XAI for Graphs
- 추천 readings
- LIME (Local Interpretation)
- SHAP (attribution)
- GNNExplainer
- GNN Explainability Taxonomy
- Trustworthy Graph Neural Networks
- GraphFramEx Evaluation
Trustworthy Graph Learning
- Trustworthy AI/GNN includes many components
- Explainability, fairness, robustness, privacy...- Algorithms to tackle combination of these aspects
- Challenges
- Role of graph topology is previously unexplored in these problems- Comprehensive quantiative evaluation
Big Picture: Aspects of Trustworthy GNNs
- Robustness
- Explainability
- Privacy
- Fairness
- Accountability
- Environmental well-being
- Others
✓ Each aspect can play a role in gaining trust from users of deep learning models
✓ Challenges in GNN context
- Role of graph topology is previously unexplored in these problems
- Quantiative evaluation is often difficult
1. Explainability and its Problem Settings
Explainability
- The black-box nature of deep learning makes it a major challenge to:
- Understand what is learned by the ML model- Extract insights of the underlying data we are trying to model
- Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) is an umbrella term for any research trying to solve the black-box problem of AI
- Why is it useful?
- Enable users to understand the decision-making of the model- Gain trust from human users of the deep learning system
Explainable Models: Linear Regression
- Linear Regression
- Slope is explainable (how much does one variable affects a prediction) - Each feature has an associated weights, indicating its importance
Explainable Models: Dimension Reduction
- Dimension Reduction
- Dimension reduction allows us to visualize the training data distribution - Decision boundary can be visualized an understood
Explainable Models: Decision Tree
- Decision trees are very explainable!
- On every node of the decision tree, we understand a criteria for prediction
- We can perform statistics for each decision node
Explainable Characteristics
- What makes model explainable?
- Importance values (for pixels, features, words, nodes in graphs)- Attributes: Stratighforward relationsjips between prediction and input features
- Encourage concepts and prototypes
Example: Computer Vision
- Explanation in Computer Vision: A particular region of the image displays the predicted class of objects
Example: Natural Language Processing
- Explanation in Natural Language Processing: importance tokens that lead to the prediction
Example: Graph Learning
- Explanation in Graph Learning: an important subgraph structure and a small subset of node features that play a crucial role in GNNs prediction
Goal of GNN Explainability
- Model's behavior might be different from the underlying phenomenon
- Explaining ground truth pehnomenon
ex) What are the characteristics of toxic molecules? - Explaining model predictions
ex) Why does the model recommend no loan for Person X?
Deep Learning Explainability Methods: Examples
- Proxy Model
- Learn an interpretable model that locally approximates the original model. - Saliency Maps
- Compute the gradients of outputs with respect to inputs - Attention Mechanisms
- Visualize attention weights in attention models, such as transformer and GAT architectures.
Reasons for Explainability
- Trust: Explainability is prerequisite for humans to trust and accept the model's prediction
- Causality: Explainability can sometimes imply causality for the target prediction: attribute X causes the data to be Y
- Transferability: The model nees to convey an understanding of decision-making by humans before it can be safely deployed to unseen data.
- Fair and Ethical Decision Making: Knowing the reasons for a certain decision is a societal need, in order to perceive if the prediction conforms to ethical standards.
Explainability Settings
By target:
- Instance-level: a local explanation for a simple input x
- Model-level: a global explanation for a specific dataset D or classes of D
By stages:
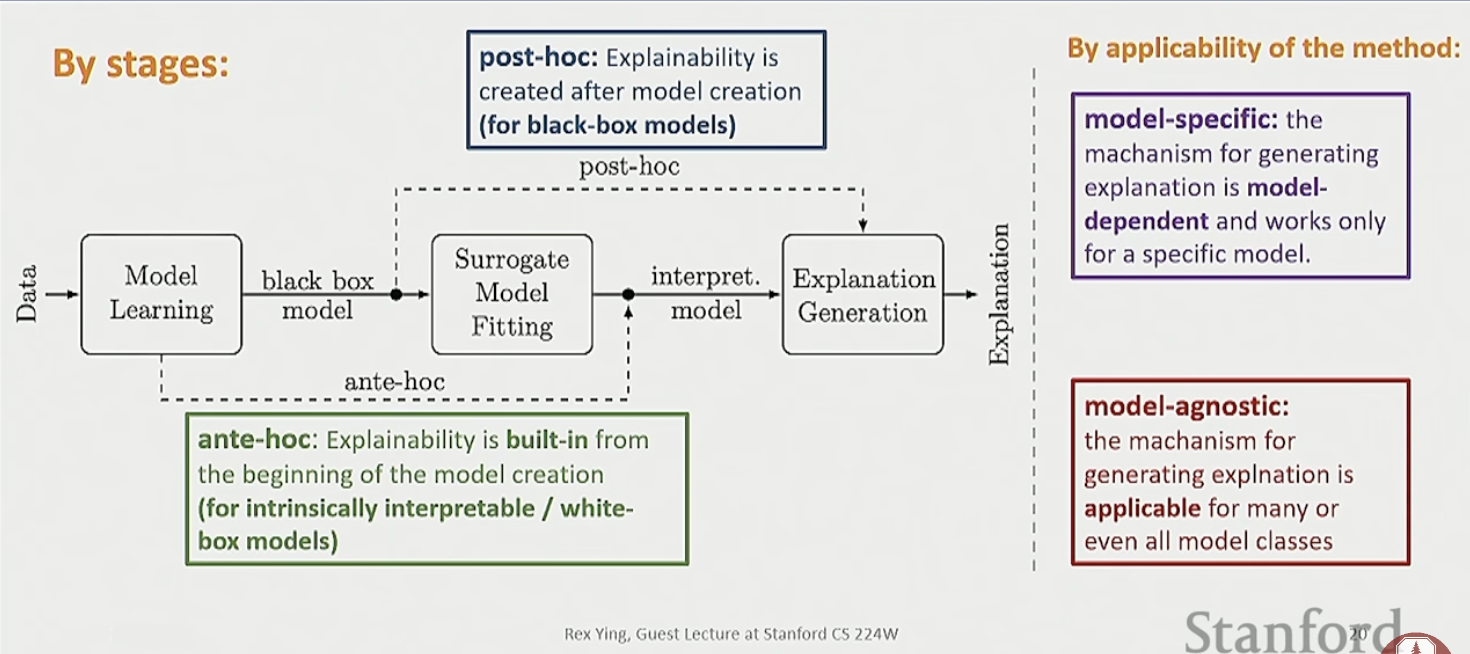
2. GNNExplainer
Example: Financial markets as graphs
each users are trustworthy or risky
GNN Explainability Use Cases
- Questions after training GNNs (post-hoc setting):
- Why is an item recommended to a user?- Why is the molecule mutagenic?
- Why is the user classified as fraudulent?
GNNExplainer Pipeline
- Training time:
- Optimize GNN on training graphs- Save the trained model
- Test time:
- Explain predictions made by the GNN- On unseen instances (nodes, edges, graphs)
Challenges
- Explain predictions for multiple tasks
- Node classification- Graph classification
- Link prediction
- Model agnostic (host-hoc)
- Need to be applied to a variety of GNN models: GCN, GraphSAGE, GAT etc - Predictions on graphs are induced by a complex combination of nodes, edges between them, and even motifs/subgraph structures/
- Unlike in CV, gradient is a less reliable signal on real-world graphs due to the discrete nature of edges
How to explain a GNN
- Consider a general message-passing framework
- The importance of node features
- GNNExplainer explain both aspects simultaneously
GNNExplainer Input
- Without loss of generality, consider node classification task:
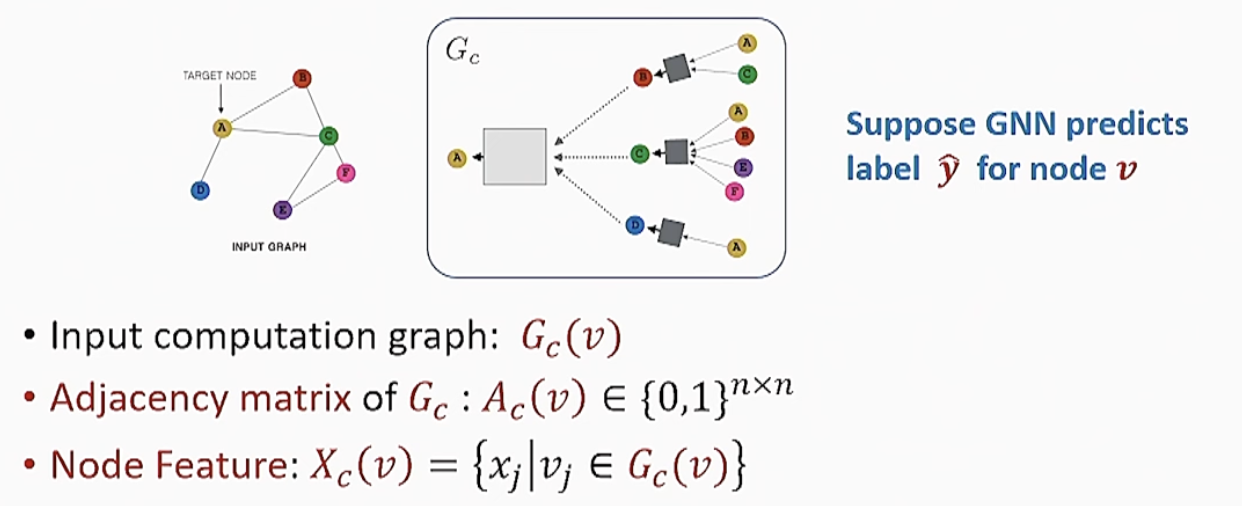
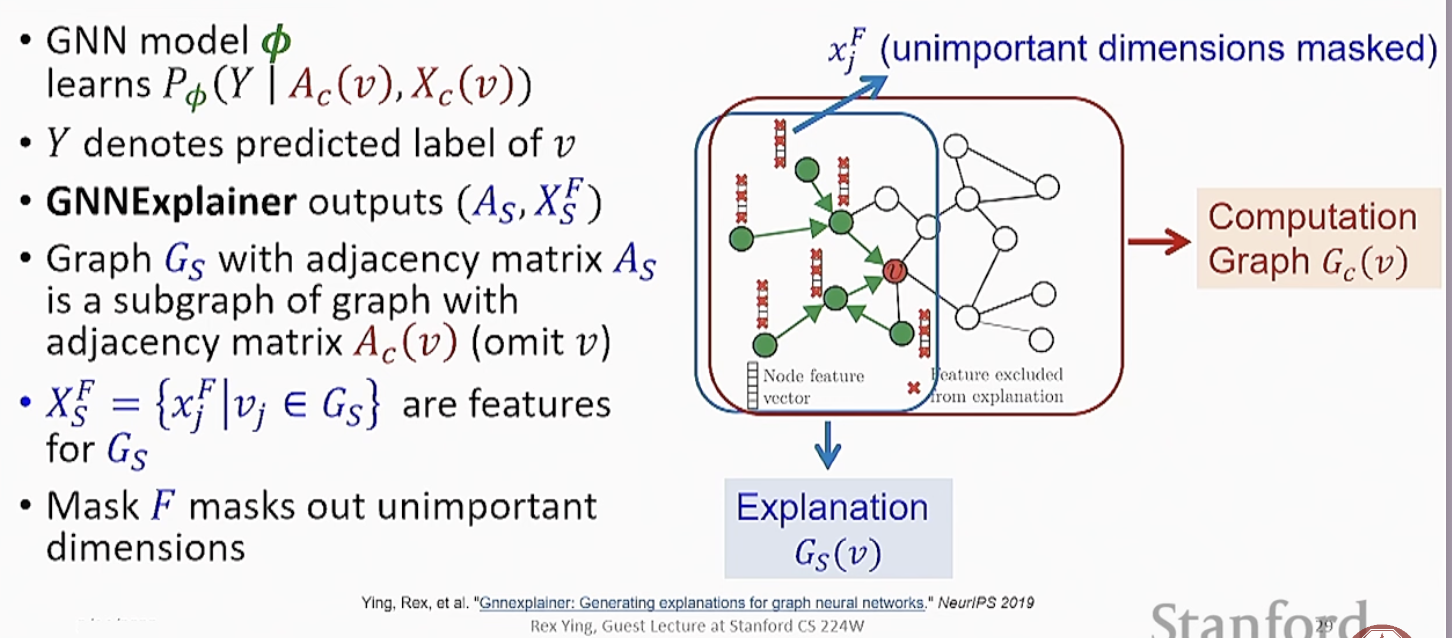
GNNExplainer Output
Explain by Mutual Information
- Mutual Information (MI)
- A measure of the mutual correlation between the two random variables.- Good explanation should have high correlation with model prediction
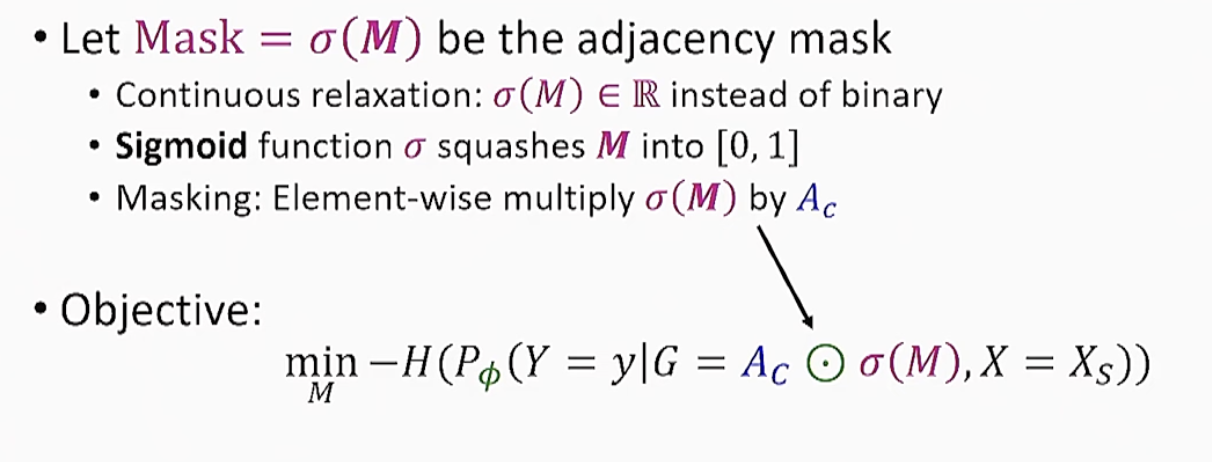
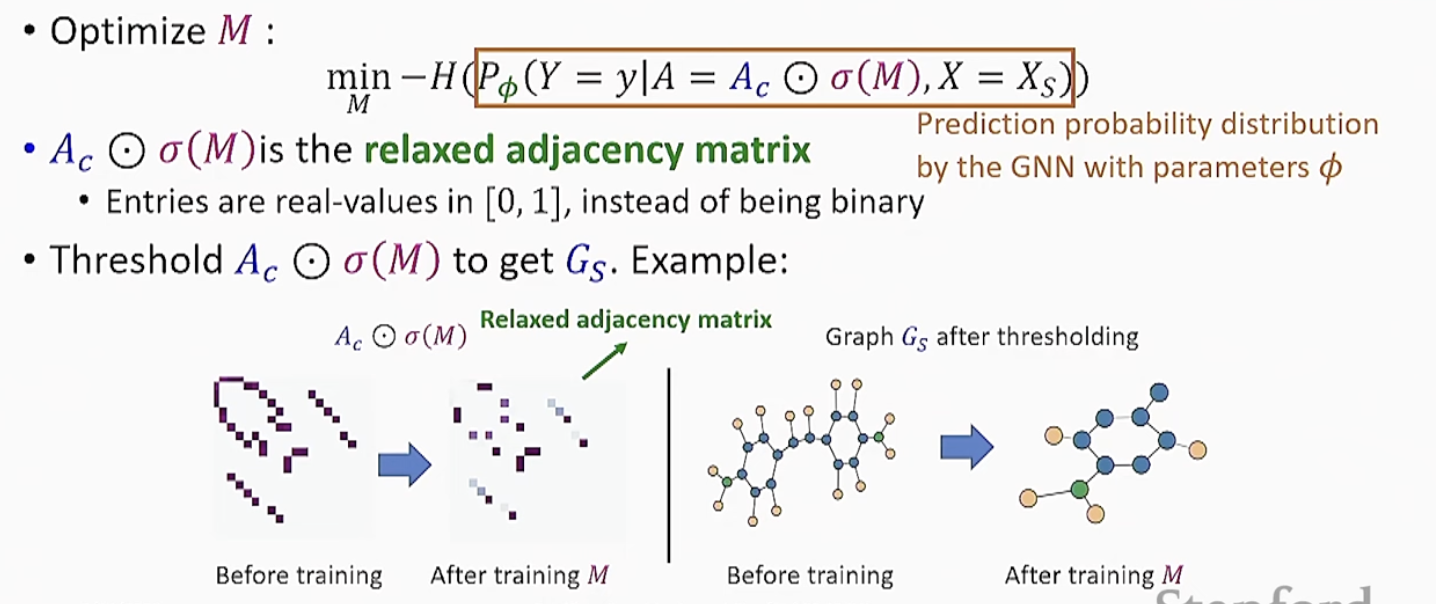
- GNNExplainer Objective
- Maximize MI between label and explanation
Explain by Optimization
- By relation to entropy, the objective is equivalnet to minimization of conditional entropy
- Finding A_s that minimizes the conditional entropy is computationally expensive!
- Issue: Exponentially many possible A_s - Soluton: Treat explanation as a distribution of "plausible explanations", instead of a single graph
GNNExplainer Model

Feature Explanation
- Similarly select features by optimizing for feature mask F
- Problem: Zero value could be important!
- Solution: Measure feature importance by how much drop in model confidence when features are replaced with explainability baselines.
- Concept: explainability baseline is the "null model" of a feature, such as the mean of the marginal distribution of each feature
