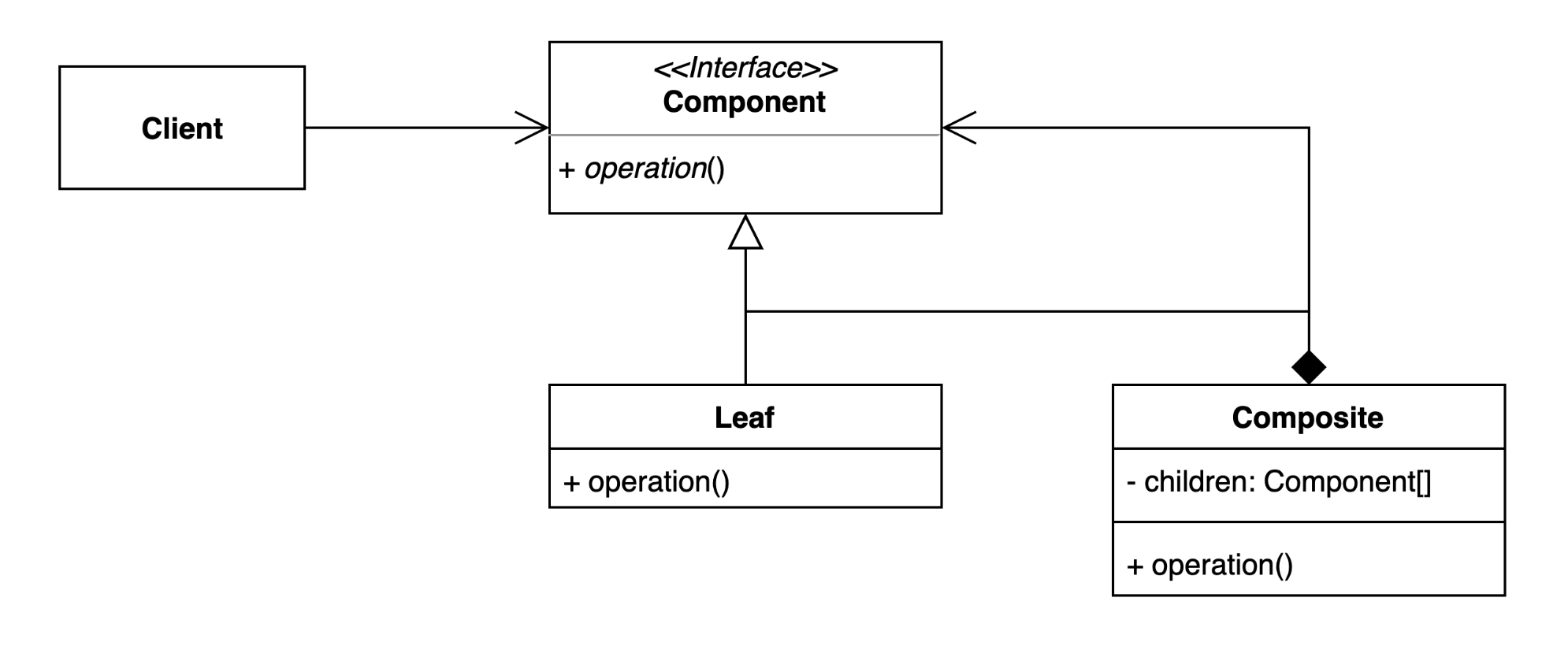
1. 컴포짓 (Composite) 패턴 : 그룹 전체와 개별 객체를 동일하게 처리할 수 있는 패턴.
컴포짓(Composite) 패턴은 개별 객체(Leaf)와 그룹 객체(Composite)를 동일하게 처리할 수 있는 계층 구조(Part-Whole Hierarchy)를 설계하는 패턴이다.
클라이언트는 전체(Composite)와 부분(Leaf)을 동일한 인터페이스(Component)로 인식하고 처리할 수 있다.
Before
Item
public class Item {
private String name;
private int price;
public Item(String name, int price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public int getPrice() {
return this.price;
}
}- 개별 항목(Leaf)를 나타낸다.
- name과 price를 가지고 있으며, 가격을 반환하는 getPrice() 메서드가 있다.
Bag
public class Bag {
private List<Item> items = new ArrayList<>();
public void add(Item item) {
items.add(item);
}
public List<Item> getItems() {
return items;
}
}- 여러 개의 Item(개별 항목)을 포함하는 그룹(Composite)을 나타낸다.
- add() 메서드로 Item을 추가하고, getItems() 메서드로 포함된 항목을 반환한다.
Client
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Item doranBlade = new Item("도란검", 450);
Item healPotion = new Item("체력 물약", 50);
Bag bag = new Bag();
bag.add(doranBlade);
bag.add(healPotion);
Client client = new Client();
client.printPrice(doranBlade);
client.printPrice(bag);
}
private void printPrice(Item item) {
System.out.println(item.getPrice());
}
private void printPrice(Bag bag) {
int sum = bag.getItems().stream().mapToInt(Item::getPrice).sum();
System.out.println(sum);
}
}- 클라이언트는 Item과 Bag을 각각 처리한다.
- printPrice() 메서드는 Item과 Bag을 별도로 처리하며, 두 개의 메서드가 필요하다.
Before 코드 문제점
1) 코드 중복:
printPrice() 메서드가 Item과 Bag에 대해 각각 정의되어 있어 중복 코드가 발생한다.
2) 확장성 문제:
Bag 외에 다른 그룹 객체가 추가되면, 클라이언트는 그 그룹 객체를 처리하는 새로운 메서드를 추가해야 한다.
3) 일관성 부족:
클라이언트는 Item과 Bag을 동일한 방식으로 처리할 수 없어, 코드의 일관성이 떨어진다.
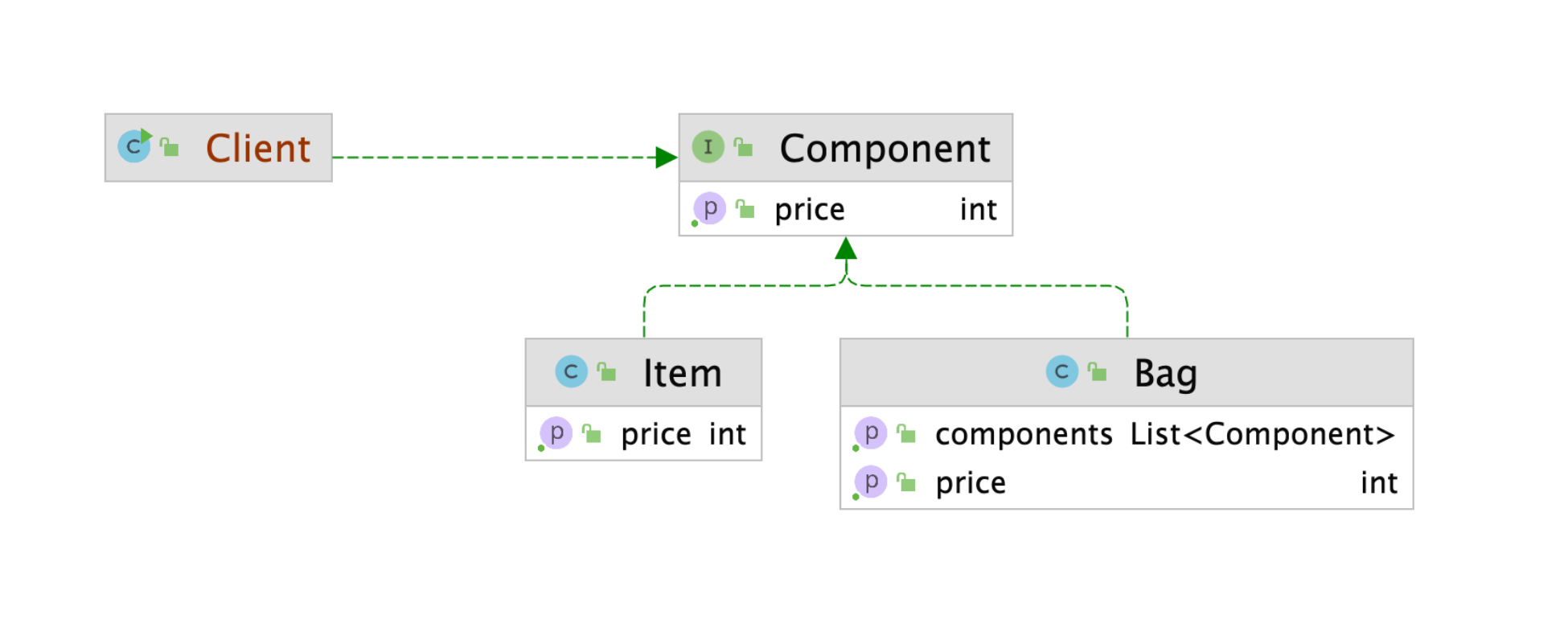
After
Component
public interface Component {
int getPrice();
}
- int getPrice() 메서드를 정의하여, 개별 객체와 그룹 객체가 동일한 인터페이스를 사용하도록 설계.
Item
public class Item implements Component {
private String name;
private int price;
public Item(String name, int price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public int getPrice() {
return this.price;
}
}
- 개별 항목(Leaf)을 나타낸다.
- Component 인터페이스를 구현하여, 가격을 반환하는 getPrice() 메서드를 제공한다.
Bag
public class Bag implements Component {
private List<Component> components = new ArrayList<>();
public void add(Component component) {
components.add(component);
}
public List<Component> getComponents() {
return components;
}
@Override
public int getPrice() {
return components.stream().mapToInt(Component::getPrice).sum();
}
}- 그룹 객체(Composite)를 나타낸다.
- 여러 Component(Item이나 다른 Bag)를 포함할 수 있으며, 포함된 모든 Component의 가격을 합산하여 반환한다.
Client
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Item doranBlade = new Item("도란검", 450);
Item healPotion = new Item("체력 물약", 50);
Bag bag = new Bag();
bag.add(doranBlade);
bag.add(healPotion);
Client client = new Client();
client.printPrice(doranBlade);
client.printPrice(bag);
}
private void printPrice(Component component) {
System.out.println(component.getPrice());
}
}
- 클라이언트는 이제 Component 인터페이스만 알면 된다.
- printPrice() 메서드는 Component 타입을 매개변수로 받아, 개별 객체(Leaf)와 그룹 객체(Composite)를 동일하게 처리한다.
다이어그램
컴포짓 패턴의 장단점
장점
1. 복잡한 트리 구조를 편리하게 사용 가능
- 트리 구조를 활용하여 객체 계층을 표현할 때, 전체와 개별 객체를 동일하게 처리할 수 있다.
- 클라이언트는 트리의 구조를 알 필요 없이 Component 인터페이스만 사용하면 된다.
2. 다형성과 재귀 활용 가능
- Composite 객체(예: 그룹) 안에 또 다른 Composite 객체를 포함할 수 있어, 재귀적인 트리 구조를 쉽게 구현할 수 있다.
- 다형성을 통해 클라이언트는 Component 인터페이스로 모든 객체를 처리할 수 있다.
(
재귀적 트리 구조 부연 설명
컴포짓 패턴의 핵심: Composite 안에 또 다른 Composite
- 컴포짓 패턴은 재귀적인 트리 구조를 형성할 수 있다.
- Composite 객체(그룹)는 다른 Component(Leaf 또는 Composite)를 포함할 수 있다.
- 즉, Composite 객체 안에 또 다른 Composite 객체를 포함하여, 트리 구조를 형성한다.
예제
Bag (Composite)
├── Item (Leaf) [도란검: 450원]
├── Item (Leaf) [체력 물약: 50원]
└── Bag (Composite)
├── Item (Leaf) [마법 물약: 200원]
└── Item (Leaf) [롱소드: 350원]-
첫 번째 Bag(Composite):
도란검과체력 물약이라는 개별 객체(Leaf)를 포함.- 또 다른 Bag(Composite)을 포함.
-
두 번째 Bag(Composite):
마법 물약과롱소드라는 개별 객체(Leaf)를 포함.
이처럼 Composite 객체 안에 또 다른 Composite 객체를 포함하여 재귀적인 트리 구조를 쉽게 구현할 수 있다.
)
3. 확장성:
- 클라이언트 코드를 수정하지 않고 새로운 엘리먼트 타입(Leaf 또는 Composite)을 추가할 수 있다.
- 새로운 개별 객체나 그룹 객체를 추가하려면, Component 인터페이스를 구현하기만 하면 된다.
4. 유지보수 용이성:
- 공통된 인터페이스(Component)를 통해 처리하므로, 로직 수정이 필요한 경우 중앙에서 관리할 수 있다.
단점
1. 과도한 일반화:
- 모든 객체(개별 객체와 그룹 객체)가 공통 인터페이스를 구현해야 하기 때문에, 지나치게 일반화된 설계를 강요받을 수 있다.
- 이는 특정 객체가 필요하지 않은 메서드를 구현해야 하는 상황을 초래할 수 있다.
2. 복잡성 증가:
- 트리 구조를 설계하고 구현하는 데 추가적인 코드가 필요하므로, 단순한 문제에 적용할 경우 오히려 복잡성을 증가시킬 수 있다.
- 트리 구조의 깊이가 깊어질수록 성능이나 유지보수에 문제가 생길 수 있다.
컴포짓 패턴 실무에서는?
1. 자바
-
Swing 라이브러리
- Java의 Swing 라이브러리에서 컴포짓 패턴이 널리 사용된다.
- 예:
JComponent는JButton,JPanel,JLabel등 모든 UI 컴포넌트의 공통 인터페이스 역할을 한다. JPanel은 또 다른JPanel이나JButton을 포함할 수 있어 재귀적인 트리 구조를 형성한다.
예제:
JPanel panel = new JPanel(); // Composite 객체 JButton button = new JButton("Click Me"); // Leaf 객체 panel.add(button); // Composite에 Leaf 추가 -
JavaServer Faces (JSF)
- JSF 컴포넌트 라이브러리에서 컴포짓 패턴이 사용된다.
- 예:
UIComponent는 모든 JSF UI 컴포넌트의 공통 인터페이스 역할을 하며, 재귀적인 트리 구조를 형성한다. - 컴포넌트 트리는 부모-자식 관계를 정의하여, 복잡한 UI 계층을 표현할 수 있다.
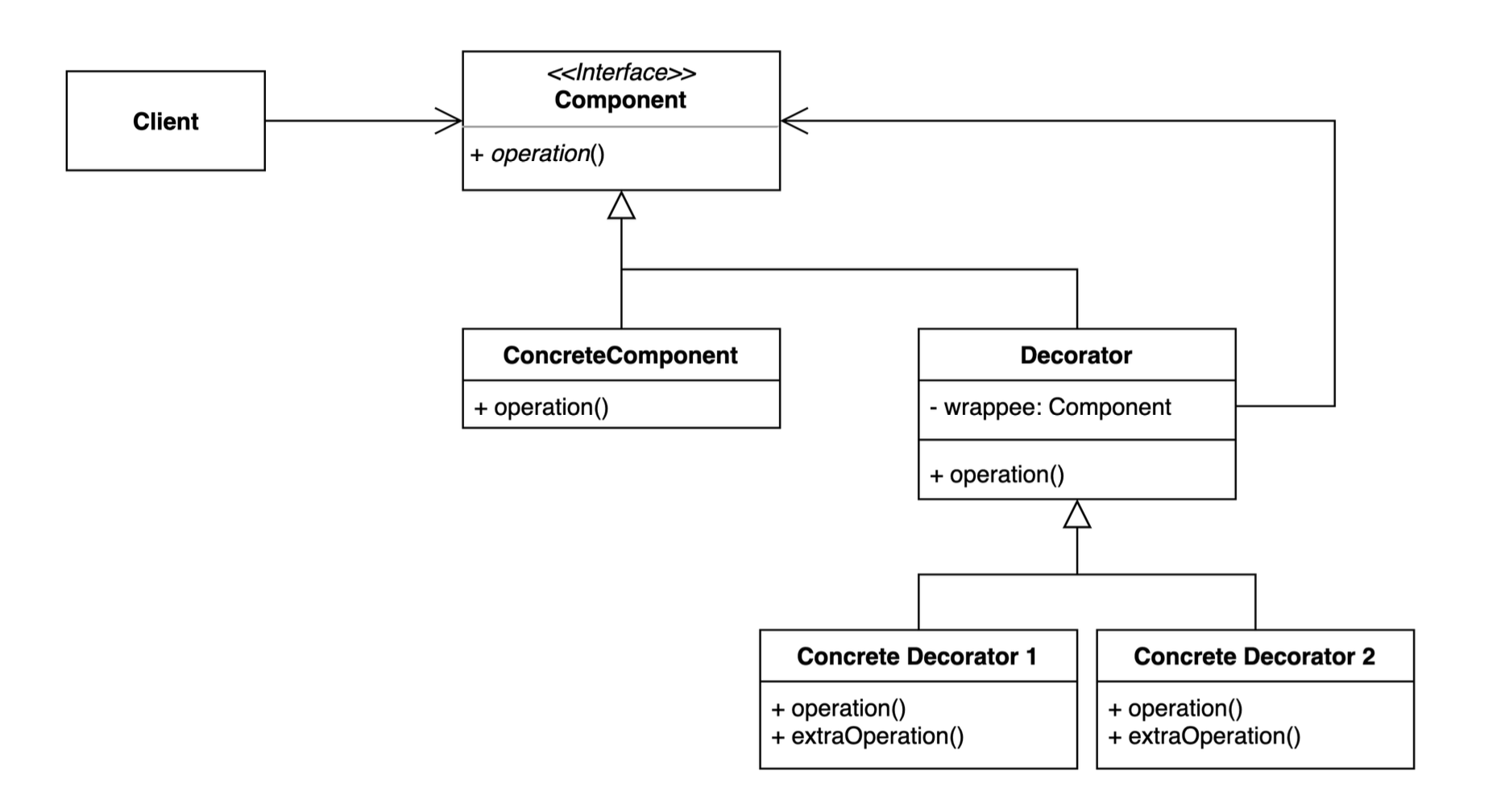
2. 데코레이터 (Decorator) 패턴 : 기존 코드를 변경하지 않고 부가 기능을 추가하는 패턴
상속이 아닌 위임을 사용해서 보다 유연하게(런타임에) 부가 기능을 추가하는 것도 가능하다.
Before
1. 구조
-
CommentService:
- 댓글을 출력하는 기본 서비스.
public class CommentService { public void addComment(String comment) { System.out.println(comment); } } -
SpamFilteringCommentService:
- 스팸 필터링 기능을 추가한 서비스.
CommentService를 상속받아, 스팸 여부를 확인한 후 댓글을 출력.
public class SpamFilteringCommentService extends CommentService { @Override public void addComment(String comment) { if (!isSpam(comment)) { super.addComment(comment); } } private boolean isSpam(String comment) { return comment.contains("http"); } } -
TrimmingCommentService:
- 댓글의 불필요한 "..."을 제거하는 기능을 추가한 서비스.
CommentService를 상속받아, 댓글을 수정한 후 출력.
public class TrimmingCommentService extends CommentService { @Override public void addComment(String comment) { super.addComment(trim(comment)); } private String trim(String comment) { return comment.replace("...", ""); } } -
Client:
- 클라이언트는 특정
CommentService를 사용해 댓글을 출력.
public class Client { private CommentService commentService; public Client(CommentService commentService) { this.commentService = commentService; } private void writeComment(String comment) { commentService.addComment(comment); } } - 클라이언트는 특정
2. 문제점
-
확장성 부족:
- 새로운 기능(예: 댓글 길이 제한)을 추가하려면, 새로운 클래스를 만들어야 함.
- 여러 기능을 조합하려면 조합된 클래스를 추가로 생성해야 함 (예:
SpamFilteringAndTrimmingCommentService).
-
상속의 단점:
- 상속은 강한 결합을 초래하며, 클래스 계층 구조가 복잡해질 수 있음.
- 다중 기능을 조합할수록 클래스 폭발 문제가 발생.
-
유연성 부족:
- 런타임에 기능을 동적으로 변경하거나 조합하는 것이 어려움.
After
1. 구조
-
CommentService 인터페이스:
- 모든 댓글 서비스의 공통 인터페이스.
public interface CommentService { void addComment(String comment); } -
DefaultCommentService:
- 기본 댓글 출력 서비스를 구현한 클래스.
public class DefaultCommentService implements CommentService { @Override public void addComment(String comment) { System.out.println(comment); } } -
CommentDecorator:
- 기본 데코레이터 클래스로,
CommentService를 감싸고 위임한다. - 모든 데코레이터는 이 클래스를 상속받아 구현.
public class CommentDecorator implements CommentService { private CommentService commentService; public CommentDecorator(CommentService commentService) { this.commentService = commentService; } @Override public void addComment(String comment) { commentService.addComment(comment); } } - 기본 데코레이터 클래스로,
-
SpamFilteringCommentDecorator:
- 스팸 필터링 기능을 추가한 데코레이터.
public class SpamFilteringCommentDecorator extends CommentDecorator { public SpamFilteringCommentDecorator(CommentService commentService) { super(commentService); } @Override public void addComment(String comment) { if (isNotSpam(comment)) { super.addComment(comment); } } private boolean isNotSpam(String comment) { return !comment.contains("http"); } } -
TrimmingCommentDecorator:
- 댓글의 불필요한 "..."을 제거하는 기능을 추가한 데코레이터.
public class TrimmingCommentDecorator extends CommentDecorator { public TrimmingCommentDecorator(CommentService commentService) { super(commentService); } @Override public void addComment(String comment) { super.addComment(trim(comment)); } private String trim(String comment) { return comment.replace("...", ""); } } -
Client:
- 클라이언트는
CommentService를 사용하며, 데코레이터로 기능을 조합.
public class Client { private CommentService commentService; public Client(CommentService commentService) { this.commentService = commentService; } public void writeComment(String comment) { commentService.addComment(comment); } } - 클라이언트는
-
App:
- 런타임에 데코레이터를 조합하여
CommentService를 생성.
public class App { private static boolean enabledSpamFilter = true; private static boolean enabledTrimming = true; public static void main(String[] args) { CommentService commentService = new DefaultCommentService(); if (enabledSpamFilter) { commentService = new SpamFilteringCommentDecorator(commentService); } if (enabledTrimming) { commentService = new TrimmingCommentDecorator(commentService); } Client client = new Client(commentService); client.writeComment("오징어게임"); client.writeComment("보는게 하는거 보다 재밌을 수가 없지..."); client.writeComment("http://whiteship.me"); } } - 런타임에 데코레이터를 조합하여
다이어그램
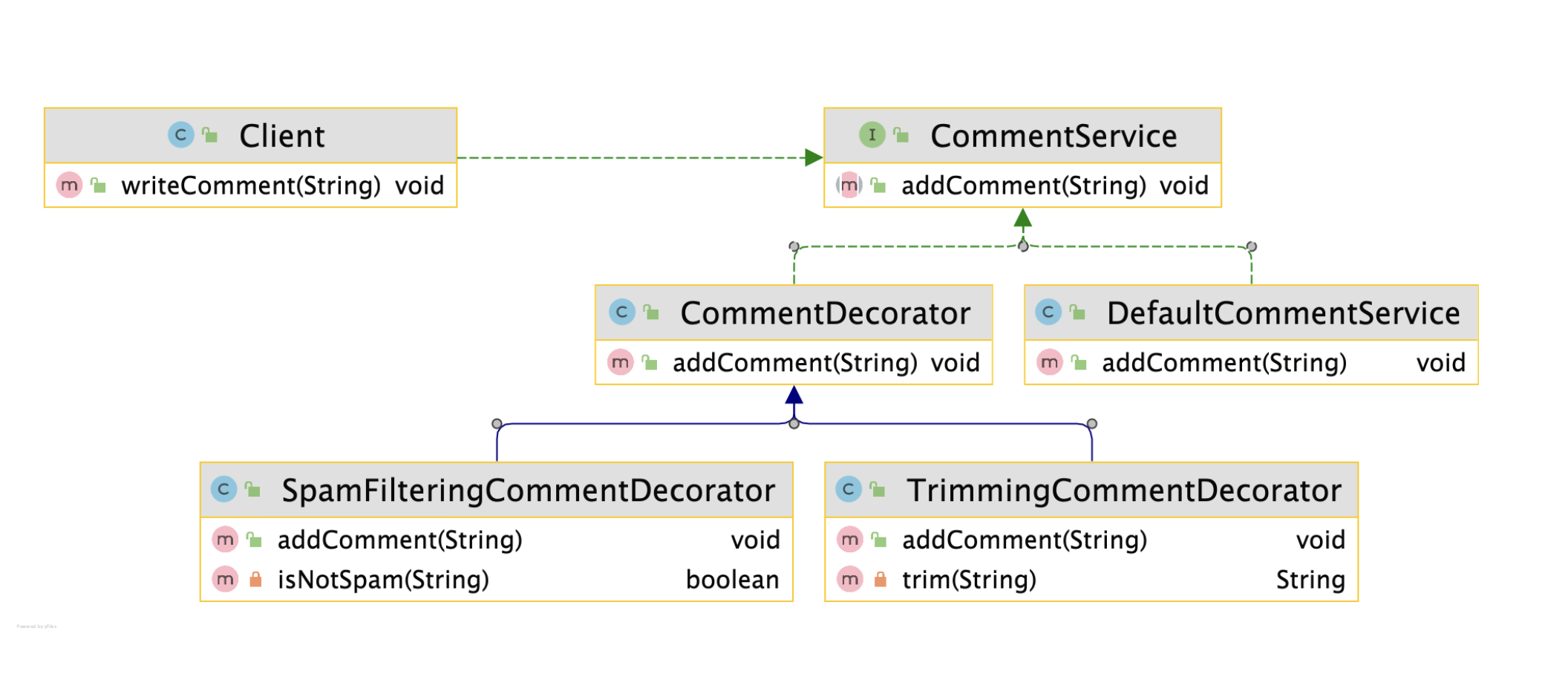
2. 개선점
-
확장성 증가:
- 새로운 기능(데코레이터)을 추가하려면
CommentDecorator를 상속받아 새로운 클래스를 구현하면 됨. - 기능 조합을 위한 새로운 클래스 생성이 불필요.
- 새로운 기능(데코레이터)을 추가하려면
-
유연성 증가:
- 기능을 런타임에 동적으로 조합 가능.
- 예:
SpamFilteringCommentDecorator와TrimmingCommentDecorator를 필요에 따라 조합.
-
상속 대신 위임:
- 상속 대신 위임을 사용하여, 데코레이터를 동적으로 조합 가능.
- 기존 클래스 계층 구조를 변경하지 않고도 기능을 추가할 수 있음.
-
클래스 폭발 문제 해결:
- 조합된 기능을 가진 클래스를 별도로 생성할 필요가 없어, 클래스 수를 줄일 수 있음.
출력 결과
입력:
"오징어게임"
"보는게 하는거 보다 재밌을 수가 없지..."
"http://whiteship.me"출력 (스팸 필터링 + Trimming 데코레이터 적용):
오징어게임
보는게 하는거 보다 재밌을 수가 없지데코레이터 패턴 장단점
장점
-
기존 코드 수정 없이 새로운 기능 추가 가능:
- 기본 클래스(
DefaultCommentService)를 수정하지 않고도 새로운 데코레이터를 추가 가능.
- 기본 클래스(
-
유연한 기능 조합:
- 데코레이터를 런타임에 동적으로 조합할 수 있어, 다양한 기능 조합 가능.
-
단일 책임 원칙 준수(SRP):
- 각 데코레이터는 자신만의 기능을 처리하며, 역할이 명확히 분리.
단점
-
복잡성 증가:
- 데코레이터 계층이 많아지면 코드의 가독성과 관리가 어려워질 수 있음.
-
위임 호출 오버헤드:
- 위임을 통해 기능을 구현하므로, 메서드 호출 체인이 길어질 수 있음.
실무에서의 활용
-
자바 I/O
InputStream과OutputStream계열 클래스.- 예:
BufferedInputStream,DataInputStream등은 데코레이터를 활용.
-
스프링
- AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming)에서 메서드 호출에 부가 기능(트랜잭션, 로깅 등)을 추가할 때 데코레이터 패턴 사용.
-
GUI 프레임워크
- 버튼, 텍스트 필드 등 기본 컴포넌트에 스크롤, 테두리 등 추가 기능을 동적으로 적용.
데코레이터 패턴 부연 설명
Decorator의 핵심
- 기존 코드를 변경하지 않고 새로운 기능을 동적으로 추가할 수 있도록 설계된 패턴이다.
- "기본 기능에 새로운 기능을 입히는" 과정이라고 이해하면 된다.
- 상속을 사용하지 않고, 위임(Delegation)을 통해 기존 클래스의 동작에 새로운 동작을 덧붙인다.
Decorator가 필요한 이유
1. 상속의 한계
- 상속을 사용하면 새로운 기능을 추가할 때마다 새로운 클래스를 생성해야 한다.
- 특히, 기능의 조합이 많아지면, 클래스 수가 기하급수적으로 증가하는 "클래스 폭발 문제"가 발생한다.
2. 유연한 기능 추가
- 상속은 정적(컴파일 타임)에 결정되지만, 데코레이터는 동적(런타임)에 조합 가능하다.
- 즉, 실행 중에 기능을 추가하거나 제거할 수 있다.
3. 단일 책임 원칙 준수
- 데코레이터는 기능을 개별 클래스로 분리하여, 각 클래스가 하나의 책임만 가지도록 설계한다.
Decorator 패턴의 비유
기본 예시: 카페 음료
- 카페에서 주문하는 음료가 있다고 가정해보자.
- 기본 음료: 아메리카노
- 추가 옵션: 우유, 초콜릿, 휘핑크림 등
전통적인 상속 기반 설계
- 모든 조합을 클래스로 정의한다면?
아메리카노: 기본 클래스아메리카노 + 우유: 새 클래스 생성아메리카노 + 초콜릿: 또 다른 새 클래스 생성아메리카노 + 우유 + 초콜릿 + 휘핑크림: 또 다른 새 클래스 생성
- 결과: 클래스 폭발 (옵션 조합마다 새로운 클래스를 만들어야 함).
Decorator를 사용한 설계
- 아메리카노를 기본 클래스로 유지하고, 옵션을 데코레이터로 구현.
- 각 데코레이터는 기본 음료에 추가 기능(옵션)을 "입히는" 역할을 한다!
코드 예시:
// 기본 음료
public interface Beverage {
String getDescription();
double getCost();
}
// 기본 아메리카노
public class Americano implements Beverage {
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return "아메리카노";
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return 3000; // 기본 가격
}
}
// 데코레이터: 우유 추가
public class MilkDecorator implements Beverage {
private Beverage beverage;
public MilkDecorator(Beverage beverage) {
this.beverage = beverage;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + ", 우유";
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return beverage.getCost() + 500; // 우유 추가 가격
}
}
// 데코레이터: 초콜릿 추가
public class ChocolateDecorator implements Beverage {
private Beverage beverage;
public ChocolateDecorator(Beverage beverage) {
this.beverage = beverage;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + ", 초콜릿";
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return beverage.getCost() + 700; // 초콜릿 추가 가격
}
}
// 데코레이터 사용
public class Cafe {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Beverage beverage = new Americano(); // 기본 아메리카노
beverage = new MilkDecorator(beverage); // 우유 추가
beverage = new ChocolateDecorator(beverage); // 초콜릿 추가
System.out.println(beverage.getDescription() + " 가격: " + beverage.getCost());
// 출력: 아메리카노, 우유, 초콜릿 가격: 4200
}
}Decorator의 동작 방식
1. 기본 객체 생성:
- 기본적인 기능만을 수행하는 객체를 생성한다. (예:
Americano).
2. 기능을 추가:
- 새로운 데코레이터를 사용해 기존 객체에 새로운 기능을 "포장"한다.
- 예:
new MilkDecorator(beverage).
3. 위임(Delegation) 호출:
- 데코레이터는 내부적으로 원본 객체(
beverage)의 메서드를 호출하고, 부가 기능을 추가로 수행한다.
Decorator와 Before 코드의 차이
Before 코드
SpamFilteringCommentService와TrimmingCommentService는 각각CommentService를 상속하여 기능을 확장.- 각 기능을 조합하려면 새로운 클래스를 만들어야 함:
SpamFilteringAndTrimmingCommentService등의 추가 클래스가 필요.
- 단점:
- 클래스 폭발 문제 발생.
- 런타임에 기능을 동적으로 변경하거나 조합할 수 없음.
After 코드
- 데코레이터 패턴을 사용하여 기능을 동적으로 조합.
- 예:
CommentService commentService = new DefaultCommentService(); commentService = new SpamFilteringCommentDecorator(commentService); commentService = new TrimmingCommentDecorator(commentService); - 장점:
- 기능을 런타임에 동적으로 추가.
- 새로운 기능 추가 시 기존 코드를 수정할 필요가 없음.
