[Paper Review] WSISA: Making Survival Prediction from Whole Slide Histopathological Images
Paper Review

WSISA: Making Survival Prediction from Whole Slide Histopathological Images
WSI를 사용한 survival analysis의 시초격이 되는 논문이다. DeepConvSurv와 동일 저자가 1년 뒤 이전 모델을 발전시켜 연구에 사용하였다.
Introduction
- WSI size를 고려한 adaptive sampling
- Group into different clusters with thumbnail
- Train an aggregation model to make patient-level predictions based on cluster-level DeepConvSurv
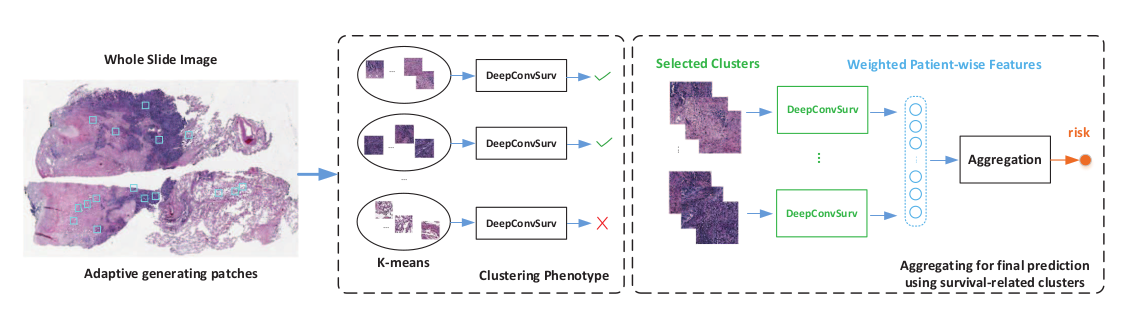
Methodology
기존 방법은 patch로부터 뽑은 local information에 집중함.
본 연구에서는 WSI로부터 general information을 얻은 framework를 개발함.
Framework
1) Generate patches
2) Clustering patch candidates according to their phenotypes
3) Selecting clusters based on path-wise survival prediction performance
4) Aggregating the selected clusters to make final prediction
Data

NLST : The National Lung Screening Trial, lung cancer dataset (very large)
TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas, glioblastoma multiforme, lung squamous cell carcinoma
Sampling from WSIs
Randomly sampled from patients WSI → catch main patterns and proportions
Patch size of 512 x 512 pixel (20X)
Clustering on Phenotypes
512 x 512 → 50 x 50 pixel thumbnail
2500 dimensions → PCA → 50 dimensions
K-means clustering 진행
각 cluster 에 속한 patch들에 대해 DeepConvSurv 로 accuracy 측정

Aggregation
단순 average pooling이 아닌, weighted sum 방식의 pooling
(단, weight는 학습을 통해 정해지는 것이 아니라 기존 cluster의 특성에 따라 미리 정해짐.)
이는 separate pattern의 contribution을 반영하기 위함임.
cluster 내부 patch features에 대해 단순 average pooling을 진행한 후
위에서 구한 weight를 각 cluster에 더해 weighted sum을 계산한 후 patient-level prediction 진행

Experiments
Comparison method
7가지 popular state-of-the-art survival model과 comparison study를 진행
1) LASSO-Cox (l1-norm penalized Cox)
2) EN-Cox (elastic-net penalized Cox)
3) Parametric censored regression models Weibull
4) Parametric censored regression models Logistic
5) RSF (Random Survival Forest)
6) BoostCI (Boosting concordance index)
7) MTLSA (Multi-task learning models)
ROI-based: annotation된 영역으로부터 patch를 추출. 1795 features.

WSISA를 사용했을 때 대부분의 실험에서 성능이 좋았다.
NLST 에서 WSISA 방법을 사용했을 때 ROI based method보다 15% 이상의 성능 향상을 보였다.
Clustering and Selecting Clusters

Selecting cluster를 진행할 때 c-index 기준 0.5를 threshold 로 설정함.
푸른색은 non-survival related cluster, 붉은색은 selected cluster임.
Among each cluster에서 heterogeneity를 볼 수 있음.
Phenotype based cluster method가 효과적으로 survival related pattern을 구별했음.
Conclusion
- selecting image patches: CNN을 통과시킨 후 patch를 clustering하여 informative 하지 않은 cluster은 drop시킴. 이후 각 cluster의 기여도를 반영한 weighted sum을 통해 aggregation을 거쳐 final risk prediction을 linear model을 통해 수행함.
