Keywords: 동적 메모리 할당, 포인터, 메모리 누수, 균형 이진 탐색 트리
학습 순서: C언어 공부, Linux/gcc 사용법 익히기 → RB tree 이론, malloc/free 사용법 파악 → RB tree 구현
어떤 자료구조?
- (루트로부터의)어떤 임의의 경로도, (루트로부터의)다른 경로 길이의 2배를 넘지 못함. (=balanced)
- 새로운 노드를 삽입하여 제 자리를 찾고, RBT(Red Black Tree) 성질을 갖추는 데에 까지 걸리는 시간이 O(logn). n은 트리의 internal 노드 개수.
- 각 노드들(c에서 구조체)은 color, key, left, right, parent(p;pointer;)를 요소로 가짐.
- left, right, parent가 없는 노드는 'NIL'이라고 칭함 -> root의 parent, leaf의 left, right를 'NIL'과 연결
기본 성질
- RED-BLACK properties
- all nodes are black or white
2. root: black - all leaves(NIL): black
4. RED node's children are BLACK( No Double RED )
5. for each node, all simple paths(node->NIL) contain same BLACKs
** 편의상, 모든 NIL들은 visually transparent.
Key Lemma
n개의 internal nodes(NIL제외)를 가진 트리는 최대 height = 2log(n+1).
proof
Prove 'at any node x, it's subtree has at least (2^bh(x) - 1) internal nodes'.
By Induction. Do yourself!
(Hint: Use above properties. Especially 1, 5)
핵심 기능들
Rotate ( right & left )
-
left : 반시계, right : 시계 방향으로 pivot을 옮긴다고 생각하면 된다.
-
동시에, 퇴출당하는 pivot은 새로운 pivot에게 자신의 자식을 내어준다.
-
rotation하는 이유: 트리의 높이를 log(N)으로 유지하기 위해서.
-
rotate는 노드 간의 총 6개 연결을 갱신해주는 작업이라고 생각하면 좋음.
-
핵심: rotate를 수행해도 BST property 는 유지된다는 점. (간단한 부등호 그려보기)
-
시간복잡도 O(1)
-
insert 시, rotate는 최대 2회 수행. (가장 하단의 코드 참조)
추천문제
(CLRS 13.2-4) Show that any arbitrary n-node binary search tree can be transformed into any other arbitrary n-node binary search tree using O(n) rotations.
(Hint: 모든 노드들이 right side에 있는 right-going chain을 떠올려보자)
(Proof)
Ref: https://walkccc.me/CLRS/Chap13/13.2/
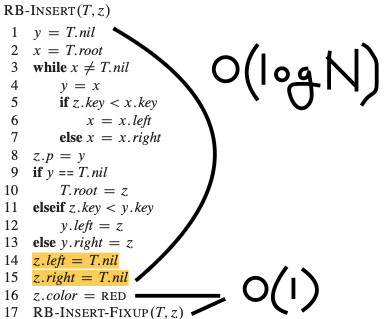
Insert
- 삽입할 노드를 RED로 간주한 후, BST적으로 올바른 위치를 찾음. 노드 삽입해보면, 무조건 트리의 leaf 부분에 자리할 수 밖에 없음.
- 이후 RED-BLACK property를 만족시키기 위한 절차(fixup)를 시행.
- 시간복잡도: 제자리 찾게하는 데까지 O(logN), 삽입노드를 RED로 칠하는 데에 O(1), Fixup에 O(1)
Insert Fix Up
-
크게 Recoloring(주변 요소들 색칠 다시하는)과 Restructuring으로 나뉨.
-
fix up 을 진행하는 진짜 이유: insert RED node하면, RED-BLACK property에서 2, 4를 violate할 수 있기에. insert 시 위반되는 성질은 둘 중 하나임.
property 2: root is BLACK
property 4: RED node has 2 BLACK nodes. (No Double REDs) -
위 상황을 좀 더 자세하게 보면,
property 2를 위반하는 경우는 항상 "z가 root, RED"일 때임.
property 4를 위반하는 경우는 항상 "z, z부모가 RED"일 때임. -
insert fix up은, z와 z부모가 Double RED인 동안 시행함.(왜 그럴까? 질문해보기)
-
이러한 상황 속에서, 또다시 3가지 상황으로 나뉘어 fix up을 시행함.(z의 부모가 z할아버지의 왼쪽 자식이냐, 오른쪽 자식이냐에 따라 나뉨. 그래서 정확히 따지면 총 6가지 상황. 아래에선 한 방향만 고려하겠음.)
1. 삽입노드(z)의 삼촌(y)이 RED일 때
-> z의 부모, z의 삼촌을 BLACK으로. z의 할아버지를 RED로 칠함. (double red문제 해결. 동시에 property 5 만족시키도록 유지.)
-> z의 포인터를 z의 할아버지로 up.
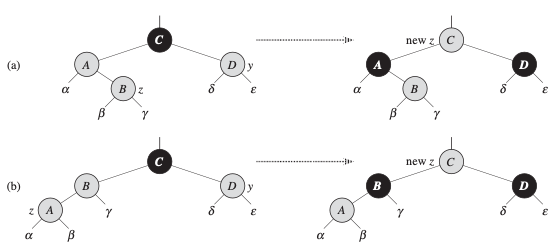
2-1. z의 삼촌이 BLACK일 때, z~z부모~z할아버지로 이어지는 구조가 '꺾인 구조'일 때
-> 1자 구조로 만들어줌.
2-2. z의 삼촌이 BLACK일 때, z~z부모~z할아버지로 이어지는 구조가 '1자 구조'일 때
-> z부모를 드디어 BLACK으로 칠하고, z할아버지는 RED로 칠하고(no double reds), 할아버지 기준으로 rotate.
-
코드보면 "z의 할아버지가 없으면, while문을 굳이 돌지 않고, root(즉 z의 부모, 혹은 z)를 BLACK"으로 칠하고 끝남.
-
Fix up의 while문을 끝내고 나면, 결과론적으로
(1) z 포인터가 트리 기준 2칸 위로 가서 while 다시 돌기
(2) 노드 색칠+최대2회 rotate하고 while 루프탈출
Deletion
transplant
- 노드를 삭제하는 과정에서, 삭제/교체되는 노드의 부모를, 다른 노드에 연결하는 작업

Delete
- 삭제하는 노드의 색깔이 BLACK이면 delete- fixup을 호출.
- 노드(z)를 삭제하는 과정을 상황을 나누면,
- (1) z의 자식이 0~1명일 때 (2) z의 자식이 2명일 때로 나뉨.
- z의 자식이 0~1명이면, y노드는 일명 '삭제되는 노드'역할을 함. z자리로 치환함(Transplant).
- z의 자식이 2명이면, y노드는 z의 successor, 일명 '치환되는 노드'역할을 함. x는 y의 원래 자리를 채워줄 노드.
- 지울 노드/대체할 노드의 색깔을 저장. ( y-original-color ) 이게 BLACK이면 property를 해치기에 문제가 됨. -> fixup진행.
Delete-fixup
-
삭제/대체하는 노드 y의 color가 BLACK이었다면, RED-BLACK property가 깨짐. 그에 따라 진행하는 프로세스. y의 검은색 카운트 1개가 없어지는 것이기에, 여분의 blackness개념을 도입함.
-
x는 항상 doubly black node를 가리킴. w는 x의 형제를 가리킴. property 5에 따라 w는 NIL이 될 수 없음.
-
핵심 아이디어: '변형(회전, 색칠)'에 의해 각 subtree의 property 5는 항상 유지된다는 것. subtree alpha의 black counts가 2였다면, 변형 이후에도 2라는 것.
-
상황은 총 4가지이다. (방향 고려하면 8가지)
-
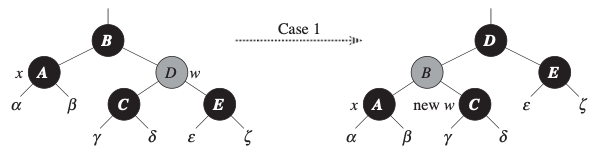
w가 RED일 때.
-> w를 BLACK으로 칠하고 그 부모를 RED로 칠하며, w를 부모로 올려버림(rotation).
위 행위를 통해 case 2~4로 변형하는 선 작업이라고 생각하면 됨.
-
w가 BLACK이고, w의 자식들이 모두 BLACK일 때.
-> w를 RED로 칠하고 x를 x의 부모로 새로 설정.(x를 한 칸 올림)
-> while문을 재차 반복. ( 단, case1->2로 온 경우는 while 루프가 바로 종료됨 ) -
w가 BLACK이고, w의 오른쪽 자식만 BLACK일 때.
-> w를 RED로 칠하고, w의 왼쪽 자식을 BLACK으로 칠하고, w를 기준으로 right rotate해버림.
-> case 4로 변모됨. -
w가 BLACK이고, w의 오른쪽 자식이 RED일 때.
-> w의 색을 x의 부모 색으로 칠하고, x의 부모 색을 BLACK으로 칠함.
-> 그리고 w의 오른쪽 자식도 BLACK으로 칠하고, x부모에 대해 left rotate.
-> x = T.root.
모두 끝난후 x 색깔을 BLACK으로 칠하면 끝.
Codes
- rotate
left rotate
void left_rotate(rbtree *t, node_t *x){
node_t *y = x->right;
x->right = y->left;
if (y->left != t->nil){
y->left->parent = x;
}
y->parent = x->parent;
if (x->parent == t->nil){
t->root = y;
}
else if (x == x->parent->left){
x->parent->left = y;
}
else{
x->parent->right = y;
}
y->left = x;
x->parent = y;
}right rotate
void right_rotate(rbtree *t, node_t *y){
node_t *x = y->left;
y->left = x->right;
if (x->right != t->nil){
x->right->parent = y;
}
x->parent = y->parent;
if (y->parent == t->nil){
t->root = x;
}
else if (y == y->parent->left){
y->parent->left = x;
}
else{
y->parent->right = x;
}
x->right = y;
y->parent = x;
}rbtree_insert
node_t *rbtree_insert(rbtree *t, const key_t key) {
// TODO: implement insert
node_t *return_node = (node_t *)calloc(1, sizeof(node_t)); //집어넣는 노드
node_t *y = t->nil;
node_t *x = t->root;
while(x != t->nil)
{
y = x;
if (key < x->key)
{
x = x->left;
}
else{
x = x->right;
}
}
return_node->parent = y;
if (y == t->nil)
{
t->root = return_node;
}
else if (key < y->key)
{
y->left = return_node;
}
else
{
y->right = return_node;
}
return_node->key = key;
return_node->left = t->nil;
return_node->right = t->nil;
return_node->color = RBTREE_RED;
rb_insert_fixup(t, return_node);
///rb_insert_fixup 구현하기
return return_node;rb_insert_fixup
void rb_insert_fixup(rbtree *t, node_t *z){
while(z->parent->color == RBTREE_RED)
{
if(z->parent == z->parent->parent->left)
{
node_t *y = z->parent->parent->right;
if (y->color == RBTREE_RED)
{
z->parent->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
y->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
z->parent->parent->color = RBTREE_RED;
z = z->parent->parent;
}
else
{
if(z == z->parent->right){
z = z->parent;
/////// left_rotate
left_rotate(t, z);
}
z->parent->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
z->parent->parent->color = RBTREE_RED;
right_rotate(t, z->parent->parent);
}
}
else
{
node_t *y = z->parent->parent->left;
if (y->color == RBTREE_RED){
z->parent->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
y->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
z->parent->parent->color = RBTREE_RED;
z = z->parent->parent;
}
else
{
if(z == z->parent->left)
{
z = z->parent;
/////// right_rotate
right_rotate(t, z);
}
z->parent->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
z->parent->parent->color = RBTREE_RED;
left_rotate(t, z->parent->parent);
}
}
}
t->root->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
}
node_t *rbtree_insert(rbtree *t, const key_t key) {
// TODO: implement insert
node_t *return_node = (node_t *)calloc(1, sizeof(node_t)); //집어넣는 노드
node_t *y = t->nil;
node_t *x = t->root;
while(x != t->nil)
{
y = x;
if (key < x->key)
{
x = x->left;
}
else{
x = x->right;
}
}
return_node->parent = y;
if (y == t->nil)
{
t->root = return_node;
}
else if (key < y->key)
{
y->left = return_node;
}
else
{
y->right = return_node;
}
return_node->key = key;
return_node->left = t->nil;
return_node->right = t->nil;
return_node->color = RBTREE_RED;
rb_insert_fixup(t, return_node);
///rb_insert_fixup 구현하기
return return_node;
}

