Lecture 1.1 - Why Graphs
- Graphs : a general language for describing and analyzing entities with relations/interactions
- 많은 type의 graph가 존재한다 ; event graphs, computer networks, disease pathways, social networks, economic networks, communication networks, knowledge graphs, regulatory networks, scene graphs, code graphs, molecules, 3D shapes
Types of Networks and Graphs
Networks
- social networks
- Communication and transactions
- Biomedicine
- Brain connections
Graphs
- Information/knowledge ; organized and linked
- Software
- Similarity networks
- Relational structures
Main Question
How do we take advantage of relational structure of better prediction?
- Modern deep learning toolbox is designed for simple sequences & grids
Why is it Hard?
Networks are complex
- Arbitrary size and complex topological structure
- No fixed node ordering or reference point
- Often dynamic and have multimodal features
How can we develop neural networks that are much more broadly applicable?
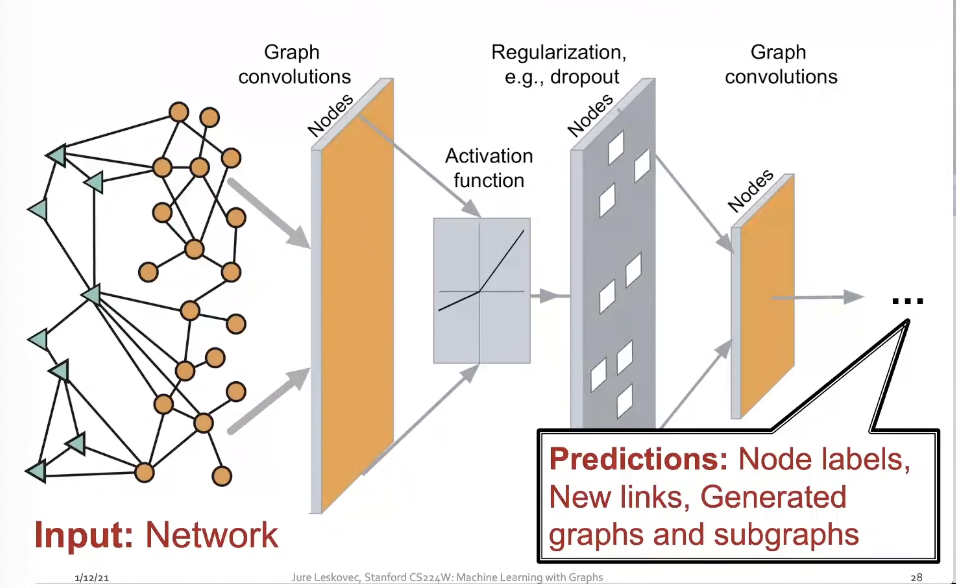
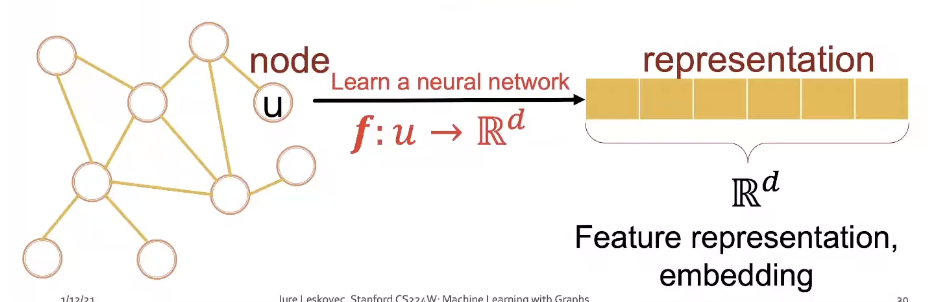
Representation Learning
- Representation Learning : Map nodes to d-dimensional embeddings such that similar nodes in the network are embedded close together
Lecture 1.2 - Applications of Graph ML
Different Types of Tasks
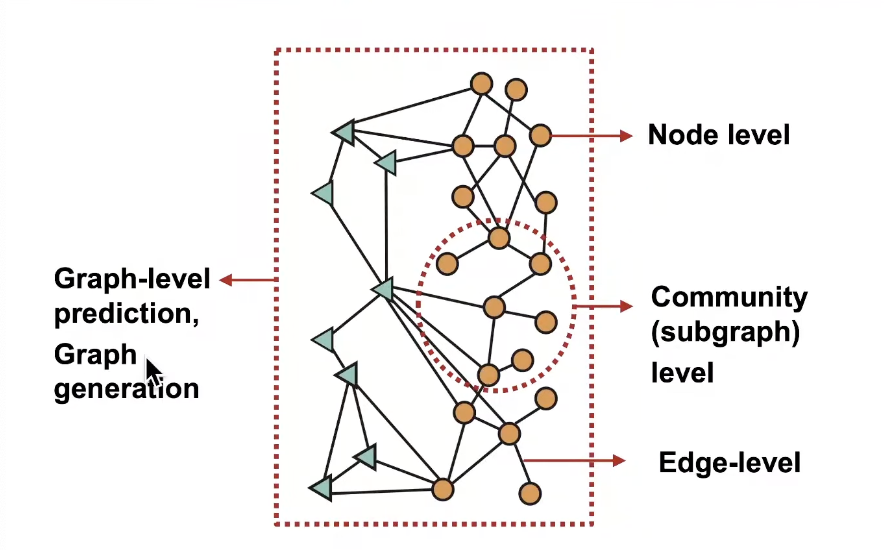
Classic Graph ML Tasks
- Node Classifiation: Predict a property of a node
- Link Prediction: Predict whether there are missing linnks between two nodes
- Graph classification: Categorize different graphs
- Clustering: Detect if nodes form a community
- Graph generation: Drug discovery
- Graph evolution: Physical simulation
Example of Node-level applications
Example 1: Proteing Folding
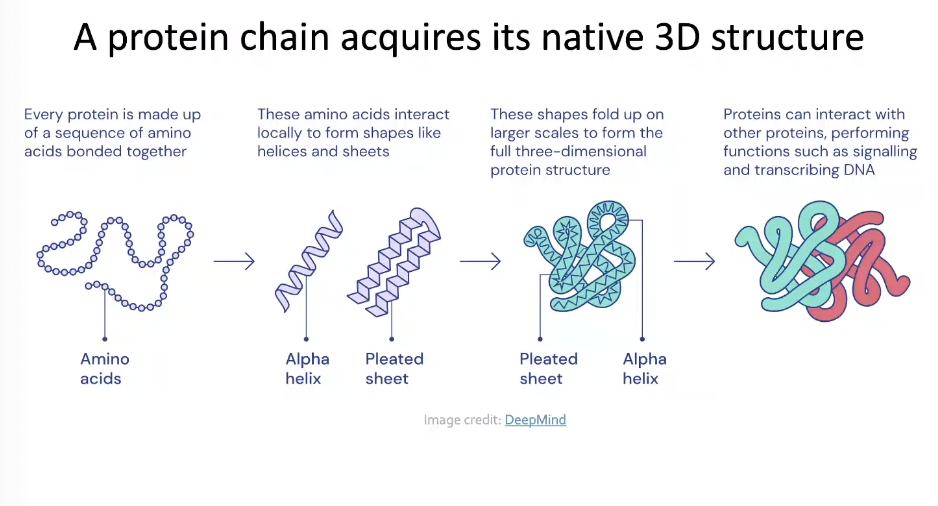
- Computationally predict a protein's 3D structure based soley on its amino acid sequence
- AlphaFold : key idea was to use "Spatial graph"
Examples of Edge-level ML Tasks
Example 2: Recommender Systems
- Users interacts with items, Recommend items users might like
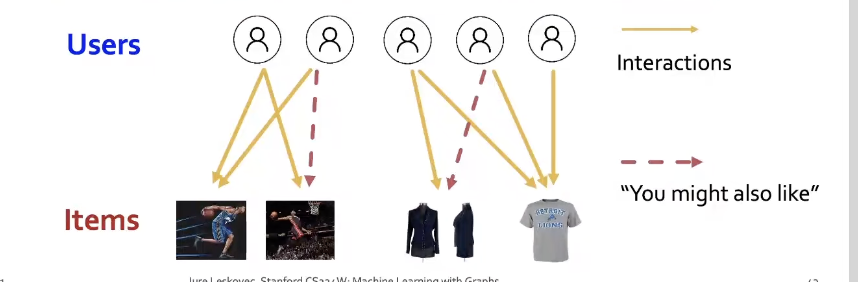
- PinSage
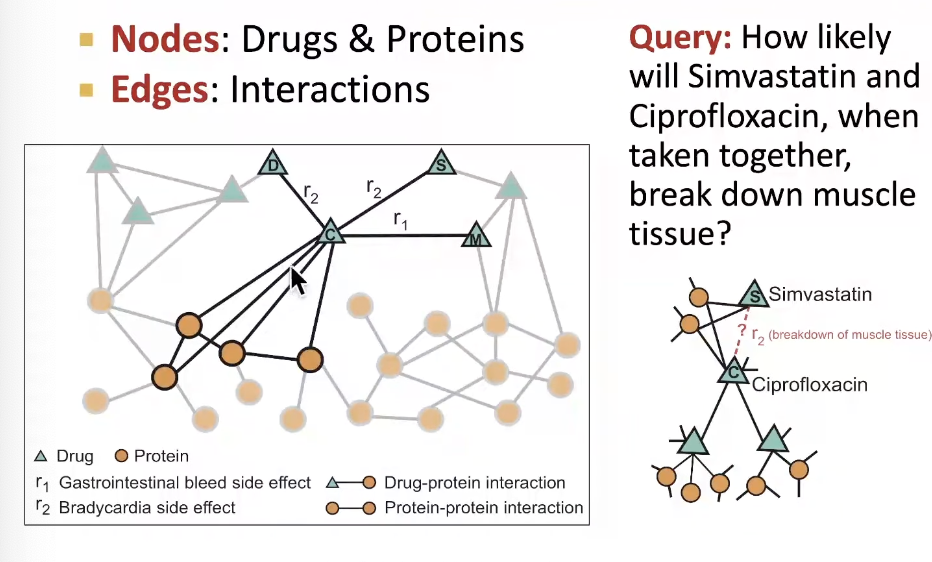
Example 3: Drug Side Effects
- Given a pair of drugs predict adverse side effects
- Biomedical Graph Link Prediction
Examples of Subgraph-level ML Tasks
Example 4: Traffic Prediction
- Road Network as a Graph
Examples of Graph-level ML Tasks
Example 5: Drug Discovery
-
Antibiotics are small molecular graphs
-
A Graph Nueral Network graph classification model
-
Predict promising molecules from a pool of candidates
-
Graph Generation: Generating novel molecules
Example 6: Physics Simulation
- Physical simulation as a graph
- A graph evolution task : Predict how a graph will evolve over
Lecture 1.3 - Choice of Graph Representation
Components of a Network
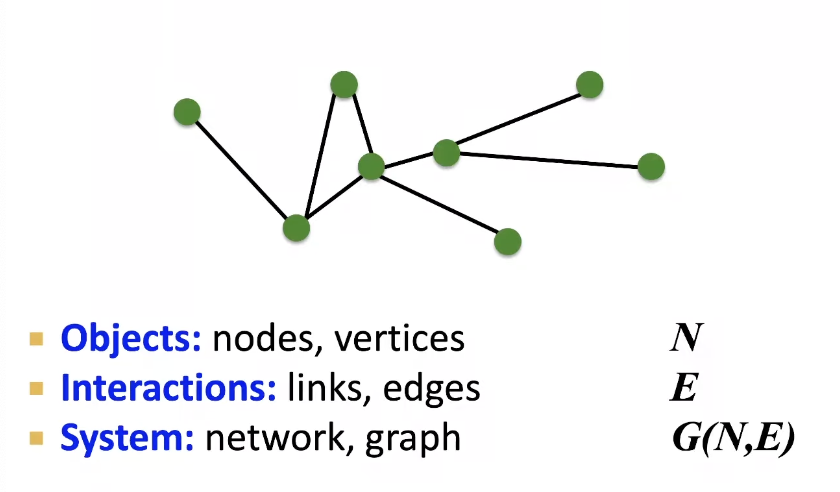
Choosing a proper representation
- If you connect individuals that work with each other, you will explore a professional network
- If you connect those that have sexual relationship, you will be exploring sexual networks
- If you connect scientific papers that cite each other, you will be studying the citation network
How do you define a graph?
- 각 node와 edge가 무엇이 될 것인지
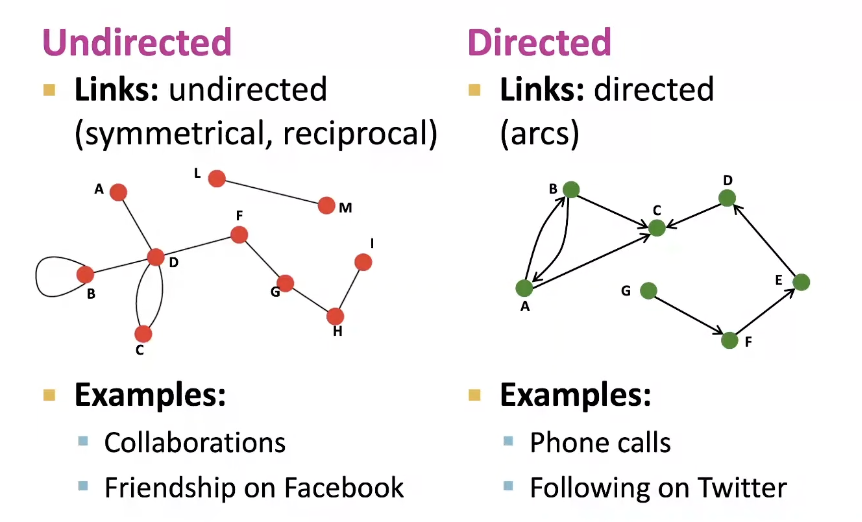
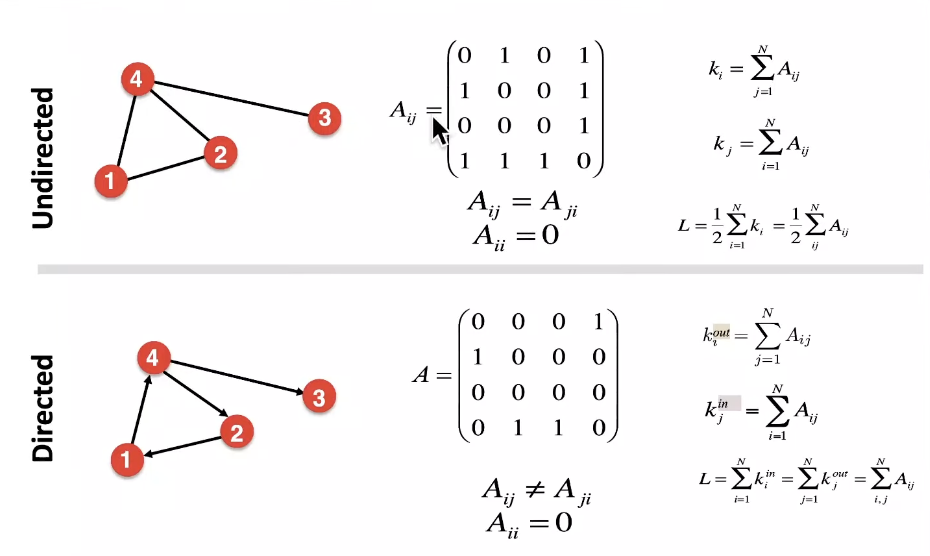
Directed vs. Undirected Graphs
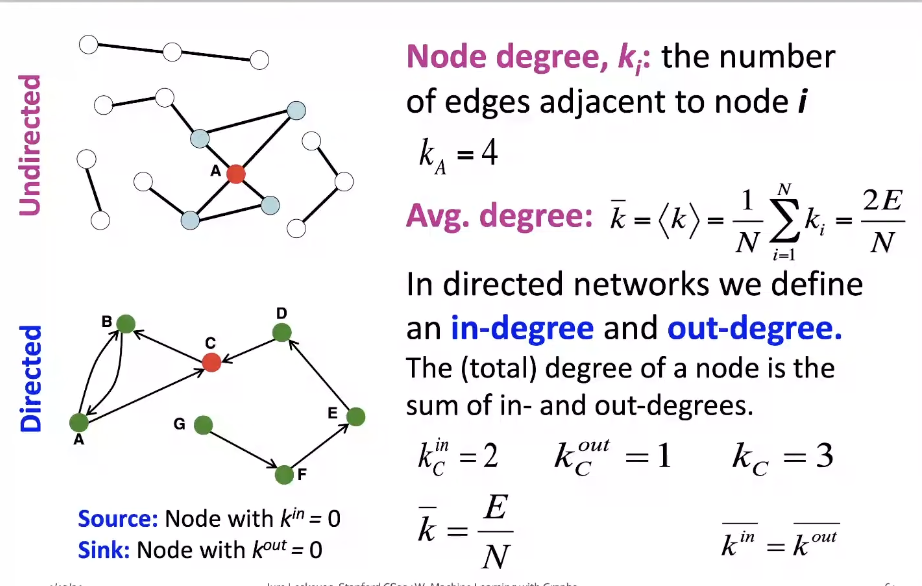
Node Degrees
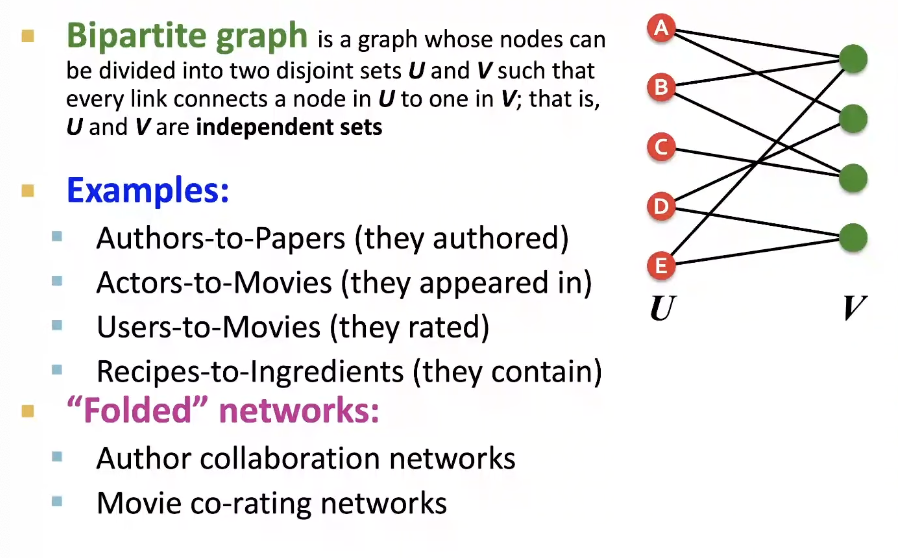
Bipartite Graph
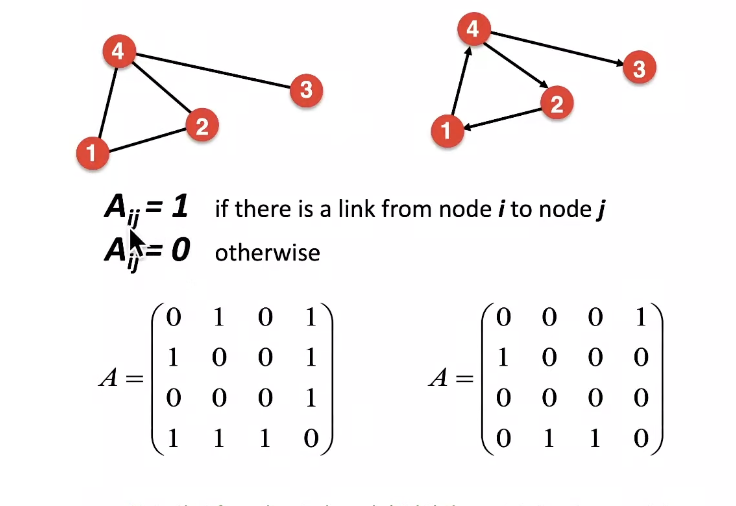
Representing Graphs: Adjacency Matrix
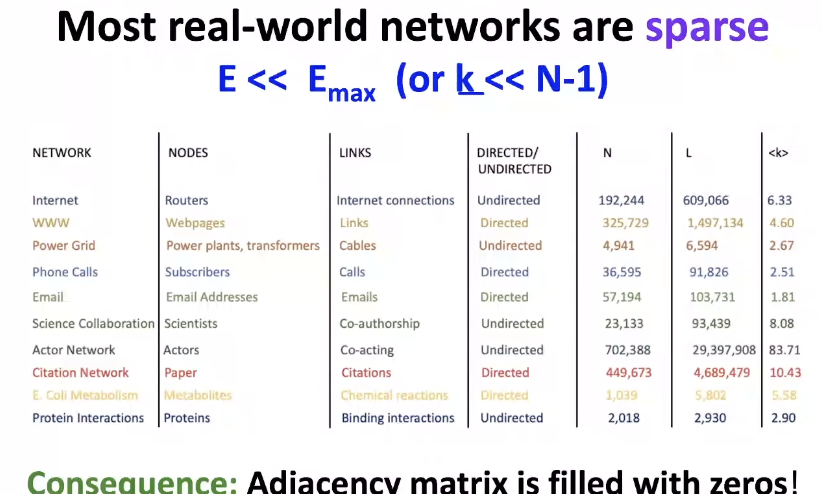
Adjacency Matrices are Sparse
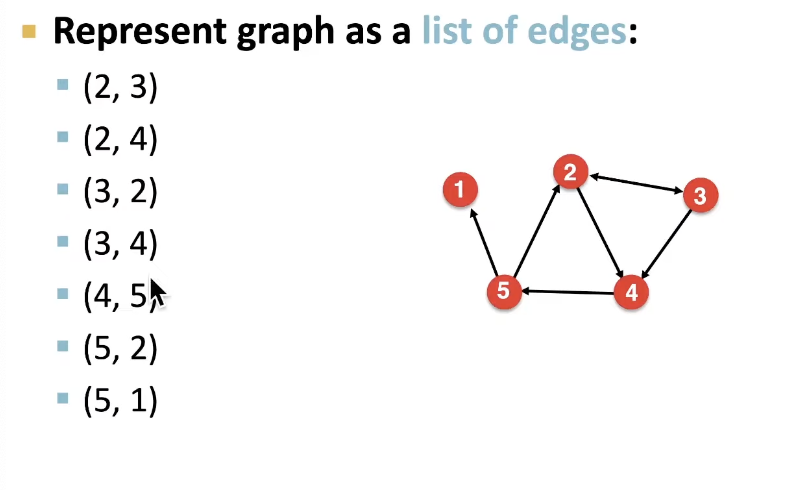
Representing Graphs: Edge list
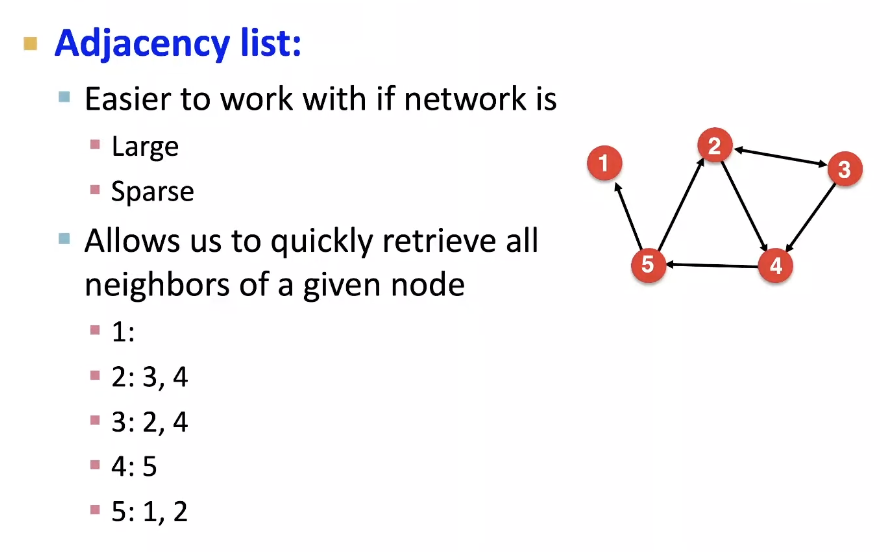
Representing Graphs: Adjacency list
More Types of Graphs
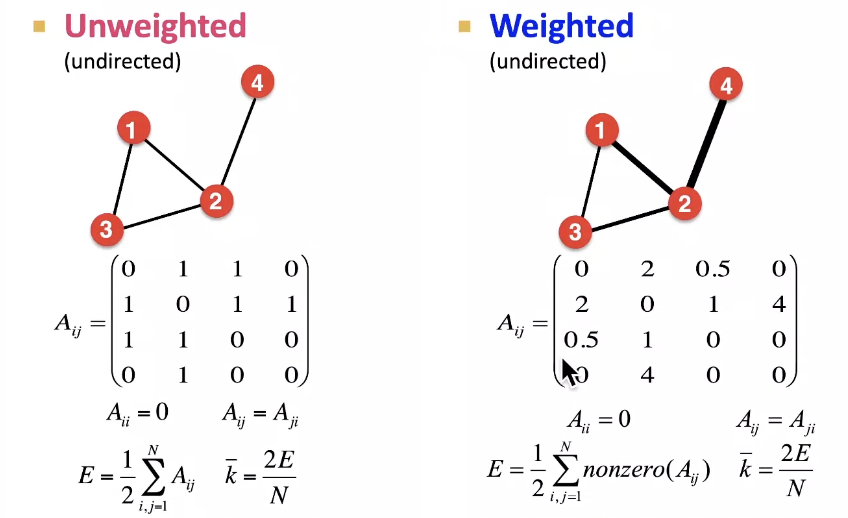
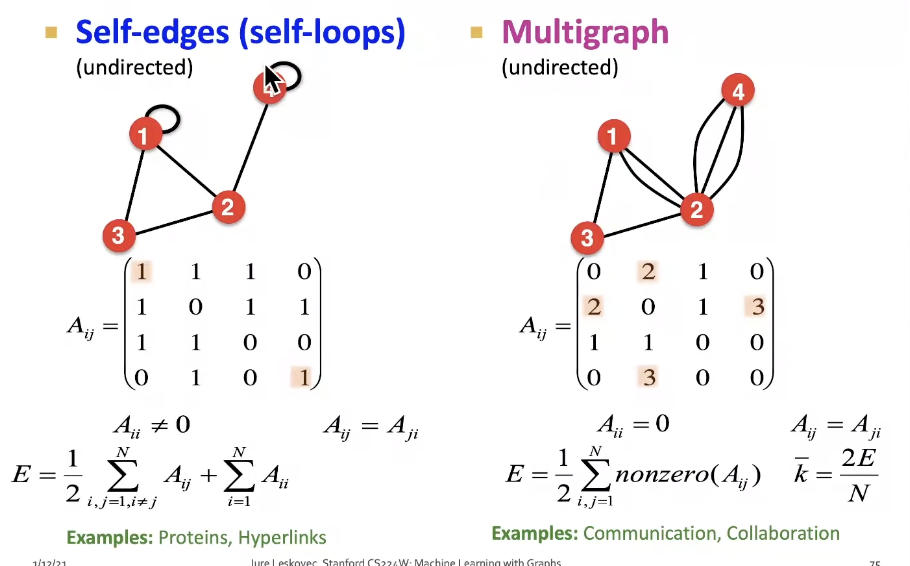
Connectivity of Undirected Graphs
- Connected (undirected) graph: any two vetrices can be joined by a path
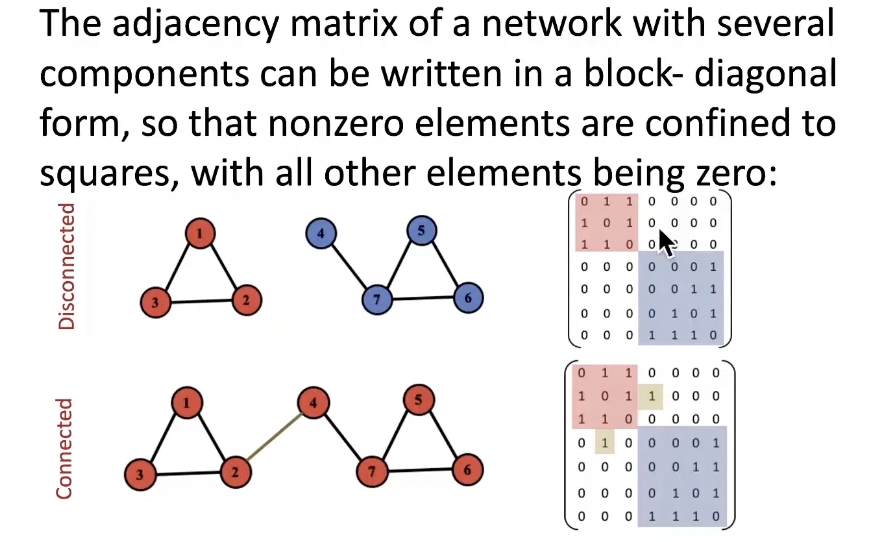
Connectivity of Directed Graphs
- Strongly connected directed graph ; has a path from each node to other node and vice versa
- Weakly connected directed graph ; is connected if we disregard the edge directions
- Strongly connected components (SCCs) ; can be identified, but not every node is part of a nontrivial strongly connected component
