Day1. Data Filtering - Big Countries
Problem
Table: World
| Column Name | Type |
|---|---|
| name | varchar |
| continent | varchar |
| area | int |
| population | int |
| gdp | bigint |
name is the primary key (column with unique values) for this table.
Each row of this table gives information about the name of a country, the continent to which it belongs, its area, the population, and its GDP value.
A country is big if:
it has an area of at least three million (i.e., 3000000 km2), or
it has a population of at least twenty-five million (i.e., 25000000).
Write a solution to find the name, population, and area of the big countries.
Return the result table in any order.
The result format is in the following example.
Example 1:
Input:
World table:
| name | continent | area | population | gdp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | Asia | 652230 | 25500100 | 20343000000 |
| Albania | Europe | 28748 | 2831741 | 12960000000 |
| Algeria | Africa | 2381741 | 37100000 | 188681000000 |
| Andorra | Europe | 468 | 78115 | 3712000000 |
| Angola | Africa | 1246700 | 20609294 | 100990000000 |
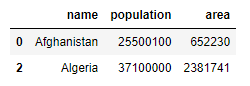
Output:
| name | population | area |
|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | 25500100 | 652230 |
| Algeria | 37100000 | 2381741 |
Solution
# my solution
import pandas as pd
def big_countries(world: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
world = world[(world['area'] >= 3000000) | (world['population'] >= 25000000)]
return world[['name','population','area']]# check result
data = [['Afghanistan', 'Asia', 652230, 25500100, 20343000000], ['Albania', 'Europe', 28748, 2831741, 12960000000], ['Algeria', 'Africa', 2381741, 37100000, 188681000000], ['Andorra', 'Europe', 468, 78115, 3712000000], ['Angola', 'Africa', 1246700, 20609294, 100990000000]]
world = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['name', 'continent', 'area', 'population', 'gdp']).astype({'name':'object', 'continent':'object', 'area':'Int64', 'population':'Int64', 'gdp':'Int64'})
big_countries(world)