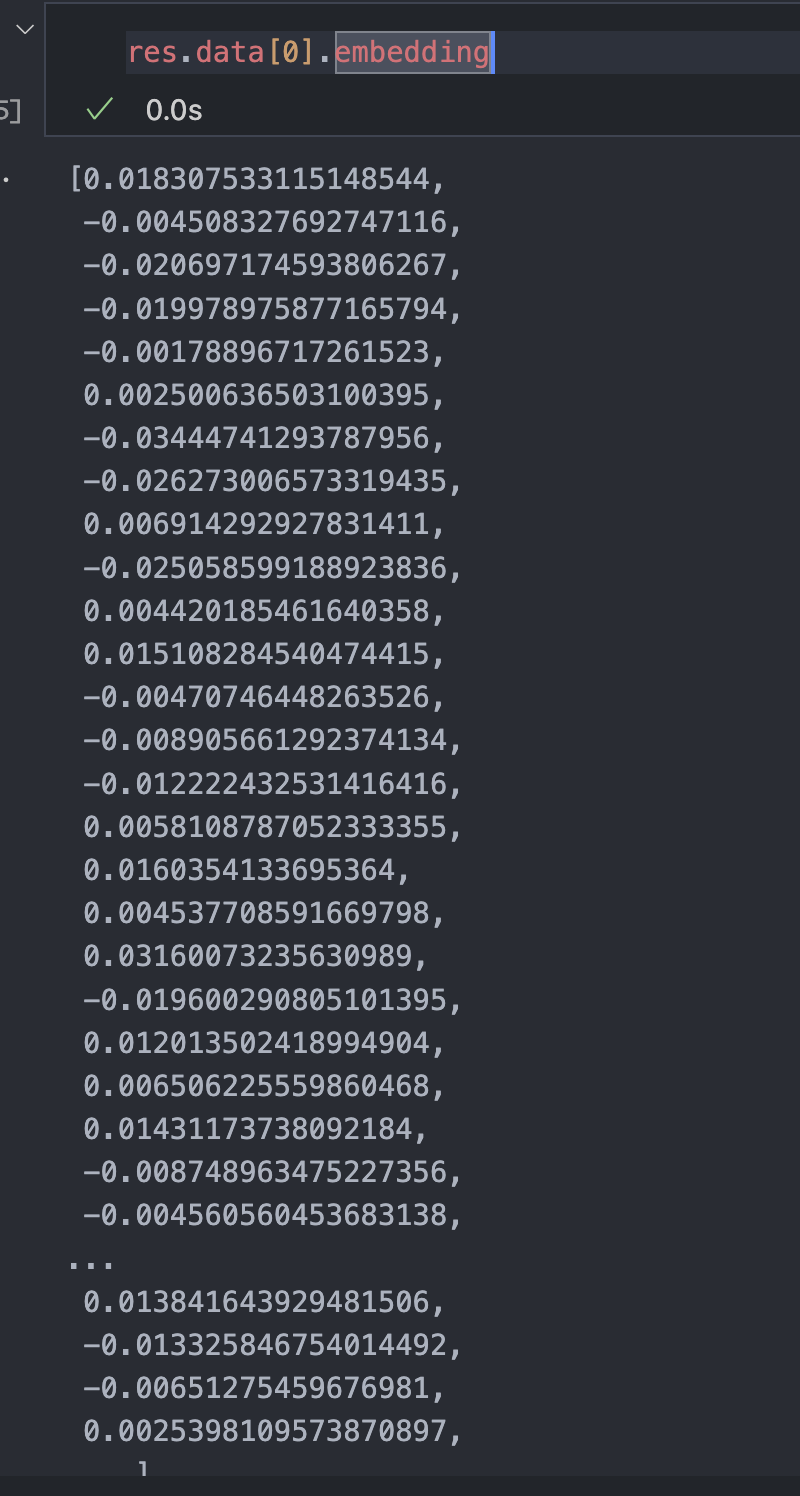
import openai # 현재 버전에서는 불가능
res = openai.embeddings.create(input="frog legs", model="text-embedding-ada-002")
res.data[0].embedding
Movie Embeddings & Visualization
- Using movie data from here
링크텍스트
- env settings
import openai
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from tenacity import retry, wait_random_exponential, stop_after_attempt
import pickle
import tiktoken
dataset_path = "./movie_plots.csv"
df = pd.read_csv(dataset_path)
# Narrow our data set to 5000 recent American movies (to save money)
movies = (
df[df["Origin/Ethnicity"] == "American"]
.sort_values("Release Year", ascending=False)
.head(5000)
)
@retry(wait=wait_random_exponential(min=1, max=20), stop=stop_after_attempt(6))
def get_embedding(text, model="text-embedding-ada-002"):
# replace newlines, which can negatively affect performance.
text = text.replace("\n", " ")
return openai.embeddings.create(input=text, model=model).data[0].embedding
enc = tiktoken.encoding_for_model("text-embedding-ada-002")
# 전체 token의 갯수 확인
total_tokens = sum([len(enc.encode(plot)) for plot in movie_plots])
# 대략적인 가격 확인
cost = total_tokens * (0.0004 / 1000)
print(f"Estimated cost ${cost:.2f}")
# establish a cache of embeddings to avoid recomputing
# cache is a dict of tuples (text, model) -> embedding, saved as a pickle file
# set path to embedding cache
embedding_cache_path = "movie_embeddings_cache2.pkl"
# load the cache if it exists, and save a copy to disk
try:
embedding_cache = pd.read_pickle(embedding_cache_path)
except FileNotFoundError:
embedding_cache = {}
with open(embedding_cache_path, "wb") as embedding_cache_file:
pickle.dump(embedding_cache, embedding_cache_file)
# define a function to retrieve embeddings from the cache if present, and otherwise request via the API
def embedding_from_string(
string, model="text-embedding-ada-002", embedding_cache=embedding_cache
):
"""Return embedding of given string, using a cache to avoid recomputing."""
if (string, model) not in embedding_cache.keys():
embedding_cache[(string, model)] = get_embedding(string, model)
print(f"GOT EMBEDDING FROM OPENAI FOR {string[:20]}")
with open(embedding_cache_path, "wb") as embedding_cache_file:
pickle.dump(embedding_cache, embedding_cache_file)
return embedding_cache[(string, model)]
# This line actaully generates the embeddings
plot_embeddings = [
embedding_from_string(plot, model="text-embedding-ada-002") for plot in movie_plots
]
- Atlas로 임베딩 시각화
nomic 회원가입 필요
from nomic import atlas
# plotting 하기를 원하는 데이터를 dictionary 형태로 넘겨야 한다.
data = movies[["Title", "Genre"]].to_dict("records")
project = atlas.map_embeddings(embeddings=np.array(plot_embeddings), data=data)
from typing import List
from scipy import spatial
def distances_from_embeddings(
query_embedding: List[float],
embeddings: List[List[float]],
distance_metric="cosine",
) -> List[List]:
"""Return the distances between a query embedding and a list of embeddings."""
distance_metrics = {
"cosine": spatial.distance.cosine,
"L1": spatial.distance.cityblock,
"L2": spatial.distance.euclidean,
"Linf": spatial.distance.chebyshev,
}
distances = [
distance_metrics[distance_metric](query_embedding, embedding)
for embedding in embeddings
]
return distances
def indices_of_nearest_neighbors_from_distances(distances) -> np.ndarray:
"""Return a list of indices of nearest neighbors from a list of distances."""
return np.argsort(distances)
def print_recommendations_from_strings(
strings,
index_of_source_string,
k_nearest_neighbors=3,
model="text-embedding-ada-002",
):
# Get all of the embeddings
embeddings = [embedding_from_string(string) for string in strings]
# get embedding for our specific query string
query_embedding = embeddings[index_of_source_string]
# get distances between our embedding and all other embeddings
distances = distances_from_embeddings(query_embedding, embeddings)
# get indices of the nearest neighbors
indices_of_nearest_neighbors = indices_of_nearest_neighbors_from_distances(
distances
)
query_string = strings[index_of_source_string]
match_count = 0
for i in indices_of_nearest_neighbors:
if query_string == strings[i]:
continue
if match_count >= k_nearest_neighbors:
break
match_count += 1
print(f"Found {match_count} closest match: ")
print(f"Distance of: {distances[i]} ")
print(strings[i])
Embedding Q&A
- Generate a bunch of embeddings on your own specific data
- When a user asks a question, take their question and turn it into an embedding
- Find the K nearest neighbors to that embedding
- Include the matching text(s) in the prompt when you query the model
F1_QA_Assistant
# %pip install python-dotenv openai pandas
from typing import Dict, List
from utilities import (
num_tokens_from_messages,
get_embedding,
get_n_nearest_neighbors,
memoize_to_sqlite,
)
from f1_utilities import wikipedia_splitter, Section
from io import StringIO
import csv
import requests
import os
import itertools
import tiktoken
import openai
import pandas as pd
openai.api_key = os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]
import hashlib
import json
import os
import sqlite3
import zipfile
from typing import Dict, List, Tuple, TypeVar
import numpy as np
import openai
import tiktoken
from tenacity import (
retry,
retry_if_exception_type,
stop_after_attempt,
wait_random_exponential,
)
def cosine_similarity(a, b):
return np.dot(a, b) / (np.linalg.norm(a) * np.linalg.norm(b))
def get_file_with_zip_fallback(file_name: str, zip_file_name: str) -> str:
# Check if the CSV file exists
if not os.path.exists(file_name):
# If not, check if the ZIP file exists and unzip it
if os.path.exists(zip_file_name):
with zipfile.ZipFile(zip_file_name, "r") as zip_ref:
zip_ref.extractall()
else:
raise ValueError(
f"Neither {file_name} nor {zip_file_name} were found in the current directory."
)
# Read the contents of the CSV file
with open(file_name, "r", encoding="utf-8") as file:
contents = file.read()
return contents
# Updated 1/4/2024
def num_tokens_from_messages(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0613"):
"""Return the number of tokens used by a list of messages."""
try:
encoding = tiktoken.encoding_for_model(model)
except KeyError:
print("Warning: model not found. Using cl100k_base encoding.")
encoding = tiktoken.get_encoding("cl100k_base")
if model in {
"gpt-3.5-turbo-0613",
"gpt-3.5-turbo-16k-0613",
"gpt-4-0314",
"gpt-4-32k-0314",
"gpt-4-0613",
"gpt-4-32k-0613",
}:
tokens_per_message = 3
tokens_per_name = 1
elif model == "gpt-3.5-turbo-0301":
tokens_per_message = (
4 # every message follows <|start|>{role/name}\n{content}<|end|>\n
)
tokens_per_name = -1 # if there's a name, the role is omitted
elif "gpt-3.5-turbo" in model:
return num_tokens_from_messages(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0613")
elif "gpt-4" in model:
print(
"Warning: gpt-4 may update over time. Returning num tokens assuming gpt-4-0613."
)
return num_tokens_from_messages(messages, model="gpt-4-0613")
else:
raise NotImplementedError(
f"""num_tokens_from_messages() is not implemented for model {model}. See https://github.com/openai/openai-python/blob/main/chatml.md for information on how messages are converted to tokens."""
)
num_tokens = 0
for message in messages:
num_tokens += tokens_per_message
for key, value in message.items():
num_tokens += len(encoding.encode(value))
if key == "name":
num_tokens += tokens_per_name
num_tokens += 3 # every reply is primed with <|start|>assistant<|message|>
return num_tokens
def memoize_to_sqlite(filename: str = "cache.db"):
"""
Memoization decorator that caches the output of a method in a SQLite database.
The database connection is persisted across calls.
"""
db_conn = sqlite3.connect(filename)
db_conn.execute(
"CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS cache (hash TEXT PRIMARY KEY, result TEXT)"
)
def memoize(func):
def wrapped(*args):
# Compute the hash of the argument
arg_hash = hashlib.sha256(repr(tuple(args)).encode("utf-8")).hexdigest()
# Check if the result is already cached
cursor = db_conn.cursor()
cursor.execute("SELECT result FROM cache WHERE hash = ?", (arg_hash,))
row = cursor.fetchone()
if row is not None:
print(f"Cached result found for {arg_hash}. Returning it.")
return json.loads(row[0])
# Compute the result and cache it
result = func(*args)
cursor.execute(
"INSERT INTO cache (hash, result) VALUES (?, ?)",
(arg_hash, json.dumps(result)),
)
db_conn.commit()
return result
return wrapped
return memoize
# This is not optimized for massive reads and writes, but it's good enough for this example
@memoize_to_sqlite(filename="embeddings.db")
@retry(
wait=wait_random_exponential(multiplier=1, max=30),
stop=stop_after_attempt(3),
retry=retry_if_exception_type(openai.APIConnectionError)
| retry_if_exception_type(openai.APIError)
| retry_if_exception_type(openai.RateLimitError),
)
def get_embedding(text: str) -> List[float]:
"""
:param text: The text to compute an embedding for
:return: The embedding for the text
"""
# replace newlines, which can negatively affect performance.
text_no_newlines = text.replace("\n", " ")
print(f"Computing embedding for {text_no_newlines[:50]}")
response = openai.embeddings.create(
input=text_no_newlines, model="text-embedding-ada-002"
)
embeddings = response.data[0].embedding
return embeddings
T = TypeVar("T") # Declare type variable
def get_n_nearest_neighbors(
query_embedding: List[float], embeddings: Dict[T, List[float]], n: int
) -> List[Tuple[T, float]]:
"""
:param query_embedding: The embedding to find the nearest neighbors for
:param embeddings: A dictionary of embeddings, where the keys are the entity type (e.g. Movie, Segment)
and the values are the that entity's embeddings
:param n: The number of nearest neighbors to return
:return: A list of tuples, where the first element is the entity and the second element is the cosine
similarity between -1 and 1
"""
# This is not optimized for rapid indexing, but it's good enough for this example
# If you're using this in production, you should use a more efficient vector datastore such as
# those mentioned specifically by OpenAI here
#
# https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/embeddings/how-can-i-retrieve-k-nearest-embedding-vectors-quickly
#
# * Pinecone, a fully managed vector database
# * Weaviate, an open-source vector search engine
# * Redis as a vector database
# * Qdrant, a vector search engine
# * Milvus, a vector database built for scalable similarity search
# * Chroma, an open-source embeddings store
#
target_embedding = np.array(query_embedding)
similarities = [
(segment, cosine_similarity(target_embedding, np.array(embedding)))
for segment, embedding in embeddings.items()
]
# Sort by similarity and get the top n results
nearest_neighbors = sorted(similarities, key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)[:n]
return nearest_neighbors
- f1_utilities.py : wiki의 큰 text를 작은 text로 바꾸는 코드
import re
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Iterable, List
import numpy as np
# Thanks to http://www.oldmanumby.com/ for his remaster and converion of the Dungeons
# and Dragons 5th Edition SRD (Systems Reference Document)
# https://github.com/OldManUmby/DND.SRD.Wiki
# Thanks to Wizards of the Coast for DnD and preserving its openness with the Open Gaming License.
def cosine_similarity(a, b):
return np.dot(a, b) / (np.linalg.norm(a) * np.linalg.norm(b))
@dataclass(frozen=True, repr=True)
class WikipediaPath:
article: str
header: str
def __str__(self):
return f"{self.article} - {self.header}"
@dataclass(frozen=True, repr=True)
class Section:
"""
A segment is defined by anything that follows an h1 header (# ...) or
an entire document if the file has no h1 headers.
"""
location: WikipediaPath
text: str
def __str__(self):
return f"{self.location}:\n{self.text}"
def wikipedia_splitter(
contents: str, article_title: str, token_limit: int, split_point_regexes: List[str]
) -> Iterable[Section]:
# Take a markdown file and the article split on `==` sections.
"""
Generate sections of Wikipedia pages.
:param contents: The contents of the wikipedia page
:param article_title: The title of the article, to be included in the emitted section object
:param token_limit: The maximum number of tokens to allow in a section
:param split_point_regexes: A list of regexes to split on. The first one is the highest precedence.
If we can't fit a section into the token limit, we'll split on the next lower regex.
"""
split_point_regex = split_point_regexes[0]
sections = re.split(split_point_regex, contents)
if not sections[0].strip():
# Remove the first section if it's empty (this happens when the file starts with a "#" line)
sections.pop(0)
else:
# Otherwise: Wikipedia articles often begin with a section that has no `==` header.
first_section = sections.pop(0)
yield Section(
location=WikipediaPath(article=article_title, header=article_title),
text=first_section,
)
# And now proceed into splitting sections based on the `==` header
for section in sections:
if not section.strip():
# Remove trailing empty sections.
continue
header = section.splitlines()[0].strip()
if "=" in split_point_regex:
# If we're splitting on equal-sign headers, then we need to remove the trailing equal signs
header = re.sub(r"=+$", "", header).strip()
# To be better steer embeddings, we include the article's title and section name with one another above the text.
emit = Section(
location=WikipediaPath(article=article_title, header=header),
text=f"{article_title}: {section}",
)
if len(str(section).replace("\n", " ")) > token_limit:
print(f"Section is too long: {emit.location}, splitting")
subtitle = f"{article_title} - {header}"
# If the section is too long, split it on a lower precedence split point
yield from wikipedia_splitter(
section, subtitle, token_limit, split_point_regexes[1:]
)
else:
yield emit
from typing import Optional
MAX_CONTEXT_WINDOW = 4097
MINIMUM_RESPONSE_SPACE = 1000
MAX_PROMPT_SIZE = MAX_CONTEXT_WINDOW - MINIMUM_RESPONSE_SPACE
def ask_embedding_store(
question: str, embeddings: Dict[Section, List[float]], max_documents: int
) -> str:
"""
Fetch necessary context from our embedding store, striving to fit the top max_documents
into the context window (or fewer if the total token count exceeds the limit)
:param question: The question to ask
:param embeddings: A dictionary of Section objects to their corresponding embeddings
:param max_documents: The maximum number of documents to use as context
:return: GPT's response to the question given context provided in our embedding store
"""
query_embedding = get_embedding(question)
nearest_neighbors = get_n_nearest_neighbors(
query_embedding, embeddings, max_documents
)
messages: Optional[List[Dict[str, str]]] = None
base_token_count = num_tokens_from_messages(get_messages([], question), chat_model)
token_counts = [
len(enc.encode(document.text.replace("\n", " ")))
for document, _ in nearest_neighbors
]
cumulative_token_counts = list(itertools.accumulate(token_counts))
indices_within_limit = [
True
for x in cumulative_token_counts
if x <= (MAX_PROMPT_SIZE - base_token_count)
]
most_messages_we_can_fit = len(indices_within_limit)
context = [x[0] for x in nearest_neighbors[: most_messages_we_can_fit + 1]]
debug_str = "\n".join(
[
f"{x[0].location}: {x[1]}"
for x in nearest_neighbors[: most_messages_we_can_fit + 1]
]
)
# print(f"Using {most_messages_we_can_fit} documents as context:\n" + debug_str)
messages = get_messages(context, question)
# print(f"Prompt: {messages[-1]['content']}")
result = openai.chat.completions.create(model=chat_model, messages=messages)
return result.choices[0].message.content
@memoize_to_sqlite("cache.db")
def wikipedia_api_fetch(article_title: str, field: str) -> str:
base_url = "https://en.wikipedia.org/w/api.php"
params = {
"action": "query",
"format": "json",
"prop": "extracts",
"titles": article_title,
"explaintext": 1,
}
response = requests.get(base_url, params=params)
data = response.json()
if "query" in data and "pages" in data["query"]:
page = list(data["query"]["pages"].values())[0]
if field in page:
return page[field]
else:
raise ValueError(f"Could not find {field} for page {page}")
else:
raise ValueError(f"Could not find page {article_title}")
# Loop through the DataFrame and fetch the content of each Grand Prix
df["Page_Content"] = df["Link"].apply(lambda x: wikipedia_api_fetch(x, "extract"))
df["Display Title"] = df["Link"].apply(lambda x: wikipedia_api_fetch(x, "title"))
sections: List[Section] = []
# The precedence of points to split on if a section cant be fit in max length
split_point_regexes = [r"\n==\s", r"\n===\s", r"\n====\s", r"\n\n", r"\n"]
# Calculate wikipedia content for each row in the data frame
for index, row in df.iterrows():
page_content = row["Page_Content"]
for section in wikipedia_splitter(
row["Page_Content"],
row["Display Title"],
token_limit=MAX_CONTEXT_WINDOW,
split_point_regexes=split_point_regexes,
):
sections.append(section)
chat_model = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
embedding_enc = tiktoken.encoding_for_model("text-embedding-ada-002")
enc = tiktoken.encoding_for_model(chat_model)
# Calculate the total number of tokens in the Page Content Column
print(str(sections[0]))
total_tokens = sum([len(embedding_enc.encode(str(section))) for section in sections])
# $0.0004 per 1000 tokens
cost = total_tokens * (0.0004 / 1000)
print(f"Estimated Cost ${cost:.2f}")
- 내가 넣은 데이터에 대한 embeddings 확인
- QA Assistant 생성
def get_messages(context: List[Section], question: str) -> List[Dict[str, str]]:
context_str = "\n\n".join([f"Path: {x.location}\nBody:\n{x.text}" for x in context])
return [
{
"role": "system",
"content": """
You will receive a question from the user and some context to help you answer the question.
Evaluate the context and provide an answer if you can confidently answer the question.
If you are unable to provide a confident response, kindly state that it is the case and explain the reason.
Prioritize offering an "I don't know" response over conveying potentially false information.
The user will only see your response and not the context you've been provided. Thus, respond in precise detail, directly repeating the information that you're referencing from the context.
""".strip(),
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": f"""
Using the following information as context, I'd like you to answer a question.
{context_str}
Please answer the following question: {question}
""".strip(),
},
]









