문제 설명
n개의 노드가 있는 그래프가 있습니다. 각 노드는 1부터 n까지 번호가 적혀있습니다. 1번 노드에서 가장 멀리 떨어진 노드의 갯수를 구하려고 합니다. 가장 멀리 떨어진 노드란 최단경로로 이동했을 때 간선의 개수가 가장 많은 노드들을 의미합니다.
노드의 개수 n, 간선에 대한 정보가 담긴 2차원 배열 vertex가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 1번 노드로부터 가장 멀리 떨어진 노드가 몇 개인지를 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성해주세요.
제한사항
노드의 개수 n은 2 이상 20,000 이하입니다.
간선은 양방향이며 총 1개 이상 50,000개 이하의 간선이 있습니다.
vertex 배열 각 행 [a, b]는 a번 노드와 b번 노드 사이에 간선이 있다는 의미입니다.
입출력 예
n 6
vertex [[3, 6], [4, 3], [3, 2], [1, 3], [1, 2], [2, 4], [5, 2]]
return 3
입출력 예 설명
예제의 그래프를 표현하면 아래 그림과 같고, 1번 노드에서 가장 멀리 떨어진 노드는 4,5,6번 노드입니다.
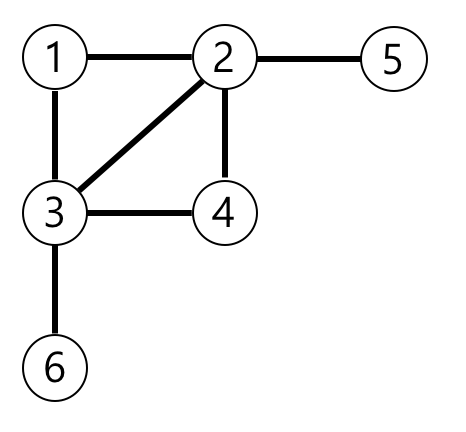
접근하기
- 그래프를 이용하는 문제였다.
- 1번으로부터 가장 먼 노드의 갯수를 찾는 문제이다.
- 1을 제외한 모든 노드의 가중치를 1로 두고 다익스트라 알고리즘을 수행하면 각 노드별로 최소 거리로 갈 수 있는 가중치 값들이 구해진다.
- 그 값들 중, 최대 값을 찾아서 그 갯수를 리턴하면 된다.
Code
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
int to, weight;
Edge(int to, int weight){
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge e){
return this.weight - e.weight;
}
}
PriorityQueue<Edge> pq;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>> adj;
int[] dist;
public int solution(int n, int[][] edge) {
int answer = 0;
pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
adj = new ArrayList<>();
dist = new int[n+1];
Arrays.fill(dist,Integer.MAX_VALUE);
for(int i=0; i<=n; ++i) adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
for(int i=0; i< edge.length; ++i){
int from = edge[i][0];
int to = edge[i][1];
int weight = 1;
adj.get(from).add(new Edge(to, weight));
adj.get(to).add(new Edge(from, weight));
}
dist[1] = 0;
pq.offer(new Edge(1,0));
dijkstra();
int max = 0;
for(int a: dist){
if(a<=n){
if(max<=a){
max = a;
}
}
}
for(int a : dist){
if(a==max) answer++;
}
return answer;
}
public void dijkstra(){
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
Edge e = pq.poll();
for(Edge ne : adj.get(e.to)){
if(dist[ne.to] > dist[e.to] + ne.weight){
dist[ne.to] = dist[e.to] + ne.weight;
pq.offer(ne);
}
}
}
}
}✅
- 다익스트라를 이용하면 쉬운 문제였다.
