Multi Task Learning (MTL)
Concept
Multitask Learning은 여러 학습 작업의 공통점, 차이점을 활용하여 효율적으로 학습하는 방식이다. 동시에 어러 작업을 해결내 나가면서 작업 모델의 정확성과 효율성을 높인다. 이는 귀납적 전이에 대한 접근방식으로, 관련 작업의 훈련신호에 포함된 도메인 정보를 귀납적 편향으로 사용하여 일반화의 성능을 높인다. 공유 표현은 동시에 작업을 학습하고, 각 작업을 학습한 내용은 다른 작업을 더 잘 배우도록 돕는다.
Multitask Learning is an approach to inductive transfer that improves generalization by using the domain information contained in the training signals of related tasks as an inductive bias. It does this by learning tasks in parallel while using a shared representation; what is learned for each task can help other tasks be learned better. This paper reviews prior work on MTL, presents new evidence that MTL in backprop nets discovers task relatedness without the need of supervisory signals, and presents new results for MTL with k-nearest neighbor and kernel regression. In this paper we demonstrate multitask learning in three domains. We explain how multitask learning works, and show that there are many opportunities for multitask learning in real domains. We present an algorithm and results for multitask learning with case-based methods like k-nearest neighbor and kernel regression, and sketch an algorithm for multitask learning in decision trees. Because multitask learning works, can be applied to many different kinds of domains, and can be used with different learning algorithms, we conjecture there will be many opportunities for its use on real-world problems.
by _Rich Caruana_
Keywords: inductive transfer, parallel transfer, multitask learning, backpropagation, k-nearest neighbor, kernel regression, supervised learning, generalization
- 귀납
- 전제가 참이라고 가정할 때 결론이 개연적으로 도출
- 관찰 -> 가설/이론
- 연역
- 전제가 참이라고 가정할 때 결론이 필연적으로 도출
- 가설/이론 -> 관찰
Features
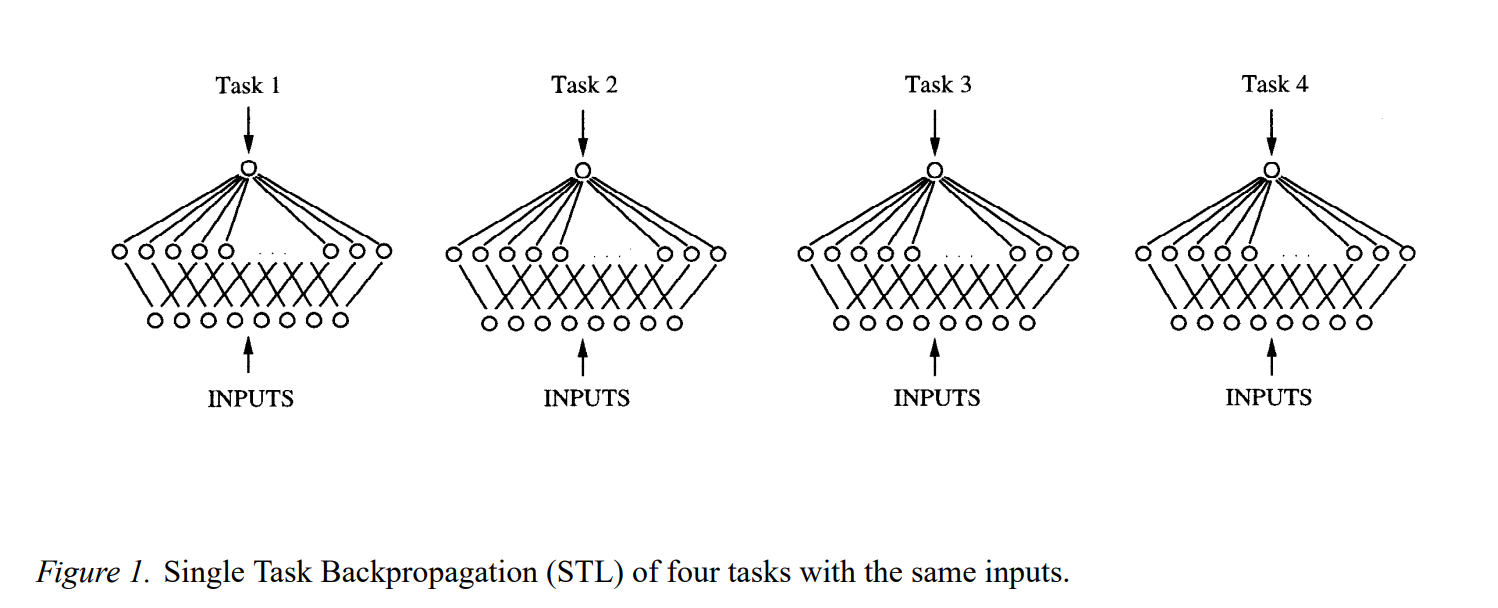
(자료 : Rich Caruana, Multi Task Learning, 1997.)

(자료 : Rich Caruana, Multi Task Learning, 1997.)
-
Shared Representations
-
Regularization Effect
-
Knowledge Transfer
-
Data Efficiency
-
Training Time Increase
-
Model Complexity Increases
-
Cooperation and Competition
-
Application
Link
Reference
[1] Rich Caruana, Multitask Learning, Springer, Volume 28, pages 41–75, 1997.
