Connected Component
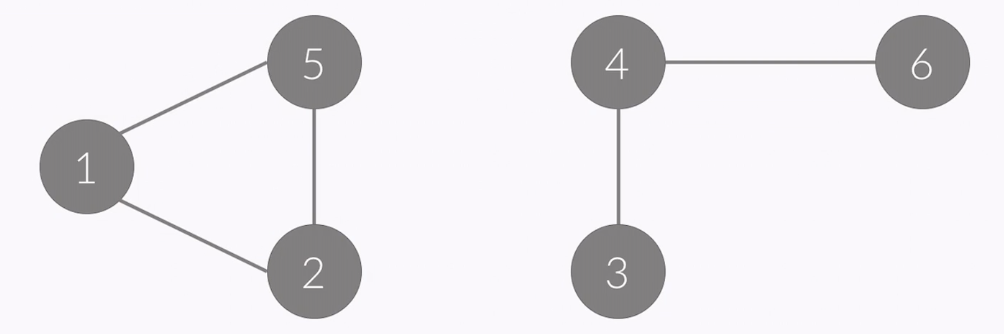
- It is possible that graphs are divided into few pieces
- like this, if graphs are separated, it is called connected component
- There should be path to connect all vertices in each connected component
- Also, there should be no path to connect vertices in other connected components to become a connected component
- Graph above has two of connected component
- to get connected component, we can use BFS or DFS search
- boj.kr/11724
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static void bfs(ArrayList<Integer>[] adjacentList) {
boolean[] checkList = new boolean[ adjacentList.length + 1 ];
ArrayDeque<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
int count = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=adjacentList.length-1; i++) {
if(checkList[i] == false) {
queue.push(i);
checkList[i] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int currentVertex = queue.poll();
if(adjacentList[currentVertex] != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < adjacentList[currentVertex].size(); j++) {
int currentEdge = adjacentList[currentVertex].get(j);
if (checkList[currentEdge] == false) {
queue.add(currentEdge);
checkList[currentEdge] = true;
}
}
}
}
count++;
}
}
System.out.print(count);
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int numOfVertices = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int numOfEdges = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
ArrayList<Integer>[] adjacentList = new ArrayList[numOfVertices + 1];
for(int i=0; i<numOfEdges; i++){
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int vNum = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int eNum = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if(adjacentList[vNum] == null) adjacentList[vNum] = new ArrayList();
if(adjacentList[eNum] == null) adjacentList[eNum] = new ArrayList();
adjacentList[vNum].add(eNum);
adjacentList[eNum].add(vNum);
}
bfs(adjacentList);
}
}Bipartite Graph
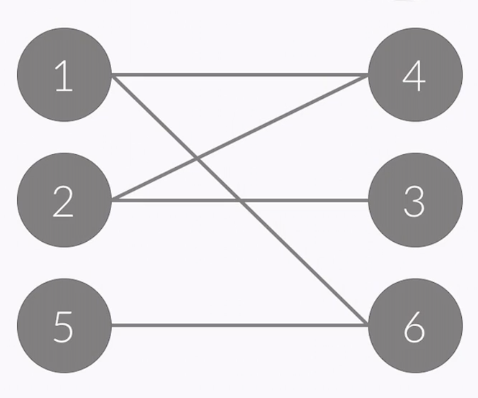
- If a graph can be divided into A and B like this, it is called Bipartite Graph
- There is no edge among vertices of A (1, 2, 5)
- There is no edge among vertices of B (4, 3, 6)
- every edge's end point is only in A and B
- by using DFS or BFS search, we can check if it is bipartite graph or not
- to check it, we can make the rule for getting it checked.
1. We will paint all the vertices in red or blue
2. after one vertex is painted, the color of paint is switched to opposite color (red | blue)
3. if All vertices are painted it will be over
4. last we have to check if red vertices' edges are all connected with blue vertices - boj.kr/1707
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static String bfs(ArrayList<Integer>[] adjacentList){
ArrayDeque<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
int[] checkList = new int[adjacentList.length];
for(int i=1; i<adjacentList.length; i++) {
if(checkList[i] == 0) {
queue.add(i);
checkList[i] = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int currentVertex = queue.poll();
if (adjacentList[currentVertex] != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < adjacentList[currentVertex].size(); j++) {
if (checkList[adjacentList[currentVertex].get(j)] == 0) {
checkList[adjacentList[currentVertex].get(j)] = 3 - checkList[currentVertex];
queue.add(adjacentList[currentVertex].get(j));
}
}
}
}
}
}
for(int i=1; i<adjacentList.length; i++){
int vertexColor = checkList[i];
if(adjacentList[i] != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < adjacentList[i].size(); j++) {
int edgeColor = checkList[adjacentList[i].get(j)];
if(vertexColor != 0 && edgeColor != 0) {
if (vertexColor == edgeColor) {
return "NO\n";
}
}
}
}
}
return "YES\n";
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for(int j=0; j<n; j++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int numOfVertices = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int numOfEdges = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
ArrayList<Integer>[] adjacentList = new ArrayList[numOfVertices + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < numOfEdges; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int vNum = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int eNum = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if (adjacentList[vNum] == null) adjacentList[vNum] = new ArrayList();
if (adjacentList[eNum] == null) adjacentList[eNum] = new ArrayList();
adjacentList[vNum].add(eNum);
adjacentList[eNum].add(vNum);
}
sb = sb.append(bfs(adjacentList));
}
System.out.print(sb);
}
}Permutation Cycle
-
boj.kr/10451
-
find the permutation cycle by searching given permutation
-
it can be solved by DFS
-
it has only one edge, so it doesn't need to make graph with adjacent matrix
-
implementation in java
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.StringTokenizer; public class Main { public static boolean[] checkArr; public static int[] edgeArr; public static int dfs(int start){ if(checkArr[start]) return 1; checkArr[start] = true; return dfs(edgeArr[start]); } public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); for(int i=0; i<n; i++){ int m = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); edgeArr = new int[m+1]; checkArr = new boolean[m+1]; StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); int j=1; while(st.hasMoreTokens()) edgeArr[j++] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int sum = 0; for(j=1; j<=m; j++) if(!checkArr[j]) sum += dfs(j); sb.append(sum + "\n"); } System.out.print(sb); } }
Repeated Progression
- boj.kr/2331
- implementation in java
- the core concept is to find a first number of cycle
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] ap = br.readLine().split(" ");
int a = Integer.parseInt(ap[0]);
int p = Integer.parseInt(ap[1]);
list.add(a);
System.out.print(dfs(a, p));
}
public static int dfs(int a, int p){
int apVal = returnAp( a, p );
if( list.contains(apVal) ) {
return list.indexOf(apVal);
}
list.add(apVal);
return dfs(apVal, p);
}
public static int returnAp(int a, int p){
int sum = 0;
while(a > 0){
sum += Math.pow(a % 10, p);
a = a / 10;
}
return sum;
}
}Term Project
- boj.kr/9466
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static int[] a;
public static int[] d;
public static int[] s;
public static int dfs(int x, int cnt, int j){
if (d[x] != 0) {
if (j != s[x]) {
return 0;
}
return cnt-d[x];
}
d[x] = cnt;
s[x] = j;
return dfs(a[x], cnt+1, j);
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
int repeat = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for(int i=0; i<repeat; i++) {
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
StringTokenizer numbers = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
a = new int[n+1];
d = new int[n+1];
s = new int[n+1];
int index = 1;
while(numbers.hasMoreTokens())
a[index++] = Integer.parseInt(numbers.nextToken());
int ans = 0;
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++) {
if(d[j] == 0){
ans += dfs(j, 1, j);
}
}
sb.append(n-ans + "\n");
}
System.out.print(sb);
}
}- in this case, i honestly say that i've seen an answer code and my result is not the best so i think it's better to analyze the best answer code.
- the best answer is below.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader((System.in)));
int tc = new Integer(in.readLine());
while (tc-->0){
int n = new Integer(in.readLine());
int mates[] = new int[n];
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(in.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
mates[i] = new Integer(st.nextToken()) - 1;
}
System.out.println(find(n, mates));
}
}
static int find(int n, int[] mates){
int[] links = new int[n];
int ans = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int current = i;
while (links[current] == 0){
links[current] = i + 1;
current = mates[current];
}
if (links[current] == i + 1){
int start = current;
ans--;
while ((current = mates[current]) != start)
ans--;
}
}
return ans;
}
}Giving a number to a village
- there is a 2 dimension array
- values which is connected with '1' is considered as a village
- print how many villages in array and the number of 1 in each village
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Main {
public static boolean[][] map;
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map = new boolean[n][n];
for(int x=0; x<n; x++){
String str = br.readLine();
for(int y=0; y<n; y++){
if(str.charAt(y) == '1') {
map[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
ArrayList<Integer> al = new ArrayList();
int count = 0;
for(int x=0; x<n; x++){
for(int y=0; y<n; y++){
int xx = lookAround(x, y, n);
if(xx > 0) {
al.add(xx);
count++;
}
}
}
Collections.sort(al);
for(int i=0; i<al.size(); i++)
sb.append("\n" + al.get(i));
System.out.print(count);
System.out.print(sb);
}
public static int lookAround(int x, int y, int n){
int sum = 0;
if(map[x][y]) {
map[x][y] = false;
if (x - 1 >= 0) {
sum += lookAround(x-1, y, n);
}
if (y - 1 >= 0) {
sum += lookAround(x, y-1, n);
}
if (x + 1 < n) {
sum += lookAround(x+1, y, n);
}
if (y + 1 < n) {
sum += lookAround(x, y+1, n);
}
return 1 + sum;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
}2개의 댓글
Algorithm Study #6 (Graph Problem Solving) explores advanced techniques for navigating and optimizing graph structures. Just like accessing the NSFAS Login portal streamlines student funding processes, efficient graph algorithms simplify complex problem-solving tasks.
답글 달기


Very useful article! I found the implementation of DFS/BFS in Java here very easy to understand. By the way, if you need to calculate the grades of subjects to balance your review time, you can try grade calculator - this tool helps me optimize my study schedule when having to balance between programming and other subjects.